

基于便携拉曼光谱仪和双层纸芯片的头发皮质醇超高灵敏检测
收稿日期: 2016-11-11
网络出版日期: 2017-02-23
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(No.21675017)资助.
Ultrasensitive Detection of Hair Cortisol Based on Portable Raman Spectrometer and Double-layer Paper Microdevice
Received date: 2016-11-11
Online published: 2017-02-23
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675017).
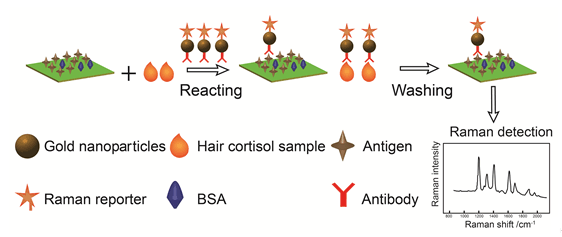
人头发中的皮质醇是反映现代人长期精神压力累积的主要临床标记物.建立了一种人发皮质醇的超高灵敏检测方法.方法基于表面增强拉曼光谱、免疫分析和双层纸芯片.纸芯片的第一层用于滤除人发提取液中的头发残渣(样品前处理),第二层用于实施竞争性免疫反应和拉曼检测.固定在纸表面的皮质醇抗原和游离的头发皮质醇竞争结合能产生拉曼信号的皮质醇单克隆抗体,通过检测结合在纸表面的皮质醇抗原-抗体复合物的拉曼信号进行游离头发皮质醇的定量.在便携式拉曼光谱仪上,皮质醇抗体的拉曼信号经过优化,方法的检测限可以达到1 pg/mL,平行测定相对标准偏差为8.38%(n=6).进行了两例实际样品检测,液质检测结果分别为0.771和0.153 ng/mL,本方法检测结果分别为0.63和0.247 ng/mL,两种方案的结果在一个数量级,证明了方法的实用性.利用此方法,一块芯片可以同时测定48个样品,专属性和准确性很好,特别适合于人群精神压力的普查.
高志刚 , 郑婷婷 , 邓九 , 李晓瑞 , 曲玥阳 , 陆瑶 , 刘婷娇 , 罗勇 , 赵伟杰 , 林炳承 . 基于便携拉曼光谱仪和双层纸芯片的头发皮质醇超高灵敏检测[J]. 化学学报, 2017 , 75(4) : 355 -359 . DOI: 10.6023/A16110598
Cortisol in the human hair is a clinical biomarker of long-term social-and-work-related mental stress, which is of high morbidity rate in the current modern society. This study developed a sensitive hair cortisol assay, featuring sur-face-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, immunoreaction, and a double-layer paper microdevice. The first layer of the paper mi-crodevice was used to remove the hair residue in the hair extract by filtration (sample pretreatment). The second layer was used for competitive immunoreaction and detection. Standard cortisol antigen immobilized in the second layer and the free cortisol in hair extract competed to bind the spiked Raman-active cortisol monoclonal antibody solution. The hair cortisol can be quantitated by the intensity of Raman signal of monoclonal antibody bound on the paper. We found the Raman signal decreased as the cortisol concentration increases in hair samples. The relative Raman intensity measured was linearly proportional to the logarithmic value of the cortisol concentration in hair samples we measured. The detection of limit (LOD) was 1 pg/mL with the portable Raman spectrometer. The RSD of measurement was 8.38% (n=6). In addition, we used LC-MS to measure two real samples as a comparison with our method as above. The results are 0.771 and 0.153 ng/mL by LC-MS method and 0.63 and 0.247 ng/mL by the proposed method. It can be observed that the results are in same order, demonstrating the validity of the proposed method. In addition, 48 samples can be measured in a single chip. These results showed that this method is sensitive, specific, and suitable for large-scale screening of hair cortisol samples.

[1] Ito, N.; Ito, T.; Kromminga, A.; Bettermann, A.; Takigawa, M.; Kees, F.; Straub, R. H.; Paus, R. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1332.
[2] Van Uum, S. H. M.; Sauve, B.; Fraser, L. A.; Morley-Forster, P.; Paul, T. L.; Koren, G. STRESS 2008, 11, 483.
[3] Manenschijn, L.; Koper, J. W.; Lamberts, S. W. J.; van Rossum, E. F. C. Steroids 2011, 76, 1032.
[4] Davenport, M. D.; Tiefenbacher, S.; Lutz, C. K.; Novak, M. A.; Meyer, J. S. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 147, 255.
[5] Raul, J. S.; Cirimele, V.; Ludes, B.; Kintz, P. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 1105.
[6] Accorsi, P. A.; Carloni, E.; Valsecchi, P.; Viggiani, R.; Garnberoni, M.; Tarnanini, C.; Seren, E. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2008, 155, 398.
[7] Lu, Y.; Shi, W. W.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J. H.; Lin, B. C. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1497.
[8] Lu, Y.; Shi, W. W.; Qin, J. H.; Lin, B. C. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 329.
[9] Klasner, S. A.; Price, A. K.; Hoeman, K. W.; Wilson, R. S.; Bell, K. J.; Culbertson, C. T. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1821.
[10] Ge, S. G.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Song, X. R.; Yu, J. H.; Huang, J. D. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9397.
[11] Vella, S. J.; Beattie, P.; Cademartiri, R.; Laromaine, A.; Martinez, A. W.; Phillips, S. T.; Mirica, K. A.; Whitesides, G. M. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2883.
[12] Yan, C.; Yu, S.; Jiang, Y.; He, Q.; Chen, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 1099. (严春芳, 余思扬, 蒋艳, 何巧红, 陈恒武, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 1099.)
[13] Zhao, L.; Yan, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1104. (赵联朝, 闫宏涛, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1104.)
[14] Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Chen, L. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1391.
[15] Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, D.; Ma, X.; Wu, A. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2066.
[16] Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, B. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2162.
[17] Fu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, J.; Choo, P.; Chen, L.; Choo, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 530.
[18] Dou, B.; Luo, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, B.; Du, Y. G.; Gao, Z. G.; Zhao, W. J.; Lin, B. C. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 485.
[19] Wang, G. F.; Lipert, R. J.; Jain, M.; Kaur, S.; Chakraboty, S.; Torres, M. P.; Batra, S. K.; Brand, R. E.; Porter, M. D. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2554.
[20] Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Xu, D.; Liu, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 1686(in Chinese). (张宗绵, 刘睿, 徐敦明, 刘景富, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 1686.)
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |