Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2026, Vol. 84 ›› Issue (1): 53-63.DOI: 10.6023/A25060236 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
投稿日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-09-03
基金资助:
Ziyi Shui*( ), Shurui Yin, Jintao Deng, Liuyun Xu, Li Guo
), Shurui Yin, Jintao Deng, Liuyun Xu, Li Guo
Received:2025-06-25
Published:2025-09-03
Contact:
* E-mail: m18182696780@163.com
Supported by:Share
Ziyi Shui, Shurui Yin, Jintao Deng, Liuyun Xu, Li Guo. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Assisted Synthesis of Metal-organic Framework-Derived Hierarchically Porous Carbon for Bifunctional Electrocatalysis[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 53-63.
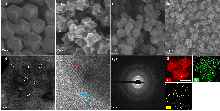

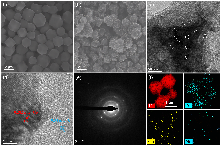

| SBET/ (m2•g-1) | SMicro/ (m2•g-1) | SMeso/ (m2•g-1) | VPore/ (cm3•g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-N-C | 188 | 46 | 142 | 0.19 |
| P-Co-N-C | 285 | 54 | 231 | 0.32 |
| P-CoNi-N-C | 296 | 58 | 238 | 0.34 |
| SBET/ (m2•g-1) | SMicro/ (m2•g-1) | SMeso/ (m2•g-1) | VPore/ (cm3•g-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-N-C | 188 | 46 | 142 | 0.19 |
| P-Co-N-C | 285 | 54 | 231 | 0.32 |
| P-CoNi-N-C | 296 | 58 | 238 | 0.34 |
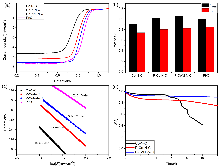
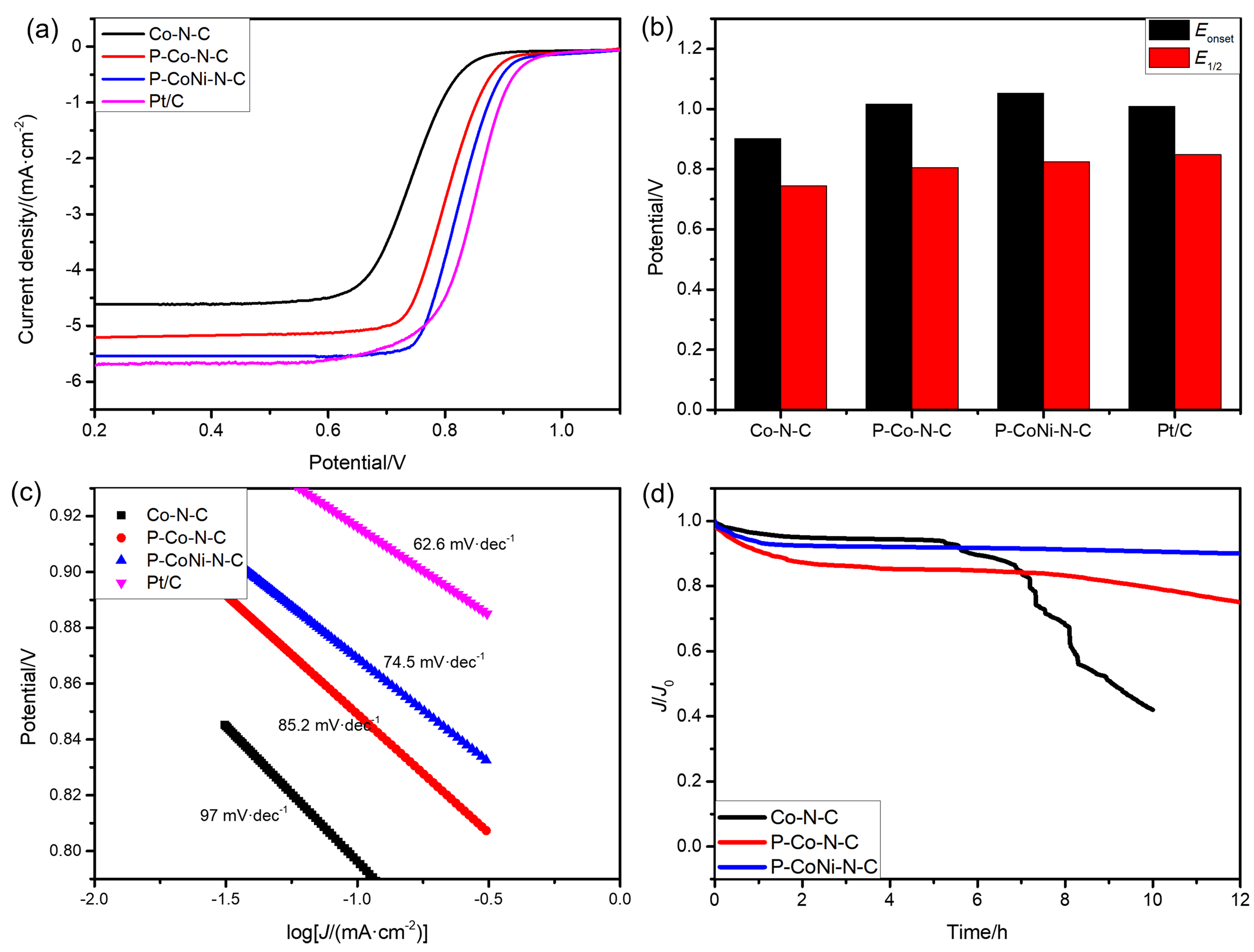
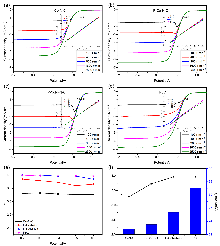
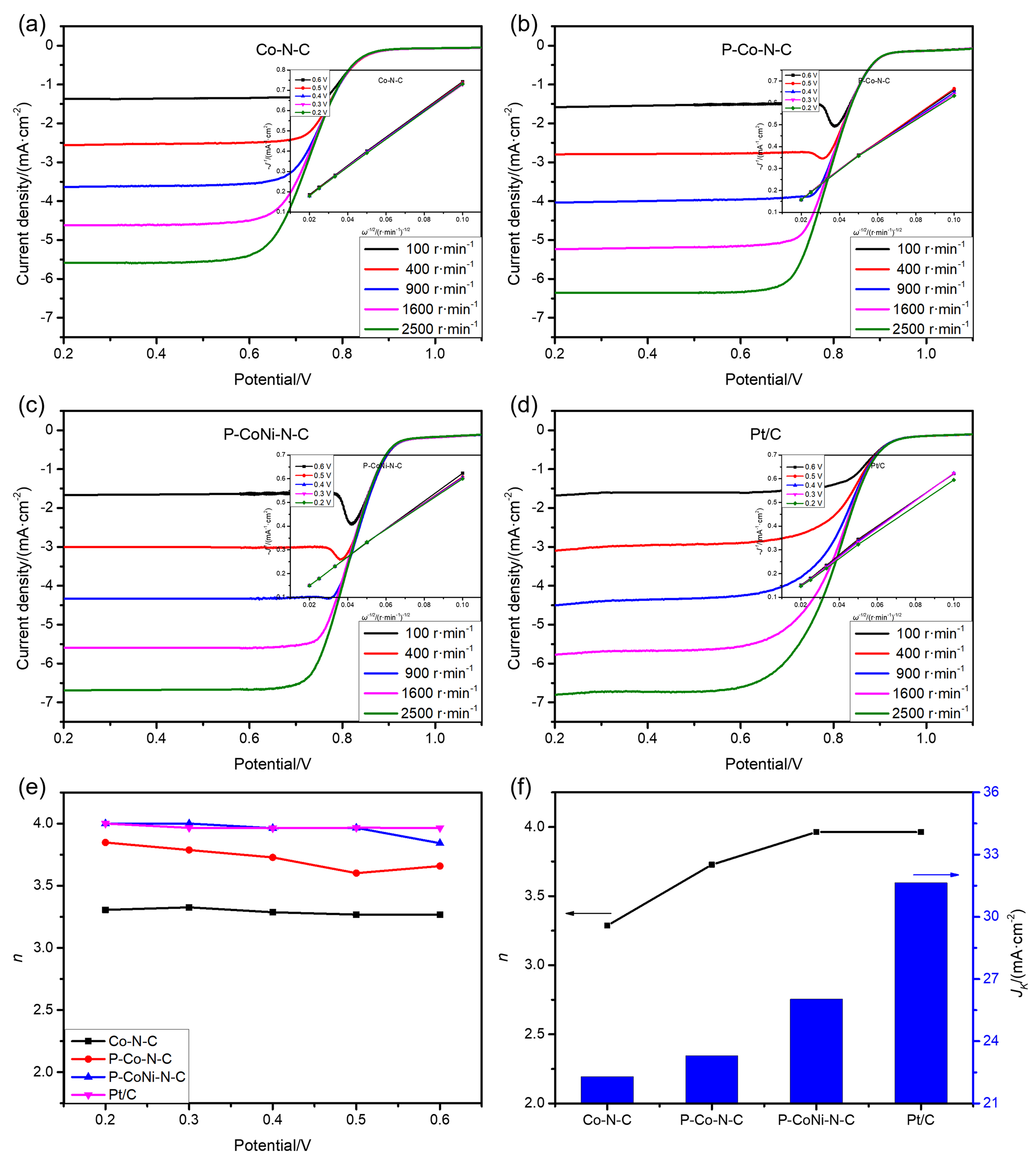
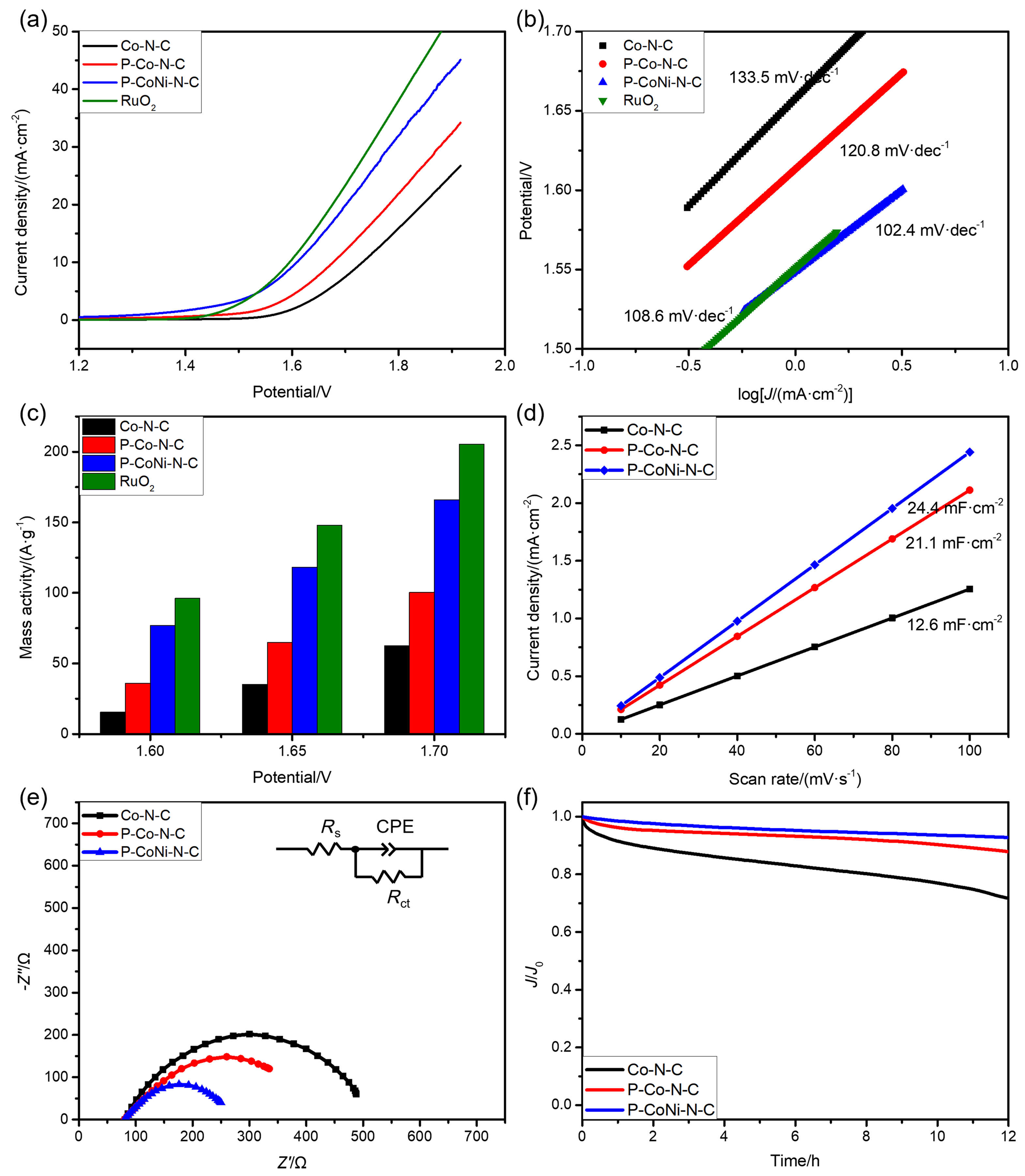
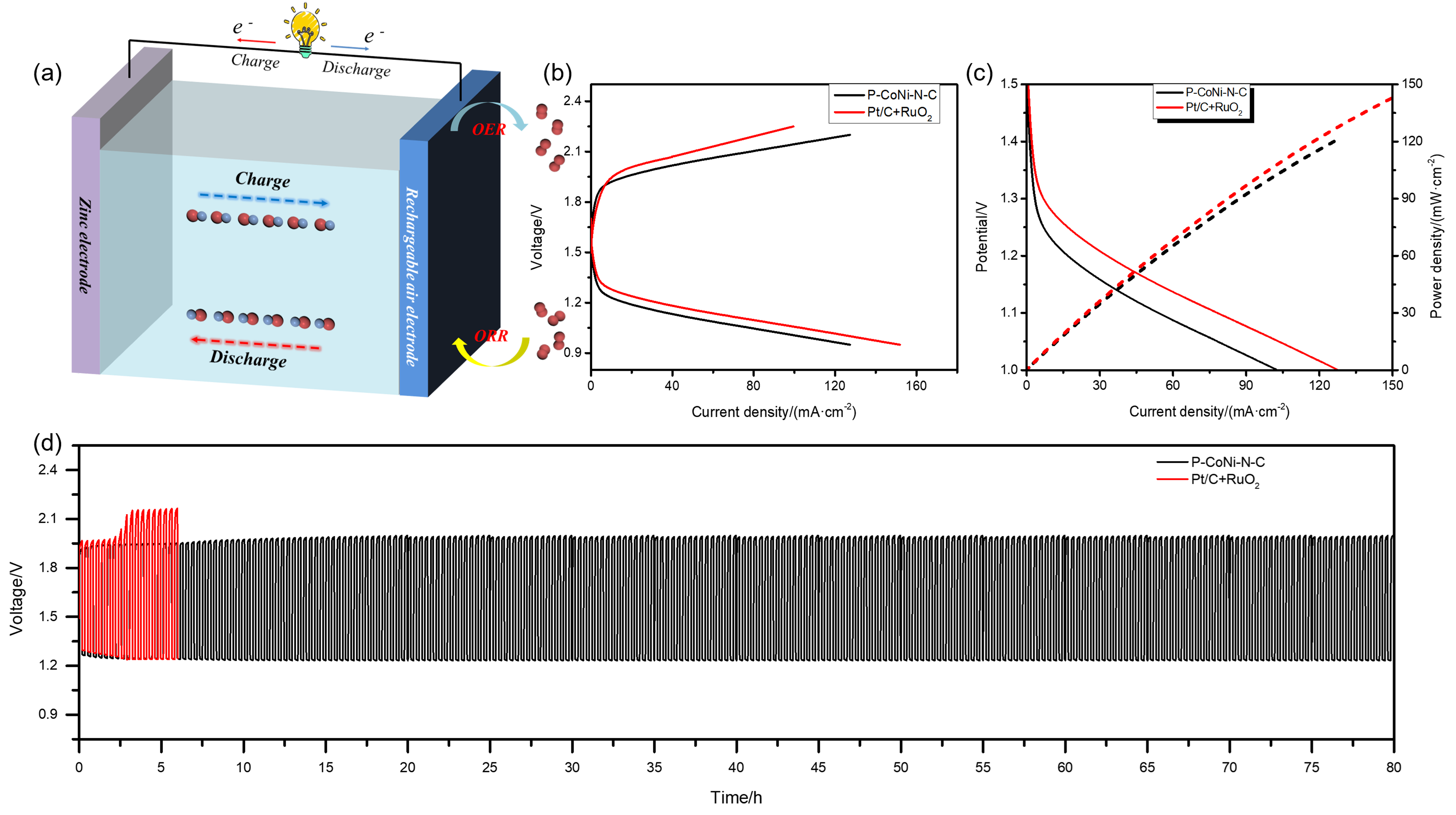
| [1] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c02289 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1002/adsu.v9.3 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v14.7 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.6023/A24050152 |
|
(税子怡, 于思乐, 陆伟, 许留云, 刘庆叶, 赵炜, 刘益伦, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 1039.)
doi: 10.6023/A24050152 |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00553 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v36.26 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v63.16 |
| [8] |
doi: 10.6023/A18080357 |
|
(王艺霖, 王敏杰, 李静, 魏子栋, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 84.)
doi: 10.6023/A18080357 |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.4c06280 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5c05171 |
| [11] |
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c04851 |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/smll.v21.1 |
| [13] |
doi: 10.1021/ja511539a |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v7.17 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2548 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.6023/A22040143 |
|
(闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1084.)
doi: 10.6023/A22040143 |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.4c00459 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1038/nchem.2515 pmid: 27325100 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01942 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.6023/A23080374 |
|
(刘健, 欧金花, 李泽平, 蒋婧怡, 梁荣涛, 张文杰, 刘开建, 韩瑜, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1701.)
doi: 10.6023/A23080374 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1039/C3CC48112C |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.10.049 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1039/C8CC02646G |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v26.45 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.10 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2017.03.027 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1002/aesr.v2.8 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.16 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1002/cctc.v17.16 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.34 |
| [1] | Huiqiong Weng, He Huang, Wenfei Wang, Heguo Li, Xiaopeng Li, Shouxin Zhang, Shuhua Li, Yue Zhao, Yufang Wu, Zhiwei Qiao. AI Big-Data Mining Empowered by MOFid for High-Performance Chemical Warfare Agent Adsorbents [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2026, 84(1): 8-19. |
| [2] | Ziyi Shui, Sile Yu, Wei Lu, Liuyun Xu, Qingye Liu, Wei Zhao, Yilun Liu. Bifunctional Electrocatalysts of Mn-doped Co3O4 for Oxygen Reduction and Oxygen Evolution Reactions in Alkaline Medium [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(10): 1039-1049. |
| [3] | Bo Sun, Wenwen Ju, Tao Wang, Xiaojun Sun, Ting Zhao, Xiaomei Lu, Feng Lu, Quli Fan. Preparation of Highly-dispersed Conjugated Polymer-Metal Organic Framework Nanocubes for Antitumor Application [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| [4] | Junchang Chen, Mingxing Zhang, Shuao Wang. Research Progress of Synthesis Methods for Crystalline Porous Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [5] | Xiaojuan Li, Ziyu Ye, Shuhan Xie, Yongjing Wang, Yonghao Wang, Yuancai Lv, Chunxiang Lin. Study on Performance and Mechanism of Phenol Degradation through Peroxymonosulfate Activation by Nitrogen/Chlorine Co-doped Porous Carbon Materials [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(9): 1238-1249. |
| [6] | Xu Yan, Hemi Qu, Ye Chang, Xuexin Duan. Application of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Gas Pre-concentration, Pre-separation and Detection [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1183-1202. |
| [7] | Linan Cao, Min Wei. Recent Progress of Electric Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks Thin Film [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 1042-1056. |
| [8] | Fang Liu, Tingting Pan, Xiurong Ren, Weiren Bao, Jiancheng Wang, Jiangliang Hu. Research on Preparation and Benzene Adsorption Performance of HCDs@MIL-100(Fe) Adsorbents [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 879-887. |
| [9] | Shihui Wang, Xiaoyu Xue, Min Cheng, Shaochen Chen, Chong Liu, Li Zhou, Kexin Bi, Xu Ji. High-Throughput Computational Screening of Metal-Organic Frameworks for CH4/H2 Separation by Synergizing Machine Learning and Molecular Simulation [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(5): 614-624. |
| [10] | Rong Zhang, Jiangping Liu, Ziyi Zhu, Shumei Chen, Fei Wang, Jian Zhang. Synthesis, Structure and Characterization of Two Ferrocene Functionalized Cadmium Metal Organic Frameworks※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 249-254. |
| [11] | Xusheng Wang, Xu Yang, Chunhui Chen, Hongfang Li, Yuanbiao Huang, Rong Cao. Graphene Quantum Dots Supported on Fe-based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction※ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(1): 22-28. |
| [12] | Si Wang, Jialing Ma, Lifang Chen, Xin Zhang. Role of Synergistic Effect in Oxygen Evolution Reaction over Layered Double Hydroxide [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(2): 216-222. |
| [13] | Yan-Wu Zhao, Xing Li, Fu-Qiang Zhang, Xiang Zhang. Precise Control of the Dimension of Homochiral Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and Their Luminescence Properties [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(11): 1409-1414. |
| [14] | Huan Liu, Li Li, Ping Li, Guangzhi Zhang, Xun Xu, Hao Zhang, Lingfang Qiu, Hui Qi, Shuwang Duo. In-situ Construction of 2D/3D ZnIn2S4/TiO2 with Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(10): 1293-1301. |
| [15] | Sun Lian, Wang Honglei, Yu Jinshan, Zhou Xingui. Recent Progress on Proton-Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(9): 888-900. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||