Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (11): 1162-1179.DOI: 10.6023/A24070219 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
刘卫涛a, 高战胜a, 黄明举a, 刘忠范b,c,*( ), 陈珂a,d,*(
), 陈珂a,d,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-07-17
发布日期:2024-10-08
作者简介: |
刘卫涛, 河南大学物理与电子学院在读博士生. 2018年毕业于郑州航空工业管理学院应用物理学专业, 同年进入河南大学物理与电子学院攻读硕士学位并于2020年转入硕博连读, 师从陈珂教授和黄明举教授. 研究方向为二维材料的生长调控与应用. |
 |
高战胜, 博士, 2023年毕业于南开大学材料学院, 同年入职河南大学物理与电子学院, 主要研究方向为低维材料及其异质结合成与器件表征. |
 |
黄明举, 博士, 河南大学教授. 河南省物理学会理事, 中国光学学会光学材料专业委员会委员, 国家高等学校“光电信息工程”类专业教学指导委员会协作分会委员, Opt. Eng.、Chin. Phys. Lett.、中国激光、光子学报等专业期刊审稿人. 河南省教育厅学术带头人, 省高校优秀骨干教师. 先后主持和参加国家自然科学基金等省部级以上项目11项, 获省部级以上优秀奖4项. 共发表SCI、EI论文160余篇. |
 |
刘忠范, 物理化学家, 日本东京大学博士. 北京大学博士生导师、博雅讲席教授、纳米科学与技术研究中心主任, 北京石墨烯研究院院长. 中国科学院院士、发展中国家科学院院士. 英国物理学会会士、英国皇家化学会会士、中国微米纳米技术学会会士. “物理化学学报”主编、“科学通报”副主编. 主要从事石墨烯等纳米碳材料研究, 在石墨烯、碳纳米管的化学气相沉积生长方法研究领域做出了一系列开拓性和引领性的工作. 发表SCI检索学术论文550余篇, 申请中国发明专利80余项. 曾获日中科技交流协会“有山兼孝纪念研究奖”(1992)、香港求是科技基金会杰出青年学者奖(1997)、中国分析测试协会科学技术奖一等奖(2005)、教育部高等学校科学技术奖自然科学一等奖(2007)、国家自然科学二等奖(2008)、中国化学会-阿克苏诺贝尔化学奖(2012)、宝钢优秀教师特等奖(2012)、日本化学会胶体与界面化学年会Lectureship Award(2016)、北京大学方正教师特别奖(2016)、“北京市优秀教师”称号(2017)、国家自然科学二等奖(2017)、ACS Nano Lectureship Award(2018)等. |
 |
陈珂, 河南大学教授, 博导, 国家万人计划青年拔尖人才(2020). 2012年获同济大学材料物理与化学博士学位并于同年入职河南大学. 2012年在英国剑桥大学化学系做访问博士生. 2013~2018年在北京大学化学与分子工程学院做博士后和访问学者. 2020~2021年在美国麻省理工学院材料科学与工程系做访问学者. 研究方向为二维材料的可控生长与纳米光学. 在Nat. Photon.、Nat. Commun.、Adv. Mater.等国际著名期刊共发表SCI论文60余篇, 参与编写石墨烯相关专著(章节)2部, 授权国家发明专利8项. 获河南省中原基础研究领军人才、中原青年拔尖人才、省教育厅学术技术带头人、省优秀青年专家、河南省青年科技奖等称号或奖励. |
基金资助:
Weitao Liua, Zhansheng Gaoa, Mingju Huanga, Zhongfan Liub,c( ), Ke Chena,d(
), Ke Chena,d( )
)
Received:2024-07-17
Published:2024-10-08
Contact:
*E-mail: kchen@henu.edu.cn; zfliu@pku.edu.cn
Supported by:Share
Weitao Liu, Zhansheng Gao, Mingju Huang, Zhongfan Liu, Ke Chen. Conformal Two-Dimensional Materials: Preparation and Applications[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(11): 1162-1179.




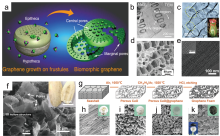

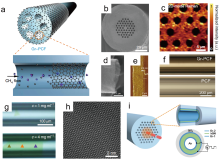

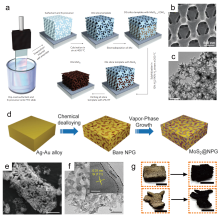

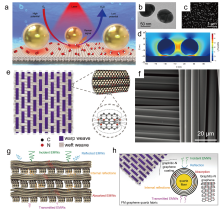




| [1] |
Novoselov, K. S.; Geim, A. K.; Morozov, S. V.; Jiang, D.-e.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S. V.; Grigorieva, I. V.; Firsov, A. A. Science 2004, 306, 666.
doi: 10.1126/science.1102896 pmid: 15499015 |
| [2] |
Li, X.; Yu, J.; Wageh, S.; Al‐Ghamdi, A. A.; Xie, J. Small 2016, 12, 6640.
|
| [3] |
Geim, A. K. Science 2009, 324, 1530.
doi: 10.1126/science.1158877 pmid: 19541989 |
| [4] |
Seabra, A. B.; Paula, A. J.; de Lima, R.; Alves, O. L.; Duran, N. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 159.
|
| [5] |
Liu, Y.; Duan, X.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6388.
|
| [6] |
Iqbal, M.; Elahi, E.; Amin, A.; Hussain, G.; Aftab, S. Superlattices Microstruct. 2020, 137, 106350.
|
| [7] |
Wu, D.; Guo, C.; Zeng, L.; Ren, X.; Shi, Z.; Wen, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, X. J.; Shan, C.-X.; Jie, J. Light-Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 5.
|
| [8] |
Chin, H.-T.; Hofmann, M.; Huang, S.-Y.; Yao, S.-F.; Lee, J.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Ting, C.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-P. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2021, 5, 28.
|
| [9] |
Moon, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, S.-I.; Hwang, H.-S.; Choi, J.-H.; Hyeong, S.-K.; Ghods, S.; Park, H. G.; Kim, E.-T.; Bae, S. Matter 2022, 5, 3935.
|
| [10] |
Ciarrocchi, A.; Avsar, A.; Ovchinnikov, D.; Kis, A. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 919.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03436-0 pmid: 29500434 |
| [11] |
Ji, H. G.; Solis‐Fernandez, P.; Yoshimura, D.; Maruyama, M.; Endo, T.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, S.; Ago, H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903613.
|
| [12] |
Chen, P.; Pan, J.; Gao, W.; Wan, B.; Kong, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Du, S.; Ji, W.; Pan, C. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108615.
|
| [13] |
Boyd, D.; Lin, W.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Teague, M.; Chen, C.-C.; Lo, Y.-Y.; Chan, W.-Y.; Su, W.-B.; Cheng, T.-C.; Chang, C.-S. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6620.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7620 pmid: 25782977 |
| [14] |
Wang, X.; Shi, G. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 790.
|
| [15] |
Han, T.-H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S.-J.; Lee, T.-W. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 118, 1.
|
| [16] |
Gwon, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, K. U.; Seo, D.-H.; Park, Y. C.; Lee, Y.-S.; Ahn, B. T.; Kang, K. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1277.
|
| [17] |
Liao, L.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12194.
doi: 10.1021/ja5048297 pmid: 25126670 |
| [18] |
Sun, P.; Xiong, W.; Bera, A.; Timokhin, I.; Wu, Z.; Mishchenko, A.; Sellers, M.; Liu, B.; Cheng, H.; Janzen, E. PNAS 2023, 120, e2300481120.
|
| [19] |
Fu, W.; Jiang, L.; van Geest, E. P.; Lima, L. M.; Schneider, G. F. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603610.
|
| [20] |
Jariwala, D.; Sangwan, V. K.; Lauhon, L. J.; Marks, T. J.; Hersam, M. C. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1102.
doi: 10.1021/nn500064s pmid: 24476095 |
| [21] |
Liu, B.; Abbas, A.; Zhou, C. Adv. Electronic. Mater. 2017, 3, 1700045.
|
| [22] |
Liao, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Ge, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 787.
|
| [23] |
Chaves, A.; Azadani, J. G.; Alsalman, H.; Da Costa, D.; Frisenda, R.; Chaves, A.; Song, S. H.; Kim, Y. D.; He, D.; Zhou, J. npj 2D Mater. 2020, 4, 29.
|
| [24] |
Kang, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Capasso, A.; Kang, H. S.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, G.-H. 2D Mater. 2020, 7, 022003.
|
| [25] |
Shrivastava, M.; Ramgopal Rao, V. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 6359.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00729 pmid: 34342450 |
| [26] |
Nakano, M.; Wang, Y.; Kashiwabara, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Iwasa, Y. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5595.
|
| [27] |
Ma, Y.; Kolekar, S.; Coy Diaz, H.; Aprojanz, J.; Miccoli, I.; Tegenkamp, C.; Batzill, M. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5130.
|
| [28] |
Poh, S. M.; Zhao, X. X.; Tan, S. J. R.; Fu, D. Y.; Fei, W. W.; Chu, L. Q.; Dan, J. D.; Zhou, W.; Pennycook, S. J.; Neto, A. H. C.; Loh, K. P. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7562.
|
| [29] |
Poh, S. M.; Tan, S. J. R.; Zhao, X. X.; Chen, Z. X.; Abdelwahab, I.; Fu, D. Y.; Xu, H.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Loh, K. P. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605641.
|
| [30] |
Hernandez, Y.; Nicolosi, V.; Lotya, M.; Blighe, F. M.; Sun, Z.; De, S.; McGovern, I. T.; Holland, B.; Byrne, M.; Gun'Ko, Y. K. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 563.
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.215 pmid: 18772919 |
| [31] |
Ciesielski, A.; Samorì, P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 381.
doi: 10.1039/c3cs60217f pmid: 24002478 |
| [32] |
Li, Z.; Young, R. J.; Backes, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhukov, A. A.; Tillotson, E.; Conlan, A. P.; Ding, F.; Haigh, S. J. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10976.
|
| [33] |
Coleman, J. N. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3680.
|
| [34] |
Grayfer, E. D.; Kozlova, M. N.; Fedorov, V. E. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 245, 40.
|
| [35] |
Zhang, W.; Huang, J. K.; Chen, C. H.; Chang, Y. H.; Cheng, Y. J.; Li, L. J. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3456.
|
| [36] |
Deng, B.; Liu, Z.; Peng, H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1800996.
|
| [37] |
Deokar, G.; Avila, J.; Razado-Colambo, I.; Codron, J.-L.; Boyaval, C.; Galopin, E.; Asensio, M.-C.; Vignaud, D. Carbon 2015, 89, 82.
|
| [38] |
Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Shenoy, V. B.; Tang, M.; Lou, J. Mater Today 2020, 40, 132.
|
| [39] |
Zhu, D.; Shu, H.; Jiang, F.; Lv, D.; Asokan, V.; Omar, O.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, C. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2017, 1, 8.
|
| [40] |
Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Ding, F. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801583.
|
| [41] |
Zhou, X.; Zhuge, F.; Wang, H.; Zhai, T. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 825.
|
| [42] |
Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Luo, H.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhai, T. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4368.
|
| [43] |
Liu, G.; Sun, Z.; Su, J. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 4036.
|
| [44] |
Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Yi, D.; Niu, J.; Wu, M.; Lin, L.; Yin, R.; Li, M.; Zhou, J. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1074.
|
| [45] |
Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Liu, C.; Lopatin, S.; Zhu, Y. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1912.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09565-4 pmid: 31015405 |
| [46] |
Gao, L.; Guest, J. R.; Guisinger, N. P. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3512.
doi: 10.1021/nl1016706 pmid: 20677798 |
| [47] |
Wood, J. D.; Schmucker, S. W.; Lyons, A. S.; Pop, E.; Lyding, J. W. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4547.
|
| [48] |
Huang, M.; Ruoff, R. S. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 800.
|
| [49] |
Sutter, P.; Sadowski, J. T.; Sutter, E. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 245411.
|
| [50] |
Barin, G. B.; Song, Y.; de Fatima Gimenez, I.; Souza Filho, A. G.; Barreto, L. S.; Kong, J. Carbon 2015, 84, 82.
|
| [51] |
Zhuang, B.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Yin, J. Carbon 2021, 173, 609.
|
| [52] |
Zhan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Najmaei, S.; Ajayan, P. M.; Lou, J. Small 2011, 8, 966.
|
| [53] |
Huang, M.; Deng, B.; Dong, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2001213.
|
| [54] |
Li, S.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Murthy, A.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhai, T. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211855.
|
| [55] |
Yan, Z.; Peng, Z.; Tour, J. M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1327.
|
| [56] |
Ji, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, D.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, X.; Tan, P. H.; Kan, M. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3870.
|
| [57] |
Dumcenco, D.; Ovchinnikov, D.; Marinov, K.; Lopez-Sanchez, O.; Krasnozhon, D.; Chen, M. W.; Gillet, P.; Morral, A. F. I.; Radenovic, A.; Kis, A. ACS Nano 2014, 9, 4611.
|
| [58] |
Ji, Q.; Kan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, D.; Shi, J.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 198.
|
| [59] |
Yang, P.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Quan, W.; Jiang, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, B.; Hu, J.; Zhu, L.; Pan, S. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3238.
|
| [60] |
Ju, M.; Liang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Mendes, R. G.; Rümmeli, M. H.; Fu, L. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 6095.
|
| [61] |
Hoffman, J. J. D. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 29, 1192.
|
| [62] |
Anwar, J.; Zahn, D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1996.
|
| [63] |
Amini, S.; Abbaschian, R. Carbon 2013, 51, 110.
|
| [64] |
Jung, Y. J.; Wei; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P. M.; Homma, Y.; Prabhakaran, K.; Ogino, T. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 561.
|
| [65] |
Jackson, K. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1984, 65, 7.
|
| [66] |
Nancollas, G.; Purdie, N. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1964, 18, 1.
|
| [67] |
Undabeytia, T.; Nir, S.; Rytwo, G.; Serban, C.; Morillo, E.; Maqueda, C. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2677.
|
| [68] |
Coraux, J.; Engler, M.; Busse, C.; Wall, D.; Buckanie, N.; Zu Heringdorf, F.-J. M.; Van Gastel, R.; Poelsema, B.; Michely, T. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 023006.
|
| [69] |
Wu, P.; Zhang, W. H.; Li, Z. Y.; Yang, J. L. Small 2014, 10, 2136.
|
| [70] |
Zhang, X.; Huangfu, L.; Gu, Z.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, J.; Nan, H.; Gu, X.; Ostrikov, K. Small 2021, 17, 2007312.
|
| [71] |
Yan, C.; Gan, L.; Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Huang, W.; Huang, J.; Jin, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhai, T.; Li, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702918.
|
| [72] |
Chen, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-J.; Liao, C.-D.; Chang, C.-F.; Tseng, C.-A.; Liu, C.-R.; Chen, Y.-T. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 6249.
|
| [73] |
Kundu, P. K.; Cohen, I. M.; Dowling, D. R. In Fluid mechanics, Ed.: Merken, S., Elsevier, London, 2015, pp. 1-15.
|
| [74] |
Munson, B. R.; Young, D.; Okiishi, T. Bernoulli Eqn. 2016, 23, 139.
|
| [75] |
Knudsen, M.; Partington, J. R. J. Phys. Chem. 2002, 39, 307.
|
| [76] |
Emyr, A.; Moelwyn, H. In Physical Chemistry, Ed.: Wheeler, D. R., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2015, pp. 4-10.
|
| [77] |
Halliday, D.; Resnick, R.; Krane, K. S. In Physics, Ed.: Sara Whight, H. N., Wiley, New York, 2002, pp. 635-652.
|
| [78] |
Rosenberger, F. E. In Fundamentals of Crystal Growth I: Macroscopic Equilibrium and Transport Concepts, Ed.: Cardona, M., Springer Science & Business Media, Stuttgart, 2012, pp. 226-234.
|
| [79] |
GokoGlu, S. A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1988, 135, 1562.
|
| [80] |
Hitchman, M. L. J. Cryst. Growth. 1980, 48, 394.
|
| [81] |
Sneed, B. T.; Brodsky, C. N.; Kuo, C. H.; Lamontagne, L. K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, F.; Huang, W.; Tsung, C. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14691.
|
| [82] |
Zhang, L.; Roling, L. T.; Wang, X.; Vara, M.; Chi, M. F.; Liu, J. Y.; Choi, S. I.; Park, J.; Herron, J. A.; Xie, Z. X.; Mavrikakis, M.; Xia, Y. N. Science 2015, 349, 412.
doi: 10.1126/science.aab0801 pmid: 26206931 |
| [83] |
Ye, H.; Wang, Q.; Catalano, M.; Lu, N.; Vermeylen, J.; Kim, M. J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xia, X. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2812.
|
| [84] |
Wang, Z.; Luan, D.; Boey, F. Y. C.; Lou, X. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4738.
|
| [85] |
Kuo, C. H.; Chu, Y. T.; Song, Y. F.; Huang, M. H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 792.
|
| [86] |
Lopez-Ortega, A.; Roca, A. G.; Torruella, P.; Petrecca, M.; Estrade, S.; Peiro, F.; Puntes, V.; Nogues, J. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8025.
|
| [87] |
Peng, S.; Sun, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4155.
|
| [88] |
Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Radjenovic, P.; Bodappa, N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z. L.; Tian, Z.; Li, J. F. Anal. Bioanal.Chem. 2019, 91, 5316.
|
| [89] |
Hwang, S. J.; Kim, S. K.; Lee, J. G.; Lee, S. C.; Jang, J. H.; Kim, P.; Lim, T. H.; Sung, Y. E.; Yoo, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19508.
|
| [90] |
Kong, D.; Wang, H.; Cha, J. J.; Pasta, M.; Koski, K. J.; Yao, J.; Cui, Y. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1341.
|
| [91] |
Peng, Z.; Jia, D.; Al-Enizi, A. M.; Elzatahry, A. A.; Zheng, G. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2015, 5, 1.
|
| [92] |
Zhang, Q.; Tan, S.; Mendes, R. G.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Xue, Y.; Ruemmeli, M. H.; Wu, X.; Chen, S. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2616.
|
| [93] |
Tong, X.; Li, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Pang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Xiong, D.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Chu, P. K. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2022, 9, 2104774.
|
| [94] |
Faber, M. S.; Dziedzic, R.; Lukowski, M. A.; Kaiser, N. S.; Ding, Q.; Jin, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10053.
|
| [95] |
Mi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Ji, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.; Shi, J. Small 2017, 13, 1701694.
|
| [96] |
Li, J. F.; Huang, Y. F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z. L.; Li, S. B.; Zhou, X. S.; Fan, F. R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Wu, D. Y. Nature 2010, 464, 392.
|
| [97] |
Luo, Y.; Tang, L.; Khan, U.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, H. M.; Zou, X.; Liu, B. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 269.
|
| [98] |
Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Teng, Y.; Chang, X.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z.; Fang, J.; Du, Z.; Swierczek, K. Adv. Electronic. Mater. 2018, 8, 1700174.
|
| [99] |
Qu, Y.; Medina, H.; Wang, S. W.; Wang, Y. C.; Chen, C. W.; Su, T. Y.; Manikandan, A.; Wang, K.; Shih, Y. C.; Chang, J. W. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9831.
|
| [100] |
Li, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; Sun, X.; Song, L.; Wang, X. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2452.
|
| [101] |
Zhang, G.; Huo, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 6 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张国强, 霍京浩, 王鑫, 郭守武, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 6.)
doi: 10.6023/A22110456 |
|
| [102] |
Pokroy, B.; Zolotoyabko, E. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 682.
|
| [103] |
Fabritius, H. O.; Sachs, C.; Triguero, P. R.; Raabe, D. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 391.
|
| [104] |
Studart, A. R. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 359.
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00836k pmid: 26750617 |
| [105] |
Ragni, R.; Cicco, S. R.; Vona, D.; Farinola, G. M. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1704289.
|
| [106] |
Zhang, C.; Mcadams, D. A.; Grunlan, J. C. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6265.
|
| [107] |
Knecht, L. D.; Pasini, P.; Daunert, S. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 977.
|
| [108] |
Jiang, L.; Feng, L. In Bioinspired Intelligent Nanostructured Interfacial Materials, Ed.: Jiang, L., Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2015, pp. 107-116.
|
| [109] |
Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 375.
|
| [110] |
Bao, Z.; Weatherspoon, M. R.; Shian, S.; Cai, Y.; Graham, P. D.; Allan, S. M.; Ahmad, G.; Dickerson, M. B.; Church, B. C.; Kang, Z. Nature 2007, 446, 172.
|
| [111] |
Losic, D.; Yu, Y.; Aw, M. S.; Simovic, S.; Thierry, B.; Addai-Mensah, J. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6323.
|
| [112] |
Aw, M. S.; Simovic, S.; Yu, Y.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Losic, D. Powder Technol. 2012, 223, 52.
|
| [113] |
Yu, Y.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Losic, D. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 015008.
|
| [114] |
Jeffryes, C.; Campbell, J.; Li, H.; Jiao, J.; Rorrer, G. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3930.
|
| [115] |
Chu, H.; Cao, D.; Dong, B.; Qiang, Z. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1573.
|
| [116] |
Chen, P. Y.; Mckittrick, J.; Meyers, M. A. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1492.
|
| [117] |
Chen, K.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Gao, T.; Liu, Z. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13440.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms13440 pmid: 27819652 |
| [118] |
Zhu, L.; Huan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, P.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y.; Cui, F.; Zhang, Y. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 6, 150.
|
| [119] |
Li, Q.; Song, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Xia, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wei, N.; Rümmeli, M. H.; Zou, X. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10240.
|
| [120] |
Oaki, Y.; Kijima, M.; Imai, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8594.
|
| [121] |
Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, D.; Xia, Y. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4223.
|
| [122] |
Chen, K.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Shi, L.; Reddy, S.; Meng, H.; Ji, Q. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 249.
|
| [123] |
Shi, L.; Chen, K.; Du, R.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Ruemmeli, M. H.; Xie, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6360.
|
| [124] |
Stockton, J.; Armen, M.; Mabuchi, H. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2002, 19, 3019.
|
| [125] |
Bhattacharya, R.; Konar, S. J. Nanophotonics 2012, 6, 3520.
|
| [126] |
Li, W.; Hao, Q.; Zhai, H.; Zeng, H.; Lu, W. Opt. Express. 2007, 15, 2354.
|
| [127] |
Yu, H. C. Y.; Eijkelenborg, M. A. V.; Leonsaval, S. G.; Argyros, A.; Barton, G. W. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 6497.
|
| [128] |
Doshi, R.; Day, P. J.; Carampin, P.; Blanch, E.; Stratford, I. J.; Tirelli, N. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2331.
|
| [129] |
Perez-Herrera, R. A.; Lopez-Amo, M. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2013, 19, 689.
|
| [130] |
Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, X.; Qiao, R.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Yu, W.; Yao, F.; Sun, Z. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 754.
doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0492-5 |
| [131] |
Cheng, Y.; Yu, W. T.; Xie, J.; Wang, R. Y.; Cui, G.; Cheng, X.; Li, M. W.; Wang, K.; Li, J. L.; Sun, Z. P.; Chen, K.; Liu, K. H.; Liu, Z. F. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 961.
|
| [132] |
Zuo, Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Qiao, R.; Liang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Zhao, Y. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 987.
|
| [133] |
Cheng, X.; Zhou, X.; Tao, L.; Yu, W.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, C.; Shang, N.; Xie, J.; Liu, K. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14472.
doi: 10.1039/d0nr03266b pmid: 32638778 |
| [134] |
Zhou, H. Q.; Yu, F.; Huang, Y. F.; Sun, J. Y.; Zhu, Z.; Nielsen, R. J.; He, R.; Bao, J. M.; Goddard, W. A.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. F. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12765.
|
| [135] |
Yao, R. Q.; Shi, H.; Wan, W. B.; Wen, Z.; Lang, X. Y.; Jiang, Q. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907214.
|
| [136] |
Al-Abawi, B. T.; Parveen, N.; Ansari, S. A. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14413.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18728-1 pmid: 36002578 |
| [137] |
Li, G.; Chang, Z.; Li, T.; Wang, K. Ionics 2019, 25, 5881.
|
| [138] |
Wei, X.; Lin, C.-C.; Wu, C.; Qaiser, N.; Cai, Y.; Lu, A.-Y.; Qi, K.; Fu, J.-H.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Z. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6006.
|
| [139] |
You, B.; Jiang, N.; Sheng, M.; Bhushan, M. W.; Sun, Y. ACS Catalysis 2016, 6, 714.
|
| [140] |
Kibsgaard, J.; Chen, Z.; Reinecke, B. N.; Jaramillo, T. F. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 963.
doi: 10.1038/nmat3439 pmid: 23042413 |
| [141] |
Xiao, X.; Beechem, T. E.; Brumbach, M. T.; Lambert, T. N.; Davis, D. J.; Michael, J. R.; Washburn, C. M.; Wang, J.; Brozik, S. M.; Wheeler, D. R. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3573.
|
| [142] |
Deng, J.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Ding, D.; Chen, M.; Liu, C.; Tian, Z.; Novoselov, K.; Ma, C.; Deng, D. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14430.
|
| [143] |
Tan, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Cong, W.; Ito, Y.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Tang, Z.; Fujita, T.; Hirata, A. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 8023.
|
| [144] |
An, W.; Gao, B.; Mei, S.; Xiang, B.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chu, P. K.; Huo, K. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1447.
|
| [145] |
Sha, J.; Li, Y.; Villegas Salvatierra, R.; Wang, T.; Dong, P.; Ji, Y.; Lee, S.-K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Smith, R. H. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6860.
|
| [146] |
Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P. J.; McQuillan, A. J. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163.
|
| [147] |
Jeanmaire, D. L.; Van Duyne, R. P. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1977, 84, 1.
|
| [148] |
Moskovits, M. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 783.
|
| [149] |
Dong, J.-C.; Zhang, X.-G.; Briega-Martos, V.; Jin, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z.-L.; Wu, D.-Y.; Feliu, J. M.; Williams, C. T. Nat. Energy. 2019, 4, 60.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-018-0292-z |
| [150] |
Xie, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, K.; Chen, B.; Shi, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, K.; Wu, Z.; Chen, K. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202982.
|
| [151] |
Knight, J. C.; Broeng, J.; Birks, T. A.; Russell, P. S. J. Science 1998, 282, 1476.
pmid: 9822375 |
| [152] |
Cregan, R.; Mangan, B.; Knight, J.; Birks, T.; Russell, P. S. J.; Roberts, P.; Allan, D. Science 1999, 285, 1537.
pmid: 10477511 |
| [153] |
Russell, P. Science 2003, 299, 358.
pmid: 12532007 |
| [154] |
Wadsworth, W. J.; Ortigosa-Blanch, A.; Knight, J. C.; Birks, T. A.; Man, T.-P. M.; Russell, P. S. J. JOSA B. 2002, 19, 2148.
|
| [155] |
Ni, Y.; Zhang, L.; An, L.; Peng, J.; Fan, C. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2004, 16, 1516.
|
| [156] |
Knight, J.; Skryabin, D. Opt. Express. 2007, 15, 15365.
pmid: 19550822 |
| [157] |
Zhao, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Wei, D.; Hou, Z.; Hou, L. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 5190.
|
| [158] |
Buczynski, R.; Bookey, H.; Pysz, D.; Stepien, R.; Kujawa, I.; McCarthy, J.; Waddie, A.; Kar, A.; Taghizadeh, M. Laser Phys. Lett. 2010, 7, 666.
|
| [159] |
Habib, M. S.; Habib, M. S.; Razzak, S. A.; Hossain, M. A. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2013, 19, 461.
|
| [160] |
Xu, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhou, C. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 63, 102485.
|
| [161] |
Tan, T.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.; Yao, B.; Zhang, H. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000058.
|
| [162] |
Yun, Q.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1903826.
|
| [163] |
Guo, Y.; Park, T.; Yi, J. W.; Henzie, J.; Kim, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Bando, Y.; Sugahara, Y.; Tang, J. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807134.
|
| [164] |
Duan, X.; Xu, J.; Wei, Z.; Ma, J.; Guo, S.; Liu, H.; Dou, S. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700156.
|
| [165] |
Muska, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, L.; Xu, Q.; Ding, H.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Q. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 6410.
|
| [166] |
Zhu, L.; Yang, P.; Huan, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Y. Adv. Energ. Sust. Res. 2021, 2, 2100089.
|
| [167] |
Chen, K.; Zhang, F.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Rummeli, M. H. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 12, 110.
|
| [168] |
Song, R.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y.; Bao, X.; Luo, Q.; Gou, L.; Fan, X.; Li, D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2024, 82, 426 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A24010019 |
|
(宋瑞, 赵铭钦, 王帅, 卢垚, 鲍晓冰, 罗巧梅, 苟蕾, 樊小勇, 李东林, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 426.)
doi: 10.6023/A24010019 |
|
| [169] |
Jia, H.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, L.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Cai, Y.; Hu, S.; Xiao, X. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1474.
|
| [170] |
Diab, M.; Shreteh, K.; Afik, N.; Volokh, M.; Abramovich, S.; Abdu, U.; Mokari, T. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1800001.
|
| [171] |
Weatherspoon, M. R.; Dickerson, M. B.; Wang, G.; Cai, Y.; Shian, S.; Jones, S. C.; Marder, S. R.; Sandhage, K. H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5724.
|
| [1] | Qian Chen, Qin Kuang, Zhaoxiong Xie. Research Progress of Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Based on Two-dimensional Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 10-22. |
| [2] | Wang Wenbin, Wen Qunlei, Liu Youwen, Zhai Tianyou. Research Progress of Surface and Interface Chemistry Regulate Two-dimensional Materials for Electrocatalytic Biomass Conversion [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(11): 1185-1199. |
| [3] | He Xuexia, Liu Fucai, Zeng Qingsheng, Liu Zheng. Electric-double-layer Transistors Based on Two Dimensional Materials [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(9): 924-935. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||