

联苯缩氨基胍衍生物的合成及其抗菌活性评价
收稿日期: 2018-11-06
修回日期: 2018-12-18
网络出版日期: 2019-01-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(No.81560561)和井冈山大学博士启动基金(No.JZB1317)资助项目.
Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation of Aminoguanidine Derivatives Containing a Biphenyl Moiety
Received date: 2018-11-06
Revised date: 2018-12-18
Online published: 2019-01-10
Supported by
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81560561), and the Doctoral Foundation of Jinggangshan University (No. JZB1317).
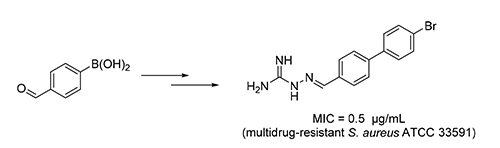
基于查尔酮缩氨基胍衍生物的结构修饰,设计合成了一系列含联苯片段的缩氨基胍衍生物.目标化合物的结构通过1H NMR、13C NMR和HRMS进行了确证,并评价了其抗菌活性.结果显示目标化合物对所选菌种显示出了较好的抑制活性,最低抑菌浓度值(MIC)大都在0.5~8 μg/mL.其中,2-((4'-溴[1,1'-二苯]-4-基)亚甲基)肼-1-甲脒(3j)的抗菌活性最好,对所选菌株包括耐药菌均显示出强的抑菌活性,其中对金葡菌CMCC(B)26003、粪肠球菌CMCC 29212和多药耐药金葡菌ATCC 33591尤为敏感,最低抑菌浓度值达到0.5 μg/mL.此外,化合物3j表现低的细胞毒性,对正常人体细胞HEK 293T的IC50值为60.90 μmol/L.该结果表明化合物3j具有较好的选择性,在抗菌药物研究领域具有研究价值.
余海红 , 周胜超 , 郭婷婷 , 梁焯 , 陈华斌 , 代卫凯 , 宋明霞 . 联苯缩氨基胍衍生物的合成及其抗菌活性评价[J]. 有机化学, 2019 , 39(5) : 1497 -1502 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc201811012
A series of aminoguanidine derivatives containing a biphenyl moiety were designed, synthesized, and characterized by spectra methods using chalcone-aminoguanidine derivative as the lead compound. The antibacterial activity of the target compounds was evaluated. The results indicated that most of the target compounds showed potent inhibitory activity with the minimum inhibitory concentration values (MICs) in range of 0.5~8 μg/mL. Among of which, 2-((4'-bromo-[1,1'- biphenyl]-4-yl)methylene)hydrazine-1-carboximidamide (3j) exhibited broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, effective to all the chosen strains including two multidrug-resistant gram-positive strains, showed the most potent inhibitory against S. aureus CMCC(B) 26003, E. faecalis CMCC 29212 and multidrug-resistant S. aureus ATCC 33591 with a MIC value of 0.5 μg/mL. Moreover, low cytotoxicity of compound 3j (HEK 293T, IC50=60.90 µmol/L) was found. These results suggested that the Compound 3j, with high safety, was potential and valuable in the research of novel antibacterial drugs.

Key words: aminoguanidine; biphenyl; antimicrobial activity
[1] Bi, Y.; Liu, X. X.; Zhang, H. Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z. Y.; Lu, J.; Lewis, P. J.; Wang, C. Z.; Xu, J. Y.; Meng, Q. G.; Ma, C.; Yuan, C. S. Molecules 2017, 22, 590.
[2] Carrel, M.; Perencevich, E. N.; David, M. Z. Emerging Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1973.
[3] Hvistendahl, M. Science 2012, 336, 795.
[4] Yezli, S.; Li, H. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 389.
[5] Azeredo da Silveira, S.; Perez, A. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 531.
[6] Kang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J. Chin. J. Antibiot. 2017, 42, 169(in Chinese). (康悦, 赵明, 张菁, 中国抗生素杂志, 2017, 42, 169.)
[7] Ward, R. S. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1999, 16, 75.
[8] Whiting, D. A. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 583.
[9] Chang, J. B.; Reiner, J.; Xie, J. X. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 4581.
[10] Chen, D. F.; Zhang S. X.; Lan, X. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1997, 5, 715.
[11] Raffa, D.; Plescia, F.; Maggio, B.; Raimondi, M. V.; D'Anneo, A.; Lauricella, M.; Daidone, G. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 262.
[12] Chen, Y.; Du, Y. J.; Suo, F. X. J. Henan Normal Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2001, 29, 43(in Chinese). (陈勇, 杜燕军, 索福喜, 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 29, 43.)
[13] Wei, Z. Y.; Chi, K. Q.; Yu, Z. K.; Liu, H. Y.; Sun, L. P.; Zheng, C. J.; Piao, H. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5920.
[14] Sidoryk, K.; Switalska, M.; Rózga, P.; Wietrzyk, J.; Bujak, I.; Zerek, B.; Kaczmarek, L.; Cybulski, M. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 3354.
[15] Gao, Z. M.; Wang, T. T.; Li, S. Z.; Wan, H. Q.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y. B.; Deng, X. Q.; Song, M. X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 2484(in Chinese). (高智敏, 王田田, 李深圳, 万慧琪, 王刚, 吴银彬, 邓先清, 宋明霞, 有机化学, 2016, 36, 2484.)
[16] Li, Y. R.; Li, C.; Liu, J. C.; Guo, M.; Zhang, T. Y.; Sun, L. P.; Zheng, C. J.; Piao, H. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5052.
[17] Xu, H.; Wang, Y. Y. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7274
[18] Mourer, M.; Dibama, H. M.; Fontanay, S.; Grare, M.; Duval, R. E.; Finance, C.; Vains, J. B. R. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5496.
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |