Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (3): 336-347.DOI: 10.6023/A23120538 Previous Articles Next Articles
Review
王敏a, 陈帮塘a, 陈桥林a, 王俊a, 陈名钊a, 蒋志龙a,*( ), 王平山a,b,*(
), 王平山a,b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-12-19
发布日期:2024-01-18
作者简介: |
王敏, 广州大学环境科学与工程学院环境工程专业在读硕士生. |
 |
蒋志龙, 广州大学大湾区环境研究院副教授, 主要的研究方向为超分子自组装及功能配合物, 参与国家自然科学基金面上项目3项, 主持贵州省科技厅科技创新项目1项, 广东省教育厅科技创新项目1项, 广州市市校联合基金1项, 目前以第一作者或者通讯作者身份在Nature Communication、J. Am. Chem. Soc.、Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.、iScience、Cell Reports Physical Science、Nano Research、Chem. Commun.、Inorg. Chem.等期刊上发表论文17篇, 授权中国发明专利6项. |
 |
王平山, 广州大学大湾区环境研究院教授, 中南大学化学化工学院特聘教授, 入选中组部海外高层次人才计划和湖南省“国家级领军人才”, 主持国家、国际环境署/环保部及美国科研项目20余项, 获省部级科技奖励3项, 目前研究领域主要集中在超分子化学、金属有机高分子能源材料和高分子环保材料, 在Science, Nat. Commun., J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.等期刊发表学术论文100余篇, 授权国际和中国发明专利30余项, 在超大单分子的构筑策略研究领域有突出贡献, 相关成果在国内外具有重要的影响. |
基金资助:
Min Wanga, Bangtang Chena, Qiaolin Chena, Jun Wanga, Mingzhao Chena, Zhilong Jianga( ), Pingshan Wanga,b(
), Pingshan Wanga,b( )
)
Received:2023-12-19
Published:2024-01-18
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:Share
Min Wang, Bangtang Chen, Qiaolin Chen, Jun Wang, Mingzhao Chen, Zhilong Jiang, Pingshan Wang. Research Progress on Metal-coordination-driven Self-assembly of 6,6"-Bis(2,6-dimethoxy-benzene)-terpyridine and Its Derivatives[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 336-347.
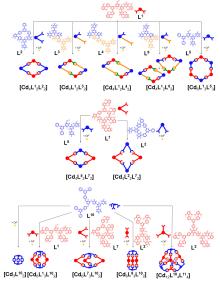
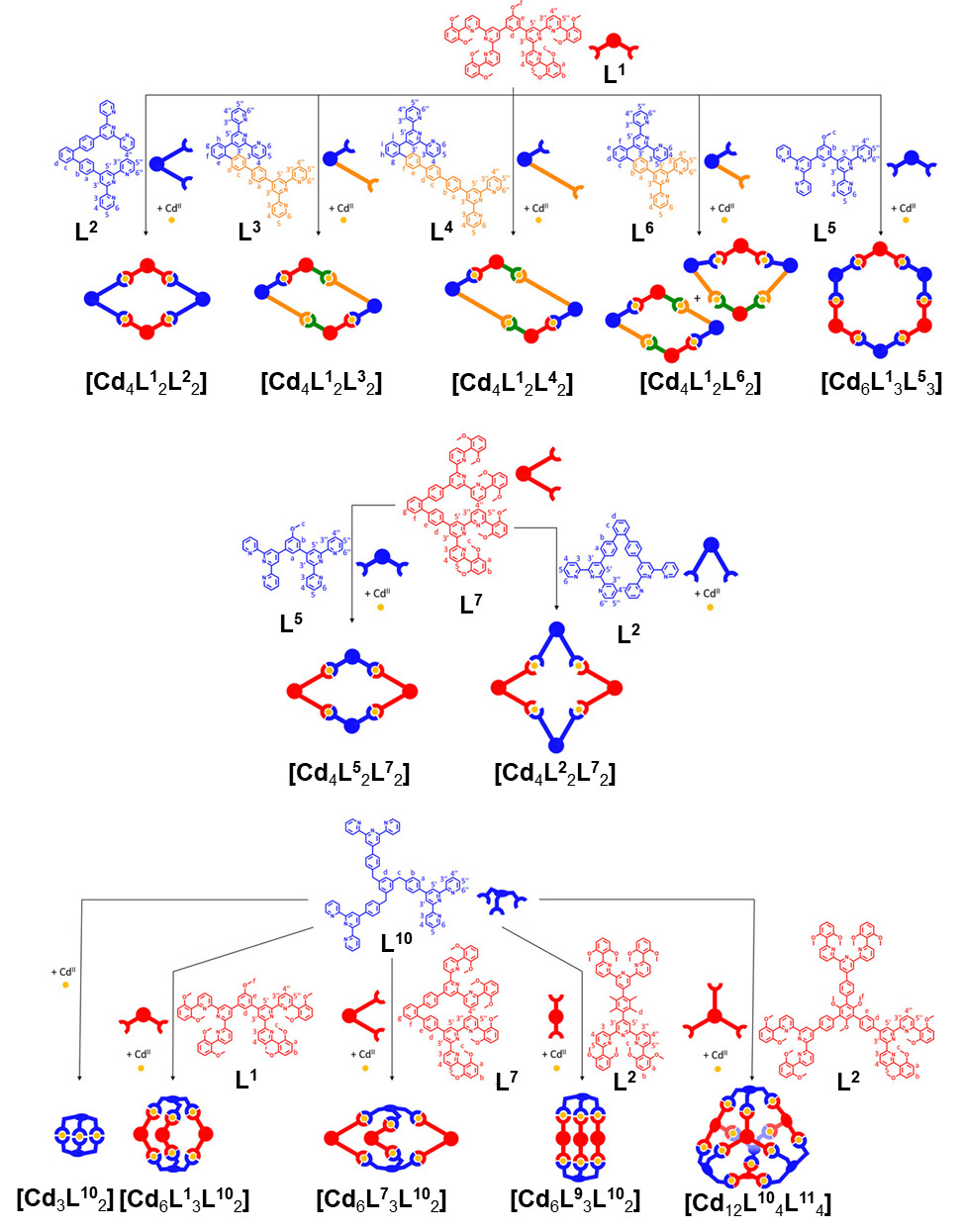

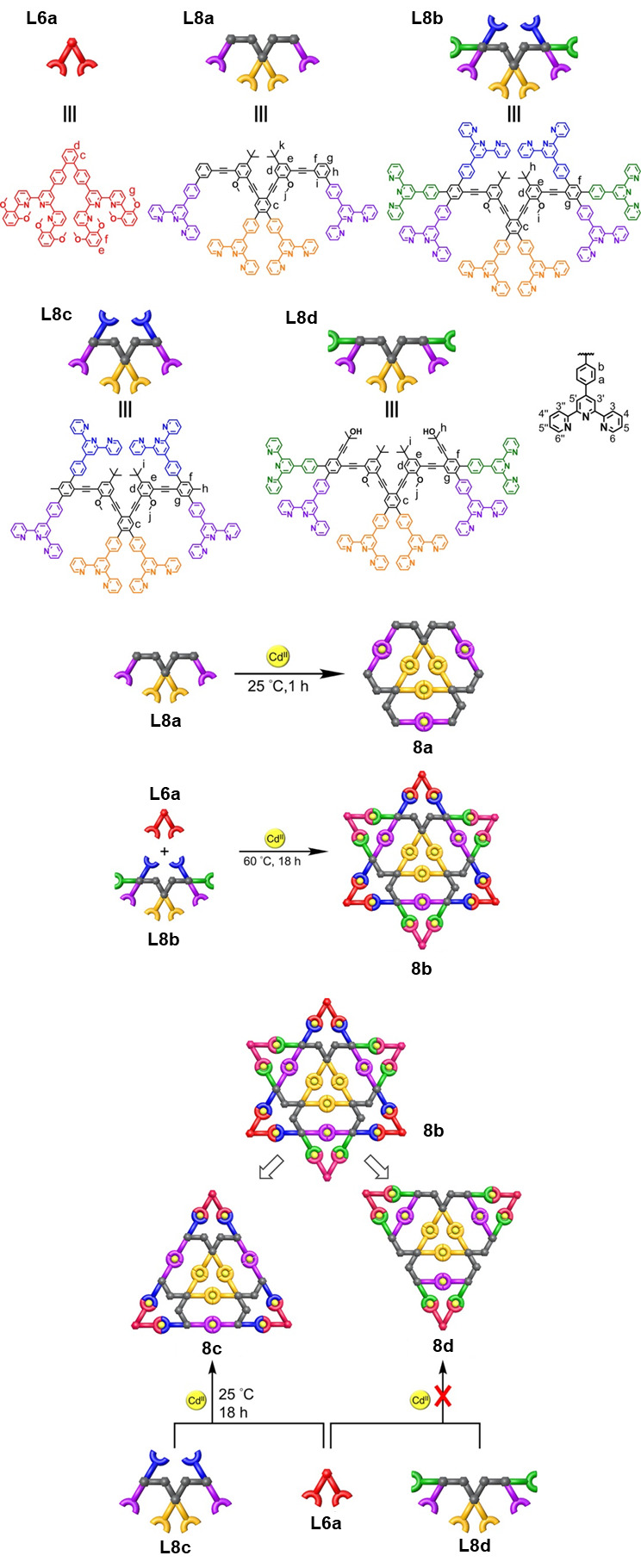
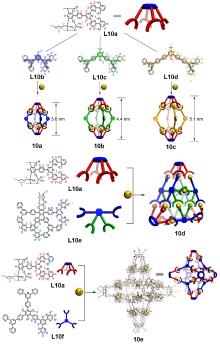

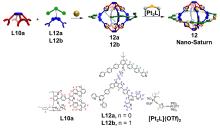
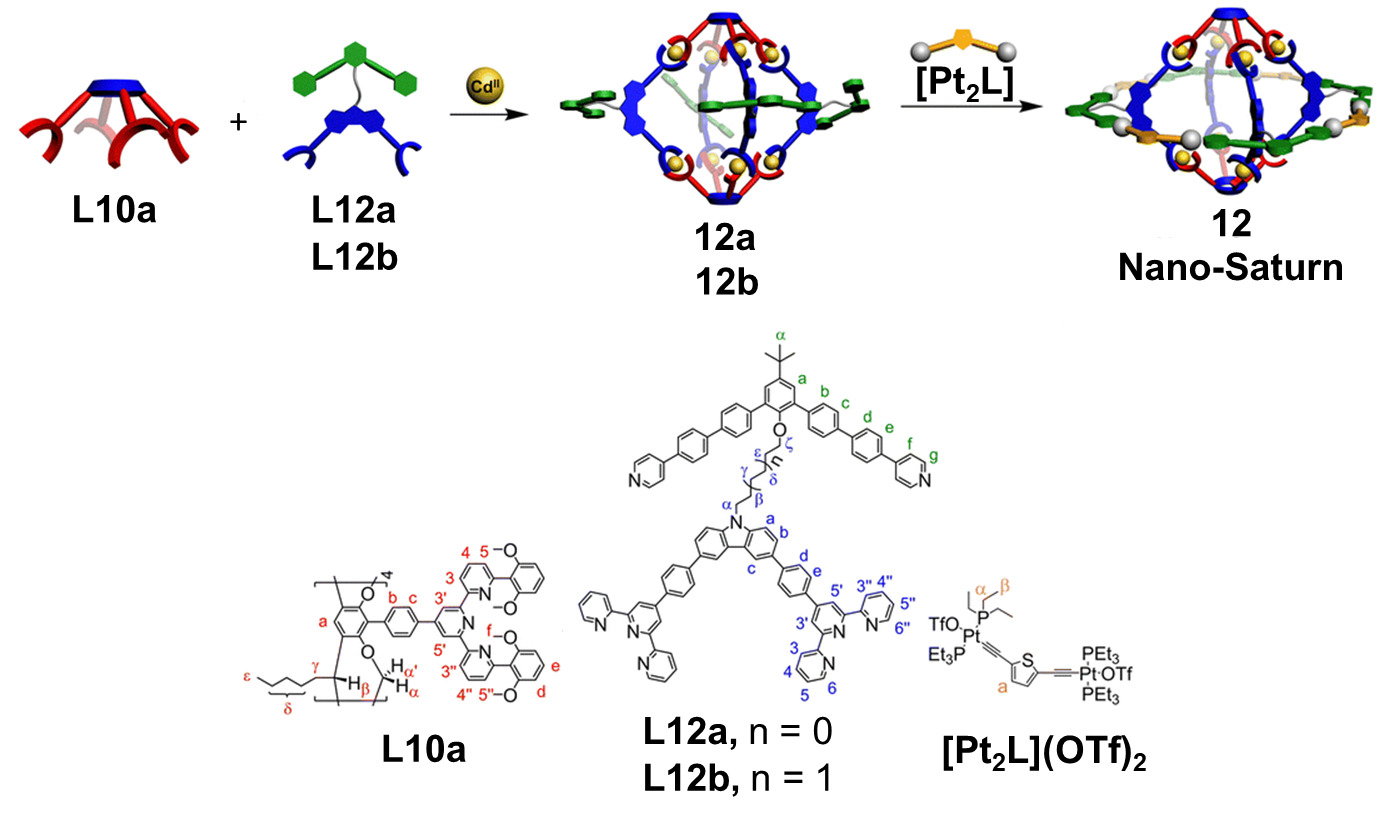
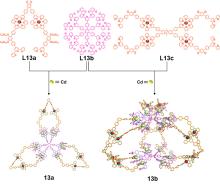
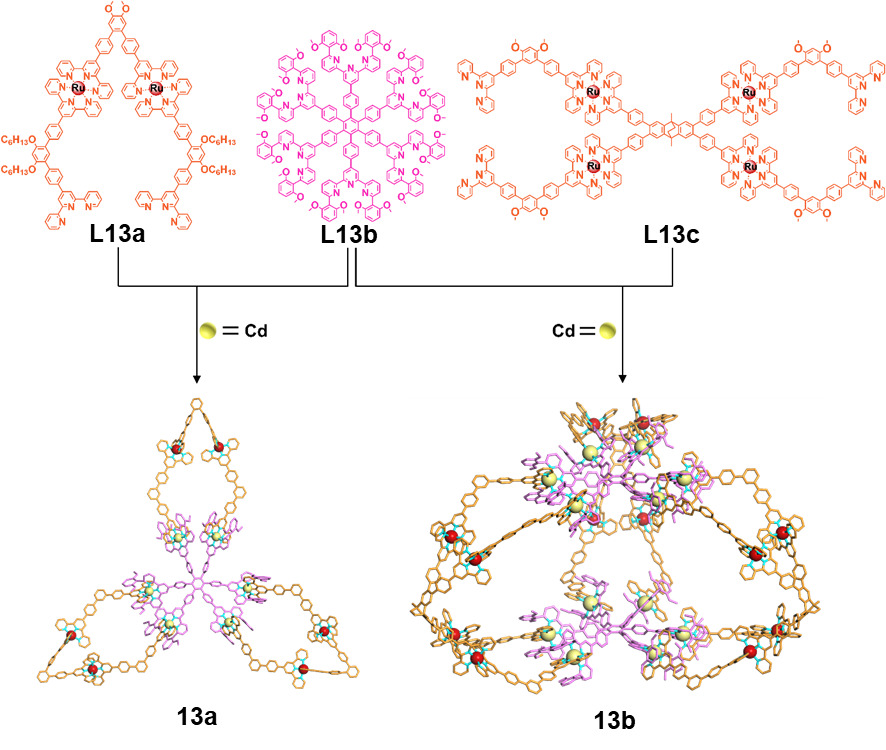



| 化合物 | 吸收最大值/nm | 发射最大值/nm | 量子产率a/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Cd4L12L22] | 286 (4.5), 355 (1.4) | 467 | 14.4 |
| [Cd4L12L32] | 278 (6.7), 330 (1.1) | 472 | 13.3 |
| [Cd4L12L42] | 283 (19.6), 343 (10.2) | 473 | 6.2 |
| [Cd6L13L53] | 279 (13.2), 336 (1.9) | 473 | 6.3 |
| [Cd4L52L72] | 279 (10.1), 333 (2.5) | 393, 463 | 14.4 |
| [Cd4L22L72] | 280 (9.8), 335 (2.8) | 393, 450 | 21.2 |
| [Cd9L73L83] | 281 (10.5), 335 (3.9) | 381, 464 | 8.2 |
| [Cd3L102] | 278 (4.9), 325 (6.3) | 407, 492 | 5.3 |
| [Cd6L13L102] | 280 (10.2), 340 (1.6) | 472 | 2.1 |
| [Cd6L73L102] | 281 (18.4), 332 (6.0) | 395, 495 | 7.1 |
| [Cd6L93L102] | 280 (10.8), 335 (1.7) | 477 | 2.1 |
| [Cd12L104L114] | 286 (3.5), 330 (1.6) | 472 | 3.4 |
| 化合物 | 吸收最大值/nm | 发射最大值/nm | 量子产率a/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Cd4L12L22] | 286 (4.5), 355 (1.4) | 467 | 14.4 |
| [Cd4L12L32] | 278 (6.7), 330 (1.1) | 472 | 13.3 |
| [Cd4L12L42] | 283 (19.6), 343 (10.2) | 473 | 6.2 |
| [Cd6L13L53] | 279 (13.2), 336 (1.9) | 473 | 6.3 |
| [Cd4L52L72] | 279 (10.1), 333 (2.5) | 393, 463 | 14.4 |
| [Cd4L22L72] | 280 (9.8), 335 (2.8) | 393, 450 | 21.2 |
| [Cd9L73L83] | 281 (10.5), 335 (3.9) | 381, 464 | 8.2 |
| [Cd3L102] | 278 (4.9), 325 (6.3) | 407, 492 | 5.3 |
| [Cd6L13L102] | 280 (10.2), 340 (1.6) | 472 | 2.1 |
| [Cd6L73L102] | 281 (18.4), 332 (6.0) | 395, 495 | 7.1 |
| [Cd6L93L102] | 280 (10.8), 335 (1.7) | 477 | 2.1 |
| [Cd12L104L114] | 286 (3.5), 330 (1.6) | 472 | 3.4 |



| [1] |
Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, D.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Newkome, G. R.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Wang, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11450.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.38 |
| [2] |
Sarkar, R.; Guo, K.; Moorefield, C. N.; Saunders, M. J.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Newkome, G. R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12182.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v53.45 |
| [3] |
Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, M.; Yuan, J.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Wang, P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10041.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06021 |
| [4] |
Schultz, A.; Li, X.; Barkakaty, B.; Moorefield, C. N.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Newkome, G. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7672.
doi: 10.1021/ja303177v |
| [5] |
Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, B.; Wang, K.; Sun, M.; Liu, D.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Moorefield, C. N.; Newkome, G. R.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, P. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15476.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms15476 |
| [6] |
Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Song, B.; Bolarinwa, O.; Reese, R. A.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.-Q.; Cai, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.-B.; Li, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8174.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01326 pmid: 28558196 |
| [7] |
Kaphan, D. M.; Levin, M. D.; Bergman, R. G.; Raymond, K. N.; Toste, F. D. Science 2015, 350, 1235.
doi: 10.1126/science.aad3087 pmid: 26785485 |
| [8] |
MacGillivray, L. R.; Atwood, J. L. Nature 1997, 389, 469.
doi: 10.1038/38985 |
| [9] |
Roberts, D. A.; Pilgrim, B. S.; Cooper, J. D.; Ronson, T. K.; Zarra, S.; Nitschke, J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10068.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b05080 |
| [10] |
Cao, L.; Wang, P.; Miao, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Duan, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Stang, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7005.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b03856 |
| [11] |
Mahata, K.; Frischmann, P. D.; Wuerthner, F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15656.
doi: 10.1021/ja4083039 |
| [12] |
Hong, C. M.; Morimoto, M.; Kapustin, E. A.; Alzakhem, N.; Bergman, R. G.; Raymond, K. N.; Toste, F. D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 6591.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b01701 |
| [13] |
Suzuki, K.; Tominaga, M.; Kawano, M.; Fujita, M. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1638.
|
| [14] |
Meng, W.; Breiner, B.; Rissanen, K.; Thoburn, J. D.; Clegg, J. K.; Nitschke, J. R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3479.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v50.15 |
| [15] |
Tan, C.; Jiao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Cui, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2085.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.8 |
| [16] |
Xie, T.-Z.; Guo, K.; Guo, Z.; Gao, W.-Y.; Wojtas, L.; Ning, G.-H.; Huang, M.; Lu, X.; Li, J.-Y.; Liao, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Moorefield, C. N.; Saunders, M. J.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Newkome, G. R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9224.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v54.32 |
| [17] |
Clingerman, D. J.; Kennedy, R. D.; Mondloch, J. E.; Sarjeant, A. A.; Hupp, J. T.; Farha, O. K.; Mirkin, C. A. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11485.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc44173c |
| [18] |
Ghosh, K.; Hu, J.; White, H. S.; Stang, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6695.
doi: 10.1021/ja902045q |
| [19] |
Olenyuk, B.; Levin, M. D.; Whiteford, J. A.; Shield, J. E.; Stang, P. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 10434.
doi: 10.1021/ja9931933 |
| [20] |
Wang, H.; Ji, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, F. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606117.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.14 |
| [21] |
Yamashina, M.; Sartin, M. M.; Sei, Y.; Akita, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Tahara, T.; Yoshizawa, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9266.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b06195 pmid: 26166243 |
| [22] |
Yan, X.; Cook, T. R.; Wang, P.; Huang, F.; Stang, P. J. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 342.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2201 |
| [23] |
Mugridge, J. S.; Zahl, A.; van Eldik, R.; Bergman, R. G.; Raymond, K. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4299.
doi: 10.1021/ja309949q pmid: 23391095 |
| [24] |
Xiao, T.; Elmes, R.; Yao, Y. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 628200.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.628200 |
| [25] |
Xiao, T.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X.-Q.; Huang, F.; Lin, C.; Wang, L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.05.011 |
| [26] |
Horiuchi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tessarolo, J.; Tanaka, H.; Sakuda, E.; Arikawa, Y.; Meggers, E.; Clever, G. H.; Umakoshi, K. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 155. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-35850-4
|
| [27] |
Jiang, B.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.-Q.; Zheng, W.; Chen, L.-J.; Sun, B.; Li, C.; Hu, B.-W.; Tan, H.; Li, X.; Yang, H.-B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 738.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b11409 pmid: 26741405 |
| [28] |
Bai, L.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2102811.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.22 |
| [29] |
Casini, A.; Crowley, J. D. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 293.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00293 |
| [30] |
Lu, Y.-L.; Song, J.-Q.; Qin, Y.-H.; Guo, J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-D.; Pan, M.; Su, C.-Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 8778.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c02692 |
| [31] |
Tan, C.; Jiao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Han, X.; Cui, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2085.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.8 |
| [32] |
Clever, G. H.; Punt, P. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2233.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00231 |
| [33] |
Turunen, L.; Warzok, U.; Schalley, C. A.; Rissanen, K. Chem 2017, 3, 861.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2017.08.010 |
| [34] |
Winter, A.; Hager, M. D.; Newkome, G. R.; Schubert, U. S. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5728.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v23.48 |
| [35] |
De, S.; Mahata, K.; Schmittel, M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1555.
doi: 10.1039/b922293f |
| [36] |
Fujita, D.; Ueda, Y.; Sato, S.; Mizuno, N.; Kumasaka, T.; Fujita, M. Nature 2016, 540, 563.
doi: 10.1038/nature20771 |
| [37] |
Dietrich-Buchecker, C. O.; Sauvage, J. P.; Kintzinger, J. P. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 5095.
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)94050-4 |
| [38] |
Sauvage, J. P.; Weiss, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 6108.
pmid: 27715037 |
| [39] |
Saha, M. L.; Pramanik, S.; Schmittel, M. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9459.
doi: 10.1039/c2cc35036j |
| [40] |
Mahata, K.; Saha, M. L.; Schmittel, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15933.
doi: 10.1021/ja108419k |
| [41] |
Saha, M. L.; Bats, J. W.; Schmittel, M. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 5592.
doi: 10.1039/c3ob41258j |
| [42] |
Saha, M. L.; Schmittel, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17743.
doi: 10.1021/ja410425k |
| [43] |
Saha, M. L.; Mittal, N.; Bats, J. W.; Schmittel, M. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12189.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC05465B |
| [44] |
Wang, S.-Y.; Fu, J.-H.; Liang, Y.-P.; He, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chan, Y.-T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3651.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b01005 |
| [45] |
Mahata, K.; Schmittel, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16544.
doi: 10.1021/ja907185k |
| [46] |
Schmittel, M.; Ganz, A. Chem. Commun. 1997, 999.
|
| [47] |
Lal Saha, M.; Schmittel, M. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 4651.
doi: 10.1039/c2ob25098e |
| [48] |
Wang, S. Y.; Huang, J. Y.; Liang, Y. P.; He, Y. J.; Chen, Y. S.; Zhan, Y. Y.; Hiraoka, S.; Liu, Y. H.; Peng, S. M.; Chan, Y. T. Chem. - Eur. J. 2018, 24, 9274.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.37 |
| [49] |
Fu, J.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Prusty, S.; Chan, Y.-T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16217.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b08731 |
| [50] |
Rousseaux, S. A. L.; Gong, J. Q.; Haver, R.; Odell, B.; Claridge, T. D. W.; Herz, L. M.; Anderson, H. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12713.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b07956 pmid: 26378660 |
| [51] |
Wang, S.-C.; Cheng, K.-Y.; Fu, J.-H.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chan, Y.-T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16661.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c06618 |
| [52] |
Song, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Hsu, C.-H.; Bolarinwa, O.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, G.-Q.; Rivera, E.; Yang, H.-B.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; Li, X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5258.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201701417 pmid: 28382756 |
| [53] |
Riwar, L.-J.; Trapp, N.; Root, K.; Zenobi, R.; Diederich, F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 17259.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.52 |
| [54] |
Xie, J.; Peng, H.-J.; Huang, J.-Q.; Xu, W.-T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16415.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.51 |
| [55] |
Yang, Y.; Jing, X.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Duan, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10136.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c00626 |
| [56] |
Kohlhaas, M.; Zähres, M.; Mayer, C.; Engeser, M.; Merten, C.; Niemeyer, J. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3298.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC10152C |
| [57] |
MacGillivray, L. R.; Atwood, J. L. Nature 1997, 389, 469.
doi: 10.1038/38985 |
| [58] |
Ugono, O.; Moran, J. P.; Holman, K. T. Chem. Commun. 2008, 1404.
|
| [59] |
Kobayashi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yamanaka, M.; Sei, Y.; Yamaguchi, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13896.
pmid: 15506730 |
| [60] |
He, L.; Wang, S.-C.; Lin, L.-T.; Cai, J.-Y.; Li, L.; Tu, T.-H.; Chan, Y.-T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7134.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c01482 |
| [61] |
He, L.; Hsu, H.-K.; Li, L.; Lin, L.-T.; Tu, T.-H.; Ong, T.-G.; Liou, G.-G.; Chan, Y.-T. Chem 2022, 8, 494.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2021.11.013 |
| [62] |
Toyota, S.; Tsurumaki, E. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 6878.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v25.28 |
| [63] |
Yamamoto, Y.; Tsurumaki, E.; Wakamatsu, K.; Toyota, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8199.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201804430 pmid: 29846033 |
| [64] |
Zhan, S.-Z.; Li, J.-H.; Zhang, G.-H.; Li, M.-D.; Sun, S.; Zheng, J.; Ning, G.-H.; Li, M.; Kuang, D.-B.; Wang, X.-D.; Li, D. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3325.
doi: 10.1039/D0CC00532K |
| [65] |
Stasyuk, O. A.; Stasyuk, A. J.; Sola, M.; Voityuk, A. A. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 2126.
doi: 10.1039/d0cp05919f pmid: 33437974 |
| [66] |
Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, T. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 3372.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-5158-9 |
| [67] |
He, L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.-C.; Chan, Y.-T. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 11500.
doi: 10.1039/D3CC03414C |
| [68] |
Schultz, A.; Li, X.; McCusker, C. E.; Moorefield, C. N.; Castellano, F. N.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Newkome, G. R. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 11569.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v18.37 |
| [69] |
Li, Z.; Luo, S.; Chen, M.; Yu, X.; Li, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1447 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A23050201 |
|
(李志凯, 罗思琪, 陈敏, 於秀君, 李霄鹏,, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1447.)
doi: 10.6023/A23050201 |
|
| [70] |
Newkome, G. R.; Cho, T. J.; Moorefield, C. N.; Cush, R.; Russo, P. S.; Godínez, L. A.; Saunders, M. J.; Mohapatra, P. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 2946.
|
| [71] |
Xie, T.-Z.; Li, J.-Y.; Guo, Z.; Ludlow, J. M., III; Lu, X.; Moorefield, C. N.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Newkome, G. R. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 1671.
|
| [72] |
Chakraborty, S.; Sarkar, R.; Endres, K.; Xie, T.-Z.; Ghosh, M.; Moorefield, C. N.; Saunders, M. J.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Newkome, G. R. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 5091.
doi: 10.1002/ejoc.v2016.30 |
| [73] |
Liu, D.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Moorefield, C. N.; Newkome, G. R.; Li, X.; Wang, P. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9773.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC04482D |
| [74] |
Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Fang, F.; Hou, Y.; Lu, C.; Mu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. JACS Au 2022, 2, 1479.
doi: 10.1021/jacsau.2c00245 |
| [75] |
Ju, H.; Tsuruoka, Y.; Hayano, M.; Lee, E.; Park, K.-M.; Ikeda, M.; Ishi-i, J.-i.; Kuwahara, S.; Habata, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 650.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.2 |
| [76] |
Jiang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Lv, W.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Fu, F.; Hwang, S.-H.; Chen, M.; Wang, P. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108334.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108334 |
| [77] |
Elbert, T.; Ray, W. J.; Kowalik, Z. J.; Skinner, J. E.; Graf, K. E.; Birbaumer, N. Physiol. Rev. 1994, 74, 1.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.1.1 pmid: 8295931 |
| [78] |
Jiang, Z.; Liu, D.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, T.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Newkome, G. R.; Wang, P. iScience 2020, 23, 101064.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101064 |
| [79] |
Li, C.; Li, R.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14417.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c05949 |
| [80] |
Jiang, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.; Fu, F.; Miao, R.; Ouyang, T.; Lv, W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, P. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 8923.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c00587 |
| [81] |
Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Gu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, S.; Peng, L.; Wu, K.; Nieckarz, D.; Szabelski, P.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13749.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05720 |
| [82] |
Sarkar, R.; Xie, T.-Z.; Endres, K. J.; Wang, Z.; Moorefield, C. N.; Saunders, M. J.; Ghorai, S.; Patri, A. K.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Dobrynin, A. V.; Newkome, G. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5526.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c01168 |
| [83] |
Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z.; Miao, R.; Fu, F.; Yin, J.-F.; Chen, B.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, H.; Li, K.; Wang, G.; Liu, D.; Yin, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e20221423.
|
| [84] |
Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yin, J.-F.; Chen, B.; Li, Y.; Yin, P.; Chan, Y.-T.; Wang, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, P. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101293.
|
| [85] |
Goodall, W.; Williams, J. A. G. Chem. Commun. 2001, 2514.
|
| [86] |
Hofmeier, H.; Schubert, U. S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 373.
pmid: 15280970 |
| [87] |
Zhang, S.-Y.; Sun, H.-Y.; Wang, R.-G.; Meng, Y.-S.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.-Y. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 9888.
doi: 10.1039/D2DT00436D |
| [88] |
Yang, R.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Wang, R.-G.; Meng, Y.-S.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.-Y. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 38, 1477 (in Chinese).
|
|
(杨蕊, 张舒雅, 王润国, 孟银杉, 刘涛, 朱元元, 无机化学学报, 2022, 38, 1477.)
|
| [1] | Zhikai Li, Siqi Luo, Min Chen, Xiujun Yu, Xiaopeng Li. Research Progress of Bis(terpyridine)-Ruthenium(II) Complexes★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1447-1461. |
| [2] | Wang Feng, Liang Wen-Jing, Wang Wen-Guang, Chen Bin, Feng Ke, Zhang Li-Ping, Tung Chen-Ho, Wu Li-Zhu. Bis-terpyridine Os(Ⅱ) Complex Sensitized [FeFe] Hydrogenase Mimic Systems: Synthesis and Photophysical Study [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(22): 2306-2310. |
| [3] | BO Ru-Xiu, TONG Bin, QI Dun-Ge, DIAO Wei, SHEN Jin-Bei, DAN Jian-Bing, DONG Yu-Beng. Full-conjugated Layer-by-Layer self-assembly Ultrathin Functional Films Fabricted from Terpyridine and Transition Metal Ions based on Coordinate Interaction [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2009, 67(24): 2779-2784. |
| [4] | DING Hui-Ying1,2; SONG Lin-Qing; CHEN Jing-Rong; WANG Xue-Song*,1; ZHANG Bao-Wen*,1. Effects of TiO2 Nanoparticles on the Photodamage of CT-DNA by Ru(II) Bis(terpyridine) Complexes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2006, 64(17): 1799-1804. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||