

金属有机框架与Pt粒子复合材料催化喹啉选择性加氢性能研究※
收稿日期: 2021-12-30
网络出版日期: 2022-02-08
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2021YFA1500403); 中国科学院战略性先导科技专项B类研发(XDB36000000); 国家自然科学基金(22173024); 国家自然科学基金(21722102); 国家自然科学基金(51672053)
Study on the Selective Hydrogenation of Quinoline Catalyzed by Composites of Metal-Organic Framework and Pt Nanoparticles※
Received date: 2021-12-30
Online published: 2022-02-08
Supported by
National Key Research & Development Program of China(2021YFA1500403); Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDB36000000); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22173024); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21722102); National Natural Science Foundation of China(51672053)
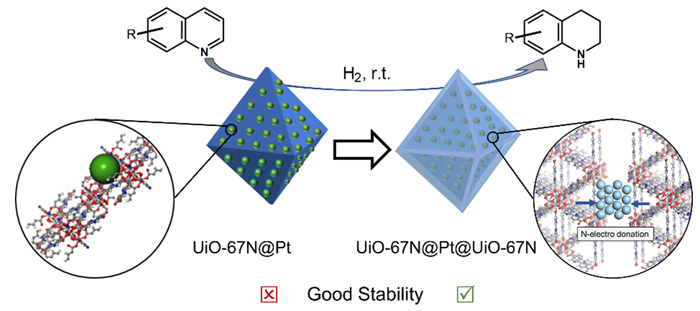
喹啉选择性加氢制备1,2,3,4-四氢喹啉在药物、农药和精细化学品等的生产中表现出巨大的应用潜力, 引起了广泛关注. 该反应通常要在高温、高压等苛刻条件下进行, 温和条件下对其选择性加氢仍具有很大挑战. 本工作以氯化锆为金属盐和2,2'-联吡啶-5,5'-二羧酸为配体制备金属有机框架材料UiO-67N, 以Pt纳米粒子为活性组分, 可控制备出具有三明治结构的UiO-67N@Pt@UiO-67N复合催化剂, 同时可调控其壳层厚度为11, 28和42 nm. 利用X射线衍射分析、扫描电子显微镜、透射电子显微镜、X射线光电子能谱、电感耦合等离子发射光谱仪、傅里叶变换红外光谱仪和氮气吸脱附测试对催化剂进行了系统表征. 研究发现, 相比于UiO-67而言, UiO-67N可以显著提高Pt纳米粒子催化喹啉选择性加氢的性能, 且UiO-67N@Pt@UiO-67N在常温下实现了高转化率(>99%)和高选择性(>99%)催化喹啉加氢制备1,2,3,4-四氢喹啉; 随着壳层厚度的增加, 其催化活性会显著降低, 但选择性保持不变. 以喹啉的衍生物作为底物, 三明治结构催化剂也可展现出优异的活性和选择性加氢性能. 相比于负载型催化剂, 三明治结构复合催化剂具有优异的循环稳定性. X射线光电子能谱和红外光谱分析表明, UiO-67N与Pt纳米粒子间的电子转移, 以及与喹啉间的强界面相互作用有助于提高催化剂的性能.
陈俊敏 , 崔承前 , 刘瀚林 , 李国栋 . 金属有机框架与Pt粒子复合材料催化喹啉选择性加氢性能研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022 , 80(4) : 467 -475 . DOI: 10.6023/A21120601
Selective hydrogenation of quinoline toward 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline shows great application potential in the production of medicine, pesticides and fine chemicals. However, the hydrogenation of quinoline is usually carried out under harsh reaction conditions such as high temperature and high pressure, and thus, it is a great challenge to achieve selective hydrogenation of quinoline under mild conditions. In this work, we construct platinum nanoparticles (Pt NPs) sandwiched in an inner core and an outer shell composed of a metal-organic framework synthesized by zirconium chloride and 2,2'-bipyridine-5,5'-dicarboxylic acid (known as UiO-67N). Different sandwich structures with shell thickness of 11, 28 and 42 nm are precisely prepared. The obtained catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICP-OES), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and nitrogen adsorption and desorption. Impressively, the selective hydrogenation of quinoline over Pt NPs is significantly enhanced by using UiO-67N as support in respect with UiO-67. Moreover, UiO-67N@Pt@UiO-67N exhibits the selective hydrogenation of quinoline with high conversion rate (>99%) and high selectivity of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (>99%) at room temperature. The shell thickness has significant influence on the catalytic activity of Pt NPs, and with increasing the shell thickness from 11 to 42 nm, the conversion rate decreases from 99% to 53.5% under the identical conditions, while the selectivity of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline is well kept. When other derivatives of quinoline are used as substrates, the excellent activity and selectivity are also achieved over sandwich catalysts. Besides, the UiO-67N@Pt@UiO-67N catalyst could be used at least 5 times without obvious deactivation, but the significant deactivation happens over supported UiO-67N@Pt catalyst. XPS and FTIR measurements show that the excellent catalytic performance mainly originates from the electron transfer between UiO-67N and Pt NPs, and the strong interfacial interaction between UiO-67N and quinoline.

| [1] | Muthukrishnan, I.; Sridharan, V.; Carlos Menendez, J. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5057. |
| [2] | Yadav, P.; Kumar, A.; Althagafi, I.; Nemaysh, V.; Rai, R.; Pratap, R. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 1587. |
| [3] | Cai, X.; Xie, B. Chem. Bull. 2012, 75, 7. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | (蔡小华, 谢兵, 化学通报, 2012, 75, 7.) |
| [4] | Chen, R.; Yang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, X.; Hagfeldt, A.; Sun, L. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4007. |
| [5] | Li, C.; Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Tao, L.; Ren, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Q. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 1288. |
| [6] | Guo, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, G. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2012, 31, 2288. (in Chinese) |
| [6] | (郭辉, 庄玉伟, 王颖, 曹健, 郭晓战, 张国宝, 化工进展, 2012, 31, 2288.) |
| [7] | Rosales, M.; Jhonatan Bastidas, L.; Gonzalez, B.; Vallejo, R.; Baricelli, P. J. Catal. Lett. 2011, 141, 1305. |
| [8] | Sun, S.; Nagorny, P. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8432. |
| [9] | Rosales, M.; Castillo, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Gonzalez, L.; Molina, K.; Navarro, J.; Pacheco, I.; Perez, H. Transit. Metal Chem. 2004, 29, 221. |
| [10] | Wang, T.; Zhuo, L.-G.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Ding, Z.; He, Y.; Fan, Q.-H.; Xiang, J.; Yu, Z.-X.; Chan, A. S. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9878. |
| [11] | Gong, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. J. Catal. 2013, 297, 272. |
| [12] | Zhang, F.; Ma, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.-M. Mol. Catal. 2018, 452, 145. |
| [13] | Bai, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Ye, Y.; Zheng, H.; Guo, J.; Yin, Y.; Gao, C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15656. |
| [14] | Zhu, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, X.; Fu, H.; Yuan, M.; Chen, H.; Li, R. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 2954. |
| [15] | Yamaguchi, R.; Ikeda, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujita, K.-I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8410. |
| [16] | Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Su, D.; Liang, C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 22. (in Chinese) |
| [16] | (郭小玲, 陈霄, 苏党生, 梁长海, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 22.) |
| [17] | Zhao, T.; Dong, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Prog. Chem. 2017, 29, 1252. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | (赵田, 董茗, 赵熠, 刘跃军, 化学进展, 2017, 29, 1252.) |
| [18] | Pan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chu, S.-Q.; Yang, Y.; Ding, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.-H.; Jiang, H.-L. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, 224. |
| [19] | Wu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, K.; Jiang, H.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 688. (in Chinese) |
| [19] | (吴浅耶, 张晨曦, 孙康, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 688.) |
| [20] | Jiao, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.-L. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 327. |
| [21] | Choe, K.; Zheng, F.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xue, G.; Qiu, X.; Ri, M.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Tang, Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3650. |
| [22] | Zhao, M.; Yuan, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, J.; Gu, L.; Hu, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z. Nature 2016, 539, 76. |
| [23] | Zhang, J.-W.; Li, D.-D.; Lu, G.-P.; Deng, T.; Cai, C. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 4980. |
| [24] | Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Yao, T.; Liu, W.; Lin, Y.; Ju, H.; Dong, J.; Zheng, L.; Yan, W.; Zheng, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; He, D.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9419. |
| [25] | Chen, F.; Shen, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Cui, J.; Li, Y. ACS Central Sci. 2019, 5, 176. |
| [26] | Shen, Y.; Pan, T.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W.; Huo, F. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007442. |
| [27] | Dou, R.; Tan, X.; Fan, Y.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M.; Fan, K.; Sun, B.; Zong, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 503. (in Chinese) |
| [27] | (窦镕飞, 谭晓荷, 范义秋, 裴燕, 乔明华, 范康年, 孙斌, 宗保宁, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 503.) |
| [28] | Ding, S.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, R.; Xing, W. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 146. |
| [29] | Ji, Z.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, G.; Chen, K. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 454. |
| [30] | Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Ge, Q.; Liu, X.; Han, J. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2017, 247, 1. |
| [31] | Lin, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 124. |
| [32] | Hester, P.; Xu, S.; Liang, W.; Al-Janabi, N.; Vakili, R.; Hill, P.; Muryn, C. A.; Chen, X.; Martin, P. A.; Fan, X. J. Catal. 2016, 340, 85. |
| [33] | Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, Z.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Cao, R. J. Catal. 2012, 292, 111. |
| [34] | Li, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, G.; Guan, Q.; Dong, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, S.-H.; Jiang, H.-L. Chem 2021, 7, 686. |
| [35] | Chen, D.; Yang, W.; Jiao, L.; Li, L.; Yu, S.-H.; Jiang, H.-L. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000041. |
| [36] | Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Garcia, H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5262. |
| [37] | Fish, R. H.; Kim, H. S.; Fong, R. H. Organometallics 1991, 10, 770. |
| [38] | Fish, R. H.; Michaels, J. N.; Moore, R. S.; Heinemann, H. J. Catal. 1990, 123, 74. |
| [39] | Li, X.; Van Zeeland, R.; Maligal-Ganesh, R. V.; Pei, Y.; Power, G.; Stanley, L.; Huang, W. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6324. |
| [40] | Cavka, J. H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850. |
| [41] | Zhang, S.; Gan, J.; Xia, Z.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Duan, X.; Qu, Y. Chem 2020, 6, 2994. |
| [42] | Huang, R.; Cao, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; Jiang, L.; Song, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2020, 12, 17651. |
| [43] | Shaikh, M. N.; Kalanthoden, A. N.; Ali, M.; Haque, M. A.; Aziz, M. A.; Abdelnaby, M. M.; Rani, S. K.; Bakare, A. I. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 14827. |
| [44] | Bravo-Sanabria, C. A.; Solano-Delgado, L. C.; Ospina-Ospina, R.; Martinez-Ortega, F.; Ramirez-Caballero, G. E. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2020, 305, 110359. |
| [45] | Ozel, A. E.; Buyukmurat, Y.; Akyuz, S. J. Mol. Struct. 2001, 565, 455. |
| [46] | Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S.; Wang, H.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Huang, K. J. Catal. 2021, 396, 342. |
| [47] | Zhan, T.; Liu, W.; Teng, J.; Yue, C.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Tan, H. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2620. |
| [48] | Yu, X.; Nie, R.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhou, D.; Xia, Q. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2018, 256, 10. |
| [49] | Li, L.; Tang, S.; Wang, C.; Lv, X.; Jiang, M.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2304. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |