

氯化膦与羟基化合物参与的P(III)→P(V)重排反应研究进展
收稿日期: 2024-06-30
修回日期: 2024-08-27
网络出版日期: 2024-09-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金(22471208); 国家自然科学基金(22471218)
Progress in the P(III)→P(V) Rearrangement Reaction of Phosphine Chlorides and Hydroxyl Containing Compounds
Received date: 2024-06-30
Revised date: 2024-08-27
Online published: 2024-09-10
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22471208); National Natural Science Foundation of China(22471218)
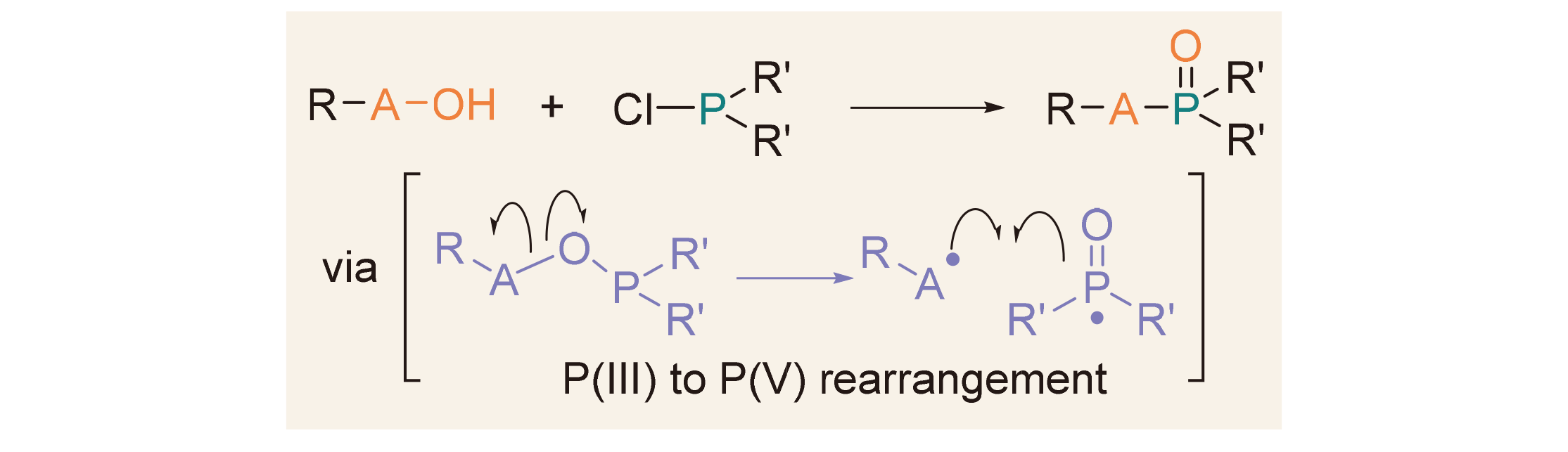
五价磷P(V)有机物广泛应用于合成、材料、生物、医药和农业等领域, 其合成方法研究一直吸引着有机化学家的兴趣. 从三价磷P(III)到五价磷P(V)的重排反应[P(III)→P(V)]是合成五价磷有机物的重要策略. 经典的Michaelis- Arbuzov反应通过亲核性亚磷酸酯[P(OR)3]与卤代烃发生P(III)→P(V)重排反应, 为膦酸酯的合成提供了重要方法. 与此相反, 亲电性氯化膦(ClPR1R2)与羟基化合物(RA—OH)作用可原位生成RA—O—PR1R2中间体, 继而发生A—O键断裂和A—P键形成, 从而实现P(III)→P(V)重排, 也为五价磷有机物的合成提供了有效方法. 这两类P(III)→P(V)重排反应都是在磷的强亲氧性驱动下实现的, 具有原子经济性高、底物简单易得等优点. 主要综述了氯化膦与不同类型羟基化合物(如醇、羧酸、肟和羟胺等)的P(III)→P(V)重排反应, 分别用于氧膦、膦酸酯、磷酰胺等五价磷化合物的合成.
杨露露 , 易翠 , 吴佳乐 , 张宇轩 , 白美琪 , 李洋 , 徐四龙 . 氯化膦与羟基化合物参与的P(III)→P(V)重排反应研究进展[J]. 有机化学, 2024 , 44(12) : 3639 -3646 . DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202406052
Pentavalent organophosphorus compounds are widely used in synthesis, materials, biology, medicine, agriculture, etc, and their synthetic methods have attracted a long-term interest from organic chemists. The P(III)→P(V) rearrangement from trivalent organophosphorus compounds is an important strategy for the synthesis of pentavalent organophosphorus compounds. The classical Michaelis-Arbuzov reaction, which involves a P(III)→P(V) rearrangement reaction between nucleophilic phosphite (P(OR)3) and alkyl halides, provides an important method for the synthesis of phosphonates. In contrast, the reaction between electrophilic phosphine chlorides (ClPR1R2) and hydroxyl containing compounds (RA—OH) generaes a RA—O—PR1R2 intermediate in situ, followed by A—O bond cleavage and A—P bond formation thus to realize P(III)→P(V) rearrangement, also provides an effective synthetic method for pentavalent organophosphorus compounds. Two types of the P(III)→P(V) rearrangement reactions are both driven by the oxophilicity of phosphorus, bearing the advantages of high atom economy and readily available substrates. The P(III)→P(V) rearrangement reactions of phosphine chlorides with different types of hydroxyl containing compounds, such as alcohols, carboxylic acids, oximes, hydroxylamines, etc, for the synthesis of phosphine oxides, phosphonates, and phosphoric amides are mainly reviewed, respectively.

| [1] | Perez H. F.; Etayo P.; Panossian A. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2119. |
| [2] | van Leeuwen P. W. N. M.; Kamer P. C. J.; Claver C.; Pàmies O.; Diéguez M. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2077. |
| [3] | Queffélec C.; Petit M.; Janvier P.; Knight D. A.; Bujoli B. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3777. |
| [4] | Genet J.-P.; Ayad T.; Ratovelomanana-Vidal V. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2824. |
| [5] | Pradere U.; Garnier-Amblard E. C.; Coats S. J.; Amblard F.; Schinazi R. F. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9154. |
| [6] | Dutartre M.; Bayardon J.; Jugé S. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5771. |
| [7] | Eymery F.; Iorga B.; Savignac P. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13109. |
| [8] | Van der Jeught S.; Stevens C. V. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2672. |
| [9] | Shao C.; Xu W.; Li L.; Zhang X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 335 (in Chinese). |
| [9] | (邵长伟, 徐炜刚, 李亮, 张兴华, 有机化学, 2017, 37, 335.) |
| [10] | Arbusow B. A. Pure Appl. Chem. 1964, 9, 307. |
| [11] | Bhattacharya A. K.; Thyagarajan G. Chem. Rev. 1981, 81, 415. |
| [12] | Xiong B.; Yuan M.; Shi C.; Zhu L.; Cao F.; Xu W.; Ren Y.; Liu Y.; Tang K. W. Top. Curr. Chem. 2024, 382, 10. |
| [13] | Chai L.; Wang J.; Yang J.; Yin J.; Zhang Z.; Cheng Y.; Zhu L.; Xue X. S.; Li C. CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 1312. |
| [14] | Lei Z.; Zhang W.; Wu J. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 16105. |
| [15] | Yin J.; Lin X.; Chai L.; Wang C.; Zhu L.; Li C. Chem 2023, 9, 1945. |
| [16] | Zhang W.; Luo H. T.; Yang J. D. Chem 2023, 9, 2735. |
| [17] | Xu W.; Fan C.; Hu X.; Xu T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202401575. |
| [18] | Rossi-Ashton J. A.; Clarke A. K.; Unsworth W. P.; Taylor R. J. K. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7250. |
| [19] | Kepp K. P. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 9461. |
| [20] | Guo H.; Fan Y. C.; Sun Z.; Wu Y.; Kwon O. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10049. |
| [21] | Wittig G.; Sch?llkopf U. Chem. Ber. 2006, 87, 1318. |
| [22] | Wang X.; Yang F.; Xue Z.; Wang X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 35, 29 (in Chinese). |
| [22] | (王小龙, 杨芳, 薛自燕, 王晓强, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 29.) |
| [23] | Appel R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003, 14, 801. |
| [24] | Liu Y.; Liu X.; Feng X. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 12290. |
| [25] | Boisselle A. P.; Meinhardt N. A. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 1828. |
| [26] | Darcel C.; Bruneau C.; Dixneuf P. H. Synthesis 1996, 1996, 711. |
| [27] | Ismailov I. E.; Ivanov I. K.; Christov V. C. Molecules 2014, 19, 6309. |
| [28] | Ismailov I. E.; Ivanov I. K.; Christov V. C. Molecules 2014, 19, 11056. |
| [29] | Christov V. C.; Ismailov I. E.; Ivanov I. K. Molecules 2015, 20, 7263. |
| [30] | Hasanov H. H.; Ivanov I. K.; Christov V. C. Heteroat. Chem 2017, 28, e21357. |
| [31] | Baumann M.; Baxendale I. R. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 10806. |
| [32] | Demay S.; Harms K.; Knochel P. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4981. |
| [33] | Liron F.; Knochel P. Chem. Commun. 2004, 304. |
| [34] | Masarwa A.; Stanger A.; Marek I. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8039. |
| [35] | Busacca C. A.; Qu B.; Farber E.; Haddad N.; Gret N.; Saha A. K.; Eriksson M. C.; Wu J.-P.; Fandrick K. R.; Han S. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1136. |
| [36] | Shevchuk M.; R?schenthaler G.-V. Synthesis 2021, 54, 171. |
| [37] | Ma Y.; Chen F.; Bao J.; Wei H.; Shi M.; Wang F. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2465. |
| [38] | Xie D.-T.; Chen H.-L.; Wei D.; Wei B.-Y.; Li Z.-H.; Zhang J.-W.; Yu W.; Han B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203398. |
| [39] | Xie X.-X.; Yang Y.-C.; Dou B.-H.; Li Z.-F.; Li G. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 403, 213100. |
| [40] | Li J.; Huang C.-Y.; Li C.-J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112770. |
| [41] | Sartori P.; Heinz Hochleitner R.; H?gele G. Naturforsch. Teil. B 1976, 31, 76. |
| [42] | Miller J. A.; Stewart D. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 1065. |
| [43] | Kondoh A.; Ojima R.; Terada M. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 7894. |
| [44] | Kaur R.; Singh R. P. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 10325. |
| [45] | Kuroboshi M.; Ishihara T.; Ando T. J. Fluorine Chem. 1988, 39, 293. |
| [46] | Sartori P.; Mosler G. Phosphorus Sulfur Relat. Elem. 1980, 8, 115. |
| [47] | Bew S. P.; Brimage R. A.; Hughes D. L.; Legentil L.; Sharma S. V.; Wilson M. A. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 2655. |
| [48] | Brown C.; Hudson R. F.; Maron A.; Record K. A. F. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1976, 663. |
| [49] | Yang L.; Wu J.; Li Y.; Tang Y.; Li J.; Xu S. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 3208. |
| [50] | Xia P. J.; Ye Z. P.; Hu Y. Z.; Song D.; Xiang H. Y.; Chen X. Q.; Yang H. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 2658. |
| [51] | Zhang J. J.; Duan X. H.; Wu Y.; Yang J. C.; Guo L. N. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 161. |
| [52] | Chen J.; He B.-Q.; Wang P.-Z.; Yu X.-Y.; Zhao Q.-Q.; Chen J.-R.; Xiao W.-J. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 4359. |
| [53] | Davies J.; Morcillo S. P.; Douglas J. J.; Leonori D. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 12154. |
| [54] | Gao F.; Auclair K. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2006, 181, 159. |
| [55] | Banks M. R.; Hudson R. F. J. Chem. Soc., 1989, 463. |
| [56] | Cheng F.; Li D.; Li J.; Tang Y.; Wu Y.; Xu S. Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 2555. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |