Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (11): 1663-1672.DOI: 10.6023/A23070328 Previous Articles
Review
韩逸之a,b, 蓝建慧b,*( ), 刘学a,*(
), 刘学a,*( ), 石伟群b,*(
), 石伟群b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-07-11
发布日期:2023-08-25
作者简介: |
韩逸之, 西安交通大学硕士研究生, 目前研究方向: 机器学习分子动力学. |
 |
蓝建慧, 副研究员, 2010年7月博士毕业于北京化工大学化学工程学院, 在中国科学院高能物理研究所工作至今. 长期致力于先进功能材料与有机萃取配体的分子设计, 主要从事核燃料循环化学以及能源环境领域中气体存储分离相关的基础研究. 在量子化学、第一性原理计算、分子动力学以及蒙特卡洛模拟等领域积累了丰富的研究经验, 擅长使用多尺度的计算模拟手段解决复杂的物理化学问题. 迄今为止, 在Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Nature Commun., ACS Nano, Adv. Funct. Mater., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, Coord. Chem. Rev., J. Electrochem. Soc., Chem. Commun., Inorg. Chem.等国内外知名期刊上发表论文150余篇, 先后主持过多项国家自然科学基金项目. |
 |
刘学, 本科毕业于天津大学化工学院, 博士毕业于荷兰莱顿大学, 后在莱顿大学从事博士后研究工作, 2020年加入西安交通大学材料学院. 长期从事框架及碳基新型分离膜材料开发工作. 以第一或通讯作者在Nature Nanotechnology, Nature Communications, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces等期刊发表论文多篇, 主持国家自然科学基金、陕西省科技厅项目等, 兼职中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会理事. |
 |
石伟群, 中国科学院高能物理研究所研究员, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 长期致力于核燃料循环化学与锕系元素化学相关基础研究, 在 JACS, Angew. Chem., Chem, CCS Chem., Nat. Commun., Adv. Mater., Environ. Sci. Technol.等国际知名期刊发表SCI论文300余篇, 成果被国内外同行广泛关注和引用. 文章总引13000余次, H因子58 (Google Scholar). 分别担任英文期刊Journal of Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Waste Tech- nology和Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology的编委与国际顾问编委, 中文期刊《核化学与放射化学》编委. 现为中国化学会核化学与放射化学专业委员会委员、中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会副理事长、中国有色金属学会熔盐化学与技术专业委员会副主任委员、中国核学会核化工分会常务理事. |
基金资助:
Yizhi Hana,b, Jianhui Lanb( ), Xue Liua(
), Xue Liua( ), Weiqun Shib(
), Weiqun Shib( )
)
Received:2023-07-11
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:Share
Yizhi Han, Jianhui Lan, Xue Liu, Weiqun Shi. Advances in Molecular Dynamics Studies of Molten Salts Based on Machine Learning[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1663-1672.
| 体系(ACln-BCl) | 物质的量比率 | T/K | RA-Cl | RB-Cl | RA-A | RB-B | RCl-Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgCl2-KCl[ | 8∶17 | 773 | 2.379 | 3.111 | 3.843 | 4.697 | 3.721 |
| — | 873 | 2.411 | 3.152 | 3.894 | 4.759 | 3.770 | |
| — | 973 | 2.307 | 3.110 | 3.982 | 4.800 | 3.803 | |
| — | 1073 | 2.335 | 3.092 | 3.976 | 4.860 | 3.850 | |
| CaCl2-KCl[ | 1∶4 | 1100 | 2.71 | 3.12 | — | — | 3.92 |
| 2∶3 | 1110 | 2.62 | 3.09 | — | — | 3.79 | |
| 1∶1 | 1058 | 2.75 | 3.09 | — | — | 3.76 | |
| 3∶2 | 1100 | 2.67 | 3.12 | — | — | 3.69 | |
| 4∶1 | 1100 | 2.66 | 3.12 | — | — | 3.57 | |
| AlCl3-LiCl[ | 1∶1 | 473 | 2.171 | 2.406 | — | — | 3.579 |
| — | 573 | 2.197 | 2.435 | — | — | 3.503 | |
| — | 673 | 2.108 | 2.349 | — | — | 3.554 | |
| — | 773 | 2.141 | 2.385 | — | — | 3.486 | |
| — | 873 | 2.175 | 2.299 | — | — | 3.542 | |
| CaCl2-NaCl[ | 4∶1 | 1100 | 2.71 | 2.71 | — | — | 3.86 |
| 3∶2 | — | 2.71 | 2.71 | — | — | 3.86 | |
| 2∶3 | — | 2.69 | 2.69 | — | — | 3.72 | |
| 1∶4 | — | 2.65 | 2.65 | — | — | 3.71 |
| 体系(ACln-BCl) | 物质的量比率 | T/K | RA-Cl | RB-Cl | RA-A | RB-B | RCl-Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgCl2-KCl[ | 8∶17 | 773 | 2.379 | 3.111 | 3.843 | 4.697 | 3.721 |
| — | 873 | 2.411 | 3.152 | 3.894 | 4.759 | 3.770 | |
| — | 973 | 2.307 | 3.110 | 3.982 | 4.800 | 3.803 | |
| — | 1073 | 2.335 | 3.092 | 3.976 | 4.860 | 3.850 | |
| CaCl2-KCl[ | 1∶4 | 1100 | 2.71 | 3.12 | — | — | 3.92 |
| 2∶3 | 1110 | 2.62 | 3.09 | — | — | 3.79 | |
| 1∶1 | 1058 | 2.75 | 3.09 | — | — | 3.76 | |
| 3∶2 | 1100 | 2.67 | 3.12 | — | — | 3.69 | |
| 4∶1 | 1100 | 2.66 | 3.12 | — | — | 3.57 | |
| AlCl3-LiCl[ | 1∶1 | 473 | 2.171 | 2.406 | — | — | 3.579 |
| — | 573 | 2.197 | 2.435 | — | — | 3.503 | |
| — | 673 | 2.108 | 2.349 | — | — | 3.554 | |
| — | 773 | 2.141 | 2.385 | — | — | 3.486 | |
| — | 873 | 2.175 | 2.299 | — | — | 3.542 | |
| CaCl2-NaCl[ | 4∶1 | 1100 | 2.71 | 2.71 | — | — | 3.86 |
| 3∶2 | — | 2.71 | 2.71 | — | — | 3.86 | |
| 2∶3 | — | 2.69 | 2.69 | — | — | 3.72 | |
| 1∶4 | — | 2.65 | 2.65 | — | — | 3.71 |
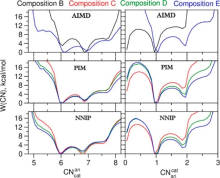

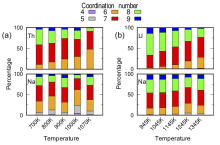

| [1] |
Abu-Khader M. M. Prog. Nucl. Energ. 2009, 51, 225.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2008.05.001 |
| [2] |
Chen G. Z.; Fray D. J.; Farthing T. W. J. N. Nature 2000, 407, 361.
doi: 10.1038/35030069 |
| [3] |
Wang K.; Jiang K.; Chung B.; Ouchi T.; Burke P. J.; Boysen D. A.; Bradwell D. J.; Kim H.; Muecke U.; Sadoway D. R. Nature 2014, 514, 348.
doi: 10.1038/nature13700 |
| [4] |
Zhong Y. K.; Liu Y. L.; Liu K.; Wang L.; Mei L.; Gibson J. K.; Chen J. Z.; Jiang S. L.; Liu Y. C.; Yuan L. Y.; Chai Z. F.; Shi W. Q. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5777.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26119-9 pmid: 34599195 |
| [5] |
alanne M.; Simon C.; Turq P.; Ohtori N.; Madden P. A. In Molten Salts Chemistry, Vol. 1, Eds.: Lantelme, F.; Groult, H., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2013, pp. 1-16.
|
| [6] |
Zhang X.; Zhang L.; Bo T.; Huang S.; Huang Z.; Shi W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3527.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2022.03.026 |
| [7] |
Jiang S.; Lan J.; Wang L.; Liu Y.; Zhong Y.; Liu Y.; Yuan L. L.; Zheng L.; Chai Z.; Shi W. Chem.-Eur. J. 2021, 27, 11721.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v27.45 |
| [8] |
Jiang S.; Liu Y.; Wang L.; Chai Z.; Shi W. Q. Chem.-Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202201145.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v28.60 |
| [9] |
Liu Y.-L.; Lan J.-H.; Wang L.; Jiang S.-L.; Liu Y.-C.; Zhong Y.-K.; Yang D.-W.; Zhang L.; Shi W.-Q. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139573.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139573 |
| [10] |
Kwon C.; Kang J.; Kang W.; Kwak D.; Han B. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 195, 216.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.123 |
| [11] |
Worth G. A.; Cederbaum L. S. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2004, 55, 127.
doi: 10.1146/physchem.2004.55.issue-1 |
| [12] |
Kresse G.; Furthmüller J. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169.
doi: 10.1103/physrevb.54.11169 pmid: 9984901 |
| [13] |
Tse J. S. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2002, 53, 249.
doi: 10.1146/physchem.2002.53.issue-1 |
| [14] |
Monticelli L.; Tieleman D. P. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 924, 197.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-017-5_8 pmid: 23034750 |
| [15] |
Perdew J. P.; Burke K.; Ernzerhof M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 pmid: 10062328 |
| [16] |
Huggins M. L.; Mayer J. E. J. Chem. Phys. 1933, 1, 643.
|
| [17] |
Salanne M.; Rotenberg B.; Jahn S.; Vuilleumier R.; Simon C.; Madden P. A. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2012, 131, 1.
|
| [18] |
Dewan L. C.; Simon C.; Madden P. A.; Hobbs L. W.; Salanne M. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 434, 322.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.12.006 |
| [19] |
Emerson M. S.; Sharma S.; Roy S.; Bryantsev V. S.; Ivanov A. S.; Gakhar R.; Woods M. E.; Gallington L. C.; Dai S.; Maltsev D. S.; Margulis C. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21751.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c09987 |
| [20] |
Wang H.; DeFever R. S.; Zhang Y.; Wu F.; Roy S.; Bryantsev V. S.; Margulis C. J.; Maginn E. J. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 214502.
doi: 10.1063/5.0023225 |
| [21] |
Howe M.; McGreevy R. L. Philp. Mag. B 1988, 58, 485.
|
| [22] |
Tosi M.; Fumi F. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1964, 25, 45.
doi: 10.1016/0022-3697(64)90160-X |
| [23] |
Fumi F.; Tosi M. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1964, 25, 31.
doi: 10.1016/0022-3697(64)90159-3 |
| [24] |
Dewan L. C.; Simon C.; Madden P. A.; Hobbs L. W.; Salanne M. J. Nucl. Mater. 2013, 434, 322.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.12.006 |
| [25] |
Nam H. O.; Bengtson A.; Vörtler K.; Saha S.; Sakidja R.; Morgan D. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 449, 148.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2014.03.014 |
| [26] |
Li X.; Song J.; Shi S.; Yan L.; Zhang Z.; Jiang T.; Peng S. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 571.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.6b10193 |
| [27] |
Kwon C.; Noh S. H.; Chun H.; Hwang I. S.; Han B. Int. J. Energ. Res. 2018, 42, 2757.
doi: 10.1002/er.v42.8 |
| [28] |
Guo H.; Li J.; Zhang H.; Li T.; Luo J.; Yu X.; Wu S.; Zong C. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 730, 587.
doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2019.06.060 |
| [29] |
Galamba N.; Costa Cabral B. J. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 124502.
doi: 10.1063/1.2711187 |
| [30] |
Glover W. J.; Madden P. A. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 7293.
doi: 10.1063/1.1792574 |
| [31] |
Mukhopadhyay S.; Demmel F. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference on Quasielastic Neutron Scattering and the Workshop on Inelastic Neutron Spectrometers Qens/Wins 2016: Probing Nanoscale Dynamics in Energy Related Materials, Eds.: Felix, F.; David, L.; Veronika, G.; Wiebke, L.; Astrid, S.; Margarita, R.; AIP Publishing LLC, Potsdam, 2018, p. 030001.
|
| [32] |
McCulloch W. S.; Pitts W. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115.
doi: 10.1007/BF02478259 |
| [33] |
Behler J.; Parrinello M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 146401.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.146401 |
| [34] |
Bartók A. P.; Payne M. C.; Kondor R.; Csanyi G. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 136403.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.136403 |
| [35] |
Schutt K. T.; Arbabzadah F.; Chmiela S.; Muller K. R.; Tkatchenko A. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13890.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms13890 |
| [36] |
Han J.; Zhang L.; Car R.; E W. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2018, 23, 629.
|
| [37] |
Wang X.; Li J.; Yang L.; Chen F.; Wang Y.; Chang J.; Chen J.; Zhang L.; Yu K. ChemRxiv, Preprint.
|
| [38] |
Lot R.; Pellegrini F.; Shaidu Y.; Kucukbenli E. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020, 256, 107402.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2020.107402 |
| [39] |
Bartók A. P.; Csányi G. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2015, 115, 1051.
doi: 10.1002/qua.v115.16 |
| [40] |
Zhang Y.; Wang H.; Chen W.; Zeng J.; Zhang L.; Wang H.; E W. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020, 253, 107206.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2020.107206 |
| [41] |
Porter T.; Vaka M. M.; Steenblik P.; Della Corte D. Commun. Chem. 2022, 5, 69.
doi: 10.1038/s42004-022-00684-6 |
| [42] |
Jiang W.; Zhang Y.; Zhang L.; Wang H. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 050706.
doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/abf134 |
| [43] |
Dai F. Z.; Wen B.; Sun Y. J.; Xiang H. M.; Zhou Y. C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 168.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.01.005 |
| [44] |
Goldsmith B. R.; Esterhuizen J.; Liu J. X.; Bartel C. J.; Sutton C. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 2311.
doi: 10.1002/aic.v64.7 |
| [45] |
Ding X.; Tao M.; Li J. H.; Li M. Y.; Shi M. C.; Chen J. S.; Tang Z.; Benistant F.; Liu J. Mater. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2022, 143, 106513.
|
| [46] |
Tovey S.; Narayanan Krishnamoorthy A.; Sivaraman G.; Guo J.; Benmore C.; Heuer A.; Holm C. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 25760.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c08870 |
| [47] |
Liang W. S.; Lu G. M.; Yu J. G. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 75, 78.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.09.040 |
| [48] |
Xie Y.; Bu M.; Zou G.; Zhang Y.; Lu G. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 254, 112275.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2023.112275 |
| [49] |
Liang W. S.; Lu G. M.; Yu J. G. Adv. Theory. Simul. 2020, 3, 2000180.
doi: 10.1002/adts.v3.12 |
| [50] |
Bu M.; Liang W.; Lu G.; Yu J. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 232, 111346.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2021.111346 |
| [51] |
Liang W.; Lu G.; Yu J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4034.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c20665 |
| [52] |
Bu M.; Liang W. S.; Lu G. M. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2022, 210, 111494.
doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2022.111494 |
| [53] |
Smirnov M. V.; Khokhlov V. A.; Filatov E. S. Electrochim. Acta 1987, 32, 1019.
doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(87)90027-2 |
| [54] |
Gheribi A. E.; Torres J. A.; Chartrand P. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 126, 11.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2014.03.028 |
| [55] |
Janz G. J.; Tomkins R. Physical Properties Data Compilations Relevant to Energy Storage. IV. Molten Salts: Data on Additional Single and multi-Component Salt Systems, National Standard Reference Data System, 1981.
|
| [56] |
Anderson N. A.; Sabharwall P. Nucl. Technol. 2012, 178, 335.
doi: 10.13182/NT12-A13598 |
| [57] |
Xu X.; Wang X.; Li P.; Li Y.; Hao Q.; Xiao B.; Elsentriecy H.; Gervasio D. J. Sol. Energ.-T. ASME 2018, 140, 051011.
doi: 10.1115/1.4040065 |
| [58] |
Xu T.; Li X.; Wang Y.; Tang Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 14184.
|
| [59] |
Zhang J.; Fuller J.; An Q. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 8876.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c03748 |
| [60] |
Rodriguez A.; Lam S.; Hu M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55367.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c17942 |
| [61] |
Smith A. L.; Capelli E.; Konings R. J. M.; Gheribi A. E. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 299, 112165.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112165 |
| [62] |
Golyshev V. D.; Gonik M. A.; Petrov V. A.; Putilin Y. M. High Temp+. 1983, 21, 684.
|
| [63] |
Abe Y.; Kosugiyama O.; Nagashima A. J. Nucl. Mater. 1981, 99, 173.
doi: 10.1016/0022-3115(81)90186-0 |
| [64] |
Chahal R.; Roy S.; Brehm M.; Banerjee S.; Bryantsev V.; Lam S. T. JACS Au 2022, 2, 2693.
doi: 10.1021/jacsau.2c00526 pmid: 36590259 |
| [65] |
Brehm M.; Kirchner B. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2007.
doi: 10.1021/ci200217w |
| [66] |
Dracopoulos V.; Vagelatos J.; Papatheodorou G. N. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 2001, 1117.
|
| [67] |
Nguyen M. T.; Rousseau R.; Paviet P. D.; Glezakou V. A. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53398.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c11358 |
| [68] |
Li B.; Dai S.; Jiang D. E. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 2019, 2, 2112.
|
| [69] |
Barraz N. M., Jr.; Salcedo E.; Barbosa M. C. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 104507.
doi: 10.1063/1.3630941 |
| [70] |
Rosenfeld Y. J. Phys.-Condens. Mat. 1999, 11, 5415.
doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/11/28/303 |
| [71] |
Feng T.; Zhao J.; Liang W.; Lu G. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2022, 210, 111014.
doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2021.111014 |
| [72] |
Iwadate Y.; Suzuki K.; Onda N.; Fukushima K.; Watanabe S.; Matsuura H.; Kajinami A.; Takase K.; Ohtori N.; Umesaki N. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408, 248.
|
| [73] |
Okamoto Y.; Shiwaku H.; Yaita T.; Narita H.; Tanida H. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 641, 71.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-2860(02)00329-0 |
| [74] |
Wasse J. C.; Salmon P. S. J. Phys.-Condens. Mat. 1999, 11, 1381.
doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/11/6/004 |
| [75] |
Ren P.; Xiao Y.; Chang X.; Huang P.-Y.; Li Z.; Chen X.; Wang X. ACM Comput. Surv. 2020, 54, 1.
|
| [76] |
Sivaraman G.; Guo J.; Ward L.; Hoyt N.; Williamson M.; Foster I.; Benmore C.; Jackson N. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 4278.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c00901 |
| [77] |
Guo J.; Merwin A.; Benmore C. J.; Mei Z.-G.; Hoyt N. C.; Williamson M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 10036.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b07479 |
| [78] |
Guo D.; Zhao J.; Liang W. S.; Lu G. M. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 348, 118380.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118380 |
| [79] |
Yin W.; Bo T.; Zhao Y.; Zhang L.; Chai Z.; Shi W. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2023, 53, 1008.
doi: 10.1360/SSC-2023-0050 |
| [1] | Liu Zhenyu, Gan Li-Hua. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Acetylene Pyrolysis into Fullerenes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 502-510. |
| [2] | Xingyi Qi, Yaofeng Hu, Ruoyu Wang, Yaqing Yang, Yufei Zhao. Recent Advance of Machine Learning in Selecting New Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 158-174. |
| [3] | Ke Zhao, Xiayu Cheng, Xuexue Ma, Minghui Geng. Mechanism of Two-photon Absorption Enhancement for a Piperazine-based Zinc Ion Probe [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1371-1378. |
| [4] | Min Cheng, Shihui Wang, Lei Luo, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Yiyang Dai, Xu Ji. Large-Scale Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Framework Membranes for Ethane/Ethylene Separation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1277-1288. |
| [5] | Yuze Liu, Kunhua Li, Jiaxing Huang, Xi Yu, Wenping Hu. Accurate Prediction of the Boiling Point of Organic Molecules by Multi-Component Heterogeneous Learning Model [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 714-723. |
| [6] | Shihui Wang, Xiaoyu Xue, Min Cheng, Shaochen Chen, Chong Liu, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Xu Ji. High-Throughput Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Frameworks for CH4/H2 Separation by Synergizing Machine Learning and Molecular Simulation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 614-624. |
| [7] | Kang Liu, Bin Li, Jipan Yu, Weiqun Shi. Carbone Derivatives of Group 14: A Class of Important Reactive Intermediates [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 373-385. |
| [8] | Yingzhe Du, Heng Zhang, Shiling Yuan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Al2O3/PDMS Composites [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(6): 787-793. |
| [9] | Haohao Fu, Haochuan Chen, Hong Zhang, Xueguang Shao, Wensheng Cai. Accurate Estimation of Protein-ligand Binding Free Energies Based on Geometric Restraints [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(4): 472-480. |
| [10] | Chang-An Liu, Shi-Bo Hong, Bei Li. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Stability Behavior of Graphene in Glycerol/Urea Solvents in Liquid-Phase Exfoliation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(4): 530-538. |
| [11] | Yichuan Liu, Yalan Liu, Shilin Jiang, Mei Li, Weiqun Shi. Recent Progress on Chemical Species of Uranium in Molten Chlorides [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1425-1437. |
| [12] | Xue Dong, Hong Cao, Lei Xu, Zhipeng Wang, Jing Chen, Chao Xu. Advances in Environmental Coordination Chemistry of Np and Pu with Inorganic Anions in Aqueous Solution [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1415-1424. |
| [13] | Zun Liang, Xin Zhang, Songtai Lv, Hongtao Liang, Yang Yang. Crystal-Melt Interface Kinetics and the Capillary Wave Dynamics of the Monolayer Confined Ice-Water Coexistence Lines [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 108-118. |
| [14] | Fan Qin, Liang Hongtao, Xu Xianqi, Lv Songtai, Liang Zun, Yang Yang. Study of the Dielectric Property of Monolayer Confined Water Using A Polarizable Model [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(6): 547-556. |
| [15] | Cai Chengzhi, Li Lifeng, Deng Xiaomei, Li Shuhua, Liang Hong, Qiao Zhiwei. Machine Learning and High-throughput Computational Screening of Metal-organic Framework for Separation of Methane/ethane/propane [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(5): 427-436. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||