Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (10): 1420-1437.DOI: 10.6023/A23050232 Previous Articles Next Articles
Special Issue: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
Review
徐赫a,b, 韩鹏博a,b, 秦安军a,b,*( ), 唐本忠b,c,d
), 唐本忠b,c,d
投稿日期:2023-05-17
发布日期:2023-07-13
作者简介: |
徐赫, 2021年在合肥工业大学获得学士学位, 现为华南理工大学2021级硕士研究生. 研究兴趣是有机/聚合物光热功能材料. |
 |
秦安军, 1999 年和2004 年分别在山西大学和中国科学院化学研究所获得学士和博士学位. 2005至2008年先后在香港科技大学化学系和浙江大学高分子科学与工程学系从事博士后研究. 2008 年12月起先后任浙江大学副研究员、副教授, 2013年9月至今任华南理工大学教授、博导. 研究兴趣为高分子合成化学以及有机/聚合物功能材料. 曾获国家自然科学一等奖(2017, 2/5). 目前, 担任Aggregate《聚集体》期刊责任主编. |
 |
唐本忠, 1982年和1988年分别在华南理工大学和日本京都大学获得学士学位和博士学位, 于1989~1994年在加拿大多伦多大学从事博士后研究. 1994年加盟香港科技大学, 2009年、2017年、2020年先后当选中国科学院院士、亚太材料科学院院士、发展中国家科学院院士. 2021年加入香港中文大学(深圳)并担任理工学院院长、校长学勤讲座教授. 主要从事高分子化学和先进功能材料研究, 是AIE概念的提出者和AIE研究的引领者. 2014年至今连续入选ESI材料和化学双领域“高被引科学家”. 曾获Biomaterials Global Impact Award, Nano Today国际科学奖、2017年度国家自然科学一等奖、何梁何利基金科学与技术进步奖等奖项. |
基金资助:
He Xua,b, Pengbo Hana,b, Anjun Qina,b( ), Ben Zhong Tangb,c,d
), Ben Zhong Tangb,c,d
Received:2023-05-17
Published:2023-07-13
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:Share
He Xu, Pengbo Han, Anjun Qin, Ben Zhong Tang. Recent Advances and Application Prospects in Photothermal Materials★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1420-1437.
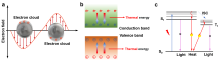
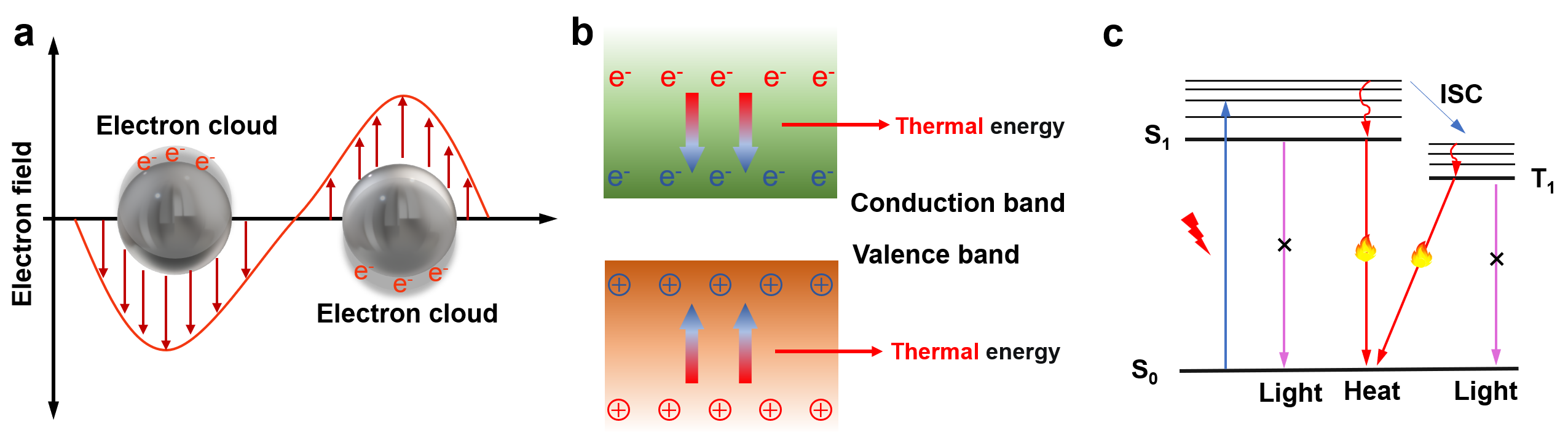
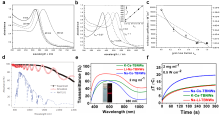

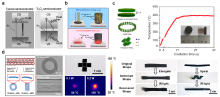

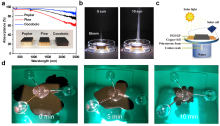

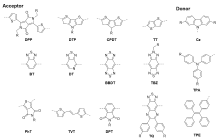
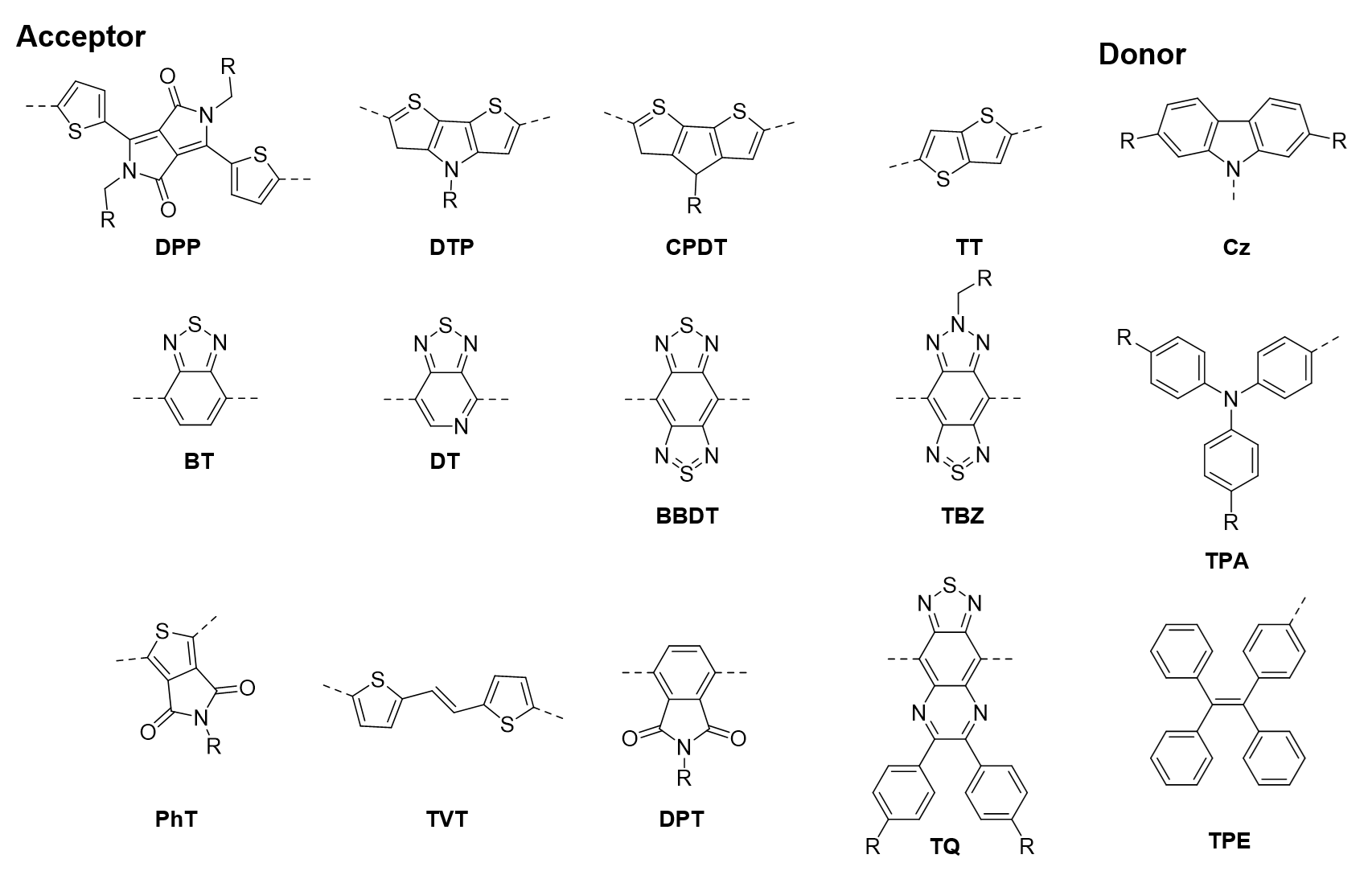
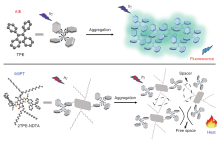





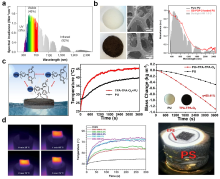

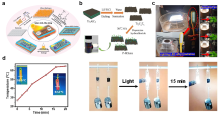

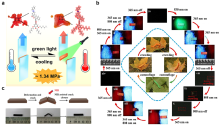

| [117] |
Bai, W.; Yang, P.; Liu, H.; Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 3493.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.2c00506 |
| [1] |
Mekonnen, M. M.; Hoekstra, A. Y. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323.
|
| [2] |
Kerr, R. A.; Service, R. F. Science 2005, 309, 101.
doi: 10.1126/science.309.5731.101 |
| [3] |
Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Nature 2012, 488, 294.
doi: 10.1038/nature11475 |
| [4] |
Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W. A. Science 2011, 333, 712.
doi: 10.1126/science.1200488 |
| [5] |
Zhao, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, S.; Williams, G. R.; Mahadi, A. H.; Ma, D. Joule 2019, 3, 920.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2019.03.003 |
| [6] |
Ni, G.; Li, G.; Boriskina, S. V.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, G. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16126.
doi: 10.1038/nenergy.2016.126 |
| [7] |
Ding, W.; Bauer, T. Engineering 2021, 7, 334.
doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2020.06.027 |
| [8] |
Song, C.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Xiao, D.; Ma, D. Chem Catalysis 2022, 2, 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.checat.2021.10.005 |
| [9] |
Gao, M.; Zhu, L.; Peh, C. K.; Ho, G. W. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 841.
doi: 10.1039/C8EE01146J |
| [10] |
Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Hu, L. Joule 2019, 3, 683.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.12.023 |
| [11] |
Aslam, U.; Rao, V. G.; Chavez, S.; Linic, S. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 656.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-018-0138-x |
| [12] |
Jiang, N.; Zhuo, X.; Wang, J. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3054.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00252 |
| [13] |
Brongersma, M. L.; Halas, N. J.; Nordlander, P. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 25.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.311 |
| [14] |
Zhou, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Nat. Photonics. 2016, 10, 393.
doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.75 |
| [15] |
Link, S.; El-Sayed, M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 4212.
doi: 10.1021/jp984796o |
| [16] |
Jain, P. K.; Lee, K. S.; El-Sayed, I. H.; El-Sayed, M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7238.
doi: 10.1021/jp057170o |
| [17] |
Liu, X.; Wei, R.; Hoang, P. T.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Keller, P. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3022.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v25.20 |
| [18] |
Yao, J.; Li, T.; Ma, S.; Qian, G.; Song, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, G. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 115040.
doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/abb572 |
| [19] |
Sun, W.; Zhong, G.; Kubel, C.; Jelle, A. A.; Qian, C.; Wang, L.; Ebrahimi, M.; Reyes, L. M.; Helmy, A. S.; Ozin, G. A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6329.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.22 |
| [20] |
Zhou, P.; Navid, I. A.; Xiao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Dong, W. J.; Wang, P.; Sun, K.; Mi, Z. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 8122.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c01459 |
| [21] |
Link, S.; Wang, Z. L.; El-Sayed, M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 3529.
doi: 10.1021/jp990387w |
| [22] |
Zhang, S.; Shi, Y.; He, T.; Ni, B.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 8727.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b04437 |
| [23] |
Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Wei, N.; Weng, Y.; Dong, S.; Qi, D.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, T. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603730.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.3 |
| [24] |
Yang, J.; Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Shaw, S. K.; Schiffbauer, J.; Pillers, M. A.; Mu, X.; Luo, S.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Ptasinska, S.; Lieberman, M.; Luo, T. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5510.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b00367 |
| [25] |
Feng, G.; Zhang, G. Q.; Ding, D. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8179.
doi: 10.1039/D0CS00671H |
| [26] |
Chen, Q.; Pei, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 623.
doi: 10.1039/C7SC02967E |
| [27] |
Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; He, Z. ; Wang, H.; Wu, A.; Fei, W.; Zheng, C.; Liu, E.; Huang, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 38550.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c10842 |
| [28] |
Nair, R. V.; Puthiyaparambath, M. F.; Chatanathodi, R.; Nair, L. V.; Jayasree, R. S. Nanoscale, 2022, 14, 13561.
doi: 10.1039/D2NR03163A |
| [29] |
Neumann, O.; Urban, A. S.; Day, J.; Lal, S.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N. J. ACS Nano. 2013, 7, 42.
doi: 10.1021/nn304948h |
| [30] |
Hogan. N. J.; Urban, A. S.; Ayala-Orozco, C.; Pimpinelli, A.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N. J. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 4640.
doi: 10.1021/nl5016975 |
| [31] |
Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Feng, R.; Bernard, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Shang, W.; Tao, P.; Song, C.; Deng, T. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2768.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v27.17 |
| [32] |
Chen, M.; He, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, J. Energy Convers. Manage. 2016, 127, 293.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.09.015 |
| [33] |
Zhou, L.; Tan, Y.; Ji, D.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J.; Gan, Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, J. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501227.
|
| [34] |
Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhu, X.; Dai, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yan, X.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Hitz, E.; Luo, W.; Lu, M.; Yang, B.; Hu, L. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701028.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.4 |
| [35] |
Zhu, G.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2016, 8, 31716.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b11466 |
| [36] |
Ding, D.; Huang, W.; Song, C.; Yan, M.; Guo, C.; Liu, S. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6744.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC01427A |
| [37] |
Chen, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yu, T.; Ye, M. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 19849.
doi: 10.1039/C7RA03007J |
| [38] |
Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Lu, Q.; Song, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1559.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00850-8 |
| [39] |
Lu, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Gu, L.; Song, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 9858.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c03607 |
| [40] |
Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18754.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b08818 |
| [41] |
Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Yu, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100703.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.20 |
| [42] |
Liu, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, H.; Shi, W.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17557.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c07375 |
| [43] |
Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhuo, S.; Shi, L.; Chang, J.; Hong, S.; Ng, K-C.; Wang, P. Joule 2018, 2, 1171.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.03.013 |
| [44] |
Cui, L.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Qu, L. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1706805.
|
| [45] |
Fu, Y.; Wang, G.; Ming, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, B.; Mei, T.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Carbon 2018, 130, 250.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.12.124 |
| [46] |
Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhou, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604031.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.5 |
| [47] |
Chen, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; Wu, B.; Cui, J.; Fang, X.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, N. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 14571.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA04420A |
| [48] |
Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Gong, A.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J. Y.; Yang, B.; Xie, J.; Hu, L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701756.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.30 |
| [49] |
Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1223.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01274 |
| [50] |
Sajadi, S. M.; Farokhnia, N.; Irajizad, P.; Hasnain, M.; Ghasemi, H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4700.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA01205A |
| [51] |
Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, D.; Cao, M.; Jiang, L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7, 13645.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b03435 |
| [52] |
Wu, J.; Lei, J. H.; He, B.; Deng, C.-X.; Tang, Z.; Qu, S. Aggregate 2021, 2, e139.
|
| [53] |
Jia, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, F.; Kuang, Y.; Pastel, G.; Xie, H.; Yang, B.; Das, S.; Hu, L. Joule 2017, 1, 588.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2017.09.011 |
| [54] |
Cheng, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, B.; Jiang, J.; Tu, C.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, K.; Yuan, H.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Liu, Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 15562.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c04454 |
| [55] |
Gao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Tao, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Aggregate. 2023, 4, e248.
|
| [56] |
Zhou, P.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, L.; Cai, Z.; Xu, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142508.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.142508 |
| [57] |
Niu, W.; Chen, G. Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, J. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2108232.
|
| [58] |
Jung, H. S.; Verwilst, P.; Sharma, A.; Shin, J.; Sessler, J. L.; Kim, J. S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2280.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00522A |
| [59] |
Xu, C.; Ye, R.; Shen, H.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202204604.
|
| [60] |
Zhu, S.; Tian, R.; Antaris, A. L.; Chen, X.; Dai, H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1900321.
|
| [61] |
Espín, J.; Garzón-Tovar, L.; Carné-Sánchez, A.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9555.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b00557 |
| [62] |
Lu, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Müllen, K.; Yin, M. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 767.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08434-4 |
| [63] |
Wang, D.; Kan, X.; Wu, C.; Gong, Y.; Guo, G.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5223.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC01834A |
| [64] |
Chen, Y.-T.; Wen, X.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Ni, S.; Chen, S.; Dang, L.; Li, M.-D. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 28781.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c03940 |
| [65] |
Xu, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Shen, J.; Keoingthong, P.; Zhang, L.; Yin, Z.; Cai, X.; Chen, Z.; Tan, W. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202571.
|
| [66] |
Li, J.; Liu, W.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, M.; Fang, Z.; Li, Z.; Tu, Z.; Huang, J. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 823.
doi: 10.1039/D1GC03571A |
| [67] |
Dai, S.; Yue, S.; Ning, Z.; Jiang, N.; Gan, Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 14668.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c03172 |
| [68] |
Cai, Y.; Liang, P.; Tang, Q.; Yang, X.; Si, W.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, X. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1054.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07927 |
| [69] |
Qi, J.; Fang, Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Ding, D.; Tang, B. Z. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7177.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b03062 |
| [70] |
Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Ji, M.; Zhao, M.; Shen, M.; Han, X.; Jia, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106247.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.49 |
| [71] |
Liu, J.; Cui, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117087.
|
| [72] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B. Z. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740.
|
| [73] |
Zhao, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Wang, F.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.; He, X.; Cai, Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, P.; Phillips, D. L.; Ding, D.; Tang, B. Z. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 768.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08722-z |
| [74] |
Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113653.
|
| [75] |
Zhang, L.; Tang, B.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Wang, P. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4889.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v27.33 |
| [76] |
Hao, D.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Cai, Z. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 141, 406.
doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.117 |
| [77] |
Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Xu, B.; Xu, H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1807716.
|
| [78] |
Bai, W.; Xiang, P.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Tang, Z.; Yang, P.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 6426.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.2c01440 |
| [79] |
Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Yang, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 8629.
doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.2c01401 |
| [80] |
Chen, J.; Qi, J.; He, J.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 12748.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c02195 |
| [81] |
Li, J.; Rao, J.; Pu, K. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 217.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.025 |
| [82] |
Liu, L.; Liu, M.-H.; Deng, L.-L.; Lin, B.-P.; Yang, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11333.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b06410 |
| [83] |
Su, Y.; Chen, Z.; Tang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 24424.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.46 |
| [84] |
Guo, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 967 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21040173 |
|
(郭彩霞, 马小杰, 王博, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 967.)
|
|
| [85] |
Yan, X.; Lyu, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Shang, P.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201900.
|
| [86] |
Jiang, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 466 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20030088 |
|
(蒋成浩, 冯霄, 王博, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 466.)
|
|
| [87] |
Zheng, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1716.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00938 |
| [88] |
Utrera-Barrios, S.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M. A.; Santana, H. M. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 2882.
doi: 10.1039/D0MH00535E |
| [89] |
Lu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Fu, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 1078.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-022-1505-8 |
| [90] |
Wang, D.; Lee, M. M. S.; Xu, W.; Shan, G.; Zheng, X.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Hu, X.; Tang, B. Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5628.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.17 |
| [91] |
Li, J.; Wang, J.; Han, T.; Hu, X.; Lee, M. M. S.; Wang, D.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2105999.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.51 |
| [92] |
Li, J; Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Pu, K. Adv. Mater. 2020, 33, 2003458.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.4 |
| [93] |
Ng, C. W.; Li, J.; Pu, K. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804688.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v28.46 |
| [94] |
Fu, Z.; Willams, G. R.; Niu, S.; Wu, J.; Gao, F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14739.
doi: 10.1039/D0NR02291H |
| [95] |
Yan, P.; Guo, W.; Liang, Z.; Meng, W.; Yin, Z.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Yan, J.; Xiao, D.; Zou, R.; Ma, D. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2341.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-019-2349-0 |
| [96] |
Zhao, H.; Liu, J.-X.; Yang, C.; Yao, S.; Su, H.-Y.; Gao, Z.; Dong, M.; Wang, J.; Rykov, A. L.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.-X.; Ma, D. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 2712.
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.020.202000555 |
| [97] |
Wu, C.; Lin, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, T.; Rui, N.; Yao, S.; Deng, Y.; Yang, F.; Xu, W.; Luo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, B.; Wen, X.; Rodriguez, J. A.; Ma, D. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5767.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19634-8 |
| [98] |
Kennedy III, J. C.; Datye, A. K. J. Catal. 1998, 179, 375.
doi: 10.1006/jcat.1998.2242 |
| [99] |
Meng, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Ouyang, S.; Li, P.; Hu, H.; Kako, T.; Iwai, H.; Tanaka, A.; Ye, J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11478.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v53.43 |
| [100] |
Wang, R.; Zou, Y.; Hong, S.; Xu, M.; Ling, L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 932 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21030118 |
|
(王瑞兆, 邹云杰, 洪晟, 徐铭楷, 凌岚, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 932.)
|
|
| [101] |
Gu, L.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Gao, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3710.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06117 |
| [102] |
Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Everitt, H. O.; Liu, J. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 1706.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04706 |
| [103] |
Gao, Q.; Tu, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 1242.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-021-1002-1 |
| [104] |
Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Yan, T.; Lou, X.; Zhang, C.; Cao, M.; Zhang, L.; Sham, T.-K.; Zhang, Q.; He, L.; Chen, J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210283.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.2 |
| [105] |
Liu, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, P.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Cao, M.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Matter 2022, 5, 1035.
|
| [106] |
Chen, G.; Jiang, Z.; Li, A.; Chen, X.; Ma, Z.; Song, H. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021, 9, 16805.
doi: 10.1039/D1TA03695E |
| [107] |
Cheng, S.; Guo, P.; Wang, X.; Che, P.; Han, X.; Jin, R.; Heng, L.; Jiang, L. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133411.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133411 |
| [108] |
Abiola, T. T.; Rioux, B.; Toldo, J. M.; Alarcan, J.; Woolley, J. M.; Turner, M. A. P.; Coxon, D. J. L.; Casal, M. T. D.; Peyrot, C.; Mention, M. M.; Buma, W. J.; Ashfold, M. N. R.; Breauning, A.; Barbatti, M.; Stavros, V. G.; Allais, F. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 15239.
doi: 10.1039/D1SC05077J |
| [109] |
Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Y.; Zou, X.; Peng, W.; Li, W.; Wu, P.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8948.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.16 |
| [110] |
Wu, Z.; Ji, C.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Mullen, K.; Pan, K.; Yin, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7385.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01056 |
| [111] |
Du, X.; Wang, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, S.; Dong, Y.; Lin, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 15225.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c00117 |
| [112] |
Yang, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, H. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2166.
doi: 10.1039/C8PY00162F |
| [113] |
Son, D. H.; Bae, H. E.; Bae, M. J.; Lee, S.-H.; Cheong, I. W.; Park, Y. I.; Jeong, J.-E.; Kim, J. C. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 3802.
doi: 10.1021/acsapm.1c01768 |
| [114] |
Huang, Y.; Bisoyi, H. K.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, X. M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11247.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.20 |
| [115] |
Nie, Z.-Z.; Zuo, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, X.-M.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, H. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2334.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22644-9 |
| [116] |
Sun, Z.; Wei, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Hao, R.; Huang, M.; He, S. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 33404.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c04110 |
| [1] | Di Yang, Xiaofan Shi, Jijie Zhang, Xian-He Bu. Recent Research Progress and Prospect of Photothermal Materials in Seawater Desalination★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 1052-1063. |
| [2] | Yuan Zhang, Beining Zheng, Meichun Fu, Shouhua Feng. Research Progress in the Application of Spinel Oxides in Tumor Therapy★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 949-954. |
| [3] | Bo Sun, Wenwen Ju, Tao Wang, Xiaojun Sun, Ting Zhao, Xiaomei Lu, Feng Lu, Quli Fan. Preparation of Highly-dispersed Conjugated Polymer-Metal Organic Framework Nanocubes for Antitumor Application [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [4] | Dongrui Su, Xiaokang Ren, Yunhao Yu, Luyang Zhao, Tianyu Wang, Xuehai Yan. Tyrosine Derivative Regulated Enzyme Catalytic Pathway for Controllable Synthesis of Functional Melanin★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1486-1492. |
| [5] | Shen Zhang, Shan Feng, Longyu Ma, Yingying Yang, Chaoqun Liu, Ningning Song, Yanwei Yang. Research of Synergistic Photothermal Antibacterial Strategy Based on Polymeric Guanidine Derivative Grafted on Mesoporous Carbon Nanospheres [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 265-271. |
| [6] | Qi Wang, Hui Xia, Yanwei Xiong, Xinmin Zhang, Jie Cai, Chong Chen, Yicong Gao, Feng Lu, Quli Fan. Simple Preparation of Near-infrared-II Organic Small Molecule-based Phototheranostics by Manipulation of the Electron-donating Unit [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1485-1493. |
| [7] | Lixiang Pan, Yanqin Huang, Kuang Sheng, Rui Zhang, Quli Fan, Wei Huang. Applications of Hyaluronic Acid Nanomaterials in Fluorescence/Photoacoustic Imaging and Phototherapy [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(9): 1097-1106. |
| [8] | Caixia Guo, Xiaojie Ma, Bo Wang. Metal-organic Frameworks-based Composites and Their Photothermal Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 967-985. |
| [9] | Ruizhao Wang, Yunjie Zou, Sheng Hong, Mingkai Xu, Lan Ling. High-performance Pt0.01Fe0.05-g-C3N4 Catalyst for Photothermal Catalytic CO2 Reduction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(7): 932-940. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||