Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (8): 868-877.DOI: 10.6023/A25040107 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
韦正兵a, 鲍梦凡a, 徐世彪a, 程怡a, 陈诗洁a, 林娜a,*( ), 冒爱琴a,b,*(
), 冒爱琴a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-04-03
发布日期:2025-06-26
通讯作者:
林娜, 冒爱琴
基金资助:
Zhengbing Weia, Mengfan Baoa, Shibiao Xua, Yi Chenga, Shijie Chena, Na Lina,*( ), Aiqin Maoa,b,*(
), Aiqin Maoa,b,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-03
Published:2025-06-26
Contact:
Na Lin, Aiqin Mao
Supported by:Share
Zhengbing Wei, Mengfan Bao, Shibiao Xu, Yi Cheng, Shijie Chen, Na Lin, Aiqin Mao. Fluorine Doping-Induced Intrinsic Defect Modulation in Rock-Salt-Type High-Entropy Oxide for Lithium Storage Performance Optimization[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(8): 868-877.


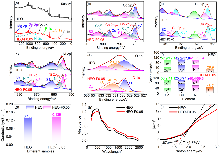
| Sample | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | Rwp | Rp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.07617 | 5.35% | 3.92% |
| HEO-F0.05 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.07606 | 3.49% | 2.46% |
| HEO-F0.1 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.07596 | 3.67% | 2.62% |
| Sample | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | V/nm3 | Rwp | Rp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.42389 | 0.07617 | 5.35% | 3.92% |
| HEO-F0.05 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.42369 | 0.07606 | 3.49% | 2.46% |
| HEO-F0.1 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.42351 | 0.07596 | 3.67% | 2.62% |


| Sample | SBET/(m2•g-1) | VBJH/(cm3•g-1) | Daver./nm | Dmost/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 7.564 | 0.022 | 11.474 | 3.278 |
| HEO-F0.05 | 18.810 | 0.016 | 3.399 | 3.092 |
| HEO-F0.1 | 9.200 | 0.018 | 11.740 | 3.290 |
| Sample | SBET/(m2•g-1) | VBJH/(cm3•g-1) | Daver./nm | Dmost/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEO | 7.564 | 0.022 | 11.474 | 3.278 |
| HEO-F0.05 | 18.810 | 0.016 | 3.399 | 3.092 |
| HEO-F0.1 | 9.200 | 0.018 | 11.740 | 3.290 |








| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
(贾洋刚, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 程捷, 林娜, 方道来, 冒爱琴, 李灿华, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 486.)
doi: 10.6023/A23020046 |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
(邵霞, 贾洋刚, 程婕, 方道来, 冒爱琴, 檀杰, 过程工程学报, 2023, 23, 771.)
doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.222242 |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
(付晨, 王立坤, 邱茹蒙, 王贵, 蔡文豪, 杨静凯, 赵洪力, 材料研究学报, 2019, 33, 277.)
doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2018.421 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
(鲍梦凡, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 邓慧娟, 冒爱琴, 檀杰, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 303.)
doi: 10.6023/A23100465 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
(陈见, 尹周澜, 张衡中, 有色金属工程, 2019, 9, 1.)
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
|
(陈诗洁, 鲍梦凡, 林娜, 杨海琴, 冒爱琴, 材料研究学报, 2024, 38, 508.)
doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2023.567 |
| [1] | Nana Zhang, Jing Li. Oxygen Vacancies Enhance the Activity of PdNi/HfO2 Catalysts for Ethylene Glycol Electrocatalytic Oxidation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(7): 709-715. |
| [2] | Meng-Xin Xu, Zhi-Jian Yang, Jing Sun, Wen-Qiang Zou, Zhong-Ning Xu, Guo-Cong Guo. Oxygen Vacancies in Pd/Pr-CeO2 Catalyst Regulate the Selectivity of CO Esterification to Dimethyl Carbonate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(7): 655-660. |
| [3] | Wei Sun, Guoxiang Xin, Fei Liu, Teng Ju, Yutong Cheng, Jinling Song, Jinxiao Bao, Chaoke Bulin. Construction of Three-dimensional Graphene/oxygen-enriched Vacancy Fe2O3 Composites to Realize Ultra-high Energy Density of Supercapacitors [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(3): 256-265. |
| [4] | Fanfan Zhang, Yuantao Cai, Jianbo Tao, Guoju Chang, Xinchen Guo, Shiyou Hao. Effect of Zn, C Introduction Amount and Calcination Temperature on the Photocatalytic Reduction of Cu2+over ZnO/C/CeO2 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(8): 871-878. |
| [5] | Guojing Wang, Yonghui Chen, Xiuqin Zhang, Junsheng Zhang, Junmin Xu, Jing Wang. Magnetic and Photoelectrocatalytic Properties of BiVO4 Surface Heterojunctions Controlled by Oxygen Vacancies [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 409-415. |
| [6] | Ziyi Shui, Sile Yu, Wei Lu, Liuyun Xu, Qingye Liu, Wei Zhao, Yilun Liu. Bifunctional Electrocatalysts of Mn-doped Co3O4 for Oxygen Reduction and Oxygen Evolution Reactions in Alkaline Medium [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(10): 1039-1049. |
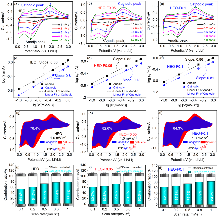
| [7] | Yanggang Jia, Shijie Chen, Xia Shao, Jie Cheng, Na Lin, Daolai Fang, Aiqin Mao, Canhua Li. Preparation and High-performance Lithium-ion Storage of Cobalt-free Perovskite High-entropy Oxide Anode Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 486-495. |
| [8] | Zhang Xuhan, Deng Bowen, Fan Haidong, Huang Wenhui, Zhang Yanwei. Photo-thermochemical CO2 Splitting Based on Zinc-germanium Binary Oxide [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(10): 1120-1126. |
| [9] | Xu Chenyu, Lin Jiayi, Pan Fuqiang, Deng Bowen, Wang Zhihua, Zhou Junhu, Chen Yun, Ma Jingcheng, Gu Zhien, Zhang Yanwei. Photo-thermochemical Cycle for CO2 Reduction based on Effective Ni ion Substitute-doped TiO2 [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2017, 75(7): 699-707. |
| [10] | DU Hai-Long, ZHANG Yong, SHENG Min-Qi, LIU Wei-Dong, ZHONG Qing-Dong, WANG Yi, ZHOU Qiong-Yu. Study on Electrochemistry of Oxide Films Formed on the Surface of Cobalt-tungsten Alloy Coatings in Alkali Solution [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(08): 881-888. |
| [11] | HAO Lan WANG Yan* CHEN Guang-Ju*. Theoretical Study on the Adsorption of CO and O2 on MgO-Supported Pd and Cu Atoms [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2008, 66(9): 1028-1036. |
| [12] | WANG Tian-Hui, LI Yue-Xiang*, PENG Shao-Qin, LÜ Gong-Xuan2, LI Shu-Ben2. Activity of Rare Earth Doped TiO2 Deposited with Pt for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(9): 797-801. |
| [13] | WANG Zhi-Min*, LI Li, LIU Jing-Bo, ZHANG Yan-Xi. LRS, Lattice Distortion and Polycrystal Microstructure of Li+-CaxPb1-xTiO3 Nano-film Used for Humidity Sensor—Application of Soft Mode Theory [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(1): 81-85. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||