Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (7): 867-873.DOI: 10.6023/A22020085 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
谢晨帆a, 徐玉平b, 高明亮a, 徐忠宁b, 江海龙a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2022-02-23
发布日期:2022-04-07
通讯作者:
江海龙
基金资助:
Chenfan Xiea, Yu-Ping Xub, Ming-Liang Gaoa, Zhong-Ning Xub, Hai-Long Jianga( )
)
Received:2022-02-23
Published:2022-04-07
Contact:
Hai-Long Jiang
Supported by:Share
Chenfan Xie, Yu-Ping Xu, Ming-Liang Gao, Zhong-Ning Xu, Hai-Long Jiang. MOF-Stabilized Pd Single Sites for CO Esterification to Dimethyl Carbonate[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 867-873.
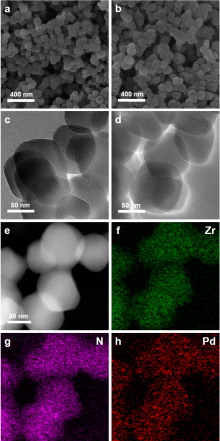


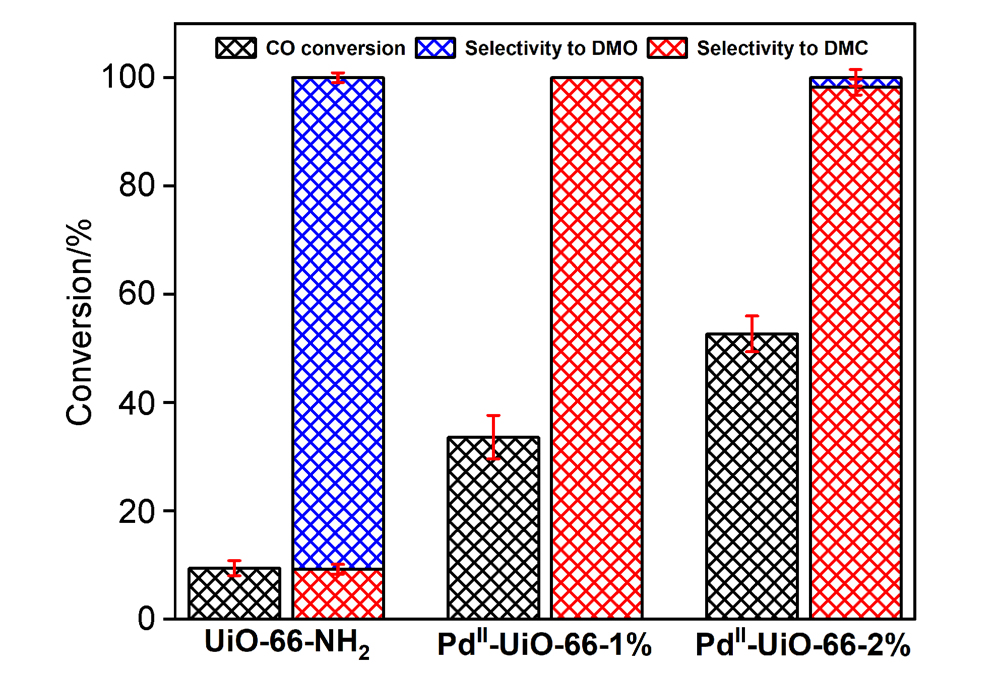
| [1] |
Tundo, P.; Musolino, M.; Aricò, F. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 28.
doi: 10.1039/C7GC01764B |
| [2] |
Tan, H.-Z.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Xu, Z.-N.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.-P.; Chen, Q.-S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, G.-C. Catal. Today 2018, 316, 2.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.02.021 |
| [3] |
Tan, H.-Z.; Chen, Z.-N.; Xu, Z.-N.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Si, R.; Zhuang, W.; Guo, G.-C. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3595.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b00286 |
| [4] |
Ji, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, D. Appl. Catal., B 2022, 304, 120922.
|
| [5] |
Tan, H.-Z.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Xu, Z.-N.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z.-N.; Chen, Q.-S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, G.-C. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3785.
doi: 10.1039/C7CY01305A |
| [6] |
Wang, Z.-Q.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z.-N.; Guo, G.-C. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 20131.
doi: 10.1039/D0NR03008B |
| [7] |
Wei, Y.-S.; Zhang, M.; Zou, R.; Xu, Q. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12089.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00757 |
| [8] |
Qi, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Su, J.; Somorjai, G. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 60.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c10728 |
| [9] |
Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Du, L.; Bu, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Hu, Z. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1657.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09596-x |
| [10] |
Shi, W.; Quan, Y.; Lan, G.; Ni, K.; Song, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.; Lin, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16718.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07963 |
| [11] |
Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.-Z.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Chang, J.-N.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.-L.; Lan, Y.-Q. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6390.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26724-8 pmid: 34737317 |
| [12] |
Jiao, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.-L. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 327.
doi: 10.1021/accountsmr.1c00009 |
| [13] |
Huang, G.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 113. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15080547 |
|
(黄刚, 陈玉贞, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 113.)
doi: 10.6023/A15080547 |
|
| [14] |
Zhang, J.-P.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Lin, J.-B.; Chen, X.-M. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1001.
doi: 10.1021/cr200139g |
| [15] |
Lü, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 869. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030099 |
|
(吕露茜, 赵娅俐, 魏嫣莹, 王海辉, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 869.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030099 |
|
| [16] |
Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K. E.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
doi: 10.1126/science.1230444 |
| [17] |
Li, H.; Li, L.; Lin, R.-B.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, S.; Chen, B. EnergyChem 2019, 1, 100006.
doi: 10.1016/j.enchem.2019.100006 |
| [18] |
Liu, D.; Wan, J.; Pang, G.; Tang, Z. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803291.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201803291 |
| [19] |
Wu, G.; Huang, J.; Zang, Y.; He, J.; Xu, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1360.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08511 |
| [20] |
Li, B.; Ju, Z.; Zhou, M.; Su, K.; Yuan, D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7687.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201902171 |
| [21] |
Pang, J.; Di, Z.; Qin, J.-S.; Yuan, S.; Lollar, C. T.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, M.; Yuan, D.; Hong, M.; Zhou, H.-C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15020.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c05758 |
| [22] |
Qiu, X.; Zhong, W.; Bai, C.; Li, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1138.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b12189 |
| [23] |
Li, J.; Huang, H.; Xue, W.; Sun, K.; Song, X.; Wu, C.; Nie, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, H.-L.; Mei, D.; Zhong, C. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 719.
doi: 10.1038/s41929-021-00665-3 |
| [24] |
Cai, G.; Jiang, H.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 563.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201610914 |
| [25] |
Bai, X.-J.; Lu, X.-Y.; Ju, R.; Chen, H.; Shao, L.; Zhai, X.; Li, Y.-N.; Fan, F.-Q.; Fu, Y.; Qi, W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 701.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202012354 |
| [26] |
Yu, F.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Duan, C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 24849.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202108892 |
| [27] |
Feng, L.; Li, J.-L.; Day, G. S.; Lv, X.-L.; Zhou, H.-C. Chem 2019, 5, 1265.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.03.003 |
| [28] |
Cai, G.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.-C.; Jiang, H.-L. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 12278.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00243 |
| [29] |
Xiao, J.-D.; Li, D.-D.; Jiang, H.-L. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2018, 48, 1058. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1360/N032018-00035 |
|
(肖娟定, 李丹丹, 江海龙, 中国科学: 化学, 2018, 48, 1058.)
|
|
| [30] |
Zhang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Gao, J.; Xiong, W.; Huang, L.; Ding, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 361. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20100478 |
|
(张雅祺, 楚奇, 石勇, 高金索, 熊巍, 黄磊, 丁越, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 361.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100478 |
|
| [31] |
Li, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, G.; Guan, Q.; Dong, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, S.-H.; Jiang, H.-L. Chem 2021, 7, 686.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2020.11.023 |
| [32] |
Jiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.-L.; Xu, Q. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703663.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201703663 |
| [33] |
Guan, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wu, P.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, G.; Ji, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Fan, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Huo, F. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606290.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201606290 |
| [34] |
Feng, R.; Jia, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Chang, Z.; Bu, X.-H. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 950.
doi: 10.1039/c7sc04192f pmid: 29629162 |
| [35] |
Yang, Q.; Jiang, H.-L. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800216.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.201800216 |
| [36] |
Zhang, K.; Xi, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lu, G.; Huang, X. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 12623.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c04112 |
| [37] |
Dong, Y.; Li, W.-H.; Dong, Y.-B. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 1818.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c02641 |
| [38] |
Sun, R.; Liu, B.; Li, B.-G.; Jie, S. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 3261.
doi: 10.1002/cctc.201600774 |
| [39] |
Chen, L.; Rangan, S.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3978.
doi: 10.1039/C4GC00314D |
| [40] |
Jung, K. T.; Bell, A. T. J. Catal. 2001, 204, 339.
doi: 10.1006/jcat.2001.3411 |
| [41] |
Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Bai, C.; Li, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15259.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA02860D |
| [42] |
Lv, D.-M.; Xu, Z.-N.; Peng, S.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Chen, Q.-S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, G.-C. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3333.
doi: 10.1039/C5CY00251F |
| [43] |
Tereshchenko, A.; Guda, A.; Polyakov, V.; Rusalev, Y.; Butova, V.; Soldatov, A. Analyst 2020, 145, 7534.
doi: 10.1039/D0AN01303J |
| [44] |
Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 840.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.031 |
| [1] | Yang Liu, Fengqin Gao, Zhanying Ma, Yinli Zhang, Wuwu Li, Lei Hou, Xiaojuan Zhang, Yaoyu Wang. Co-based Metal-organic Framework for High-efficiency Degradation of Methylene Blue in Water by Peroxymonosulfate Activation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| [2] | Bo Sun, Wenwen Ju, Tao Wang, Xiaojun Sun, Ting Zhao, Xiaomei Lu, Feng Lu, Quli Fan. Preparation of Highly-dispersed Conjugated Polymer-Metal Organic Framework Nanocubes for Antitumor Application [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [3] | Fengbin Zheng, Kun Wang, Tian Lin, Yinglong Wang, Guodong Li, Zhiyong Tang. Research Progress on the Preparation of Metal-Organic Frameworks Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticle Composites and Their Catalytic Applications★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 669-680. |
| [4] | Kaiqing Wang, Shuo Yuan, Wangdong Xu, Dan Huo, Qiulin Yang, Qingxi Hou, Dehai Yu. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of ZIF-8@B-CNF Composite Aerogel [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 604-612. |
| [5] | Zheng Yin, Yingbo Zhao, Minghua Zeng. Challenge, Advance and Emerging Opportunities for Metal-Organic Framework Glasses: from Dynamic Chemistry to Material Science and Noncrystalline Physics [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 246-252. |
| [6] | Junchang Chen, Mingxing Zhang, Shuao Wang. Research Progress of Synthesis Methods for Crystalline Porous Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [7] | Xiaojuan Li, Ziyu Ye, Shuhan Xie, Yongjing Wang, Yonghao Wang, Yuancai Lv, Chunxiang Lin. Study on Performance and Mechanism of Phenol Degradation through Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Nitrogen/Chlorine Co-doped Porous Carbon Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1238-1249. |
| [8] | Min Cheng, Shihui Wang, Lei Luo, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Yiyang Dai, Xu Ji. Large-Scale Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Framework Membranes for Ethane/Ethylene Separation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1277-1288. |
| [9] | Shaobing Yan, Long Jiao, Chuanxin He, Hailong Jiang. Pyrolysis of ZIF-67/Graphene Composite to Co Nanoparticles Confined in N-Doped Carbon for Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | Xu Yan, Hemi Qu, Ye Chang, Xuexin Duan. Application of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Gas Pre-concentration, Pre-separation and Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1183-1202. |
| [11] | Linan Cao, Min Wei. Recent Progress of Electric Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks Thin Film [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 1042-1056. |
| [12] | Ben Niu, Zhenyu Zhai, Xiaoke Hao, Tingli Ren, Congju Li. Flexible Acetone Gas Sensor based on ZIF-8/Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Composite Film [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 946-955. |
| [13] | Fang Liu, Tingting Pan, Xiurong Ren, Weiren Bao, Jiancheng Wang, Jiangliang Hu. Research on Preparation and Benzene Adsorption Performance of HCDs@MIL-100(Fe) Adsorbents [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 879-887. |
| [14] | Shihui Wang, Xiaoyu Xue, Min Cheng, Shaochen Chen, Chong Liu, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Xu Ji. High-Throughput Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Frameworks for CH4/H2 Separation by Synergizing Machine Learning and Molecular Simulation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 614-624. |
| [15] | Junmin Chen, Chengqian Cui, Hanlin Liu, Guodong Li. Study on the Selective Hydrogenation of Quinoline Catalyzed by Composites of Metal-Organic Framework and Pt Nanoparticles※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 467-475. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||