

大共轭芳香基桥联双杯[4]芳烃的合成与染料配合性能
收稿日期: 2016-02-21
修回日期: 2016-03-23
网络出版日期: 2016-04-20
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No. 21406036)、福建省自然科学基金(No. 2014J01034)、福建省科技重点(No. 2014N0025)和福建省高校科技创新团队支持计划(闽教科[2012]03号)资助项目.
Novel Biscalix[4]arene with Large Conjugated Aromatic Bridges: Synthesis and Complexation Properties for Dyes
Received date: 2016-02-21
Revised date: 2016-03-23
Online published: 2016-04-20
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21406036), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2014J01034), the Science and Technology Key Project of Fujian Province (No. 2014N0025) and the Program for Innovative Research Team in Science and Technology in Fujian Province University (No. [2012]03).
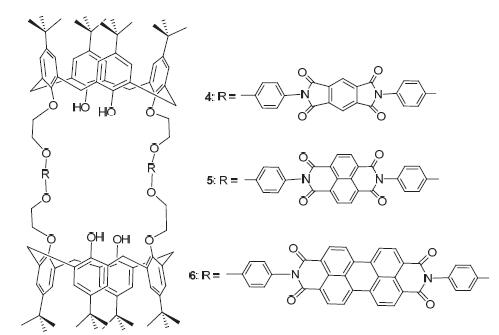
杯[4]-1,3-二氨基衍生物3分别与均苯四甲酸酐、1,4,5,8-萘四甲酸酐、3,4,9,10-苝四甲酸酐反应,以“2+2”的模式合成了三种大共轭芳香基桥联的双杯[4]芳烃4、5和6,产率为60%~70%. 液液两相萃取实验表明化合物4~6对染料分子橙黄I(OI)和维多利亚蓝(VB)有较好萃取能力,化合物6对OI的萃取率达88.3%. 紫外配合光谱、紫外滴定工作曲线和配合质谱均表明,主客体在DMSO溶液中形成1:1的配合物,化合物6对OI的配合常数达2.80×105 L·mol-1. 化合物4~6的染料配合能力强弱次序为化合物4< 化合物5< 化合物6,这表明桥联芳香共轭基团在配合过程中有重要作用.
林梁斌 , 郭红玉 , 杨发福 , 袁锦 . 大共轭芳香基桥联双杯[4]芳烃的合成与染料配合性能[J]. 有机化学, 2016 , 36(8) : 1863 -1868 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201602019
By reacting calix[4]arene-1,3-bis-amino derivative 3 with pyromellitic dianhydride, 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracar- boxylic dianhydride and perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxylic dianhydride, respectively, three novel biscalix[4]arene derivatives 4, 5 and 6 with large conjugated aromatic bridges were prepared in “2+2” mode in yields of 60%~70%. The liquid-liquid extraction experiments of compounds 4, 5 and 6 suggested that they possess excellent extraction abilities for orange I (OI) and victoria blue B (VB). The extraction percentage of compound 6 for OI is as high as 88.3%. The complexation titration UV-vis spectra, Job plot titration and the ESI-MS complexation spectrum implied the formation of 1:1 complexes in DMSO solution. The highest association constant is 2.80×105 L·mol-1 for compound 6 with OI. The complexation abilities of compounds 4, 5 and 6 exhibit the order of compound 4< compound 5< compound 6, indicating that the aromatic conjugate bridges in biscalix[4]arene play important role for the dye complexation.

Key words: calix[4]arene; perylene; synthesis; dye; complexation
[1] Wong, Y.; Yu, J. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3512.
[2] Parker, H. L.; Hunt, A. J.; Budarin, V. L.; Shuttleworth, P. S.; Miller, K. L.; Clark, J. H. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8992.
[3] Guo Y. L.; Hou W. G.; Liang J. L.; Liu J. Q.; Rinaudo M. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 837.
[4] Apostol, L. C.; Pereira, L.; Pereira, R.; Gavrilescu, M.; Alves, M. M. Biodegradation 2012, 23, 725.
[5] Moghaddam, S. S.; Alavi Moghaddama, M. R.; Arami, M. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 651.
[6] Muthuraman, G. Desalination 2011, 277, 7308.
[7] Kamboh, M. A.; Akoz, E.; Memon, S. Yilmaz, M. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1424.
[8] Kim, J. S.; Quang, D. T. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3780.
[9] Yuan, Z.; Liang, F. Curr. Org. Chem. 2014, 18, 2016.
[10] Rebek, J. Chem. Commun. 2000, 637.
[11] Guo, D. S.; Liu, Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5907.
[12] Akceylan, E.; Bahadir, M.; Yilmaz, M. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 960.
[13] Yilmaz, E. O.; Sirit, A.; Yilmaz, M. J. Macromol. Sci. A: Pure Appl. Chem. 2007, 44, 167.
[14] Yilmaz, A.; Yilmaz, E.; Yilmaz, M. Dyes Pigm. 2007, 74, 54.
[15] Kamboh, M. A.; Solangi, I. B.; Sherazi, S. T. H. Desalination 2011, 268, 83.
[16] Kamboh, M. A.; Solangi, I. B.; Memon, S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 651.
[17] Akceylan, E.; Erdemir, S. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem. 2015, 82, 471.
[18] Bandela, A. K.; Hinge, V. K.; Yarramala, D. S.; Rao, C. P. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11555.
[19] Hong, B. Q.; Yang, F. F.; Guo, H. Y.; Liu, Z. Q. J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 424 (in Chinese).
(洪碧琼, 杨发福, 郭红玉, 刘志强, 有机化学, 2014, 34, 424.)
[20] Yan, Z. X.; Guo, H. Y.; Yang, F. F.; Yuan, J. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1088 (in Chinese).
(严祯曦, 郭红玉, 杨发福, 袁锦, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 1088.)
[21] Fang, X. T.; Guo, H. Y.; Yang, F. F.; Bai, X. Y. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2015, 31, 1051.
[22] Guo, H. Y.; Yang, F. F.; Jiao, Z. Y.; Lin, J. R. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 450.
[23] Geng, X. T.; Zhu, S. Y.; Guo, H. Y.; Yang, F. F. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem. 2015, 82, 93.
[24] Tsai, C. C.; Ho, I. T.; Chu, J. H.; Shen, L. C.; Huang, S. L.; Chung, W. S. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 2254.
[25] Yang, F. F.; Hong, B. Q.; Chai, X. F.; Yin, F. J.; Chen, Y. Y. Supramol. Chem. 2009, 21, 691.
[26] Yang, F. F.; Zheng, X. H.; Guo, H. Y.; Liu, Z. H.; Guo, Y. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocyclic Chem. 2008, 62, 371.
[27] Zhao, B. T.; Zhu, W. M. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 34, 1992 (in Chinese).
(赵邦屯, 朱卫民, 有机化学, 2014, 34, 1992.)
[28] Guo, H. Y.; Yang, F. F.; Yuan, J.; Bai, X. Y. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2015, 12, 197.
[29] Jin, C. M.; Lu, G. Y., Liu,Y.; You, X. Z.; Wang, Z. H.; Wu, H. M. Chin. J. Chem. 2002, 20, 1080.
[30] Renny, J. S.; Tomasevich, L. L.; Tallmadge, E. H.; Collum, D. B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |