Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (1): 26-35.DOI: 10.6023/A23090403 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
投稿日期:2023-09-04
发布日期:2023-11-23
基金资助:Received:2023-09-04
Published:2023-11-23
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:Share
Zhiqiang Wang, Jinzhan Su. Investigation of the Kinetic Properties and Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting of Cu3V2O8/ZnO Photoanode Modified by Cobalt Phosphate[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(1): 26-35.
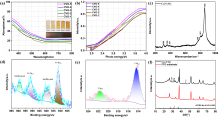


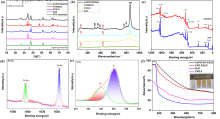
| 样品 | Dn/(cm2•s-1) | τd/ms | ktr | krec | ηtr/% | LD/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVO-1 | 1.20×10-4 | 0.40 | 3.65 | 1.36 | 72.86 | 141.36 |
| CVO-2 | 7.60×10-5 | 0.63 | 3.73 | 2.58 | 59.05 | 112.28 |
| CVO-3 | 7.60×10-5 | 0.63 | 4.06 | 2.53 | 61.59 | 112.28 |
| CVO-4 | 6.04×10-5 | 0.80 | 2.96 | 3.35 | 46.85 | 100.08 |
| CVO-5 | 6.04×10-5 | 0.80 | 2.24 | 2.78 | 44.62 | 100.08 |
| 样品 | Dn/(cm2•s-1) | τd/ms | ktr | krec | ηtr/% | LD/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVO-1 | 1.20×10-4 | 0.40 | 3.65 | 1.36 | 72.86 | 141.36 |
| CVO-2 | 7.60×10-5 | 0.63 | 3.73 | 2.58 | 59.05 | 112.28 |
| CVO-3 | 7.60×10-5 | 0.63 | 4.06 | 2.53 | 61.59 | 112.28 |
| CVO-4 | 6.04×10-5 | 0.80 | 2.96 | 3.35 | 46.85 | 100.08 |
| CVO-5 | 6.04×10-5 | 0.80 | 2.24 | 2.78 | 44.62 | 100.08 |

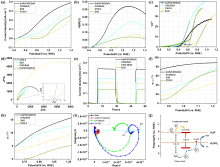

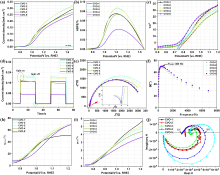
| 样品 | Dn/(cm2•s-1) | τd/ms | ktr | krec | ηtr/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVO-3 | 7.60×10-5 | 0.63 | 4.06 | 2.53 | 61.59 |
| ZnO | 1.67×10-4 | 0.29 | 3.61 | 1.40 | 72.23 |
| CVO/ZnO | 9.06×10-5 | 0.53 | 3.73 | 2.15 | 63.41 |
| CoPi/CVO/ZnO | 1.14×10-4 | 0.42 | 5.72 | 0.84 | 87.22 |
| 样品 | Dn/(cm2•s-1) | τd/ms | ktr | krec | ηtr/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVO-3 | 7.60×10-5 | 0.63 | 4.06 | 2.53 | 61.59 |
| ZnO | 1.67×10-4 | 0.29 | 3.61 | 1.40 | 72.23 |
| CVO/ZnO | 9.06×10-5 | 0.53 | 3.73 | 2.15 | 63.41 |
| CoPi/CVO/ZnO | 1.14×10-4 | 0.42 | 5.72 | 0.84 | 87.22 |
| [1] |
Zhao, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, H.-Z.; Li, M.-Z.; Song, Y.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 9. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17070320 |
|
(赵聪, 马颖, 汪洋, 周雪, 李会增, 李明珠, 宋延林, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 9.)
doi: 10.6023/A17070320 |
|
| [2] |
Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Lian, Z.; Fan, J.; Tao, Y.; Li, G.; Li, H. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135132.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135132 |
| [3] |
Pirrone, N.; Bella, F.; Hernández, S. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 5379.
doi: 10.1039/D2GC00292B |
| [4] |
An, P.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.-X.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-M.; Jiang, G.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1629. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22080362 |
|
(安攀, 张庆慧, 杨状, 武佳星, 张佳颖, 王雅君, 李宇明, 姜桂元, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1629.)
doi: 10.6023/A22080362 |
|
| [5] |
Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Guo, P.; Su, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12602.
|
| [6] |
Tayebi, M.; Tayyebi, A.; Masoumi, Z.; Lee, B.-K. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 502, 144189.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144189 |
| [7] |
Wang, J.; Perry, N. H.; Guo, L.; Vayssieres, L.; Tuller, H. L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 11, 2031.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b16911 |
| [8] |
Tayebi, M.; Kolaei, M.; Tayyebi, A.; Masoumi, Z.; Belbasi, Z.; Lee, B.-K. Sol. Energy. 2019, 190, 185.
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.08.020 |
| [9] |
Zhang, T.; Paulose, M.; Neupane, R.; Schaffer, L. A.; Rana, D. B.; Su, J.; Guo, L.; Varghese, O. K. Sol. Energy Mater. 2020, 209, 110472.
|
| [10] |
Hao, R.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y.-B.; Chen, D.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 1199. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A14080593 |
|
(郝锐, 邓霄, 杨毅彪, 陈德勇, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 1199.)
doi: 10.6023/A14080593 |
|
| [11] |
Sivula, K.; Van De Krol, R. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1.
|
| [12] |
Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, X. Catal. Today 2019, 335, 31.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.01.067 |
| [13] |
Seabold, J. A.; Neale, N. R. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1005.
doi: 10.1021/cm504327f |
| [14] |
Jiang, C.-M.; Farmand, M.; Wu, C. H.; Liu, Y.-S.; Guo, J.; Drisdell, W. S.; Cooper, J. K.; Sharp, I. D. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3334.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00807 |
| [15] |
Pulipaka, S.; Boni, N.; Meduri, P. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 6060.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.0c00780 |
| [16] |
Tahir, M.; Iqbal, T.; Zeba, I.; Hasan, A.; Muhammad, S.; Siddeeg, S. M.; Shahzad, K. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage. 2020, 17, 011002.
doi: 10.1115/1.4043491 |
| [17] |
Lian, X.; Duan, H.; Zeng, W.; Yu, B.; Guo, W.; Lou, Q. Mol. Catal. 2022, 528, 112493.
|
| [18] |
Fujimoto, I.; Wang, N.; Saito, R.; Miseki, Y.; Gunji, T.; Sayama, K. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 2454.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.08.114 |
| [19] |
Hossain, M. K.; Sarker, H. P.; Sotelo, P.; Dang, U.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, I.; Blawat, J.; Vali, A.; Xie, W.; Oskam, G.; Huda, M. N. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 6247.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c02227 |
| [20] |
He, X.; Gan, J.; Li, H. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 127, 119.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2021.07.034 |
| [21] |
Hong, S.; Burkhow, S. J.; Doughty, R. M.; Cheng, Y.; Ryan, B. J.; Mantravadi, A.; Roling, L. T.; Panthani, M. G.; Osterloh, F. E.; Smith, E. A. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 1667.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c04155 |
| [22] |
Liu, C.; Su, J.; Guo, L. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27557.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA25601A |
| [23] |
Chai, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Hu, G.; Jin, J. Appl. Catal., B 2022, 305, 121011.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.121011 |
| [24] |
Mana, P. M.; Bhujbal, P. K.; Pathan, H. M. Energy Environ. 2020, 12, 77.
|
| [25] |
Bertoluzzi, L.; Lopez-Varo, P.; Tejada, J.; Bisquert, J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 2873.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA03210E |
| [26] |
Sang, L.-X.; Lin, J.; Ge, H.; Lei, L. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica 2017, 33, 2454. (in Chinese)
|
|
(桑丽霞, 蔺佳, 葛昊, 雷蕾, 物理化学学报, 2017, 33, 2454.)
|
|
| [27] |
Franco, G.; Gehring, J.; Peter, L.; Ponomarev, E.; Uhlendorf, I. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 692.
doi: 10.1021/jp984060r |
| [28] |
Zhang, H.; Jin, S.; Duan, G.; Wang, J.; Cai, W. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1118.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2014.04.006 |
| [29] |
Kumar, V.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, A. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 6212.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c01012 |
| [30] |
Wei, Y.; Su, J.; Wan, X.; Guo, L.; Vayssieres, L. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1561.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-016-1050-9 |
| [31] |
Tieu, D. T.; Trang, T. N. Q.; Thu, V. T. H. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 808, 151735.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151735 |
| [32] |
Doan, Q. K.; Nguyen, M. H.; Sai, C. D.; Mai, H. H.; Pham, N. H.; Bach, T. C.; Nguyen, V. T.; Nguyen, T. T.; Ho, K. H.; Tran, T. H. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144593.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144593 |
| [33] |
Fang, W.; Lin, Y.; Xv, R.; Shang, X.; Fu, L. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 437, 141511.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141511 |
| [34] |
Balachandran, S.; Swaminathan, M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 26306.
doi: 10.1021/jp306874z |
| [35] |
Jin, T.; Xu, D.; Diao, P.; Xiang, M. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica 2012, 28, 2276. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201209101 |
|
(金涛, 许頔, 刁鹏, 项民, 物理化学学报, 2012, 28, 2276.)
|
|
| [36] |
Kim, J. Y.; Jang, J. W.; Youn, D. H.; Magesh, G.; Lee, J. S. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1400476.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v4.13 |
| [37] |
Chen, Y.-C.; Wu, Z.-J.; Hsu, Y.-K. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 12292.
doi: 10.1039/D0NR00058B |
| [1] | Shanshan Jin, Sinong Wang, Hongdong Zhang, Yuliang Yang. A Study on the Comprehensive Evaluation of Chinese Handmade Paper Deacidification Effectiveness Based on Life Expectancy★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(12): 1681-1686. |
| [2] | Juan Wang, Huamin Xiao, Ding Xie, Yuanru Guo, Qingjiang Pan. Density Functional Theory Study of Structures of Copper-doped and Graphitic Carbon Nitride-combined Zinc Oxides and Their Boosted Nitrogen Dioxide-sensing Performance [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(11): 1493-1499. |
| [3] | Tiantian Lü, Wen Ma, Dongsun Zhan, Yanmin Zou, Jilong Li, Meiling Feng, Xiaoying Huang. Two New Three-Dimensional Lanthanide Metal-organic Frameworks for the Highly Efficient Removal of Cs+ Ions※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 640-646. |
| [4] | Yaru Wei, Jing Ma, Tingting Yuan, Jiawei Jiang, Yinli Duan, Juanqin Xue. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Lithium Chloride Intercalation Carbon Nitride [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 494-502. |
| [5] | Min Dai, Gangtie Lei, Zhao Zhang, Zhi Li, Hujun Cao, Ping Chen. Room Temperature Hydrogen Absorption of V2O5 Catalyzed MgH2/Mg※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 303-309. |
| [6] | Zun Liang, Xin Zhang, Songtai Lv, Hongtao Liang, Yang Yang. Crystal-Melt Interface Kinetics and the Capillary Wave Dynamics of the Monolayer Confined Ice-Water Coexistence Lines [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(1): 108-118. |
| [7] | Ni Yuxin, Zhang Chenjie, Yuan Yaxian, Xu Minmin, Yao Jianlin. Determination on Origination of Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Effect on Nano ZnO Substrate [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(7): 641-646. |
| [8] | Qi Qige, Yang Chunfan, Xia Ye, Liu Kunhui, Su Hongmei. Photo-induced Electron Transfer between 4-Thiouracil and Tryptophan [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(6): 515-519. |
| [9] | Meng Shuangyan, Wang Mingming, Lü Bolin, Xue Qunji, Yang Zhiwang. Preparation of Eu-Doped ZnO/MIL-53(Fe) Photocatalyst and Its Catalytic Performance for Selective Oxidation of Alcohols [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(11): 1184-1193. |
| [10] | Sun Mengjia, Wu Tianyi, Li Tianyu, Guo Fengqiao, Tang Yang, Mo Hengliang, Yang Zhitao, Wan Pingyu. Research on High Performance Ammonium Removal Materials Based on δ-MnO2 Nanoplate Arrays Decorated Graphite Felt [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2018, 76(6): 467-474. |
| [11] | Yuan Pei, Chen Jian, Pan Deng, Bao Xiaojun. Adsorption and Reaction Kinetic Studies of the Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Polystyrene [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(7): 603-611. |
| [12] | Zhao Mi, Li Haohua, Shen Xiaoping. Facile Electrochemical Synthesis of CeO2@Ag@CdSe Nanotube Arrays with Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74(10): 825-832. |
| [13] | Jia Yunsheng, Wang Huoyan, Zhao Xuesong, Liu Xiaowei, Wang Yiliu, Fan Qunlong, Zhou Jianmin. Exploring and Evaluation of CaAl Hydrotalcite-like Adsorbents on Phosphate Recycling [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2015, 73(11): 1207-1213. |
| [14] | Hao Yanzhong, Fan Longxue, Sun Bao, Sun Shuo, Pei Juan. A Photoelectrochemical Study of p-n Heterojunction between P3HT and Nanodendrite CdTe Sensitized ZnO Nanotube Array [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014, 72(1): 114-120. |
| [15] | Li Yuesheng, Li Benqiang, Sun Shaofa. Microcalorimetric and Microscopic Studies on the Antibacterial Activities of CdTe(QDs)/TiO2 Nanocomposites and the Mechanism of Cell Damage on Escherichia coli [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(12): 1656-1662. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
