Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 250-265.DOI: 10.6023/cjoc202504032 Previous Articles Next Articles
ARTICLES
粟晓微†, 徐浩†, 周华锋, 王夏洁, 李培源, 夏星, 陈文雅*( ), 霍丽妮*(
), 霍丽妮*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-28
修回日期:2025-07-01
发布日期:2025-08-26
作者简介:† 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Xiaowei Su, Hao Xu, Huafeng Zhou, Xiajie Wang, Peiyuan Li, Xing Xia, Wenya Chen*( ), Lini Huo*(
), Lini Huo*( )
)
Received:2025-04-28
Revised:2025-07-01
Published:2025-08-26
Contact:
* E-mail: 364874916@qq.com;
huolini@126.com
About author:† The authors contributed equally to this work
Supported by:Share
Xiaowei Su, Hao Xu, Huafeng Zhou, Xiajie Wang, Peiyuan Li, Xing Xia, Wenya Chen, Lini Huo. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity Evaluation of Novel Nitrogen-Containing Heterocyclic Compounds Based on Nitidine Skeleton[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2026, 46(1): 250-265.

| Entry | Temp./℃ | Time/h | Catalyst/mmol | Solvent | Yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 120 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 67.6 |
| 2 | 100 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 66.3 |
| 3 | 80 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 66.4 |
| 4 | 60 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 67.1 |
| 5 | 40 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 45.9 |
| 6 | 60 | 12 | 0.2 | DMF | 65.9 |
| 7 | 60 | 6 | 0.2 | DMF | 65.7 |
| 8 | 60 | 3 | 0.2 | DMF | 65.4 |
| 9 | 60 | 1.5 | 0.2 | DMF | 55.2 |
| 10 | 60 | 3 | 0.1 | DMF | 65.3 |
| 11 | 60 | 3 | 0.05 | DMF | 35.3 |
| 12 | 60 | 3 | 0.1 | EtOAc | 71.3 |
| Entry | Temp./℃ | Time/h | Catalyst/mmol | Solvent | Yield/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 120 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 67.6 |
| 2 | 100 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 66.3 |
| 3 | 80 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 66.4 |
| 4 | 60 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 67.1 |
| 5 | 40 | 24 | 0.2 | DMF | 45.9 |
| 6 | 60 | 12 | 0.2 | DMF | 65.9 |
| 7 | 60 | 6 | 0.2 | DMF | 65.7 |
| 8 | 60 | 3 | 0.2 | DMF | 65.4 |
| 9 | 60 | 1.5 | 0.2 | DMF | 55.2 |
| 10 | 60 | 3 | 0.1 | DMF | 65.3 |
| 11 | 60 | 3 | 0.05 | DMF | 35.3 |
| 12 | 60 | 3 | 0.1 | EtOAc | 71.3 |
| Compd. | HL-60 | HeLa | HepG2 | H460 | LO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13a | >40 | 19.47±0.19 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13b | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13d | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13e | >40 | 11.75±1.16 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14a | >40 | 9.27±1.45 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14b | >40 | 7.39±0.24 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14c | >40 | 1.83±0.24 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14d | 0.96±0.01 | 17.48±2.80 | >40 | >40 | 1.07±0.10 |
| 14e | >40 | 4.20±0.12 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16a | >40 | 4.89±0.42 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16b | >40 | 19.35±0.48 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16d | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16e | 16.47±0.48 | 14.69±0.49 | 19.97±0.12 | 19.82±0.52 | 27.15±1.13 |
| 16f | 13.78±0.09 | 9.62±0.51 | 14.54±0.15 | >40 | 16.23±0.19 |
| 16g | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16h | 13.29±0.11 | 10.35±0.67 | 14.24±0.53 | 17.61±0.12 | 15.69±0.02 |
| 17a | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 17b | 7.38±0.33 | 5.03±0.38 | 16.76±0.16 | 16.66±0.25 | 16.63±0.12 |
| 17c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 17d | 9.68±0.46 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 17e | >40 | 14.48±0.11 | 16.04±0.24 | 16.88±0.41 | 15.90±0.23 |
| 17f | 16.70±0.92 | 3.47±0.10 | 10.52±0.28 | 4.657±0.07 | 11.13±0.06 |
| 17g | 10.22±0.51 | 18.55±0.50 | >40 | >40 | 25.17±0.31 |
| 17h | 12.92±0.65 | 7.59±0.84 | 17.09±0.13 | 17.25±0.29 | 16.10±0.17 |
| 19a | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 19b | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 19c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 20a | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 20b | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 20c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| NC | 13.47±0.38 | 1.48±0.11 | 3.41±0.09 | 3.37±0.22 | 4.10±0.11 |
| cisplatin | 2.44±0.08 | 2.01±0.14 | 3.86±0.15 | 15.08±0.39 | 8.65±0.10 |
| Compd. | HL-60 | HeLa | HepG2 | H460 | LO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13a | >40 | 19.47±0.19 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13b | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13d | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 13e | >40 | 11.75±1.16 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14a | >40 | 9.27±1.45 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14b | >40 | 7.39±0.24 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14c | >40 | 1.83±0.24 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 14d | 0.96±0.01 | 17.48±2.80 | >40 | >40 | 1.07±0.10 |
| 14e | >40 | 4.20±0.12 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16a | >40 | 4.89±0.42 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16b | >40 | 19.35±0.48 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16d | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16e | 16.47±0.48 | 14.69±0.49 | 19.97±0.12 | 19.82±0.52 | 27.15±1.13 |
| 16f | 13.78±0.09 | 9.62±0.51 | 14.54±0.15 | >40 | 16.23±0.19 |
| 16g | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 16h | 13.29±0.11 | 10.35±0.67 | 14.24±0.53 | 17.61±0.12 | 15.69±0.02 |
| 17a | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 17b | 7.38±0.33 | 5.03±0.38 | 16.76±0.16 | 16.66±0.25 | 16.63±0.12 |
| 17c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 17d | 9.68±0.46 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 17e | >40 | 14.48±0.11 | 16.04±0.24 | 16.88±0.41 | 15.90±0.23 |
| 17f | 16.70±0.92 | 3.47±0.10 | 10.52±0.28 | 4.657±0.07 | 11.13±0.06 |
| 17g | 10.22±0.51 | 18.55±0.50 | >40 | >40 | 25.17±0.31 |
| 17h | 12.92±0.65 | 7.59±0.84 | 17.09±0.13 | 17.25±0.29 | 16.10±0.17 |
| 19a | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 19b | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 19c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 20a | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 20b | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| 20c | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 | >40 |
| NC | 13.47±0.38 | 1.48±0.11 | 3.41±0.09 | 3.37±0.22 | 4.10±0.11 |
| cisplatin | 2.44±0.08 | 2.01±0.14 | 3.86±0.15 | 15.08±0.39 | 8.65±0.10 |

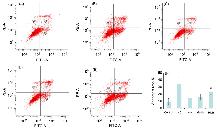

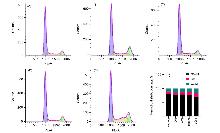

| [1] |
(a)
doi: 10.3322/caac.v74.3 |
|
(b)
|
|
|
(李煜昊, 游以勒, 王胜锋, 科学通报, 2024, 69, 5197.)
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
(秦舒琴, 李海云, 宋静茹, 李典鹏, 广西植物, 2018, 38, 1248.)
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2006.05.012 |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01122 |
| [7] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
|
|
|
(c)
|
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2009.12.005 |
| [9] |
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3076 pmid: 20924131 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.1038/nm.2919 pmid: 23104132 |
| [11] |
(a)
|
|
(刘志千, 博士论文,第二军医大学, 上海, 2014.)
|
|
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jm040025z |
|
| [12] |
(a)
|
|
(b)
doi: 10.1007/s11094-022-02597-z |
|
|
(c)
|
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0416 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1080/10406638.2022.2144909 |
|
| [13] |
(a)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.02.057 pmid: 19012996 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/jm049447z pmid: 19012996 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.09.048 pmid: 19012996 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201412036 pmid: 19012996 |
|
|
(许旭升, 刘志千, 邵文浩, 叶霁, 孙青龑, 何薇薇, 张卫东, 有机化学, 2015, 35, 1353.)
pmid: 19012996 |
|
|
(e)
pmid: 19012996 |
|
| [14] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/jm401895u pmid: 24805037 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.12.099 pmid: 24805037 |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00137-2 |
| [1] | Guochao Liang, Tingting Dong, Haiying Ji, Chunyan Wang, Yali Song, Wei Zhang. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of Novel 3,3'-((4-Chloro-2H-thiochromen-3-yl)methylene)bis(1H-indole)-Like Topoisomerase II Inhibitors [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2024, 44(6): 1949-1956. |
| [2] | Ruixia Cao, Yuping Jia. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine Derivatives Containing Coumarin [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(9): 3304-3311. |
| [3] | Weishu Zhang, Lifei Nie, Khurshed Bozorov, Haji Akber Aisa, Jiangyu Zhao. Synthesis of Diethyl 2,5-Diaminothiophene-3,4-dicarboxylate Derivatives and Antitumor Activity Study [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(7): 2543-2552. |
| [4] | Weiqin Liu, Lihui Shao, Chengpeng Li, Yayu Zou, Haitao Long, Yan Li, Qiangsheng Ge, Zhenchao Wang, Guiping Ouyang. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of 3-Hydrazone Quinazolinone Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(1): 214-222. |
| [5] | Xing Huang, Changhao Zhang, Hao Deng, Qingkun Shen, Hongyan Guo, Zheshan Quan, Zhiyong Li, Lili Jin. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of Hederagenin Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(9): 2877-2887. |
| [6] | Junzhe Yang, Zichao Xu, Chunpu Li, Yuanzheng Cheng, Hong Liu. Research Progress of Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase (TRK) Inhibitors [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(7): 2055-2069. |
| [7] | Jing Zhao, Zhe Jin, Run Wang, Xin'geng Zhang, Yingmei Han, Chun Hu, Xiaoping Liu, Chuanming Zhang, Liping Jin. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of 2-((Pyridin- 2-ylmethyl)thio)-1H-benzimidazole Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(7): 2172-2183. |
| [8] | Yan Zeng, Lifei Nie, Chao Niu, Aytilla Mamatjan, Khurshed Bozorov, Jiangyu Zhao, Haji Akber Aisa. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Dihydrooxazolo[5,4-d]-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidinones [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(2): 543-556. |
| [9] | Yajun Mao, Xiangmin Shao, Yangjie Li, Ruimei Cao, Yali Feng, Guangyu Zhai. Research Progress on the Synthesis of Quercetin Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 42(11): 3588-3605. |
| [10] | Shenghui Wang, Yongfeng Guan, Xiujuan Liu, Xinying Yuan, Guangxi Yu, Yinru Li, Yanbing Zhang, Jian Song, Wen Li, Saiyang Zhang. Design, Synthesis and Anticancer Activity Studies of Novel Quinoline-Indole Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(9): 3617-3624. |
| [11] | Xin Liu, Runmei Xu, Lin Wang, Yaxue Liu, Zhihao Chen, Wei Qin, Yushun Tian. Synthesis and Evaluation in vitro of Dihydrothiophenopyridine-Chalcone Derivatives as Anticancer Activity Agents [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(9): 3550-3559. |
| [12] | Zheng Zhang, Chengqiu Dai, Honghong Wu, Jingya Li, Fajun Nan. Design and Synthesis of Alkyl Phenols Inhibitors of Death Associated Apoptotic Protein Kinase 2 (DRAK2) [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(8): 3204-3213. |
| [13] | Ruixue Rong, Jimin Li, Yaowen Li, Xiaoyu Guo, Chong Wang, Yanjun Li, Jinmei Li, Baojun Han, Zhiran Cao, Kerang Wang, Xiaoliu Li. Synthesis and Anti-tumor Effects of Naphthalimide Derivatives Targeted in Cell Nucleus [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(4): 1599-1606. |
| [14] | Yang Zhang, Luye Zhang, Jikuan Wang, Limin Liu, Tao Wang, Na Li, Zhengjie Wang, Xiujuan Liu, Yaxin Chen, Danlin Zhao, Jiaxin Zheng, Lihong Shan, Hongmin Liu, Qiurong Zhang. Design, Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation Research of Novel 2,4,6-Substituted Pyrimidine Derivatives [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(1): 310-317. |
| [15] | Maihesuti Liwaliding, Yu Junjie, Wang Qi, Cao Jianguo, Huang Guozheng. Synthesis and Anticancer Evaluation of Amido-Derivative of Hydnocarpin D [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 40(9): 2764-2771. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||