

用于石墨负极的高性能聚丙烯酸锂基复合粘结剂的制备及性能研究
收稿日期: 2024-05-16
网络出版日期: 2024-07-02
基金资助
国家重点研发专项课题(2022YFB2502103); 厦门市重大科技项目(3502Z20231057); 国家自然科学基金(22309153); 国家自然科学基金(22288102); 中央高校基本科研业务费(20720230039)
A Lithium Polyacrylate-based High-performance Composite Binder for Graphite Anode
Received date: 2024-05-16
Online published: 2024-07-02
Supported by
National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFB2502103); Xiamen Science and Technology Project(3502Z20231057); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22309153); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22288102); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(20720230039)
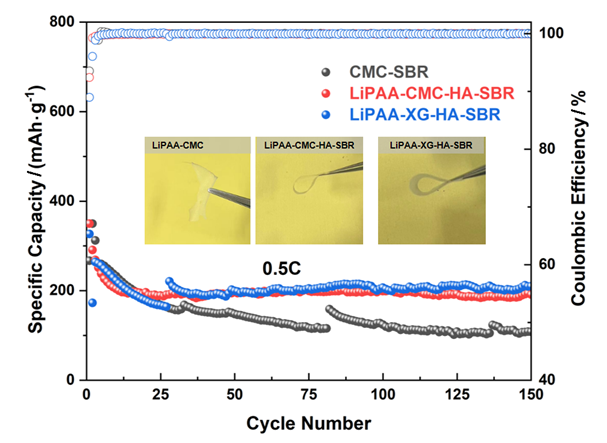
聚丙烯酸锂(LiPAA)由于其较高的离子电导率和良好的化学稳定性被广泛用作锂离子电池负极的粘结剂, 但是LiPAA粘度低、硬度大, 作为粘结剂时负极极片的粘接性能、柔韧性和可加工性是较大挑战. 本工作将LiPAA与多种高分子聚合物复配, 通过添加羧甲基纤维素(CMC)或黄原胶(XG)提高粘结剂粘度, 采用透明质酸钠(HA)降低粘结剂脆性, 添加丁苯橡胶(SBR)提高剥离强度, 开发了两款基于LiPAA的复配型粘结剂(LiPAA-CMC-HA-SBR及LiPAA-XG-HA-SBR). 与商用负极粘结剂(CMC-SBR)相比, 所得两款基于LiPAA的复配粘结剂不仅具有合适的粘接强度及柔韧性, 且可显著改善石墨颗粒、导电剂、电解液之间的亲和性, 促进锂离子在电极/电解液界面的传输, 从而获得高电化学性能. 在0.5 C的电流密度下, 在循环150圈后, 采用上述两款复配粘结剂制备的石墨负极容量分别为209 mAh•g−1及191 mAh•g−1, 远高于使用CMC-SBR粘结剂的石墨负极(108 mAh•g−1). 此外, 传统配方需添加大量SBR (≈50%), 而基于LiPAA的配方中只需少量SBR即可保持极片完整性, 且可在低粘结剂含量(≈3%)和高活性物质载量(≈95%)时保持良好力学性能, 制备的石墨负极极片也拥有良好的电化学性能, 具有较好工业化应用前景.
郑坤贵 , 刘君珂 , 胡轶旸 , 尹祖伟 , 周尧 , 李君涛 , 孙世刚 . 用于石墨负极的高性能聚丙烯酸锂基复合粘结剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024 , 82(8) : 833 -842 . DOI: 10.6023/A24050160
Lithium polyacrylate (LiPAA) is widely used as a binder for lithium-ion battery anodes due to its high ionic conductivity and good chemical stability. However, LiPAA has disadvantages such as low viscosity and high hardness, resulting in the adhesive performance, flexibility and processability of the anode becoming an issue when LiPAA is used as a binder. In this paper, a composite formula was developed by integrating LiPAA with other polymers, including carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) or Xanthan gum (XG) to tune the viscosity, sodium hyaluronate (HA) to reduce the brittleness, and benzene butadiene rubber (SBR) to improve the stripping strength. On this basis, two LiPAA-based composite binders (LiPAA-CMC-HA-SBR and LiPAA-XG-HA-SBR) were developed. Compared with the commercial anode binder (CMC-SBR), the two LiPAA-based composite binders both demonstrate well-tuned bonding strength and flexibility; more importantly, they also can significantly improve the interfacial affinity between the graphite particles, the conductive agent and the electrolyte, which hence promotes the diffusion kinetics of lithium ions at the electrode/electrolyte interface and thus improves the electrochemical performance of the graphite anode. At the current density of 0.5 C, after 150 cycles, the graphite anode prepared with our two composite binders displayed a capacity of 209 mAh•g−1 and 191 mAh•g−1, respectively, which was much higher than the graphite anode prepared with the commercial CMC-SBR binder (which is 108 mAh•g−1). The graphite anode prepared with our binder also demonstrates much higher rate capability and better cycling stability compared to the control. Characterizations of the cycled anode reveal that, in the anode prepared with our binders, a much more homogeneous distribution of the conductive carbon and the graphite particles was observed, and a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) with a higher fraction of LiF was formed. In addition, in the commercial CMC-SBR formula, a mass fraction of SBR up to 50% is required; in comparison, in our two LiPAA-based formulations, only a small fraction of SBR is employed yet which can still maintain the integrity of the anode sheet. It is worth noting that, at a low binder content (≈3%) and high active material load (≈95%), the graphite anode elec trode prepared by these two composite binders can still maintain remarkable mechanical strength, and it also demonstrates excellent electrochemical performance, showing the promising industrialization potential of such LiPAA-based composite binders.

| [1] | Boudet, H. S. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 446. |
| [2] | Wang, X.; Li, Y. B.; Du, L. Y.; Gao, F. J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L. J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X. Z.; Hu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 627 (in Chinese). |
| [2] | (王啸, 李有彬, 杜玲玉, 高福杰, 吴强, 杨立军, 陈强, 王喜章, 胡征, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 627.) |
| [3] | Wu, M. Y.; Xiao, X. C.; Vukmirovic, N.; Xun, S. D.; Das, P. K.; Song, X. Y.; Olalde-Velasco, P.; Wang, D. D.; Weber, A. Z.; Wang, L. W.; Battaglia, V. S.; Yang, W. L.; Liu, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12048. |
| [4] | Kovalenko, I.; Zdyrko, B.; Magasinski, A.; Hertzberg, B.; Milicev, Z.; Burtovyy, R.; Luzinov, I.; Yushin, G. Science 2011, 334, 75. |
| [5] | Agubra, V. A.; Fergus, J. W. J. Power Sources 2014, 268, 153. |
| [6] | Xu, T.; Sun, W.; Kong, T. C.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. T. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2024, 40, 85 (in Chinese). |
| [6] | (许涛, 孙伟, 孔天赐, 周杰, 钱逸泰, 物理化学学报, 2024, 40, 85.) |
| [7] | Tang, S. Y.; Lu, G. T.; Su, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, X. Z.; Zhang, G. Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y. G. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sinica 2022, 38, 33 (in Chinese). |
| [7] | (唐诗怡, 鹿高甜, 苏毅, 王广, 李炫璋, 张广琦, 魏洋, 张跃钢, 物理化学学报, 2022, 38, 33.) |
| [8] | Park, T. S.; Oh, E. S.; Lee, S. M. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 1191. |
| [9] | Hofmann, K.; Hegde, A. D.; Liu-Theato, X.; Gordon, R.; Smith, A.; Willenbacher, N. J. Power Sources 2024, 593, 233996. |
| [10] | Wang, X. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Wei, L. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 24 (in Chinese). |
| [10] | (王晓钰, 张渝, 马磊, 魏良明, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 24.) |
| [11] | Lee, J. H.; Paik, U.; Hackley, V. A.; Choi, Y. M. J. Power Sources 2006, 161, 612. |
| [12] | Magasinski, A.; Zdyrko, B.; Kovalenko, I.; Hertzberg, B.; Burtovyy, R.; Huebner, C. F.; Fuller, T. F.; Luzinov, I.; Yushin, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3004. |
| [13] | Li, Z. H.; Tang, W. T.; Yang, Y. J.; Lai, G. Y.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, H. Y.; Qiu, J. C.; Wei, X. J.; Wu, S. X.; Lin, Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2206615. |
| [14] | Dang, D. Y.; Wang, Y. K.; Wang, M.; Hu, J. Z.; Ban, C. M.; Cheng, Y. T. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 10940. |
| [15] | Guo, M. J.; Xiang, C. C.; Hu, Y. Y.; Deng, L.; Pan, S. Y.; Lv, C.; Chen, S. X.; Deng, H. T.; Sun, C. D.; Li, J. T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, S. G. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 425, 140704. |
| [16] | Wei, L. M.; Chen, C. X.; Hou, Z. Y.; Wei, H. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19583. |
| [17] | Luo, C.; Wu, X. F.; Zhang, T.; Chi, S. S.; Liu, Z. Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Y.; Deng, Y. H. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 306, 2000525. |
| [18] | Lee, H. A.; Shin, M. Y.; Kim, J. M.; Choi, J. W.; Lee, H. S. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007460. |
| [19] | Li, Y.; Jin, B. Y.; Wang, K. Y.; Song, L. N.; Ren, L. H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhan, X. L.; Zhang, Q. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132235. |
| [20] | Hu, L. L.; Jin, M. H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. X.; Ajdari, F. B.; Song, J. X. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111560. |
| [21] | Wang, R.; Liu, Z. K.; Yan, C.; Jia, L.; Huang, Y. H. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2023, 39, 81 (in Chinese). |
| [21] | (汪茹, 刘志康, 严超, 伽龙, 黄云辉, 物理化学学报, 2023, 39, 81.) |
| [22] | Pieczonka, N. P. W.; Borgel, V.; Ziv, B.; Leifer, N.; Dargel, V.; Aurbach, D.; Kim, J. H.; Liu, Z. Y.; Huang, X. S.; Krachkovskiy, S. A.; Goward, G. R.; Halalay, I.; Powell, B. R.; Manthiram, A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501008. |
| [23] | Wang, Y. Q.; Ma, Z.; Cao, Z.; Cai, T.; Liu, G.; Cheng, H. R.; Zhao, F.; Cavallo, L.; Li, Q.; Ming, J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305974. |
| [24] | Lee, Y. S.; Ryu, K. S. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16617. |
| [25] | Rahim, S.; Naveed, A.; Amir, A. R.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. J.; Hu, J. P.; Zhao, X. H.; Peng, Y.; Deng, Z. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2019, 35, 1382 (in Chinese). |
| [25] | (拉希姆?沙阿, 纳维德?阿拉姆, 阿米尔?拉扎克, 杨成, 陈宇杰, 胡加鹏, 赵晓辉, 彭扬, 邓昭, 物理化学学报, 2019, 35, 1382.) |
| [26] | Weisenberger, C.; Harrison, D. K.; Zhou, C. K.; Knoblauch, V. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 461, 142629. |
| [27] | Pan, S. Y.; Yang, X. R.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, C.; Deng, H, T.; Guo, M. J.; Chen, S. X.; Hu, Y. Y.; Deng, L.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J. T.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S. G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55700. |
| [28] | Huang, Y. S.; Wang, C. A.; Lv, H. F.; Xie, Y. S.; Zhou, S. Y.; Ye, Y. D.; Zhou, E.; Zhu, T. Y.; Xie, H. Y.; Jiang, W.; Wu, X. J.; Kong, X. H.; Jin, H. C.; Ji, H. X. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2308675. |
| [29] | Yang, Y. Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H. L. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7666. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |