有机化学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (7): 2079-2088.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202201039 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
曹廷舒, 魏向阳, 罗敏, 汪逸飞, 潘子俊, 徐程*( ), 殷国栋*(
), 殷国栋*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-24
修回日期:2022-04-12
发布日期:2022-08-09
通讯作者:
徐程, 殷国栋
基金资助:
Tingshu Cao, Xiangyang Wei, Min Luo, Yifei Wang, Zijun Pan, Cheng Xu( ), Guodong Yin(
), Guodong Yin( )
)
Received:2022-01-24
Revised:2022-04-12
Published:2022-08-09
Contact:
Cheng Xu, Guodong Yin
Supported by:文章分享
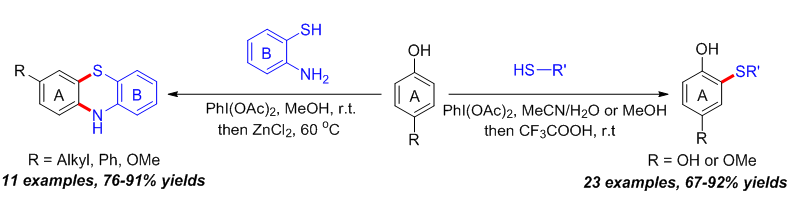
报道了一种醋酸碘苯促进苯酚邻位C(sp2)—H与硫酚S—H之间通过氧化脱氢直接构建C—S键合成2-硫芳(烷)基苯酚衍生物的新方法. 当底物为2-氨基苯硫酚时, 则实现了缩合环化产物10H-吩噻嗪的高效合成. 未见文献报道的新化合物均通过了1H NMR、13C NMR、IR和HRMS的表征, 其中2-((4-溴苯基)硫代)-1,4-苯二酚(3i)的结构还通过了X-ray单晶衍射的证实. 该方法原料易得、条件温和、操作简便, 同时具有良好的原子经济性.
曹廷舒, 魏向阳, 罗敏, 汪逸飞, 潘子俊, 徐程, 殷国栋. 醋酸碘苯促进的脱氢氧化反应合成2-硫芳(烷)基苯酚及10H-吩噻嗪[J]. 有机化学, 2022, 42(7): 2079-2088.
Tingshu Cao, Xiangyang Wei, Min Luo, Yifei Wang, Zijun Pan, Cheng Xu, Guodong Yin. PhI(OAc)2-Promoted Dehydrogenation Oxidation for the Synthesis of 2-(Aryl/alkylthio)phenols and 10H-Phenothiazines[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(7): 2079-2088.
| Entry | Additive (equiv.) | Solvent | Temp./℃ | Yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 70 |
| 2 | HCOOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 64 |
| 3 | HCl (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 68 |
| 4 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 92 |
| 5 | FeCl3 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 86 |
| 6 | ZnCl2 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 67 |
| 7 | ZrCl4 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 75 |
| 8 | AgOTf (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 83 |
| 9 | Cu(OTf)2 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 80 |
| 10 | I2 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 42 |
| 11 | CF3COOH (0.3) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 89 |
| 12 | CF3COOH (0.1) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 76 |
| 13 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶2) | r.t. | 64 |
| 14 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=2∶1) | r.t. | 62 |
| 15 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=5∶1) | r.t. | 51 |
| 16 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | 40 | 82 |
| 17 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | 60 | 65 |
| Entry | Additive (equiv.) | Solvent | Temp./℃ | Yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | None | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 70 |
| 2 | HCOOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 64 |
| 3 | HCl (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 68 |
| 4 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 92 |
| 5 | FeCl3 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 86 |
| 6 | ZnCl2 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 67 |
| 7 | ZrCl4 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 75 |
| 8 | AgOTf (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 83 |
| 9 | Cu(OTf)2 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 80 |
| 10 | I2 (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 42 |
| 11 | CF3COOH (0.3) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 89 |
| 12 | CF3COOH (0.1) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | r.t. | 76 |
| 13 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶2) | r.t. | 64 |
| 14 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=2∶1) | r.t. | 62 |
| 15 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=5∶1) | r.t. | 51 |
| 16 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | 40 | 82 |
| 17 | CF3COOH (0.2) | MeCN/H2O (V∶V=1∶1) | 60 | 65 |
| [1] |
Smith, G.; Mikkelsen, G.; Eskildsen, J.; Bundgaard, C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3981.
doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.05.017 |
| [2] |
Amorati, R.; Valgimigli, L.; Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 9857.
doi: 10.1021/jo401522q |
| [3] |
(a) García, A. M.; Brea, J.; Morales-García, J. A.; Perez, D. I.; González, A.; Alonso-Gil, S.; Gracia-Rubio, I.; Ros-Simó, C.; Conde, S.; Cadavid, M. I.; Loza, M. I.; Perez-Castillo, A.; Valverde, O.; Martinez, A.; Gil, C. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8590.
doi: 10.1021/jm501090m pmid: 10498202 |
|
(b) Dumas, J.; Brittelli, D.; Chen, J.; Dixon, B.; Hatoum-Mokdad, H.; König, G.; Sibley, R.; Witowsky, J.; Wong, S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 2531.
pmid: 10498202 |
|
| [4] |
(a) Guzmán-Percástegui, E.; Hernández, D. J.; Castillo, I. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3111.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC09232A pmid: 19154131 |
|
(b) Fernández-Rodríguez, M. A.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1663.
doi: 10.1021/jo802594d pmid: 19154131 |
|
|
(c) Lan, M. T.; Wu, W. Y.; Huang, S. H.; Luo, K. L.; Tsai, F. Y. RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 1751.
doi: 10.1039/c1ra00406a pmid: 19154131 |
|
|
(d) Xu, X. B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. J.; Wang, Y. W.; Peng, Y. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 550.
doi: 10.1021/ol303366u pmid: 19154131 |
|
|
(e) Liu, Y.; Huang, B.; Cao, X.; Wu, D.; Wan, J. P. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37733.
doi: 10.1039/C4RA07187E pmid: 19154131 |
|
| [5] |
Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Xu, W.; Zeng, M. T.; Dong, Z. B. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5795.
doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201701081 |
| [6] |
Yoshida, S.; Sugimura, Y.; Hazama, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Shimizu, S.; Hosoya, T. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16613.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC07463K |
| [7] |
(a) Xu, R.; Wan, J. P.; Mao, H.; Pan, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15531.
doi: 10.1021/ja107758d |
|
(b) Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Yao, W.; Xu, Z.; Wan, H. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 5211.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.10.028 |
|
| [8] |
(a) Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Yao, W.; Hu, W.; Ge, C.; Shi, X. Chem.-Eur. J. 2016, 22, 5543.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201600597 |
|
(b) Wang, L.; Xie, Y. B.; Huang, N. Y.; Zhang, N. N.; Li, D. J.; Hu, Y. L.; Liu, M. G.; Li, D. S. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2017, 359, 779.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201600861 |
|
| [9] |
(a) Prasad, C. D.; Balkrishna, S. J.; Kumar, A.; Bhakuni, B. S.; Shrimali, K.; Biswas, S.; Kumar, S. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 1434.
doi: 10.1021/jo302480j pmid: 23327334 |
|
(b) Komeyama, K.; Aihara, K.; Kashihara, T.; Takaki, K. Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 1254.
doi: 10.1246/cl.2011.1254 pmid: 23327334 |
|
| [10] |
(a) Liao, Y.; Jiang, P.; Chen, S.; Qi, H.; Deng, G. J. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 3302.
doi: 10.1039/c3gc41671b |
|
(b) Ge, W.; Zhu, X.; Wei, Y. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2013, 355, 3014.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201300493 |
|
|
(c) Lin, Y. M.; Lu, G. P.; Wang, G. X.; Yi, W. B. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 4100.
doi: 10.1002/adsc.201600846 |
|
| [11] |
(a) Kamimura, A.; Nokubi, T.; Watanabe, R.; Ishikawa, M.; Nasu, K.; Uno, H.; Sumimoto, M. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 1068.
doi: 10.1021/jo402522y pmid: 24400983 |
|
(b) Kamimura, A.; Nokubi, T.; Nasu, K.; Takechi, Y.; Ishihara, Y.; Kato, K.; Noguchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Shirai, M.; Sumimoto, M.; Uno, H. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 950.
doi: 10.1246/cl.2012.950 pmid: 24400983 |
|
|
(c) Kokorekin, V. A.; Solomatin, Y. A.; Gening, M. L.; Petrosyan, V. A. Mendeleev Commun. 2017, 27, 586.
doi: 10.1016/j.mencom.2017.11.016 pmid: 24400983 |
|
|
(d) Farzaliev, V. M.; Allakhverdiev, M. A.; Shamkhalova, S. A.; Rzaeva, I. A. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2004, 77, 783.
doi: 10.1023/B:RJAC.0000038812.89494.22 pmid: 24400983 |
|
|
(e) Carreño, M. C.; García Ruano, J. L.; Urbano, A.; Remor, C. Z.; Arroyo, Y. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 453.
doi: 10.1021/jo9913107 pmid: 24400983 |
|
|
(f) Mbiya, W.; Chipinda, I.; Siegel, P. D.; Mhike, M.; Simoyi, R. H. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 112.
doi: 10.1021/tx300417z pmid: 24400983 |
|
| [12] |
Rostami, A.; Khakyzadeh, V.; Zolfigol, M. A.; Rostami, A. Mol. Catal. 2018, 452, 260.
|
| [13] |
Han, D. Y.; Liu, X. P.; Li, R. P.; Xu, D. Z. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 10166.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00898 |
| [14] |
Liang, G.; Wang, J. H.; Lei, T.; Cheng, Y. Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y. J.; Ye, C.; Chen, B.; Tung, C. H.; Wu, L. Z. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 8082.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03090 pmid: 34609892 |
| [15] |
(a) Kamitanaka, T.; Morimoto, K.; Dohi, T.; Kita, Y. Synlett 2019, 30, 1125.
doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1611735 |
|
(b) Chandra, G.; Patel, S. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 12885.
doi: 10.1002/slct.202003802 |
|
|
(c) Taneja, N.; Peddinti, R. K. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 3958.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.07.078 |
|
| [16] |
(a) Kamitanaka, T.; Morimoto, K.; Tsuboshima, K.; Koseki, D.; Takamuro, H.; Dohi, T.; Kita, Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15535.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201608013 |
|
(b) Gao, H.; Xu, Q. L.; Keene, C.; Yousufuddin, M.; Ess, D. H.; Kîrti, L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 566.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201508419 |
|
|
(c) Sharma, S.; Parumala, S. K. R.; Peddinti, R. K. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 9367.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b00684 |
|
| [17] |
Yin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Green, R.; Li, S.; Zheng, S. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 2854.
doi: 10.1039/c4ob00391h |
| [18] |
(a) Shen, R.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, J.; Dong, C.; Han, L. B. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5111.
doi: 10.1039/C8GC02918K pmid: 30810153 |
|
(b) Zhang, M.; Jia, X.; Zhu, H.; Fang, X.; Ji, C.; Zhao, S.; Han, L. B.; Shen, R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2972.
doi: 10.1039/c9ob00129h pmid: 30810153 |
|
| [19] |
(a) Huang, M.; Huang, D.; Zhu, X.; Wan, Y. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4835.
doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201500667 |
|
(b) Lin, Y. M.; Lu, G. P.; Wang, R. K.; Yi, W. B. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6424.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03324 |
|
|
(c) Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Fan, R. Org. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 1055.
doi: 10.1039/C4QO00201F |
|
|
(d) Gautam, N.; Yadav, A.; Khandelwal, N.; Gautam, D. C. J. Chem. Sci. 2014, 126, 197.
doi: 10.1007/s12039-013-0551-2 |
|
|
(e) Greiner, I.; Sypaseuth, F. D.; Grun, A.; Karsai, E.; Keglevich, G. Lett. Org. Chem. 2009, 6, 529.
doi: 10.2174/157017809789869546 |
|
| [20] |
(a) Tan, L.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Yu, M. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 817. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201311024 pmid: 30564820 |
|
( 谭丽泉, 刘卫兵, 黄敏, 余梅, 有机化学, 2014, 34, 817.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201311024 pmid: 30564820 |
|
|
(b) Zhao, G. H.; Li, B. Q.; Wang, S. S.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 9367.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c00971 pmid: 30564820 |
|
|
(c) Jacob, A.; Roy, T.; Kaicharla, T.; Biju, A. T. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 11269.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b02033 pmid: 30564820 |
|
|
(d) Liu, L.; Tan, C.; Fan, R.; Wang, Z.; Du, H.; Xu, K.; Tan, J. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 252.
doi: 10.1039/c8ob02826e pmid: 30564820 |
|
|
(e) Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, F.; Gao, W.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.; Deng, X.; Lu, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, T.; Wang, Z. Chem.-Eur. J. 2020, 26, 17289.
doi: 10.1002/chem.202001414 pmid: 30564820 |
|
|
(f) Yan, Y.; Cui, C.; Li, Z. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 2501. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201805016 pmid: 30564820 |
|
|
( 闫溢哲, 崔畅, 李政, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 2501.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201805016 pmid: 30564820 |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||