

NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+单颗粒微米棒偏振上转换发光及其取向示踪※
收稿日期: 2021-12-31
网络出版日期: 2022-02-17
基金资助
中国科学院青年创新促进会专项(2020305); 国家自然科学基金(12174391); 国家自然科学基金(U1805252); 国家自然科学基金(21875250); 国家自然科学基金(12074379); 国家自然科学基金(12104456); 福建省自然科学基金对外合作项目(2020I0037)
Polarized Upconversion Luminescence from a Single NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ Microrod for Orientation Tracking※
Received date: 2021-12-31
Online published: 2022-02-17
Supported by
Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(2020305); National Natural Science Foundation of China(12174391); National Natural Science Foundation of China(U1805252); National Natural Science Foundation of China(21875250); National Natural Science Foundation of China(12074379); National Natural Science Foundation of China(12104456); Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province(2020I0037)
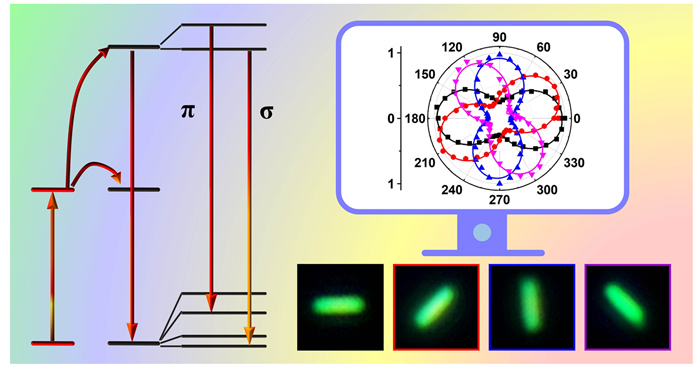
稀土掺杂微/纳材料的偏振上转换发光在单颗粒示踪和生物医学等领域具有广泛的应用前景. 稀土离子的偏振上转换发光主要取决于其局域态的电子结构和激发态动力学. 利用单颗粒偏振上转换光学测试平台对β-NaYF4:Yb3+/ Er3+微米棒的偏振上转换发光进行了系统研究. 随发射偏振角的变化, 单个微米棒的上转换发光强度发生周期性改变, 且来自Er3+同一光谱支项的不同晶体场子能级跃迁的偏振方向不同. 与光谱支项整体的上转换发光相比, 其晶体场子能级上转换发光表现出更大的发射偏振度. 利用Er3+高度偏振的晶体场跃迁谱线, 实现了对单个微米棒空间取向的动态分析, 揭示了NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+微米棒作为偏振各向异性的上转换荧光探针在单颗粒取向示踪方面的潜在应用.
胡晓柯 , 商晓颖 , 黄萍 , 郑伟 , 陈学元 . NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+单颗粒微米棒偏振上转换发光及其取向示踪※[J]. 化学学报, 2022 , 80(3) : 244 -248 . DOI: 10.6023/A21120618
Polarized upconversion luminescence (UCL) of lanthanide (Ln3+)-doped micro/nano-crystals has shown great promise in areas such as single-particle tracking and biomedicine. The polarized UCL of Ln3+ ions is governed by their localized electronic structures and excited-state dynamics. In this work, β-NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ microrods with controllable morphologies and sizes were synthesized through a solvothermal method. Based on the customized confocal laser microscopic system, the polarized UCL of a single β-NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ microrod was systematically investigated. The emission polarization was probed by placing a half-wave plate coupled with a polarizer in front of the detector. As such, the polarized UCL spectra of a single NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ microrod can be recorded by rotating the half-wave plate under 980-nm excitation. It was observed that the UCL intensity of the microrod exhibited a periodic variation with the emission polarization angle tuning from 0° to 360°, indicating polarization anisotropy of the microrod. Specifically, different crystal-field (CF) transition lines originating from two identical multiplets of Er3+ displayed drastically distinct polarization dependence. This results in a higher degree of polarization (DOP) of the UCL intensity for a certain CF transition of Er3+ in comparison with that of the integrated UCL intensity of the multiplet. Polar plots of the UCL intensities for the CF transitions of Er3+ as a function of polarization angle could provide a qualitative vision of the DOP, with a narrower “neck” indicative of a larger DOP. Moreover, the polar plots of a certain CF transition of Er3+ showed a consistent orientation with the corresponding NaYF4:Yb3+/ Er3+ microrod and rotated with the rotating of the single microrod. Therefore, by utilizing the polar plots of the highly-polarized CF transition lines of Er3+, the spatial orientations of the microrod could be monitored, thus revealing the great potential of NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ microrods as sensitive anisotropic UCL probes for single-particle tracking.

| [1] | Lei, P. P.; An, R.; Yao, S.; Wang, Q. S.; Dong, L. L.; Xu, X.; Du, K. M.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H. J. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700505. |
| [2] | Dong, H.; Sun, L. D.; Yan, C. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20546. |
| [3] | Zheng, W.; Huang, P.; Tu, D. T.; Ma, E.; Zhu, H. M.; Chen, X. Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1379. |
| [4] | Qiu, X. C.; Zhou, Q. W.; Zhu, X. J.; Wu, Z. G.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Y. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4. |
| [5] | Yang, D. D.; Peng, Z. X.; Zhan, Q. Q.; Huang, X. J.; Peng, X. Y.; Guo, X.; Dong, G. P.; Qiu, J. R. Small 2019, 15, 1904298. |
| [6] | Yang, D. D.; Peng, Z. X.; Guo, X.; Qiao, S. Q.; Zhao, P.; Zhan, Q. Q.; Qiu, J. R.; Yang, Z. M.; Dong, G. P. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100044. |
| [7] | Wang, F. Y.; Han, Y. M.; Wang, S. M.; Ye, Z. J.; Wei, L.; Xiao, L. H. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11856. |
| [8] | Li, X.; Wei, L.; Pan, L. L.; Yi, Z. Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, Z. J.; Xiao, L. H.; Li, H. W.; Wang, J. F. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4807. |
| [9] | Zhanghao, K.; Gao, J. T.; Jin, D. Y.; Zhang, X. D.; Xi, P. J. Innov. Opt. Heal. Sci. 2018, 11, 1730002. |
| [10] | Zhanghao, K.; Chen, L.; Yang, X. S.; Wang, M. Y.; Jing, Z. L.; Han, H. B.; Zhang, M. Q.; Jin, D. Y.; Gao, J. T.; Xi, P. Light Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16166. |
| [11] | Zhanghao, K. R.; Chen, X. Y.; Liu, W. H.; Li, M. Q.; Liu, Y. Q.; Wang, Y. M.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Shan, C. Y.; Xie, H.; Gao, J. T.; Chen, X. W.; Jin, D. Y.; Li, X. D.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q. H.; Xi, P. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4694. |
| [12] | Zhanghao, K.; Liu, W. H.; Li, M. Q.; Wu, Z. H.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Y.; Shan, C. Y.; Wang, H. Q.; Chen, X. W.; Dai, Q. H.; Xi, P.; Jin, D. Y. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5890. |
| [13] | Cruz, C. A. V.; Shaban, H. A.; Kress, A.; Bertaux, N.; Monneret, S.; Mavrakis, M.; Savatier, J.; Brasselet, S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, E820. |
| [14] | Jin, D. Y.; Xi, P.; Wang, B. M.; Zhang, L.; Enderlein, J.; van Oijen, A. M. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 415. |
| [15] | Liu, X.; Chen, H. M.; Wang, Y. T.; Si, Y. G.; Zhang, H. X.; Li, X. M.; Zhang, Z. C.; Yan, B. A.; Jiang, S.; Wang, F.; Weng, S. J.; Xu, W. D.; Zhao, D. Y.; Zhang, J. Y.; Zhang, F. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5662. |
| [16] | Zheng, K. Z.; Loh, K. Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q. S.; Fan, J. Y.; Jung, T.; Nam, S. H.; Suh, Y. D.; Liu, X. G. Nano Today 2019, 29, 100797. |
| [17] | Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1049. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | (黄菊, 李贞, 刘志洪, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1049). |
| [18] | Wang, P. P.; Liang, T.; Zuo, M. M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 797. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | (王培培, 梁涛, 左苗苗, 李贞, 刘志洪, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 797.) |
| [19] | Panov, N.; Lu, D. S.; Ortiz-Rivero, E.; Rodrigues, E. M.; Haro-Gonzalez, P.; Jaque, D.; Hemmer, E. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100101. |
| [20] | Lyu, Z. Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, X. F.; Sun, L. D.; Yan, C. H. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 11288. |
| [21] | Rodriguez-Sevilla, P.; Zhang, Y. H.; de Sousa, N.; Marques, M. I.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Jaque, D.; Liu, X. G.; Haro-Gonzalez, P. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 8005. |
| [22] | Chen, P.; Song, M.; Wu, E.; Wu, B. T.; Zhou, J. J.; Zeng, H. P.; Liu, X. F.; Qiu, J. R. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6462. |
| [23] | Zhou, J. J.; Chen, G. X.; Wu, E.; Bi, G.; Wu, B. T.; Teng, Y.; Zhou, S. F.; Qiu, J. R. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2241. |
| [24] | Shi, S.; Sun, L. D.; Xue, Y. X.; Dong, H.; Wu, K.; Guo, S. C.; Wu, B. T.; Yan, C. H. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 2964. |
| [25] | He, H. L.; Liu, J. X.; Li, K.; Yin, Z.; Wang, J. W.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y. J. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4204. |
| [26] | Wei, S. Q.; Shang, X. Y.; Huang, P.; Zheng, W.; Ma, E.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M. R.; Tu, D. T.; Chen, X. Y. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 220. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |