化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (4): 517-525.DOI: 10.6023/A21110529 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
樊小勇*( ), 张帅, 朱永强, 敬茂森, 王凯鑫, 张露露, 李巨龙, 许磊, 苟蕾, 李东林
), 张帅, 朱永强, 敬茂森, 王凯鑫, 张露露, 李巨龙, 许磊, 苟蕾, 李东林
投稿日期:2021-11-23
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
樊小勇
基金资助:
Xiaoyong Fan( ), Shuai Zhang, Yongqiang Zhu, Maosen Jing, Kaixin Wang, Lulu Zhang, Julong Li, Lei Xu, Lei Gou, Donglin Li
), Shuai Zhang, Yongqiang Zhu, Maosen Jing, Kaixin Wang, Lulu Zhang, Julong Li, Lei Xu, Lei Gou, Donglin Li
Received:2021-11-23
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Xiaoyong Fan
Supported by:文章分享
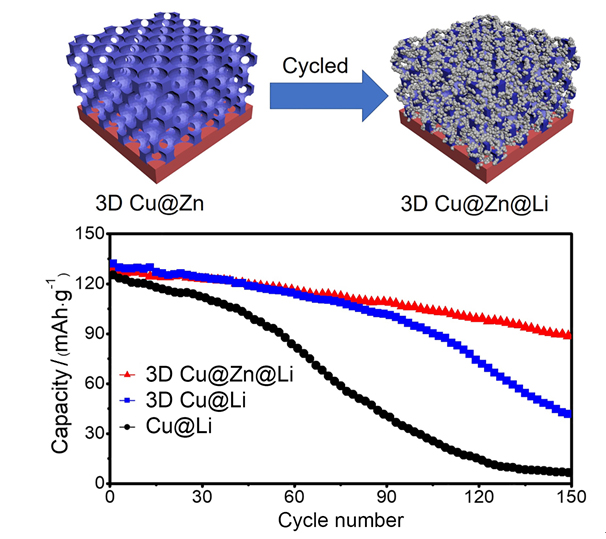
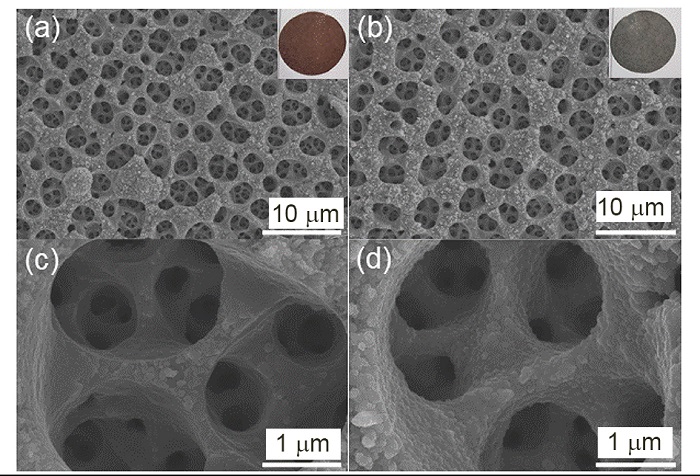
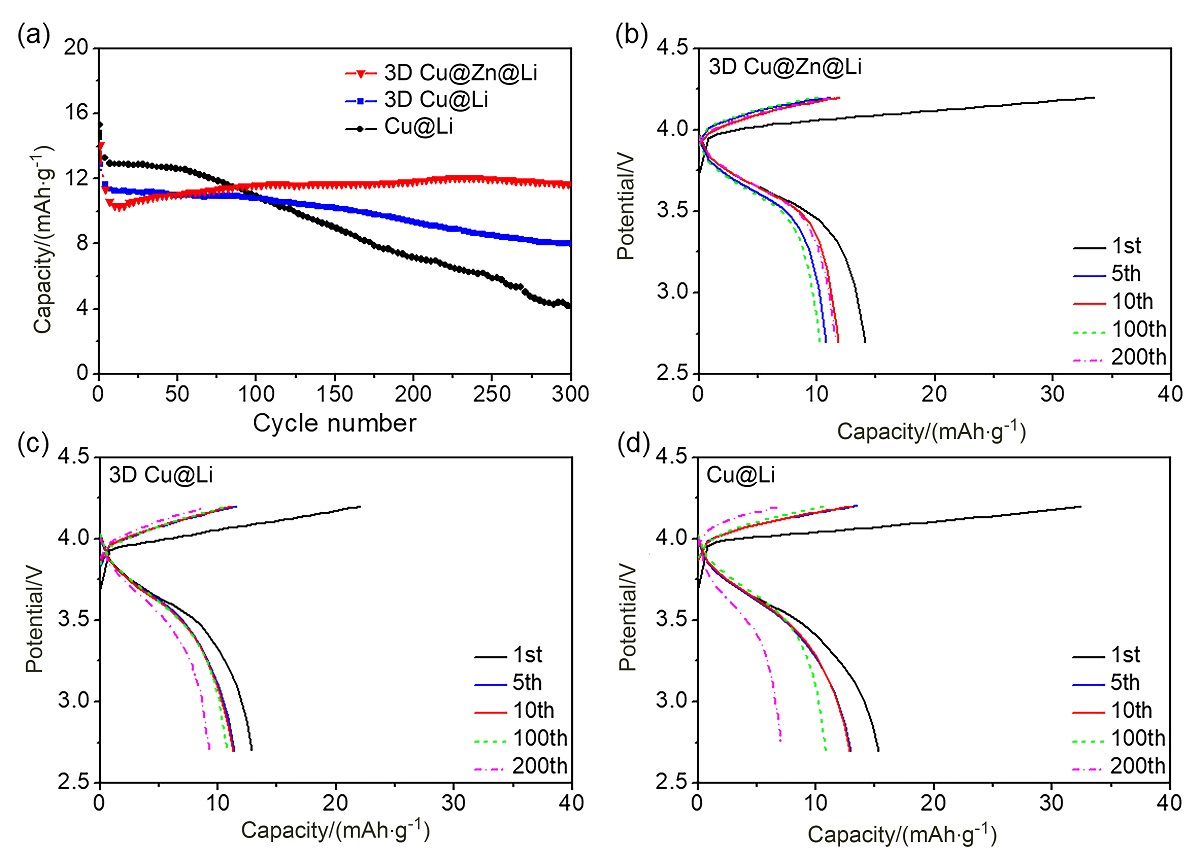
金属锂具有高理论比容量和低氧化还原电位, 被认为是高能量密度二次电池最理想的负极材料之一, 但其在循环过程中的枝晶生长和体积变化易造成电池失效和安全隐患. 以孔径为5 μm左右的自制三维多孔铜为基底, 在其表面电沉积锌层(3D Cu@Zn), 作为金属锂沉积的集流体, 构筑无枝晶锂金属电极. 三维多孔铜的孔结构稳定, 孔径大小适宜, 可有效降低局部电流密度和缓解体积变化. 锌镀层可降低锂金属的形核过电位, 诱导锂的均匀沉积, 有效抑制锂枝晶生长. 以3D Cu@Zn为集流体, 锂沉积面积容量为4 mAh•cm–2, 电极表面仍无枝晶出现, 经过锂剥离后表面仍然光滑; 而铜箔上沉积的锂显示明显的枝晶和不均匀性, 3D Cu上沉积的锂显示局部不均匀性和一定量枝晶. 在电流密度为0.5和 1 mA•cm–2, 面积容量为1 mAh•cm–2条件下, Li||3D Cu@Zn半电池获得了稳定的库伦效率; 在2 mA•cm–2的高电流密度和1 mAh•cm–2的面积容量条件下, Li||3D Cu@Zn@Li对称电池可稳定循环700 h以上; 以3D Cu@Zn@Li为负极, LiFePO4为正极的全电池, 在1 C倍率下, 经过150次循环后仍保持88 mAh•g–1的容量, 均明显优于Cu片和3D Cu作为集流体的锂金属电极.
樊小勇, 张帅, 朱永强, 敬茂森, 王凯鑫, 张露露, 李巨龙, 许磊, 苟蕾, 李东林. 三维多孔铜和锌镀层协同构筑无枝晶锂金属电极[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 517-525.
Xiaoyong Fan, Shuai Zhang, Yongqiang Zhu, Maosen Jing, Kaixin Wang, Lulu Zhang, Julong Li, Lei Xu, Lei Gou, Donglin Li. Construction of Dendrite-free Lithium Metal Electrode Using Three-Dimensional Porous Copper and Zinc Coatings[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 517-525.

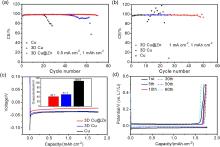
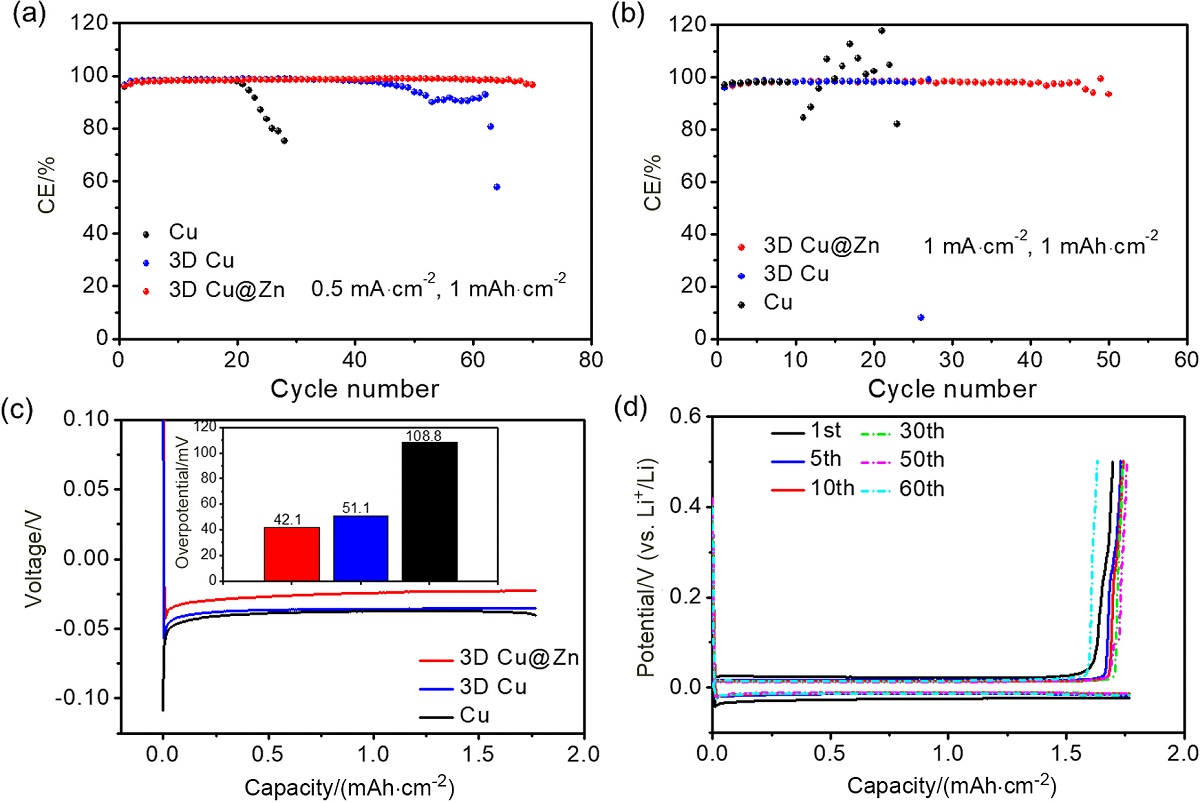
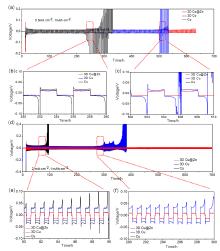

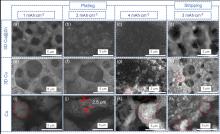





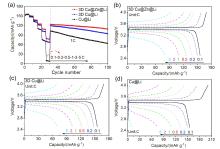

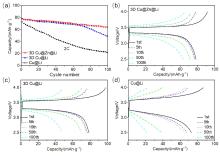
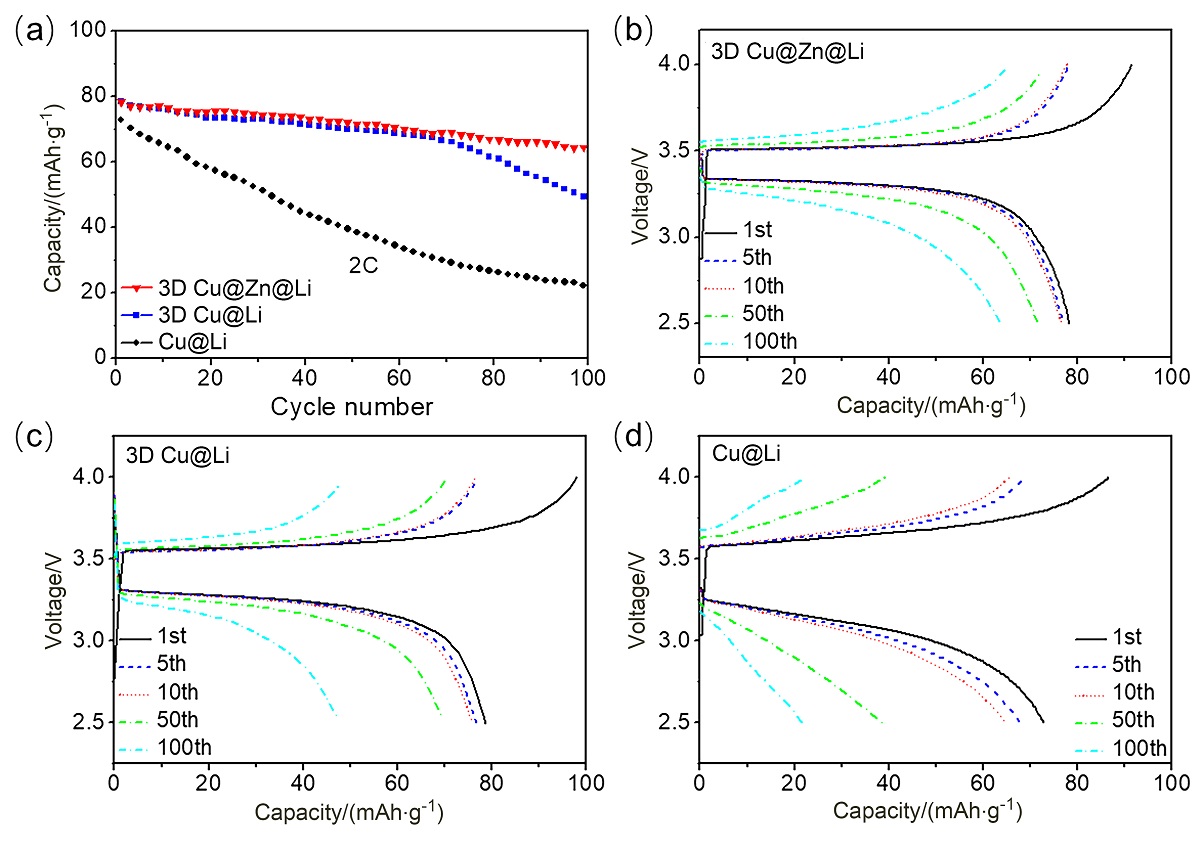
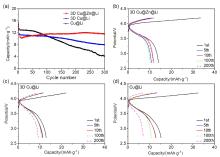
| [1] |
Balogun, M.-S.; Qiu, W.; Luo, Y.; Meng, H.; Mai, W.; Onasanya, A.; Olaniyi, T. K.; Tong, Y. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2823.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-016-1171-1 |
| [2] |
Cheng, X. B.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C. Z.; Zhang, Q. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10403.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00115 |
| [3] |
Winter, M.; Barnett, B.; Xu, K. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11433.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00422 |
| [4] |
Jin, L.; Shen, C.; Shellikeri, A.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Andrei, P.; Zhang, J.-G.; Zheng, J. P. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2341.
doi: 10.1039/D0EE00807A |
| [5] |
Liang, X.; Pang, Q.; Kochetkov, I. R.; Sempere, M. S.; Huang, H.; Sun, X.; Nazar, L. F. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17119.
doi: 10.1038/nenergy.2017.119 |
| [6] |
Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Yu, T.; Xu, S.; Qu, C.; Xu, X.; Zhuang, R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 378. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20100462 |
|
(徐飞, 王洪强, 于涛, 徐顺奇, 曲昌镇, 许潇洒, 庄容, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 378.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100462 |
|
| [7] |
Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Mao, Q.; Yang, S.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Zhou, K. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 126861.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126861 |
| [8] |
Chen, K.-H.; Wood, K. N.; Kazyak, E.; LePage, W. S.; Davis, A. L.; Sanchez, A. J.; Dasgupta, N. P. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11671.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA00371D |
| [9] |
Louli, A. J.; Eldesoky, A.; Weber, R.; Genovese, M.; Coon, M.; deGooyer, J.; Deng, Z.; White, R. T.; Lee, J.; Rodgers, T.; Petibon, R.; Hy, S.; Cheng, S. J. H.; Dahn, J. R. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 693.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-020-0668-8 |
| [10] |
Wood, K. N.; Kazyak, E.; Chadwick, A. F.; Chen, K. H.; Zhang, J. G.; Thornton, K.; Dasgupta, N. P. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 790.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.6b00260 |
| [11] |
Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Qian, Z.; Wang, R. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2020, 42, 1017. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王增强, 孙一翎, 钱正芳, 王任衡, 高等化学学报, 2020, 42, 1017.)
|
|
| [12] |
Zhou, H.; He, P.; Zhu, X.; Deng, H.; Yang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Chang, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 139. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20090442 |
|
(周豪慎, 何平, 朱星宇, 邓瀚, 杨慧军, 乔羽, 常智, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 139.)
doi: 10.6023/A20090442 |
|
| [13] |
Chi, S. S.; Wang, Q.; Han, B.; Luo, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2724.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00352 |
| [14] |
Zhan, Y.; Shi, P.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 1569. (in Chinese)
|
|
(詹迎新, 石鹏, 张学强, 魏俊宇, 张乾魁, 黄佳琦, 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42, 1569.)
|
|
| [15] |
Zhang, D.; Dai, A.; Fan, B.; Li, Y.; Shen, K.; Xiao, T.; Hou, G.; Cao, H.; Tao, X.; Tang, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 31542.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c09503 |
| [16] |
Liu, H.; Wang, E.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Yu, H. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 17, 253.
|
| [17] |
Lin, K.; Xu, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, M.; Lv, F.; Xia, Y.; Kang, F.; Chen, G.; Li, B. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 26, 250.
|
| [18] |
Ke, X.; Liang, Y.; Ou, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Lai, Y.; Liu, P.; Shi, Z. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 547.
|
| [19] |
Chi, S.-S.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.-L.; Fan, L.-Z.; Zhang, Q. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700348.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201700348 |
| [20] |
Ke, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, N.; Liu, J.; Zhi, C.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13552.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b01978 |
| [21] |
Medvedev, A. Z.; Zherebilov, A. F.; Masliiy, A. I.; Poddubnyi, N. P. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2008, 44, 761.
doi: 10.1134/S1023193508060189 |
| [22] |
Meng, X.; Song, Y.; Shu, T. J. Power Sources 2020, 27, 1069.
|
| [23] |
Singh, H.; Dheeraj, P. B.; Singh, Y. P.; Rathore, G.; Bhardwaj, M. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 785, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.12.013 |
| [24] |
Wang, N.; Hu, W. C.; Lu, Y. H.; Deng, Y. F.; Wan, X. B.; Zhang, Y. W.; Du, K.; Zhang, L. Trans. IMF 2013, 89, 261.
doi: 10.1179/174591911X13119320025636 |
| [25] |
Yun, Q.; He, Y.-B.; Lv, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Kang, F.; Yang, Q.-H. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6932.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201601409 |
| [26] |
Zhang, D.; Dai, A.; Wu, M.; Shen, K.; Xiao, T.; Hou, G.; Lu, J.; Tang, Y. ACS Energy. Lett. 2019, 5, 180.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b01987 |
| [27] |
Zhao, H.; Lei, D.; He, Y.-B.; Yuan, Y.; Yun, Q.; Ni, B.; Lv, W.; Li, B.; Yang, Q.-H.; Kang, F.; Lu, J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800266.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201800266 |
| [28] |
Qiu, H.; Tang, T.; Asif, M.; Huang, X.; Hou, Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808468.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808468 |
| [29] |
Fan, X.; Sun, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gou, L.; Lu, L.; Li, D. Small 2021, 18, e2106161.
|
| [30] |
Fan, X.-Y.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Sun, R.; Gou, L.; Li, D.-L.; Ding, Y.-L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20344.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b23501 |
| [31] |
Fan, X.-Y.; Han, J.; Ding, Y.-L.; Deng, Y.-P.; Luo, D.; Zeng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Gou, L.; Li, D.-L.; Chen, Z. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900673.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.201900673 |
| [32] |
Chi, S.-S.; Wang, Q.; Han, B.; Luo, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Deng, Y. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2724.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00352 |
| [33] |
Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y. J. Power Sources 2020, 472, 228520.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228520 |
| [34] |
Zhao, F.; Zhou, X.; Deng, W.; Liu, Z. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 55.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.04.087 |
| [35] |
Wang, G.; Xiong, X.; Zou, P.; Fu, X.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, M. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122243.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122243 |
| [36] |
Fan, X.-Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, P.; Gou, L.; Xu, L.; Li, D.-L. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 22224.
doi: 10.1039/C6CP03374A |
| [37] |
Zhang, Q.; Luan, J.; Tang, Y.; Ji, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18444.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA07612J |
| [38] |
Liu, J.; Ma, H.; Wen, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Pei, N.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J. J. Energy. Chem. 2022, 64, 354.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.04.044 |
| [39] |
Yang, T.; Qian, T.; Shen, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhong, J.; Yan, C.; Rosei, F. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 14496.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA02640A |
| [40] |
Luo, N.; Ji, G.-J.; Wang, H.-F.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.-C.; Xu, J.-J. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3281.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b08844 pmid: 32119516 |
| [41] |
Huang, G.; Han, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Kashani, H.; Watanabe, K.; Chen, M. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805334.
|
| [42] |
Zhang, C.; Lyu, R.; Lv, W.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Gu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, Q. H.; Kang, F. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1904991.
|
| [43] |
Domínguez-Ríos, C.; Moreno, M. V.; Torres-Sánchez, R.; Antúnez, W.; Aguilar-Elguézabal, A.; González-Hernández, J. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 4848.
doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.04.069 |
| [44] |
Wang, R.; Shi, F.; He, X.; Shi, J.; Ma, T.; Jin, S.; Tao, Z. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 64, 1087.
doi: 10.1007/s40843-020-1528-5 |
| [45] |
Vinokurov, E. G.; Kandyrin, K. L.; Bondar', V. V. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2010, 83, 659.
doi: 10.1134/S1070427210040166 |
| [1] | 王志强, 苏进展. 磷酸钴修饰Cu3V2O8/ZnO光阳极的动力学特性及光电化学水分解研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 26-35. |
| [2] | 李奎琛, 郑开元, 何静嘉, 金泽浩, 何秋, 王丽丽. 单相硫化锌量子点制作白光发光二极管(WQLEDs)[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1327-1333. |
| [3] | 赵珂, 程夏宇, 马雪雪, 耿明慧. 含哌嗪基团锌离子探针的双光子吸收增强机理[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1371-1378. |
| [4] | 姬慧敏, 谢春霖, 张旗, 李熠鑫, 李欢欢, 王海燕. 水系锌离子电池负极集流体关键问题及设计策略[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 29-41. |
| [5] | 梁世硕, 康树森, 杨东, 胡建华. 锂金属负极界面修饰及其在硫化物全固态电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1264-1268. |
| [6] | 田宋炜, 周丽雪, 张秉乾, 张建军, 杜晓璠, 张浩, 胡思伽, 苑志祥, 韩鹏献, 李素丽, 赵伟, 周新红, 崔光磊. 聚环氧乙烷聚合物电解质基高电压固态锂金属电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1410-1423. |
| [7] | 张欣欣, 刘荣, 王蕾, 付宏刚. 细菌纤维素基柔性锌离子电池正极的构筑及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 670-677. |
| [8] | 庄容, 许潇洒, 曲昌镇, 徐顺奇, 于涛, 王洪强, 徐飞. 多孔聚合物在锂金属负极保护中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 378-387. |
| [9] | 周家正, 徐啸, 段碧雯, 石将建, 罗艳红, 吴会觉, 李冬梅, 孟庆波. 铜锌锡硫硒薄膜太阳能电池一价金属替位的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 303-318. |
| [10] | 张璐, 王文凤, 张洪明, 韩树民, 王利民. 水系锌离子电池研究进展和挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 158-175. |
| [11] | 李燕丽, 于丹丹, 林森, 孙东飞, 雷自强. α-MnO2纳米棒/多孔碳正极材料的制备及水系锌离子电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 200-207. |
| [12] | 杜重阳, 陈耀峰. 二乙基锌促进CO2的硅氢化反应以及CO2为C1合成子的有机胺甲酰化或脲化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(9): 938-944. |
| [13] | 康树森, 杨程响, 杨泽林, 吴宁宁, 赵姗, 陈晓涛, 刘富亮, 石斌. 旋涂法制备PEO-PAN-PMMA三组分共混凝胶聚合物电解质[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1441-1447. |
| [14] | 何锦俊, 张昊喆, 刘晓庆, 卢锡洪. 原位包覆纳米碳提升钴锰氧化物材料储锌性能[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(10): 1069-1075. |
| [15] | 林伟芬, 陈念嘉, 游乐星, 周顺桂. 希瓦氏菌MR-1影响玻碳表面电沉积Cd的机理[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(7): 543-548. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||