化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (8): 1106-1114.DOI: 10.6023/A22010044 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2022-01-24
发布日期:2022-09-01
通讯作者:
周波
基金资助:Received:2022-01-24
Published:2022-09-01
Contact:
Bo Zhou
Supported by:文章分享

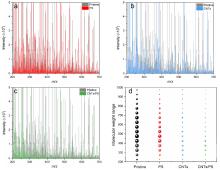
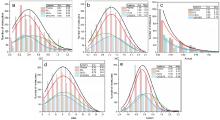
本研究对比分析了不同处理工艺对制药废水中溶解性有机质(DOM)的降解, 通过三维荧光图谱(EEM)、总有机碳(TOC)、zeta电位以及动态光散射技术进行表征分析, 并利用超高分辨质谱进一步探究了过硫酸钾(PS), 碳纳米管(CNTs), CNTs/PS工艺诱导的DOM分子转化机制. 结果表明, PS通过静电聚合作用和氧化作用对DOM中的缩合芳香类化合物(76%)和蛋白质/多肽类(65%)去除较大, CNTs通过吸附作用对不饱和水平较低的含氧化合物(木质素类、蛋白质/多肽类和氨基糖类(90%))的去除最为显著, 而CNTs/PS则是通过吸附作用、电子转移以及单线态氧(1O2)的生成以实现不同组分的DOM的高效去除. 化学参数定量分布以及线性拟合分析表明, PS和CNTs/PS体系对于DOM分子的化学参数分布影响较小, 而CNTs的吸附作用会导致残留分子的平均氧碳比(O/C)、芳香指数(AImod)、等价双键(DBE)和碳的名义氧化态(NOSC)数值增加, 且氧原子对DBE的贡献作用增大. 本研究结果为进一步理解DOM在水环境中的去除和分子转化提供了理论依据.
成受明, 周波. 基于超高分辨质谱的溶解性有机质分子转化机理分析[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1106-1114.
Shouming Cheng, Bo Zhou. Molecular Insights into the Transformation Mechanisms of Dissolved Organic Matter Based on Ultrahigh Resolution Mass Spectrometry[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(8): 1106-1114.
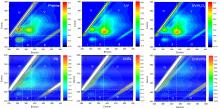

| Region | Typical substance class | Excitation wavelength/nm | Emission wavelength/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Aromatic protein I | 200~250 | 280~330 |
| II | Aromatic protein II | 200~250 | 330~380 |
| III | Fulvic acid-like | 200~250 | 380~550 |
| IV | Soluble microbial byproduct-like | 250~400 | 280~380 |
| V | Humic acid-like | 250~400 | 380~550 |
| Region | Typical substance class | Excitation wavelength/nm | Emission wavelength/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Aromatic protein I | 200~250 | 280~330 |
| II | Aromatic protein II | 200~250 | 330~380 |
| III | Fulvic acid-like | 200~250 | 380~550 |
| IV | Soluble microbial byproduct-like | 250~400 | 280~380 |
| V | Humic acid-like | 250~400 | 380~550 |



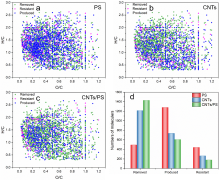

| Region | Compound class | H/C | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Lipids | 1.5~2.0 | 0~0.3 |
| II | Proteins | 1.5~2.2 | 0.3~0.52 |
| III | Aminosugars | 1.5~2.2 | 0.67~1.2 |
| IV | Lignins | 0.7~1.5 | 0.1~0.67 |
| V | Carbohydrates | 1.5~2.4 | 0.67~1.2 |
| VI | Unsaturated hydrocarbons | 0.7~1.5 | 0~0.1 |
| VII | Condensed aromatic structures | 0.2~0.7 | 0~0.67 |
| VIII | Tannins | 0.5~1.5 | 0.67~1.2 |
| Region | Compound class | H/C | O/C |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Lipids | 1.5~2.0 | 0~0.3 |
| II | Proteins | 1.5~2.2 | 0.3~0.52 |
| III | Aminosugars | 1.5~2.2 | 0.67~1.2 |
| IV | Lignins | 0.7~1.5 | 0.1~0.67 |
| V | Carbohydrates | 1.5~2.4 | 0.67~1.2 |
| VI | Unsaturated hydrocarbons | 0.7~1.5 | 0~0.1 |
| VII | Condensed aromatic structures | 0.2~0.7 | 0~0.67 |
| VIII | Tannins | 0.5~1.5 | 0.67~1.2 |







| [1] |
Kalinichev, A.-G.; Kirkpatrick, R.-J. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2007, 58, 909.
|
| [2] |
Adusei-Gyamfi, J.; Ouddane, B.; Rietveld, L.; Cornard, J.-P.; Criquet, J. Water Res. 2019, 160, 130.
doi: S0043-1354(19)30452-X pmid: 31136847 |
| [3] |
Bravo, A.-G; Bouchet, S.; Tolu, J.; Bjorn, E.; Mateos-Rivera, A.; Bertilsson, S. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14255.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms14255 |
| [4] |
Knauer, K.; Homazava, N.; Junghans, M.; Werner, I. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manage. 2017, 13, 585.
doi: 10.1002/ieam.1867 |
| [5] |
Chu, W.; Krasner, S.-W.; Gao, N.; Templeton, M.-R.; Yin, D. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 388.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b04856 |
| [6] |
Davis, C.-C.; Edwards, M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11652.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02038 |
| [7] |
Metsämuuronen, S.; Sillanpää, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Mänttäri, M. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2014, 43, 1.
doi: 10.1080/15422119.2012.712080 |
| [8] |
Li, H.; Li, A.; Shuang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, W. Water. Res. 2014, 66, 233.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.027 |
| [9] |
Von Gunten, U. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5062.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b00586 pmid: 29672032 |
| [10] |
Liu, Y.-C.; Su, M.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, J.-M.; Li, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 72. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18090365 |
|
(刘玉灿, 苏苗苗, 张岩, 段晋明, 李伟, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 72.)
doi: 10.6023/A18090365 |
|
| [11] |
Fang, Z.; Huang, R.; How, Z.-T.; Jiang, B.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Shi, Q.; Xu, C.; Gamal El-Din, M. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 730, 139072.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139072 |
| [12] |
Yang, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, W.; Wang, J.-Q; Guo, H.-G. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2021, 8, 100127.
doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2021.100127 |
| [13] |
Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Korshin, G. V.; Yang, B. Water. Res. 2019, 157, 406.
doi: S0043-1354(19)30297-0 pmid: 30978663 |
| [14] |
Lv, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Luo, L.; Cao, D.; Christie, P. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2328.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b04996 |
| [15] |
Zhou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.-M.; Pang, S.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Duan, J.-B.; Guo, Q.; Guan, C.-T.; Ma, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122378.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122378 |
| [16] |
Yang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Jian, H.; Wang, C.; Xing, B.; Sun, H.; Hao, Y. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122598.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122598 |
| [17] |
Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Tian, Z.; Chu, W.; Korshin, G.-V.; Guo, H.-G. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117379.
doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117379 |
| [18] |
Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 1017. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A19060203 |
|
(杨波, 张永丽, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1017.)
doi: 10.6023/A19060203 |
|
| [19] |
Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Water. Res. 2017, 113, 80.
doi: S0043-1354(17)30091-X pmid: 28199865 |
| [20] |
Yuan, Z.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, H.; Ni, J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8110.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02194 |
| [21] |
Bae, E.; Yeo, I. J.; Jeong, B.; Shin, Y.; Shin, K. H.; Kim, S. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4193.
doi: 10.1021/ac200464q |
| [22] |
Yang, B; Zhang, Y.-L.; Guo, H.-G. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1494. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21080408 |
|
(杨波, 张永丽, 郭洪光, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1494.)
doi: 10.6023/A21080408 |
|
| [23] |
Riedel, T.; Biester, H.; Dittmar, T. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4419.
doi: 10.1021/es203901u |
| [24] |
Ren, X.-D.; Xiong, Z.-H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 625. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12110910 |
|
(任晓东, 熊振湖, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 625.)
doi: 10.6023/A12110910 |
|
| [25] |
Schaumann, G. E.; Thiele-Bruhn, S. Geoderma 2011, 166, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.04.024 |
| [1] | 赵天成, 蒋鸿宇, 张琨, 徐一帆, 康欣悦, 胥鉴宸, 周旭峰, 陈培宁, 彭慧胜. 基于环烷烃/乙醇混合碳源高性能碳纳米管纤维的连续化制备[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 565-571. |
| [2] | 刘稳, 王昱捷, 杨慧琴, 李成杰, 吴娜, 颜洋. 离子液体非共价诱导制备碳纳米管/石墨烯集流体用于钠金属负极[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1379-1386. |
| [3] | 王超峰, 郑国栋, 王悦, 宋慧佳, 陈小艺, 高瑞霞. 金属卟啉-Sn网络可控非共价功能化碳纳米管的制备及蛋白吸附应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 126-132. |
| [4] | 张欣欣, 刘荣, 王蕾, 付宏刚. 细菌纤维素基柔性锌离子电池正极的构筑及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 670-677. |
| [5] | 崔丽瑞, 张劲, 孙一焱, 卢善富, 相艳. 碳纳米管添加剂对质子交换膜燃料电池低铂载量膜电极性能的影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 47-53. |
| [6] | 朱明晶, 彭娟, 唐萍, 邱枫. 高稳定性和水溶性的共轭聚电解质/单壁碳纳米管复合物的制备和表征[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(6): 453-459. |
| [7] | 李磊, 贾桂霄, 王晓霞, 吴铜伟, 宋希文, 安胜利. 基于缺陷曲率对含有V1~V4空位(5,5)单壁碳纳米管[1+1]和[2+1]加成反应的第一性原理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(3): 284-292. |
| [8] | 周智伟, 李庆威, 陈鲁倬, 刘长洪, 范守善. 一种基于碳纳米管/高分子复合材料的流量控制致动器[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(9): 738-743. |
| [9] | 李来才, 张明, 毛双, 杨春, 田安民. B掺杂SWCNT表面吸附DNA碱基的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(2): 143-150. |
| [10] | 王新华, 冯莉, 曹泽星. 受限于单壁碳纳米管中水分子结构、能量以及振动频率的密度泛函研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(4): 487-494. |
| [11] | 赵冬梅, 李振伟, 刘领弟, 张艳红, 任德财, 李坚. 石墨烯/碳纳米管复合材料的制备及应用进展[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(2): 185-200. |
| [12] | 高珍珍, 佟浩, 陈建慧, 岳世鸿, 白文龙, 张校刚, 潘燕飞, 石明, 宋玉翔. 聚苯胺共价接枝碳纳米管复合材料的制备及其超电容性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(11): 1175-1181. |
| [13] | 陈建慧, 佟浩, 高珍珍, 朱佳佳, 张校刚, 梁彦瑜. 聚苯胺共价接枝碳纳米管负载Pt催化剂的制备及对甲醇电催化性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(12): 1647-1655. |
| [14] | 邹琼, 刘娟, 朱刚兵, 张小华, 陈金华. 一种新型酶生物燃料电池阳极构建及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(08): 1154-1160. |
| [15] | 任晓东, 熊振湖. 磁性多壁碳纳米管对水中三种硝基咪唑类药物的吸附行为[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(04): 625-633. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
