

含烷氧基取代的三唑类结构的尿酸转运体1抑制剂的高效合成方法
收稿日期: 2017-01-19
修回日期: 2017-02-22
网络出版日期: 2017-03-17
基金资助
天津市科技支撑计划重点项目基金(No.16YFZCSY00910)和山东省自然科学基金(No.16YFZCSY00910)资助项目.
Efficient Synthetic Approaches to Uric Acid Transporter 1 Inhibitors Bearing Alkoxyl Group-Substituted Triazoles
Received date: 2017-01-19
Revised date: 2017-02-22
Online published: 2017-03-17
Supported by
Project supported by the Key Projects of Tianjin Science and Technology Support Plan (No.16YFZCSY00910) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No.ZR2015BM028).
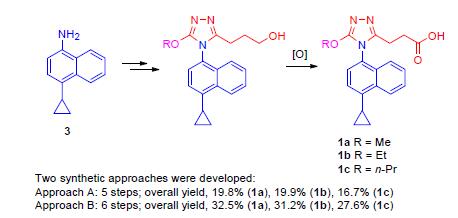
含烷氧基取代的三唑类结构的尿酸转运体1(URAT1)抑制剂3-(4-(4-环丙基萘-1-基)-5-甲氧基-4H-1,2,4-三唑-3-基)丙酸(1a)和3-[4-(4-环丙基萘-1-基)-5-乙氧基-4H-1,2,4-三唑-3-基]丙酸(1b)是一类重要的药物先导化合物,但是其现有合成路线收率非常低(1a和1b的总收率分别为3.3%和3.0%),为了对其进行进一步的构效关系研究,需要收率高的路线.经过详细研究发现了两条高效的合成路线(A和B),分别以CuCl催化的醇钠对溴代三唑进行芳香族亲核取代反应和醇钠直接对甲磺酰基取代的三唑进行芳香族亲核取代反应作为关键反应,并对重要步骤的反应条件进行深入优化.这两条路线具有收率高的优点,除了可以作为先导化合物1a和1b继续进行构效关系研究的合成路线外,还可以为含烷氧基取代的其他杂环化合物的合成提供有价值的借鉴.
田禾 , 吴景卫 , 刘钰强 , 谢亚非 , 王建武 , 赵桂龙 . 含烷氧基取代的三唑类结构的尿酸转运体1抑制剂的高效合成方法[J]. 有机化学, 2017 , 37(7) : 1748 -1756 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201701038
Uric acid transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitors bearing alkoxy group-substituted triazoles 3-(4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-5-methoxy-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)propanoic acid (1a) and 3-(4-(4-cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-yl)-5-ethoxy-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)propanoic acid (1b) are structurally interesting lead compounds in drug design. The current synthetic approach to them suffers from quite low overall yields (3.3% and 3.0% for 1a and 1b, respectively). In order to explore the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of 1a and 1b, synthetic approach with higher overall yield is urgently needed. In the present study, two efficient synthetic approaches to 1a and 1b were developed (approaches A and B), with CuCl-catalyzed nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) reaction of bromotriazole with sodium alkoxides and SNAr reaction of methylsulfonyltriazole with sodium alkoxides as key steps, and the conditions for important steps were fully optimized. The two synthetic approaches are characterized by dramatically higher yields, and not only valuable to the further SAR exploration of 1a and 1b but also very helpful to the synthesis of heterocycles with alkoxyl groups.

Key words: URAT1 inhibitor; gout; hyperuricemia; synthetic route; SNAr; CuCl catalysis
[1] Richette, P.; Bardin T. Lancet 2010, 375, 318.
[2] Pillinger, M. H.; Rosenthal, P.; Abeles, A. M. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2007, 65, 215.
[3] Punzi, L.; Scanu, A.; Ramonda, R.; Oliviero, F. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 66.
[4] Choi, H. K.; Mount, D. B.; Reginato, A. M. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 143, 499.
[5] Miao, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Sun, R.; Hu, J.; Song, W.; Yan, S.; Wang, C. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1859.
[6] Dubchak, N.; Falasca, G. F. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2010, 3, 145.
[7] Enomoto, A.; Kimura, H.; Chairoungdua, A.; Shigeta, Y.; Jutabha, P.; Cha, S. H.; Hosoyamada, M.; Takeda, M.; Sekine, T.; Igarashi, T.; Matsuo, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Oda, T.; Ichida, K.; Hosoya, T.; Shimokata, K.; Niwa, T.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H. Nature 2002, 417, 447.
[8] Adams, J. U. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 309.
[9] Hoy, S. M. Drugs 2016, 76, 509.
[10] Miner, J. N.; Tan, P. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 71, 446.
[11] Tian, H.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Shang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, G. Molecules 2016, 21, 1543.
[12] Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Mano, E.; Song, Z.; Tschaen, D. M.; Grabowski, E, J. J.; Reider, P. J. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 2564.
[13] Hirata, K.; Kotoku, M.; Seki, N.; Maeba, T.; Maeda, K.; Hirashima, S.; Sakai, T.; Obika, S.; Hori, A.; Hase, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katsuda, Y.; Hata, T.; Miyagawa, N.; Arita, K.; Nomura, Y.; Asahina, K.; Aratsu, Y.; Kamada, M.; Adachi, T.; Noguchi, M.; Doi, S.; Crowe, P.; Bradley, E.; Steensma, R.; Tao, H.; Fenn, M.; Babine, R.; Li, X.; Thacher, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Shiozaki, M. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 23.
[14] Ragan, J. A.; Makowski, T. W.; Castaldi, M. J.; Hill, P. D. Synthesis 1998, 1599.
[15] Bonanomi, G.; Braggio, S.; Capelli, A. M.; Checchia, A.; Di Fabio, R.; Marchioro, C.; Tarsi, L.; Tedesco, G.; Terreni, S.; Worby, A.; Heibreder, C.; Micheli, F. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 705.
[16] Xie, M.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Guo, H.; Qu, G. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 2589(in Chinese). (谢明胜, 唐浩鑫, 张一铭, 郭真, 郭海明, 渠桂荣, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 2589.)
[17] Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hou, B. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 1184(in Chinese). (傅颖, 赵兴玲, 侯博, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 1184.)
[18] Cai, W.; Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, G. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2017, 33, 49.
[19] Reddy, T. R.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Fischer, P. M.; Dekker, L. V. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 5378.
[20] Colanceska-Ragenovic, K.; Dimova, V.; Kakurinov, V.; Gabor, D. M. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2003, 40, 905.
[21] Kane, J. M.; Staeger, M. A.; Dalton, C. R.; Miller, F. P.; Dudley, M. W.; Ogden, A. M.; Kehne, J. H.; Ketteler, H. J.; McCloskey, T. C.; Senyah, Y.; Chmielewski, P. A.; Miller, J. A. J Med Chem. 1994, 37, 125.
[22] Ström, P.; Malmquist, J. J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm. 2008, 51, 419.
[23] Liu, M.; Shi, D. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2014, 51, E335.
[24] Huisgen, R.; Möbius, L.; Szeimies, G. Chem. Ber. 1965, 98, 1138.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |