化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (10): 1371-1378.DOI: 10.6023/A23050248 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2023-05-25
发布日期:2023-07-18
基金资助:
Ke Zhao( ), Xiayu Cheng, Xuexue Ma, Minghui Geng
), Xiayu Cheng, Xuexue Ma, Minghui Geng
Received:2023-05-25
Published:2023-07-18
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

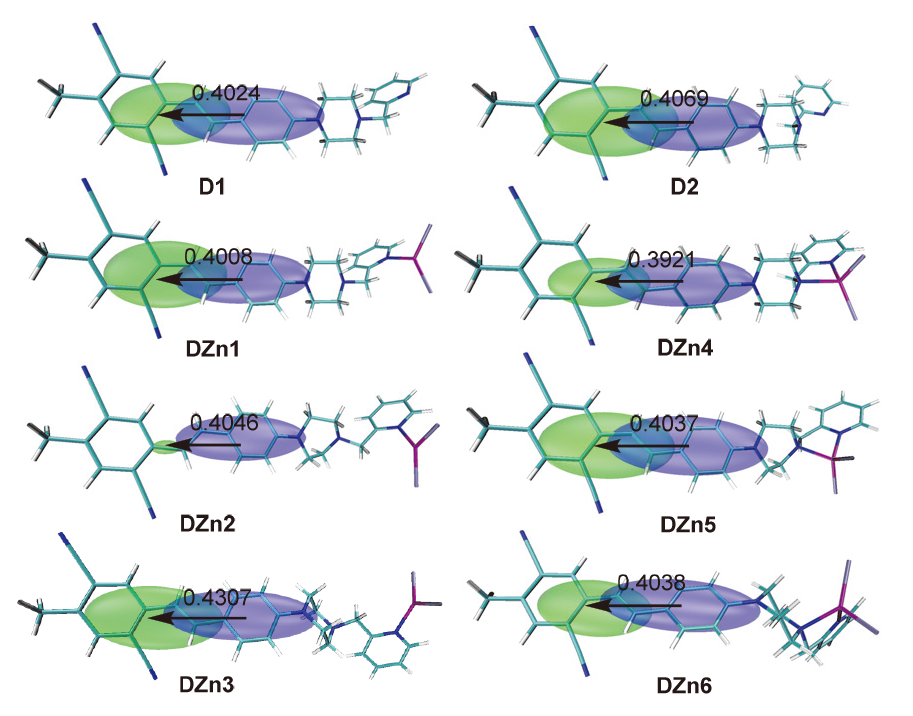
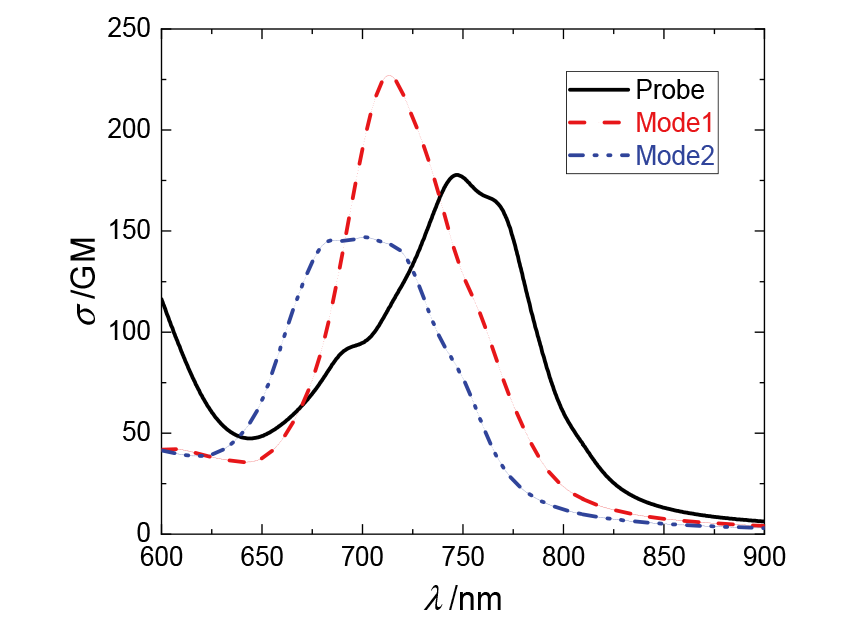
为了探寻锌离子配位诱导的双光子吸收增强机理, 采用分子动力学和量子化学方法, 研究了探针及其锌配合物的双光子吸收性质. 模拟了溶液中探针的结构演化和锌离子配位过程, 发现存在单配位和双配位两种配位模式, 与探针相比, 锌配合物主体平面性增强, 结构更稳定. 基于模拟结构, 采用量子化学方法优化了一系列探针和两种配位模式下的配合物结构, 并应用响应理论方法和两态模型计算了双光子吸收性质, 分析了分子内电荷转移过程. 结果表明, 配位模式和哌嗪结构对双光子吸收有重要影响. 单配位模式下, 当哌嗪环发生扭曲时, 双光子吸收截面增大, 波长几乎不变. 双配位模式下, 锌配合物的双光子吸收截面普遍减小, 波长发生蓝移. 通过对模拟结构进行采样, 计算了探针和两种配位模式下配合物的平均双光子吸收谱, 讨论了结构动态变化对双光子吸收性质的影响. 由于探针结构更加灵活, 导致平均双光子吸收降低, 从而使单配位模式下锌配合物的平均双光子吸收显著增强. 因此, 特殊的单配位结构和灵活的探针结构共同作用, 产生了配位后双光子吸收增强现象. 该研究有助于理解和预测双光子锌离子探针的光物理性质.
赵珂, 程夏宇, 马雪雪, 耿明慧. 含哌嗪基团锌离子探针的双光子吸收增强机理[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1371-1378.
Ke Zhao, Xiayu Cheng, Xuexue Ma, Minghui Geng. Mechanism of Two-photon Absorption Enhancement for a Piperazine-based Zinc Ion Probe[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1371-1378.
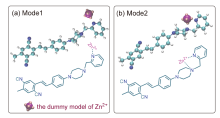
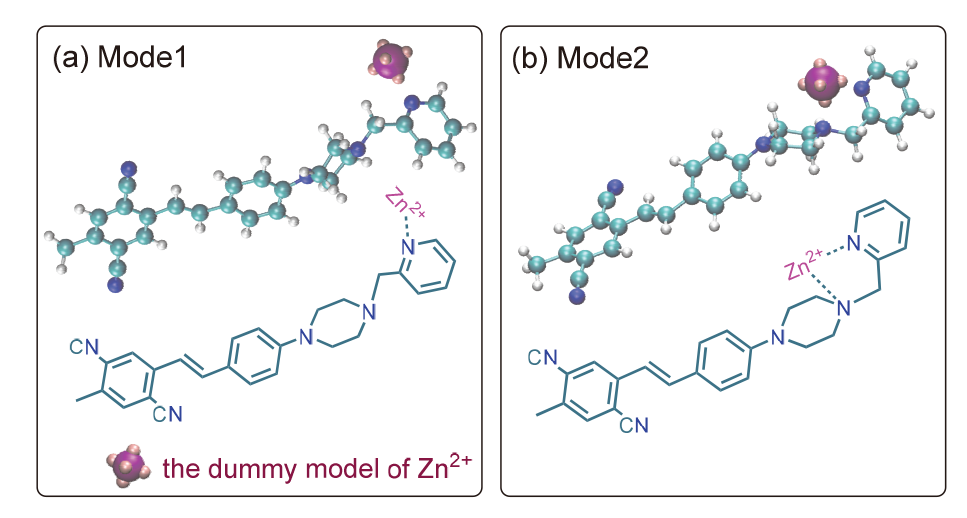
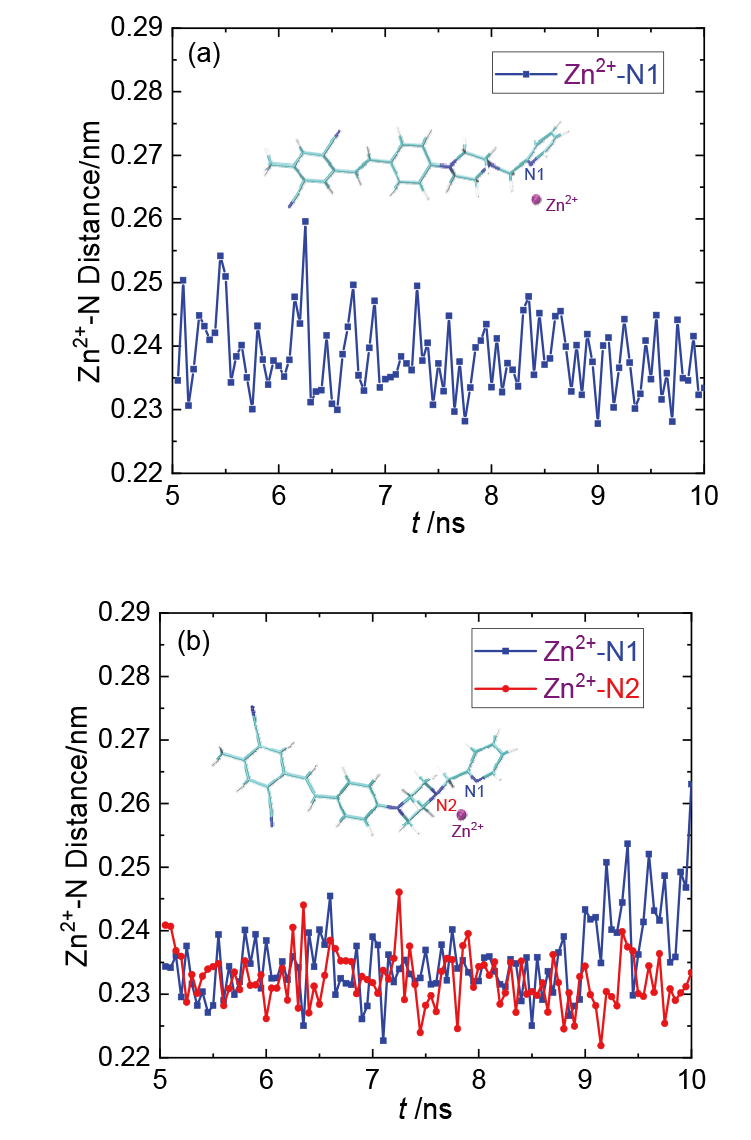
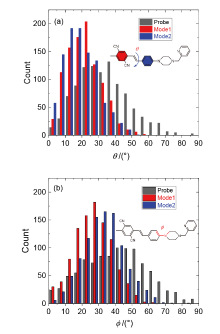
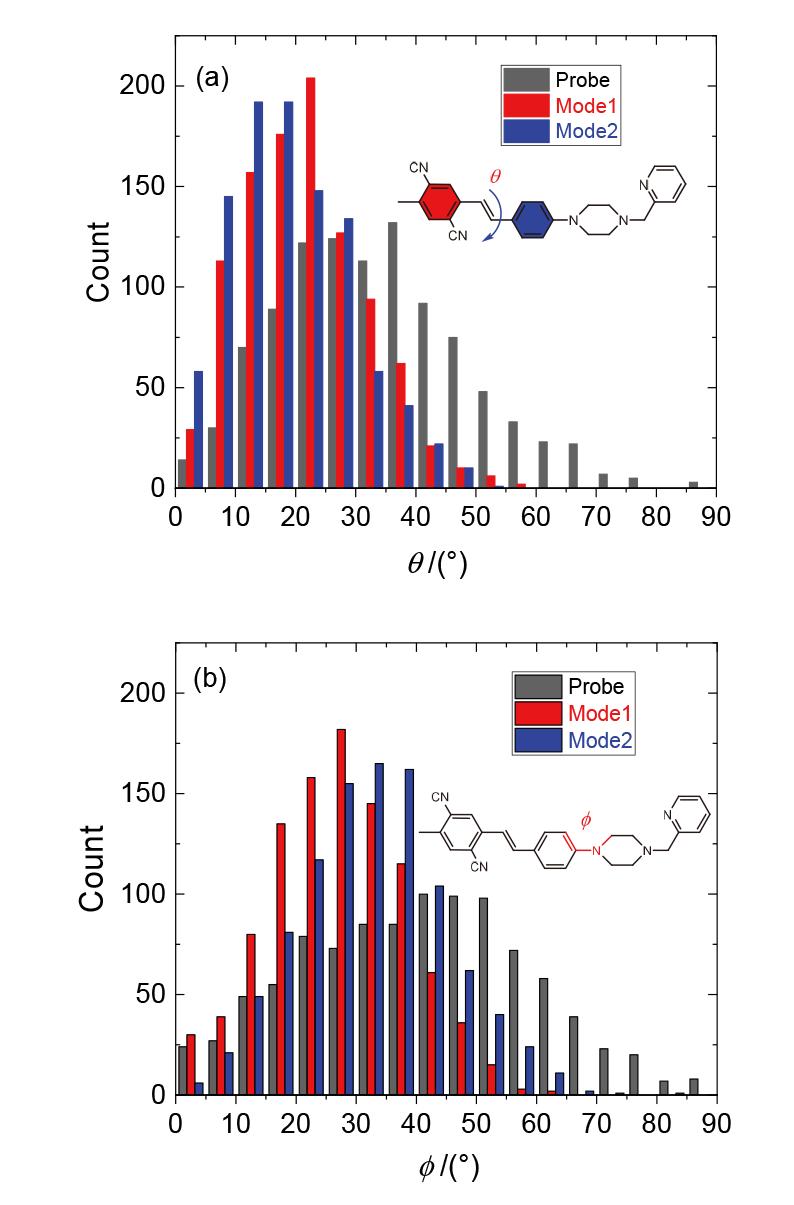
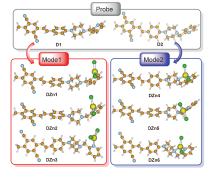

| 分子 | λ/nm | σ/GM | 分子 | λ/nm | σ/GM | 分子 | λ/nm | σ/GM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 790 | 444 | DZn1 | 785 | 428 | DZn4 | 763 | 360 |
| D2 | 793 | 469 | DZn2 | 788 | 537 | DZn5 | 805 | 471 |
| DZn3 | 814 | 572 | DZn6 | 783 | 438 |
| 分子 | λ/nm | σ/GM | 分子 | λ/nm | σ/GM | 分子 | λ/nm | σ/GM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 790 | 444 | DZn1 | 785 | 428 | DZn4 | 763 | 360 |
| D2 | 793 | 469 | DZn2 | 788 | 537 | DZn5 | 805 | 471 |
| DZn3 | 814 | 572 | DZn6 | 783 | 438 |
| 分子 | μ01 | μ0 | μ1 | ∆μ | α/(°) | ω | δ2SM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 3.401 | 1.591 | 7.013 | 5.577 | 2.01 | 0.119 | 81700 (57900) |
| D2 | 3.422 | 1.935 | 7.159 | 5.732 | 2.25 | 0.118 | 88100 (62200) |
| DZn1 | 3.414 | 5.189 | 8.269 | 5.542 | 1.97 | 0.119 | 80900 (55800) |
| DZn2 | 3.767 | 5.587 | 9.940 | 5.729 | 2.74 | 0.119 | 105000(70000) |
| DZn3 | 3.501 | 4.784 | 8.341 | 6.403 | 0.56 | 0.114 | 122800(81200) |
| DZn4 | 3.365 | 6.518 | 8.398 | 5.302 | 2.06 | 0.122 | 68700 (44700) |
| DZn5 | 3.517 | 6.436 | 9.813 | 5.684 | 1.43 | 0.116 | 95800 (64600) |
| DZn6 | 3.440 | 5.791 | 7.635 | 5.720 | 1.40 | 0.118 | 88900 (58100) |
| 分子 | μ01 | μ0 | μ1 | ∆μ | α/(°) | ω | δ2SM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 3.401 | 1.591 | 7.013 | 5.577 | 2.01 | 0.119 | 81700 (57900) |
| D2 | 3.422 | 1.935 | 7.159 | 5.732 | 2.25 | 0.118 | 88100 (62200) |
| DZn1 | 3.414 | 5.189 | 8.269 | 5.542 | 1.97 | 0.119 | 80900 (55800) |
| DZn2 | 3.767 | 5.587 | 9.940 | 5.729 | 2.74 | 0.119 | 105000(70000) |
| DZn3 | 3.501 | 4.784 | 8.341 | 6.403 | 0.56 | 0.114 | 122800(81200) |
| DZn4 | 3.365 | 6.518 | 8.398 | 5.302 | 2.06 | 0.122 | 68700 (44700) |
| DZn5 | 3.517 | 6.436 | 9.813 | 5.684 | 1.43 | 0.116 | 95800 (64600) |
| DZn6 | 3.440 | 5.791 | 7.635 | 5.720 | 1.40 | 0.118 | 88900 (58100) |
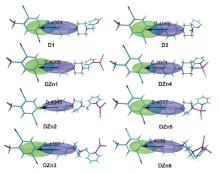
| [1] |
Bush, A. I.; Pettingell, W. H.; Multhaup, G.; Paradis, M. D.; Vonsattel, J. P.; Gusella, J. F.; Beyreuther, K.; Masters, C. L.; Tanzi, R. E. Science 1994, 265, 1464.
doi: 10.1126/science.8073293 |
| [2] |
Cuajungco, M. P.; Lees, G. J. Neurobiol. Dis. 1997, 4, 137.
doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1997.0163 |
| [3] |
Bush, A. I.; Tanzi, R. E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002, 99, 7317.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.122249699 |
| [4] |
Kim, H. M.; Cho, B. R. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5014.
doi: 10.1021/cr5004425 |
| [5] |
Xue, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2011, 156, 410.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.04.066 |
| [6] |
Sarkar, A. R.; Kang, D. E.; Kim, H. M.; Cho, B. R. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 1794.
doi: 10.1021/ic402475f |
| [7] |
Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y. Spectrochim. Acta A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 204, 446.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2018.06.065 |
| [8] |
Wu, Q.; Feng, L.; Chao, J. B.; Wang, Y.; Shuang, S. Analyst 2021, 146, 4348.
doi: 10.1039/D1AN00749A |
| [9] |
Zhang, J.; Yan, W.; Hu, W.; Guo, D.; Zhang, D.; Quan, X.; Bu, X.; Chen, S. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 326 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202207004 |
|
(张继东, 颜婉琳, 胡文强, 郭典, 张大龙, 权校昕, 卜贤盼, 陈思宇, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 326.)
|
|
| [10] |
Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, S. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 1401 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201712009 |
|
(王忠龙, 杨金来, 杨益琴, 徐徐, 李明新, 张燕, 方华, 徐海军, 王石发, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 1401.)
|
|
| [11] |
Diao, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, N.; Liu, G.; Pu, S. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 39, 1930 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201901038 |
|
(刁璐, 王仁杰, 王念省, 刘刚, 蒲守智, 有机化学, 2019, 39, 1930.)
|
|
| [12] |
Tang, J.; Yin, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.-L. Inorganic and Organometallic Transition Metal Complexes with Biological Molecules and Living Cells, Academic, Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, 2017, p. 10.1016/B978-0-12-803814-7.00001-0.
|
| [13] |
Zhang, X.-B.; Feng, J.-K.; Ren, A.-M. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 1328.
doi: 10.1021/jp0669097 |
| [14] |
Shao, Z.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Zhao, K. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 053302.
doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/ac46c6 |
| [15] |
Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, K. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 083304.
doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/aba9b9 |
| [16] |
Bednarska, J.; Zaleśny, R.; Murugan, N. A.; Bartkowiak, W.; Ågren, H.; Odelius, M. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 9067.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b04949 |
| [17] |
Şimşek, Y.; Brown, A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 5738.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b00885 |
| [18] |
Zhang, W. Y.; Geng, M. H.; Ma, X. X.; Zhao, K. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 36, 434.
doi: 10.1063/1674-0068/cjcp2209139 |
| [19] |
Huang, C.; Qu, J.; Qi, J.; Yan, M.; Xu, G. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 1462.
doi: 10.1021/ol200146j |
| [20] |
Li, W.; Fang, B.; Jin, M.; Tian, Y. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2553.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04781 |
| [21] |
Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Fang, B.; Jin, M.; Tian, Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111666.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111666 |
| [22] |
Pond, S. J. K.; Tsutsumi, O.; Rumi, M.; Kwon, O.; Zojer, E.; Brédas, J.-L.; Marder, S. R.; Perry, J. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9291.
doi: 10.1021/ja049013t |
| [23] |
Luo, Y.; Norman, P.; Macak, P.; Ågren, H. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 4718.
doi: 10.1021/jp993803l |
| [24] |
Olsen, J.; Jørgensen, P. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 3235.
doi: 10.1063/1.448223 |
| [25] |
Monson, P. R.; McClain, W. M. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 53, 29.
doi: 10.1063/1.1673778 |
| [26] |
Cronstrand, P.; Luo, Y.; Ågren, H. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 11102.
doi: 10.1063/1.1522408 |
| [27] |
Murugan, N. A.; Kongsted, J.; Ågren, H. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3660.
doi: 10.1021/ct400357t |
| [28] |
van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B. GROMACS 2014, User Manual version 4.6.7, www.gromacs.org.
|
| [29] |
Duarte, F.; Bauer, P.; Barrozo, A.; Amrein, B. A.; Purg, M.; Åqvist, J.; Kamerlin, S. C. L. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 4351.
doi: 10.1021/jp501737x |
| [30] |
Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1996, 14, 33.
|
| [31] |
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Li, X.; Caricato, M.; Marenich, A. V.; Bloino, J.; Janesko, B. G.; Gomperts, R.; Mennucci, B.; Hratchian, H. P.; Ortiz, J. V.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Williams-Young, D.; Ding, F.; Lipparini, F.; Egidi, F.; Goings, J.; Peng, B.; Petrone, A.; Henderson, T.; Ranasinghe, D.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Gao, J.; Rega, N.; Zheng, G.; Liang, W.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Throssell, K.; Montgomery, J. A.; Jr., Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M. J.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E. N.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Keith, T. A.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A. P.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Adamo, C.; Cammi, R.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J. B.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016.
|
| [32] |
Dalton, A Molecular Electronic Structure Program, Release Dalton2013.3, 2013, see http://daltonprogram.org.
|
| [33] |
Lu, T.; Chen, F. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580.
doi: 10.1002/jcc.v33.5 |
| [34] |
Murugan, N. A.; Zaleśny, R.; Kongsted, J.; Ågren, H. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 778.
doi: 10.1021/ct400924u |
| [35] |
Pawlicki, M.; Collins, H. A.; Denning, R. G.; Anderson, H. L. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3244.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v48:18 |
| [1] | 王海朋, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 抗冻剂抗冻机制的近红外光谱与分子模拟研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1167-1174. |
| [2] | 武虹乐, 郭锐, 迟涵文, 唐永和, 宋思睿, 葛恩香, 林伟英. 喹啉基粘度荧光探针的合成及其检测应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 905-911. |
| [3] | 李兰英, 陶晴, 闻艳丽, 王乐乐, 郭瑞妍, 刘刚, 左小磊. 多聚腺嘌呤DNA探针及其生物传感应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 681-690. |
| [4] | 刘祯钰, 甘利华. 乙炔热解为富勒烯的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 502-510. |
| [5] | 郝良朦, 朱伟钢. 有机共晶非线性光学材料及应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 191-206. |
| [6] | 李畅, 郑振东, 郑江南, 田瑞军. 基于可断裂双功能探针的糖蛋白分析★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1673-1680. |
| [7] | 贺晓梦, 袁方, 张素雅, 张健健. 基于尼罗红类ONOO–近红外荧光探针的开发及其成像应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1515-1521. |
| [8] | 韩逸之, 蓝建慧, 刘学, 石伟群. 基于机器学习势函数的熔盐体系分子动力学研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1663-1672. |
| [9] | 孙丽, 王亚静, 李涛, 郭英姝, 张书圣. 金纳米笼探针用于线粒体成像和光热损伤细胞★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1301-1310. |
| [10] | 宋思睿, 唐永和, 孙良广, 郭锐, 姜冠帆, 林伟英. 基于香豆素荧光团的新型极性检测荧光探针的开发及其成像应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(9): 1217-1222. |
| [11] | 张沛森, 荆莉红. 肿瘤病理可视化纳米探针的研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 805-816. |
| [12] | 廉纬, 方泽铠, 涂大涛, 李嘉尧, 韩思远, 李仁富, 商晓颖, 陈学元. 模板法控制合成AgInSe2:Zn2+近红外荧光量子点及其生物标记应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 625-632. |
| [13] | 吴志芬, 柯建熙, 刘永升, 孙蓬明, 洪茂椿. 稀土近红外二区纳米荧光影像探针及其生物医学应用※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 542-552. |
| [14] | 杜英喆, 张恒, 苑世领. Al2O3/PDMS复合材料热传导的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 787-793. |
| [15] | 张欣欣, 刘荣, 王蕾, 付宏刚. 细菌纤维素基柔性锌离子电池正极的构筑及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 670-677. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||