

2-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)硫基]-1H-苯并咪唑类化合物的设计、合成和抗癌活性研究
收稿日期: 2022-01-02
修回日期: 2022-02-26
网络出版日期: 2022-04-11
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(21342006); 教育部创新团队(IRT_14R36)
Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of 2-((Pyridin- 2-ylmethyl)thio)-1H-benzimidazole Derivatives
Received date: 2022-01-02
Revised date: 2022-02-26
Online published: 2022-04-11
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(21342006); Program for Innovative Research Team of the Ministry of Education(IRT_14R36)
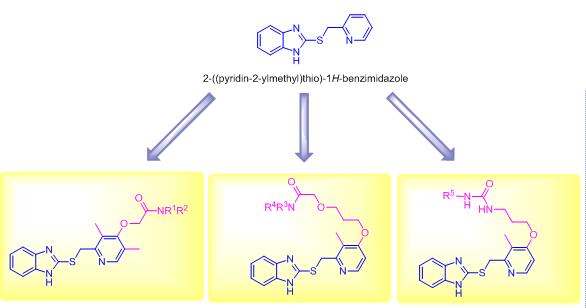
苯并咪唑类化合物具有多种生物活性, 是一类重要的含氮杂环化合物. 合成了一系列具有全新结构的2-[(吡啶- 2-基甲基)硫代]-1H-苯并咪唑类化合物, 并采用噻唑蓝(MTT)比色法考察了化合物对人肺癌细胞株A549、人结直肠癌细胞株HCT116和人前列腺癌细胞株PC3的抑制活性. 结果表明, 部分目标化合物对上述癌细胞株具有较强的抑制活性. 其中, 2-{3-{{2-{[(1H-苯并咪唑-2-基)硫基]甲基}-3-甲基吡啶基-4-基}氧基}丙氧基}-1-(4-二苯甲基哌嗪-1-基)乙酮(7c)对上述三种癌细胞株的抑制活性最强, 其对人肺癌细胞株A549、人结直肠癌细胞株HCT116和人前列腺癌细胞株PC3的半数抑制浓度值分别是1.14、1.67和2.34 μmol/L. 初步构效关系和细胞机制研究显示, 化合物7c可诱导细胞发生G0/G1期阻滞. AnnexinV-PI双染的结果表明, 化合物7c可浓度依赖的诱导A549细胞凋亡. 上述结果提示, 具有2-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)硫基]-1H-苯并咪唑的化学结构骨架的化合物有望成为潜在的癌症化疗药物.
赵静 , 金辄 , 王润 , 张新庚 , 韩英妹 , 胡春 , 刘晓平 , 张传明 , 金丽萍 . 2-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)硫基]-1H-苯并咪唑类化合物的设计、合成和抗癌活性研究[J]. 有机化学, 2022 , 42(7) : 2172 -2183 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202201002
Benzimidazole is an important class of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds, which has diverse biological activities. A series of novel 2-((pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio)-1H-benzimidazole derivatives were reported and their antiproliferative activities against human lung cancer A549, human colorectal cancer HCT116 and human prostate cancer PC3 cell lines were evaluated with the MTT assay. Some target compounds demonstrated obvious antiproliferative activities against A549, HCT116 and PC3 cancer cell lines. Among them, 2-(3-((2-(((1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)thio)methyl)-3-methylpyridin-4-yl)oxy)propoxy)-1-(4-benzhydrylpiperazin-1-yl)ethanone (7c) showed the most potent antiproliferative activity with IC50 values of 1.14 μmol/L for A549, 1.67 μmol/L for HCT116 and 2.34 μmol/L for PC3, respectively. Preliminary structure-activity relationships were summaried and preliminary cellular mechanism studies elucidated that compound 7c could arrest the cell cycle at G0/G1 phase. The flow cytometry analysis showed that compound 7c could dose-dependently induce A549 cells apoptosis. It is suggested that the 2-((pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio)-1H-benzimidazole scaffold might be regarded as new scaffold structure for the development of potent cancer chemotherapeutic agents in the drug discovery process.

Key words: benzimidazole derivatives; synthesis; anticancer activity; apoptosis
| [1] | Shewach, D. S.; Kuchta, R. D. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2859. |
| [2] | Kanwal, A.; Saddique, F. A.; Aslam, S.; Ahmad, M.; Zahoor, A. F.; Mohsin, N. Pharm. Chem. J. 2018, 51, 1068. |
| [3] | Anand, K.; Wakode, S. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 350. |
| [4] | Hranjec, M.; Kralj, M.; Piantanida, I.; Sedić, M.; Šuman, L.; Pavelić, K.; Karminski-Zamola, G. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5696. |
| [5] | Piskin, A. K.; Ates-Alagoz, Z.; Atac, F. B.; Musdal, Y.; Buyukbingol, E. Turk. J. Biochem. 2009, 34, 39. |
| [6] | Shaaban, M. A.E.; Kamal, A. M.; Teba, H. E.S. J. Chem. Res. 2016, 40, 228. |
| [7] | Abe, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Kito, K.; Ueda, N. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21525. |
| [8] | Gaudet, S.; Branton, D.; Lue, R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2000, 97, 5167. |
| [9] | Kim, D.; Li, Y.; Reddy, K.; Lee, M.; Kim, M.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Bode, A.; Dong, Z. Cancer. Res. 2012, 72, 3060. |
| [10] | Matsuo, Y.; Park, J.; Miyamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Hisada, S.; Alachkar, H.; Nakamura, Y. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 251. |
| [11] | Savarino, E.; Marabotto, E.; Zentilin, P.; Furnari, M.; Bodini, G.; Pellegatta, G.; Lorenzon, G.; Coletta, M. D.; Ghisa, M.; Coppo, C.; Marinelli, C.; Savarino, V. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 785. |
| [12] | Gillies, R. J.; Pilot, C.; Marunaka, Y.; Fais, S. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 273. |
| [13] | Ikemura, K.; Hiramatsu, S.; Okuda, M. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 911. |
| [14] | Lugini, L.; Federici, C.; Borghi, M.; Azzarito, T.; Marino, M. L.; Cesolini, A.; Spugnini, E. P.; Fais, S. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 538. |
| [15] | Zeng, X.; Liu, L.; Zheng, M.; Sun, H.; Xiao, J.; Lu, T.; Huang, G.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.; Li, H.; Duan, Q. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22460. |
| [16] | Zheng, M.; Luan, S.; Gao, S.; Cheng, L.; Hao, B.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Chen, L.; Li, H. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39143. |
| [17] | Ng, H.-L.; Chen, S.; Chew, E.-H.; Chui, W.-K. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 115, 63. |
| [18] | Wu, P.; Nielsen, T. E.; Clausen, M. H. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 422. |
| [19] | Viegas-Junior, C.; Danuello, A.; Bolzani, V.; Barreiro, E.; Fraga, C. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1829. |
| [20] | Sobhy, M. K.; Mowafy, S.; Lasheen, D. S.; Farag, N. A.; Abouzid, K. A. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 102988. |
| [21] | Sanmartín, C.; Plano, D.; Domínguez, E.; Font, M.; Calvo, A.; Prior, C.; Encío, I.; Palop, J. A. Molecules 2009, 14, 3313. |
| [22] | Zhivotova, T. S.; Gazaliev, A. M.; Fazylov, S. D.; Aitpaeva, Z. K.; Turdybekov, D. M. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 42, 448. |
| [23] | Seto, M.; Miyamoto, N.; Aikawa, K.; Aramaki, Y.; Kanzaki, N.; Iizawa, Y.; Baba, M.; Shiraishi, M. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 363. |
| [24] | Liu, D.; Tian, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wu, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.; Yang, C. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2960. |
| [25] | Diaz-Moralli, S.; Tarrado-Castellarnau, M.; Miranda, A.; Cascante, M. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 255. |
| [26] | Liu, X. P.; Xu, H. L.; Sun, R; Li, X.; Hu, B. H.; Hu, C. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2015, 34, 126. |
| [27] | Reddy, G. M.; Bhaskar, B. V.; Reddy, P. P.; Sudhakar, P.; Babu, J. M.; Vyas, K.; Reddy, P. R.; Mukkanti, K. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 4, 1262. |
| [28] | Mosmann, T. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55. |
| [29] | Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. B.; Yang, S.; Zhang, A.; Yin, L.; Swarts, S.; Vidyasagar, S.; Zhang, L.; Okunieff, P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4263. |
| [30] | Xie, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Jiao, D.; Ma, Q.; Jin, Z.; Meng, Q.; Hu, C. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1000. |
| [31] | Zhang, L.; Deng, X.-S.; Zhang, C.; Meng, G.-P.; Wu, J.-F.; Li, X.-S.; Zhao, Q.-C.; Hu, C. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2180. |
| [32] | Zhang, C.; Tan, X.; Feng, J.; Ding, N.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Meng, Q.; Liu, X.; Hu, C. Molecules 2019, 24, 2108. |
| [33] | Hou, S.; Liang, S.; Zhang, C.; Han, Y.; Liang, J.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Molecules 2021, 26, 3496. |
| [34] | Yan, Q.; Li, R.; Xin, A.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Di, D. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 6542. |
| [35] | Xu, Y.; Jing, D.; Chen, R.; Rashid, H. U.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Xie, P. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4136. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |