

新型咔唑类衍生物的合成、光谱性质及其与Ct-DNA作用的研究
收稿日期: 2013-09-23
修回日期: 2013-11-18
网络出版日期: 2013-12-06
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No. 21102095)、辽宁省自然科学基金(No. 201102209)、辽宁省高校杰出青年学者成长计划(No. LJQ2012090)、辽宁省首批“博士后集聚工程”(No. 2011921013)和辽宁省“大学生创新创业训练计划” (No. 201210163012)资助项目
Syntheses, Spectral Properties of Novel Carbazole Derivatives and Evaluations of Its Ct-DNA Interaction
Received date: 2013-09-23
Revised date: 2013-11-18
Online published: 2013-12-06
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21102095), the Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 201102209), the Program of Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (No. LJQ2012090), the Liaoning Provincial Postdoctoral Converging Project (No. 2011921013), and the Undergraduates Innovative Entrepreneurship Training Project of Liaoning Province (No. 201210163012).
简勇 , 李刚 , 杨鹏 , 邓拓 , 周雪 , 徐海燕 . 新型咔唑类衍生物的合成、光谱性质及其与Ct-DNA作用的研究[J]. 有机化学, 2014 , 34(4) : 809 -816 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201309030
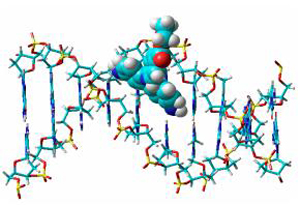
A series of carbazole derivatives were synthesized via reactions of C—N bond formation catalyzed by CuBr·SMe2, nitration, reduction as well as Pd-catalyzed C—N crossing coupling, respectively. Their UV-Vis and fluorescence spectra in different solvents were investigated, as well as the evaluation of the interaction between compound 2 hydrochloride and Ct-DNA. The results showed that all compounds exhibited distinct solvatochromism effects and among them, compound 4 was the most obvious one. Upon binding with DNA, the fluorescence of compound 2 hydrochloride turned on, instead of quenching, and the minor groove of DNA is the most possible position for the molecule to bind with. The calculated binding constant is around 104 L·mol-1, showing a moderate binding affinity.
Key words: carbazole; C—N cross coupling; solvatochromism; spectral properties; Ct-DNA
[1] Dalton, L. R.; Sapochak, L. S. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 2871.
[2] Galabrase, X. J.; Chem, L. T.; Green, J. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 227.
[3] Zhou, G. Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X. M.; Xu, X. G.; Shao, Z. S.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, M. H. Opt. Tech. 2002, 28, 372 (in Chinese).(周广勇, 王东, 王筱梅, 许心光, 邵宗书, 赵显, 方奇, 蒋民华, 光学技术, 2002, 28, 372.)
[4] Kotle, Z.; Segal, J.; Sigalov, M.; Benaasally, A.; Khodorkobsky, A. Synth. Met. 2000, 115.
[5] Han, L. Z.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Y. J.; Ren, A. M.; Liu, Y. L.; Liu, P. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 579 (in Chinese).(韩立志, 王卓, 华英杰, 任爱民, 刘艳玲, 刘朋军, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 579.)
[6] Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Li, Y. W.; Tu, Y. F. J. Chin. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 31, 1439.
[7] Nsib, F.; Ayed, N.; Chevalier, Y. Dye Pigm. 2007, 74, 133.
[8] Mishra, A. K.; Jacob, J.; MÜllen, K. Dye Pigm. 2007, 75, 1.
[9] Yoon, K. R.; Ko, S. O.; Lee, S. M.; Lee, H. S. Dye Pigm. 2007, 75, 567.
[10] Curiel, D.; Cowley, A.; Beer, P. D. Chem. Commun. 2005, 236.
[11] Yu, M.; Lin, H.; Lin, H. Supramol. Chem. 2008, 20, 357.
[12] Omura, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Iwai, Y.; Takeshima, H. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 535.
[13] Chen, W. J.; Zhou, C. X.;Yao, P. F.; Wang, X. X.; Tan, J. H.; Li, D.; Ou, T. M.; Gu, L. Q.; Huang, Z. S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2829.
[14] Huang, F. C.; Chang, C. C.; Lou, P. J.; Kuo, I. C.; Chien, C. W.; Chen, C. T.; Shieh, F. Y.; Chang, T. C.; Lin, J. J. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 955.
[15] Jia, T.; Xiang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, P.; Yu, J. P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 5512.
[16] Yang, P.; Yang, Q.; Qian, X. H. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11895.
[17] Monchaud, D.; Yang, P.; Lacroix, L.; Teulade-Fichou, M.-P.; Mergny, J.-L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4858.
[18] House, H. O.; Chu, C. Y.; Wilkins, J. M.; Umen, M. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 1460.
[19] Kato, Y.; Conn, M. M.; Rebek, Jr. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 3279.
[20] Freeman, H. S.; Butler, J. R. J. Org. Chem. 1978, 26, 4975.
[21] Pasternack, R. F.; Gibbs, E. J.; Villafranca, J. J. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 2406.
[22] Pyle, A. M.; Rehmann, J. P.; Meshoyrer, R.; Kumar, C. V.; Turro, N. J.; Barton, J. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 3051.
[23] Dumat, B.; Bordeau, G.; Faurel-Paul, E.; Mahuteau-Betzer, F.; Saettel, N.; Bombled, M.; Metgé, G.; Charra, F.; Fiorini-Debuisschert, C.; Teulade-Fichou, M. P. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1209.
[24] Bag, S. S.; Ghorai, S.; Pradhan, M. K.; Kundu, R.; Jana, S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 96.
[25] Bag, S. S.; Ghorai, S.; Jana, S.; Mukherjee, C. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 5374.
[26] Lepecq, J. B.; Paoletti, C. J. Mol. Biol. 1967, 27, 87.
[27] Dunlop, H. G.; Tucker, S. H. J. Chem. Soc. 1939, 1945.
[28] Benson, S. C.; Singh, P.; Glazer, A. N. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 5727.
[29] Demas, J. N.; Crosby, G. A. J. Phys. Chem. 1971, 75, 991.Karstens, T.; Kobs, K. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 1871.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |