Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (6): 604-612.DOI: 10.6023/A23020049 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
王凯晴a, 袁硕a, 徐王东a, 霍丹a,b, 杨秋林a,*( ), 侯庆喜a,*(
), 侯庆喜a,*( ), 于得海a,c
), 于得海a,c
投稿日期:2023-03-06
发布日期:2023-05-12
基金资助:
Kaiqing Wanga, Shuo Yuana, Wangdong Xua, Dan Huoa,b, Qiulin Yanga( ), Qingxi Houa(
), Qingxi Houa( ), Dehai Yua,c
), Dehai Yua,c
Received:2023-03-06
Published:2023-05-12
Contact:
*E-mail: qiulinyang@tust.edu.cn; qingxihou@tust.edu.cn
Supported by:Share
Kaiqing Wang, Shuo Yuan, Wangdong Xu, Dan Huo, Qiulin Yang, Qingxi Hou, Dehai Yu. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of ZIF-8@B-CNF Composite Aerogel[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 604-612.
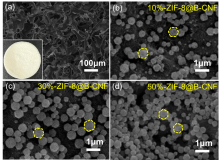

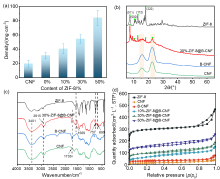
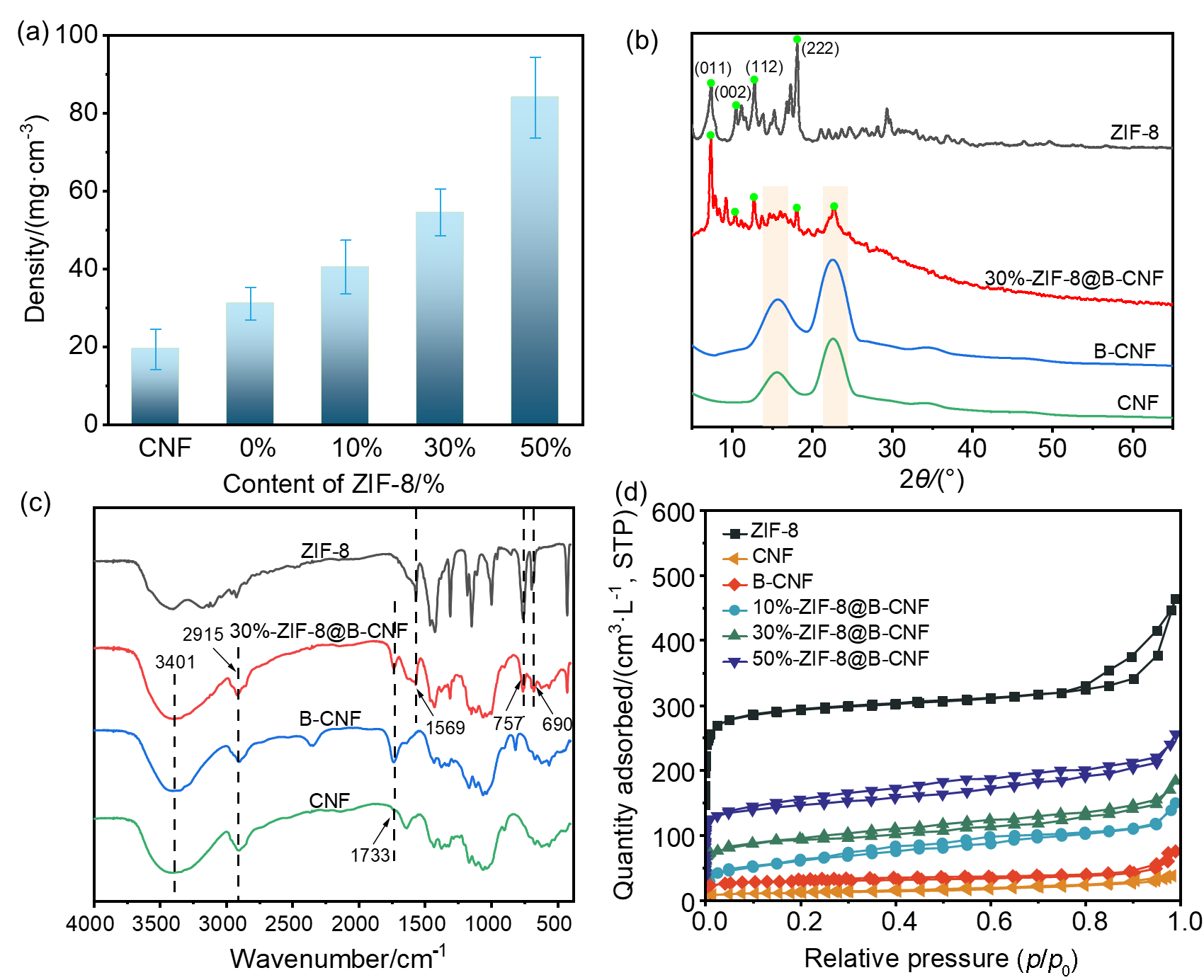
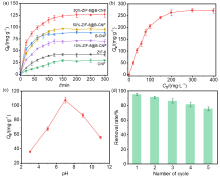
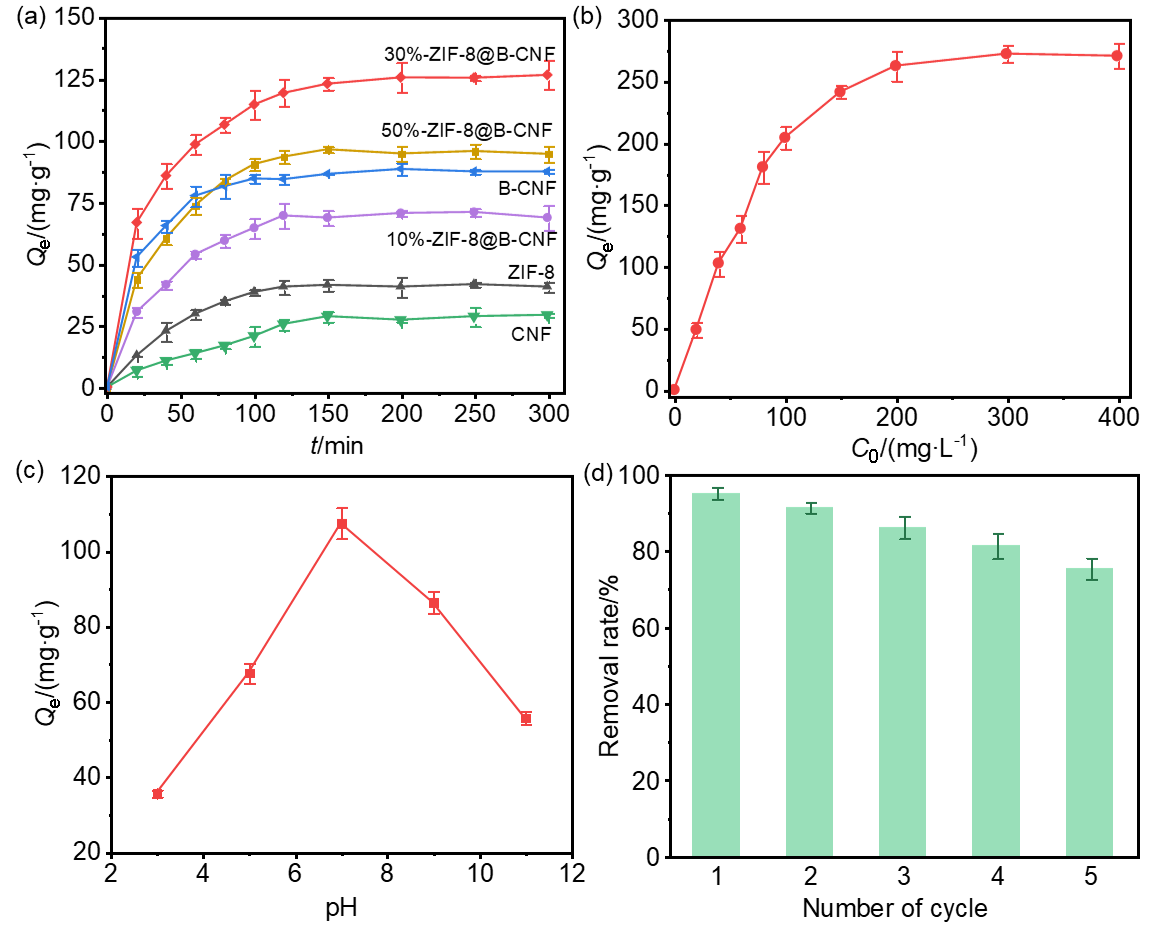
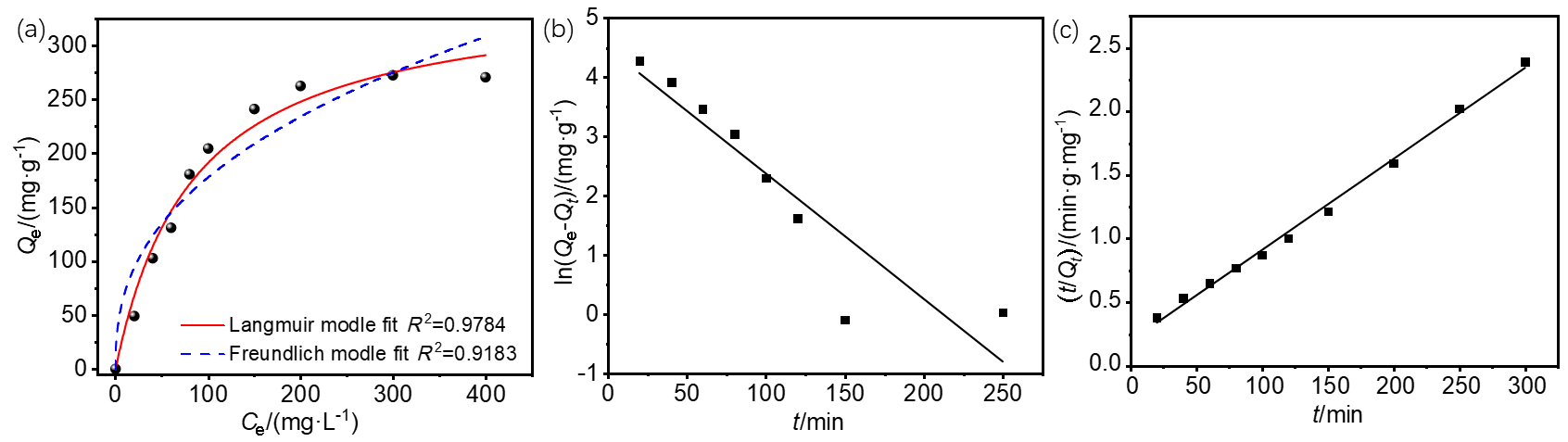
| Langmuir model | Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg•g−1) | KL/(L•mg−1) | R2 | 1/n | KF/(mg•g−1) | R2 | |
| 352.59 | 0.0118 | 0.9784 | 0.3976 | 28.4781 | 0.9183 | |
| Langmuir model | Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mg•g−1) | KL/(L•mg−1) | R2 | 1/n | KF/(mg•g−1) | R2 | |
| 352.59 | 0.0118 | 0.9784 | 0.3976 | 28.4781 | 0.9183 | |
| Adsorption material | T/℃ | pH | C0/(mg•L−1) | Qe/(mg•g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic activated carbon | 25 | 10 | 50 | 169.49 | [ |
| Graphene oxide-chitosan composite aerogel | 25 | 11 | 50 | 110.90 | [ |
| Ni-MOFs@GO composites | 25 | — | 25 | 235.37 | [ |
| TiO2-MIL-101 nano-composite | 30 | — | 20 | 20.70 | [ |
| MIL-53(Fe)@montmorillonite | — | — | 200 | 313.70 | [ |
| Waste cellulose/ZIF-8 aerogel | 25 | — | 50 | 10.31 | [ |
| ZIF-8@B-CNF composite aerogel | 25 | — | 60 | 352.59 | This study |
| Adsorption material | T/℃ | pH | C0/(mg•L−1) | Qe/(mg•g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic activated carbon | 25 | 10 | 50 | 169.49 | [ |
| Graphene oxide-chitosan composite aerogel | 25 | 11 | 50 | 110.90 | [ |
| Ni-MOFs@GO composites | 25 | — | 25 | 235.37 | [ |
| TiO2-MIL-101 nano-composite | 30 | — | 20 | 20.70 | [ |
| MIL-53(Fe)@montmorillonite | — | — | 200 | 313.70 | [ |
| Waste cellulose/ZIF-8 aerogel | 25 | — | 50 | 10.31 | [ |
| ZIF-8@B-CNF composite aerogel | 25 | — | 60 | 352.59 | This study |
| Qe,exp /(mg•g−1) | Quasi-first-order kinetic | Quasi-second-order kinetic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe,cal/(mg•g−1) | k1/min−1 | R2 | Qe,cal/(mg•g−1) | k2/(g•mg−1•min−1) | R2 | ||
| 124.59 | 89.12 | -0.0211 | 0.8468 | 139.86 | 0.0185 | 0.9956 | |
| Qe,exp /(mg•g−1) | Quasi-first-order kinetic | Quasi-second-order kinetic | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe,cal/(mg•g−1) | k1/min−1 | R2 | Qe,cal/(mg•g−1) | k2/(g•mg−1•min−1) | R2 | ||
| 124.59 | 89.12 | -0.0211 | 0.8468 | 139.86 | 0.0185 | 0.9956 | |
| [1] |
Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; O'keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Nature 1999, 402, 276.
doi: 10.1038/46248 |
| [2] |
Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Cranston, E. D.; Zhu, S. P. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7652.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201601351 |
| [3] |
Lu, L. X.; Zhao, L. Y.; Wei, Y. R.; Wang, H. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 869. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21030099 |
|
(吕露茜, 赵娅俐, 魏嫣莹, 王海辉, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 869.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030099 |
|
| [4] |
Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Y.; Liu, S. C.; Yao, J. F. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 109608.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA23870J |
| [5] |
Ahsan, M. A.; Jabbari, V.; El-Gendy, A. A.; Curry, M. L.; Noveron, J. C. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143608.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143608 |
| [6] |
Zeng, J. Y.; Wang, X. S.; Zhang, X. Z.; Zhuo, R. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1156. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19070259 |
|
(曾锦跃, 王小双, 张先正, 卓仁禧, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1156.)
doi: 10.6023/A19070259 |
|
| [7] |
Li, J. L.; Yuan, S.; Qin, J. S.; Pang, J. D.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y. M.; Huang, Y. Y.; Drake, H. F.; Liu, W. S. R.; Zhou, H. C. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 9405.
doi: 10.1002/ange.v132.24 |
| [8] |
Cheng, P.; Wang, C. H.; Kaneti, Y. V.; Eguchi, M.; Lin, J. J.; Yamauchi, Y.; Na, J. Langmuir 2020, 36, 4231.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00236 pmid: 32293183 |
| [9] |
Zhang, Z. H.; Zhang, J. L.; Liu, J. M.; Xiong, Z. H.; Chen, X. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 471.
doi: 10.1007/s11270-016-3166-7 |
| [10] |
Li, Y. F.; Yan, X. L.; Hu, X. Y.; Feng, R.; Zhou, M.; Han, D. Z. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 1109.
doi: 10.1007/s10934-020-00887-z |
| [11] |
Wang, B.; Cote, A. P.; Furukawa, H.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Nature 2008, 453, 207.
doi: 10.1038/nature06900 |
| [12] |
Niu, B.; Zhai, Z. Y.; Hao, X. K.; Ren, T. L.; Li, C. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 946. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22020093 |
|
(牛犇, 翟振宇, 郝肖柯, 任婷莉, 李从举, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 946.)
doi: 10.6023/A22020093 |
|
| [13] |
Abdollahi, B.; Najafidoust, A.; Asl, E. A.; Sillanpaa, M. Arabian J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103444.
doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103444 |
| [14] |
Isogai, A. J. Wood Sci. 2013, 59, 449.
doi: 10.1007/s10086-013-1365-z |
| [15] |
Du, H. S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M. M.; Kong, Q. S.; Li, B.; Xian, M. Prog. Chem. 2018, 30, 448. (in Chinese)
|
|
(杜海顺, 刘超, 张苗苗, 孔庆山, 李滨, 咸漠, 化学进展, 2018, 30, 448.)
doi: 10.7536/PC170830 |
|
| [16] |
Mondal, S. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 301.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.050 |
| [17] |
Mo, L. T.; Pang, H. W.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, S. F.; Li, J. Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122157.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122157 |
| [18] |
Dhali, K.; Ghasemlou, M.; Daver, F.; Cass, P.; Adhikari, B. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145871.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145871 |
| [19] |
Zhu, L. T.; Zong, L.; Wu, X. C.; Li, M. J.; Wang, H. S.; You, J.; Li, C. X. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4462.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b00566 |
| [20] |
Abdelhamid, H. N.; Mathew, A. P. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131733.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131733 |
| [21] |
Moghaddam, S. S.; Moghaddam, M. R. A.; Arami, M. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 651.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.058 pmid: 19944532 |
| [22] |
Sachdeva, S.; Kumar, A. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 329, 2.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.10.050 |
| [23] |
El-Desoky, H. S.; Ghoneim, M. M.; El-Sheikh, R.; Zidan, N. M. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 858.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.089 pmid: 19926217 |
| [24] |
Li, Z. J.; Zhang, X. W.; Lin, J.; Han, S.; Lei, L. C. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4440.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.114 |
| [25] |
Song, Y. R.; Wang, K. S.; An, G. Y.; Zhao, F. J.; Men, B.; Du, Z. X.; Wang, D. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1592. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22080375 |
|
(宋亚瑞, 王凯升, 安广宇, 赵法军, 门彬, 杜昭兮, 王东升, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1592.)
doi: 10.6023/A22080375 |
|
| [26] |
Feng, A. H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Song, L. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 757. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18060250 |
|
(冯爱虎, 于洋, 于云, 宋力昕, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 757.)
doi: 10.6023/A18060250 |
|
| [27] |
Peer, F. E.; Bahramifar, N.; Younesi, H. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 87, 225.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2018.03.039 |
| [28] |
Wang, S. S.; Zhang, L.; Long, C.; Li, A. M. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 185.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.04.055 |
| [29] |
Lu, Y.; Liu, C. Z.; Mei, C. T.; Sun, J. S.; Lee, J.; Wu, Q. L.; Hubbe, M. A.; Li, M. C. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 461, 214496.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214496 |
| [30] |
Sauperl, O.; Stana-kleinschek, K.; Ribitsch, V. Text. Res. J. 2009, 79, 780.
doi: 10.1177/0040517508096222 |
| [31] |
Ma, X. F.; Liu, C. Z.; Anderson, D. P.; Chang, P. R. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 399.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.033 |
| [32] |
Liu, Y. P.; Hu, H. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 735.
doi: 10.1007/s12221-008-0115-0 |
| [33] |
He, M.; Yao, J. F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, K.; Chen, F. Y.; Wang, H. T. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 184, 55.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.10.003 |
| [34] |
Maiti, S.; Jayaramudu, J.; Das, K.; Reddy, S. M.; Sadiku, R.; Ray, S. S.; Liu, D. G. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 562.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.029 |
| [35] |
Xu, S.; Huo, D.; Wang, K. Q.; Yang, Q. L.; Hou, Q. X.; Zhang, F. S. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118118.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118118 |
| [36] |
Meng, W. Y.; Wang, S. J.; Lv, H. F.; Wang, Z. X.; Han, X. W.; Zhou, Z. J.; Pu, J. W. Bioresources 2022, 17, 2615.
doi: 10.15376/biores |
| [37] |
Zhang, S. H.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Ran, F. Applied Surface Science 2020, 505, 144533.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144533 |
| [38] |
Ahmad, R.; Ansari, K. Process Biochem. 2021, 108, 90.
doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2021.05.013 |
| [39] |
Do, N. H. N.; Truong, B. Y.; Nguyen, P. T. X.; Le, K. A.; Duong, H. M.; Le, P. K. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120200.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120200 |
| [40] |
El Haouti, R.; Ouachtak, H.; El Guerdaoui, A.; Amedlous, A.; Amaterz, E.; Haounati, R.; Addi, A. A.; Akbal, F.; El Alem, N.; Taha, M. L. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111139.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111139 |
| [41] |
Chen, W. J.; Ma, H. Z.; Ma, H. Z. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1342.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.249 |
| [42] |
Zhang, Q. L.; Cheng, Y. L.; Fang, C. Q.; Shi, J. Y.; Chen, J.; Han, H. Z. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 302, 122361.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122361 |
| [43] |
Chen, W. J.; Ma, H. Z.; Xing, B. S. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1342.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.249 |
| [44] |
Abuzerr, S.; Darwish, M.; Mahvi, A. H. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2, 534.
|
| [45] |
Shi, Y. W.; Song, G. B.; Li, A. Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. A.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. H. Colloids Surf., A 2022, 641, 128595.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128595 |
| [46] |
Zhang, A. J.; Shan, F. J.; Ji, X. Y.; Chen, Y. Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yv, J. New Chem. Mater. 2023, 51, 233. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张爱佳, 单凤君, 纪馨越, 陈玥琪, 赵宇, 喻靓, 化工新型材料, 2023, 51, 233.)
|
|
| [47] |
Chang, N.; Zhang, H.; Shi, M. S.; Li, J.; Yin, C. J.; Wang, H. T.; Wang, L. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 266, 47.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.02.051 |
| [48] |
Dai, F. L.; Guo, J. H.; He, Y. F.; Song, P. F.; Wang, R. M. Clay Minerals 2021, 56, 99.
doi: 10.1180/clm.2021.23 |
| [49] |
Zhang, Q. L.; Cheng, Y. L.; Fang, C. Q.; Shi, J. Y.; Chen, J.; Han, H. Z. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 299, 122190.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122190 |
| [50] |
Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Y. S. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109568.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109568 |
| [51] |
Liang, Y. X.; Li, H. B.; Li, X. T.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Fei, J. Y.; Li, S. M.; Chen, S. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 113450.
|
| [52] |
Karami, A.; Shomal, R.; Sabouni, R.; Al-Sayah, M. H.; Aidan, A. Energ. 2022, 15, 4642.
|
| [53] |
Nazir, M. A.; Najam, T.; Zarin, K.; Shahzad, K.; Javed, M. S.; Jamshaid, M.; Bashir, M. A.; Shah, S. S. A.; Rehman, A. U. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 3, 1931855.
|
| [54] |
Foo, K. Y.; Hameed, B. H. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013 |
| [55] |
Iftekhar, S.; Ramasamy, D. L.; Srivastava, V.; Asif, M. B.; Sillanpaa, M. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 413.
doi: S0045-6535(18)30695-7 pmid: 29677649 |
| [56] |
Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A. N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y. H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 616.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.042 pmid: 18656309 |
| [57] |
Qiu, H.; Lv, L.; Pan, B. C.; Zhang, Q. J.; Zhang, W. M.; Zhang, Q. X. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2009, 10, 716.
doi: 10.1631/jzus.A0820524 |
| [1] | Yang Liu, Fengqin Gao, Zhanying Ma, Yinli Zhang, Wuwu Li, Lei Hou, Xiaojuan Zhang, Yaoyu Wang. Co-based Metal-organic Framework for High-efficiency Degradation of Methylene Blue in Water by Peroxymonosulfate Activation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| [2] | Bo Sun, Wenwen Ju, Tao Wang, Xiaojun Sun, Ting Zhao, Xiaomei Lu, Feng Lu, Quli Fan. Preparation of Highly-dispersed Conjugated Polymer-Metal Organic Framework Nanocubes for Antitumor Application [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [3] | Fengbin Zheng, Kun Wang, Tian Lin, Yinglong Wang, Guodong Li, Zhiyong Tang. Research Progress on the Preparation of Metal-Organic Frameworks Encapsulated Metal Nanoparticle Composites and Their Catalytic Applications★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(6): 669-680. |
| [4] | Zheng Yin, Yingbo Zhao, Minghua Zeng. Challenge, Advance and Emerging Opportunities for Metal-Organic Framework Glasses: from Dynamic Chemistry to Material Science and Noncrystalline Physics [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(3): 246-252. |
| [5] | Junchang Chen, Mingxing Zhang, Shuao Wang. Research Progress of Synthesis Methods for Crystalline Porous Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [6] | Xiaojuan Li, Ziyu Ye, Shuhan Xie, Yongjing Wang, Yonghao Wang, Yuancai Lv, Chunxiang Lin. Study on Performance and Mechanism of Phenol Degradation through Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Nitrogen/Chlorine Co-doped Porous Carbon Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1238-1249. |
| [7] | Min Cheng, Shihui Wang, Lei Luo, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Yiyang Dai, Xu Ji. Large-Scale Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Framework Membranes for Ethane/Ethylene Separation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1277-1288. |
| [8] | Xu Yan, Hemi Qu, Ye Chang, Xuexin Duan. Application of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Gas Pre-concentration, Pre-separation and Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1183-1202. |
| [9] | Shaobing Yan, Long Jiao, Chuanxin He, Hailong Jiang. Pyrolysis of ZIF-67/Graphene Composite to Co Nanoparticles Confined in N-Doped Carbon for Efficient Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [10] | Chenfan Xie, Yu-Ping Xu, Ming-Liang Gao, Zhong-Ning Xu, Hai-Long Jiang. MOF-Stabilized Pd Single Sites for CO Esterification to Dimethyl Carbonate [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 867-873. |
| [11] | Linan Cao, Min Wei. Recent Progress of Electric Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks Thin Film [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 1042-1056. |
| [12] | Ben Niu, Zhenyu Zhai, Xiaoke Hao, Tingli Ren, Congju Li. Flexible Acetone Gas Sensor based on ZIF-8/Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Composite Film [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 946-955. |
| [13] | Fang Liu, Tingting Pan, Xiurong Ren, Weiren Bao, Jiancheng Wang, Jiangliang Hu. Research on Preparation and Benzene Adsorption Performance of HCDs@MIL-100(Fe) Adsorbents [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 879-887. |
| [14] | Shihui Wang, Xiaoyu Xue, Min Cheng, Shaochen Chen, Chong Liu, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Xu Ji. High-Throughput Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Frameworks for CH4/H2 Separation by Synergizing Machine Learning and Molecular Simulation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 614-624. |
| [15] | Yaru Wei, Jing Ma, Tingting Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Yinli Duan, Juanqin Xue. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Lithium Chloride Intercalation Carbon Nitride [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 494-502. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||