

吲哚分子间不对称去芳构化氧化Heck反应
收稿日期: 2023-10-27
网络出版日期: 2023-12-20
基金资助
项目受国家自然科学基金(22371255); 项目受国家自然科学基金(22371254); 项目受国家自然科学基金(22071217)
Intermolecular Enantioselective Dearomative Oxidative Heck Reaction of Indoles
Received date: 2023-10-27
Online published: 2023-12-20
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22371255); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22371254); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22071217)
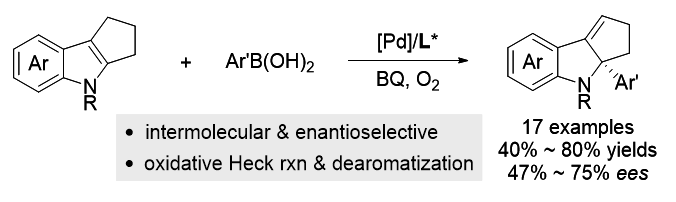
过渡金属催化的不对称去芳构化反应是合成手性环状化合物的直接方法之一. 近年来, 基于Heck反应已成功实现吲哚、苯并呋喃、吡咯、呋喃及萘等芳香化合物的不对称去芳构化反应. 然而, 现有报道往往局限于分子内反应, 分子间不对称去芳构化Heck反应仍有待研究. 与Heck反应相比, 氧化Heck反应由于反应条件相对温和且可能经历离子型催化机理, 利于实现分子间去芳构化反应并控制其对映选择性. 本工作发展了钯催化吲哚与芳基硼酸的分子间不对称去芳构化氧化Heck反应. 以Pd(OAc)2为催化剂前体、吡啶-噁唑啉为手性配体、苯醌-氧气为氧化剂, 以中等至良好的收率及中等水平的ee值, 合成了一系列含有C2-季碳手性中心的手性吲哚啉衍生物.
高炜洋 , 邓伟超 , 高扬 , 梁仁校 , 贾义霞 . 吲哚分子间不对称去芳构化氧化Heck反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024 , 82(1) : 1 -4 . DOI: 10.6023/A23100472
Transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric dearomatization reaction represents a straightforward method to access chiral cyclic compounds. In recent years, enantioselective dearomative Heck reactions of indoles, benzofurans, pyrroles, furans, and naphthalenes have been successfully developed. Nevertheless, current reports are mainly limited to the intramolecular reaction, the intermolecular asymmetric dearomative Heck reactions are still underdeveloped. In consideration of the relatively mild reaction conditions in oxidative Heck reaction, we envisioned that the intermolecular dearomative oxidative Heck reaction and its asymmetric induction might be possible due to its commonly-proposed cationic rather than neutral mechanism for Heck reaction. In the present work, an enantioselective palladium-catalyzed intermolecular dearomative Heck reaction of indoles with arylboronic acids has been developed. By employing Pd(OAc)2 as the catalyst precursor, pyridine- oxazoline as the chiral ligand, oxygen as an oxidant, and benzoquinone (BQ) as the co-oxidant, a series of chiral indolines bearing a C2-substituted quaternary stereocenter were afforded in moderate to good yields and moderate ee values. A general procedure for this enantioselective dearomative oxidative Heck reaction is described as the following: To a dried Schlenk tube were charged with Pd(OAc)2 (4.5 mg, 10 mol%) and ligand L9 (15.1 mg, 20 mol%) under O2 atmosphere. 2 mL of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solvent was then introduced via a syringe and the Schlenk tube was sealed using a Teflon cap. The mixture was stirred at 60 ℃ for 30 min in order to form the catalyst complex. After cooling to room temperature, indole substrates 1 (0.2 mmol), aryl boronic acids (0.6 mmol), and co-oxidant BQ (4.3 mg, 20 mol%) were added to the reaction system under O2 atmosphere. The resulting mixture was then stirred at 80 ℃ for 12 h. When the reaction was completed [monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC)], 10 mL of water was added to the reaction system and the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography on silica gel [V(ethyl acetate)∶V(petroleum ether)=1∶15] to afford products 2.

Key words: oxidative Heck reaction; indole; intermolecular; dearomatization; chiral indoline
| [1] | (a) Mizoroki, T.; Mori, K.; Ozaki, A. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 44, 581. |
| [1] | (b) Heck, R. F.; Nolley, J. P. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 2320. |
| [2] | For selected reviews of Heck reaction, see: (a) Heck, R. F. Acc. Chem. Res. 1979, 12, 146. |
| [2] | (b) Cabri, W.; Candiani, I. Acc. Chem. Res. 1995, 28, 2. |
| [2] | (c) Le Bras, J.; Muzart, J. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1170. |
| [2] | (d) Paul, D.; Das, S.; Saha, S.; Sharma, H.; Goswami, R. K. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 2057. |
| [3] | (a) Sato, Y.; Sodeoka, M.; Shibasaki, M. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 4738. |
| [3] | (b) Carpenter, N. E.; Kucera, D. J.; Overman, L. E. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 5846. |
| [4] | For selected reviews of asymmetric Heck reaction, see: (a) Dounay, A. B.; Overman, L. E.; Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2945. |
| [4] | (b) Shibasaki, M.; Vogl, E. M.; Ohshima, T. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1533. |
| [4] | (c) Cartney, D. M.; Guiry, P. J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5122. |
| [4] | (d) Li, H.; Ding, C.; Xu, B.; Hou, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 765. (in Chinese) |
| [4] | (李浩, 丁昌华, 许斌, 侯雪龙, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 765.) |
| [4] | (e) Xie, J.-Q.; Liang, R.-X.; Jia, Y.-X. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 710. |
| [4] | (f) Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Zhang, J. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 374. |
| [5] | For selected reviews of catalytic dearomatization reactions, see: (a) Pouység, L.; Deffieux, D.; Quideau, S.; Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 2235. |
| [5] | (b) Roche, S. P.; Porco, J. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 4068. |
| [5] | (c) Zhuo, C.-X.; Zhang, W.; You, S.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12662. |
| [5] | (d) Zheng, C.; You, S.-L. Chem 2016, 1, 830. |
| [5] | (e) Wu, W.-T.; Zhang, L.; You, S.-L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1570. |
| [5] | (f) Sun, W.; Li, G.; Hong, L.; Wang, R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 2164. |
| [5] | (g) Huang, G.; Yin, B. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 405. |
| [5] | (h) Wang, Z. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 4354. |
| [5] | (i) Zheng, C.; You, S.-L. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 432. |
| [5] | (j) Liang, R.-X.; Jia, Y.-X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 734. |
| [6] | (a) Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Chang, L.; Xu, J.; Yao, H.; Wu, X. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2066. |
| [6] | (b) Douki, K.; Ono, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Shimokawa, J.; Kitamura, M.; Fukuyama, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14578. |
| [6] | (c) Li, X.; Zhou, B.; Yang, R.-Z.; Yang, F.-M.; Liang, R.-X.; Liu, R.-R.; Jia, Y.-X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13945. |
| [6] | (d) Yang, P.; You, S.-L. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7684. |
| [6] | (e) Liang, R.-X.; Song, L.-J.; Lu, J.-B.; Xu, W.-Y.; Ding, C.; Jia, Y.-X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7412. |
| [6] | (f) Han, X.-Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, P.; Liu, J.-L.; Xu, W.-Y.; Zheng, C.; Liang, R.-X.; You, S.-L.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y.-X. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 665. |
| [7] | Yang, P.; Xu, R.-Q.; Zheng, C.; You, S.-L. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 235. |
| [8] | Cho, C. S.; Uemura, S. J. Organomet. Chem. 1994, 465, 85. |
| [9] | Penn, L.; Shpruhman, A.; Gelman, D. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 3875. |
| [10] | Lee, A.-L. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5357. |
| [11] | Gao, S.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Yao, H.; Lin, A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 840. |
| [12] | For recent asymmetric transformations of indole: (a) Gao, H.; Miao, Y.-H.; Sun, W.-N.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, X.; Hua, Y.-Z.; Jia, S.-K.; Wang, M.-C.; Mei, G.-J. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2305101. |
| [12] | (b) Zhang, H.; Shi, F. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 3351. (in Chinese) |
| [12] | (张洪浩, 石枫, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 3351.) |
| [12] | (c) Sheng, F.-T.; Yang, S.; Wu, S.-F.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Shi, F. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2151. |
| [12] | (d) Sheng, F.-T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Shi, F. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3967. |
| [12] | (e) Zhang, Y.-C.; Jiang, F.; Shi, F. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 425. |
| [12] | (f) Zheng, C.; You, S.-L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 974. |
| [12] | (g) Chen, J.-B.; Jia, Y.-X. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 3550. |
| [12] | (h) Dalpozzo, R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 742. |
| [12] | (i) Bartoli, G.; Bencivenni, G.; Dalpozzo, R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4449. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |