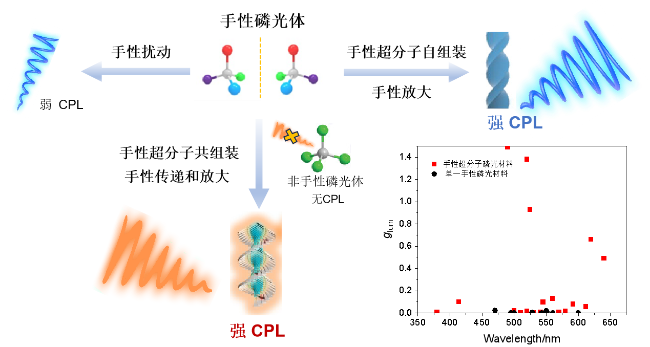
1 引言
2 基于分子间作用力的手性超分子室温磷光材料
2.1 基于分子间氢键相互作用的CP-RTP材料
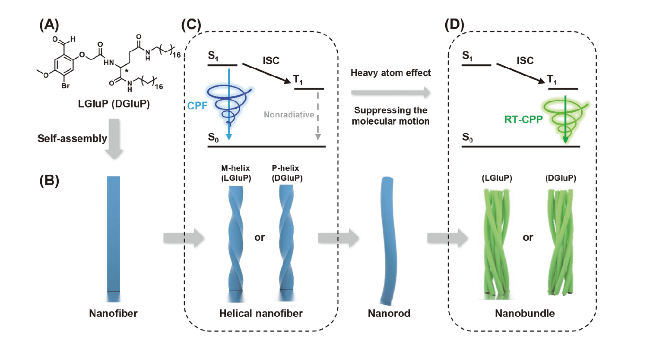
图2 (A) LGluP (DGluP)的化学结构; (B)从纳米纤维到纳米束的自组装机制; (C)螺旋纳米纤维激发能图; (D)纳米束激发能图[40].Figure 2 (A) Chemical structure of LGluP (DGluP); (B) self-assembly mechanisms from nanofiber to nanobundle; excitation energy diagram of helical nanofiber (C) and nanobundle (D)[40] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH. |
2.2 基于主客体相互作用策略的CP-RTP材料
2.3 基于手性超分子凝胶的CP-RTP材料
图5 (a) HTB-DG/LG的结构和刺激响应性手性单组分溶胶-凝胶体系示意图; HTB-DG/LG凝胶的(b) CD光谱和(c) glum值图(λex=365 nm); (d)在环境光(顶部)和紫外光(底部)的凝胶态和溶胶态的HTB-DG图像[51]Figure 5 (a) Structures of HTB-DG/LG and a schematic of the stimuli-responsive chiral single-component sol-gel system; (b) CD spectra and (c) corresponding glum curves (λex=365 nm) for HTB-DG/LG organogels; (d) photographs of HTB-DG in gel and sol states under ambient light (top) and UV light (bottom)[51] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry. |
图6 (a) L-Lys-C14/18和L-Lys-Amide-C18自组装形成纳米管、纳米片和纤维的分子结构; (b) L-Lys-C18的激发波长依赖CP-RTP和多色圆偏振余辉示意图[54]Figure 6 (a) Molecular structure of L-Lys-C18, L-Lys-C14 and L-Lys-Amide-C18, which self-assembled to form nanotube, nanosheet and fiber, respectively; (b) Schematic diagram of excitation wavelength-dependent CP-RTP and multicolor CP afterglow of L-Lys-C18 [54] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. |
2.4 基于超分子聚合物的CP-RTP材料
2.5 基于手性多孔金属-有机骨架的CP-RTP材料
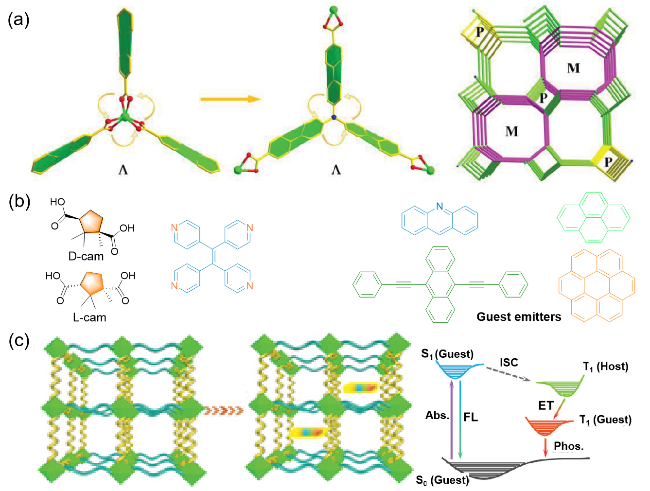
图9 (a)三齿配体, 其中臂侧在配位相互作用的驱动下沿一个方向发生旋转, 以及具有两种螺旋链的简化网络[60]; (b) D/L-cam、四吡啶乙烯和客体分子结构式; (c)将客体发射体封装到手性孔中以形成三明治结构和客体和主体之间的传输模型[61]Figure 9 (a) Tridentate ligand like a fan, where the arm side occurs the rotation in one direction driven by coordination interaction and simplified network with two kinds of helix chains[60], Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH; (b) the molecular structures of D/L-cam, 1,1,2,2-tetra(pyridin-4-yl)ethene and guest emitters; (c) guest emitters were encapsulated into chiral pores to form the sandwich structure and proposed transfer model between guest and host[61], Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH |
2.6 基于手性环铂络合物的CP-RTP材料
图10 (a)由PtN和PtBox组成的超螺旋共组装获得圆偏振磷光的策略[62]; (b)结合自下而上和自上而下的方法提高磷光Pt(II)配合物的CPL性能[63]Figure 10 (a) Strategy to obtaining circularly polarized phosphorescence from superhelical co-assemblies consisting of PtN and PtBox[62], Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry; (b) Combined bottom-up and top-down approach toward improving the CPL performance of phosphorescent Pt(II) complexes[63], Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2022, Wiley-VCH. |
3 基于液晶的手性超分子室温磷光材料
3.1 自液晶体系有机圆偏振室温磷光材料
3.2 共组装液晶有机圆偏振室温磷光材料
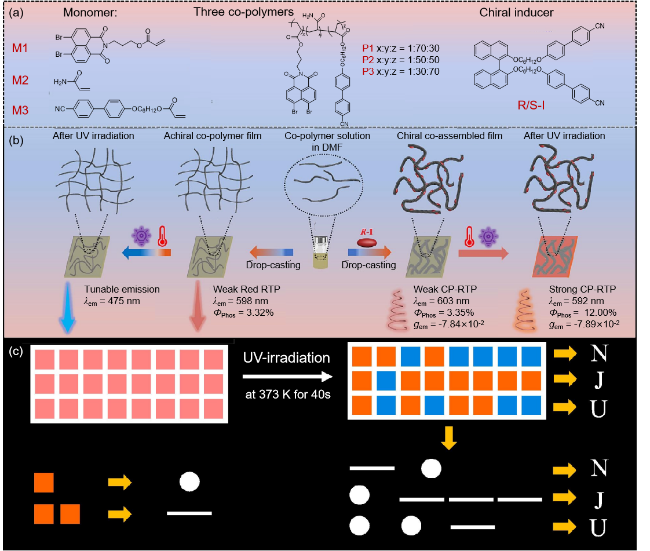
图13 (a)液晶单体、共聚物和手性诱导剂的化学结构式; (b)共组装原理图; (c)信息的有效加密和传输应用[83]Figure 13 (a) The chemical structures of monomers, co-polymers and chiral inducer; (b) schematic diagram of co-assembly; (c) The application of effective encryption and transmission of information[83] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2024, Elsevier. |
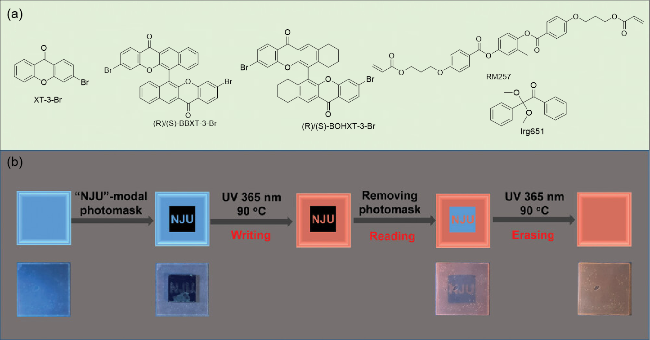
图14 (a) XT-3-Br, BBXT-3-Br, BOHXT-3-Br, RM257和Irg651化学结构式; (b)基于BOHXT-3-Br@PRM257薄膜的写入、读取和擦除的智能信息存储应用[86]Figure 14 (a) The chemical structures of XT-3-Br, BBXT-3-Br, BOHXT-3-Br, RM257 and Irg651; (b) the intelligent information storage device based on BOHXT-3-Br@PRM257 film, including writing, removing and erasing of information[86] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH. |
图15 (a) RTP polymer, RM257, R811和IRG 651的化学结构式[87]; (b)在“UV开启、UV关闭后无偏振片、UV关闭后左旋圆偏片, UV关闭后右旋圆偏片”条件下的数字图案照片[87]; (c)光响应材料M1的化学结构式[88]; (d) 405 nm 紫外光照射下P1-SHS-M1薄膜通过不同掩模的动态、可逆光控制[88]Figure 15 (a) The molecular structures of RTP polymer, RM257, R811 and IRG 651[87]; (b) photographs of number patterns under the conditions of UV on, UV off without filter, UV off with L-CPF, and UV off with R-CPF[87], Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH; (c) chemical structures of the photo-responsive material M1[88]; (d) dynamic and reversible light control of P1-SHS-M1 film upon the irradiation of 405 nm UV by passing through different masks[88], Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2024, Wiley-VCH. |
图16 (a)基于CLCES的可调CP-RTP原理图; (b) CLCE的合成路线; (c)结合CP-RTP和CLCE动态可重构特性的4D信息加密[91]Figure 16 (a) Schematic diagram of tunable CP-RTP based on CLCEs; (b) synthesis route of CLCE; (c) 4D information encryption combining CP-RTP with dynamic reconfigurable features of CLCEs[91] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2022, Elsevier. |
图17 (a) 多环芳烃掺杂PMMA的CNCs复合膜的制备工艺; (b)基于CNC膜的结构色、RTP和CP-RTP原理图; (c)基于CNC薄膜的3×3像素阵列生成的5通道(结构色、磷光、3 s延迟发射、在L-CPF和R-CPF下的CP-RTP)信息加密[97]Figure 17 (a) Fabrication process of hybrid film based on CNCs infiltrated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon doped PMMA; (b) Schematic illustration of CNC based hybrid film pad with structural color, RTP and CP-RTP; (c) information encryption with 5 channels (structural color, phosphorescence, delayed emission with 3 s, CP-RTP with L-CPF and R-CPF) information created by 3×3 pixels’ array based on hybrid CNCs film[97] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2024, Elsevier. |