化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (10): 1379-1386.DOI: 10.6023/A23050220 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
刘稳a, 王昱捷a, 杨慧琴a, 李成杰b,*( ), 吴娜c,*(
), 吴娜c,*( ), 颜洋a,*(
), 颜洋a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-05-10
发布日期:2023-07-21
基金资助:
Wen Liua, Yujie Wanga, Huiqin Yanga, Chengjie Lib( ), Na Wuc(
), Na Wuc( ), Yang Yana(
), Yang Yana( )
)
Received:2023-05-10
Published:2023-07-21
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
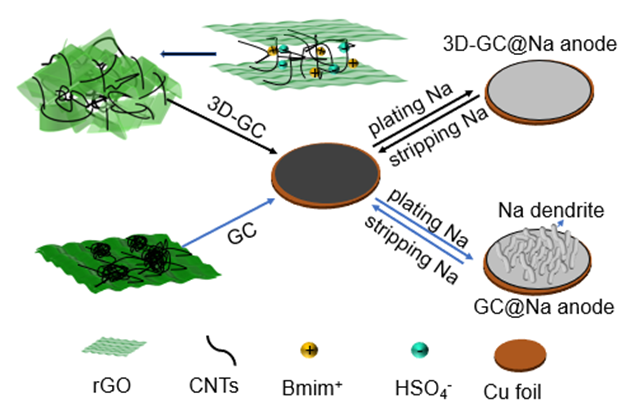
钠金属电池因丰富的钠资源储备在大规模储能中具有广泛的应用前景. 然而钠金属电池存在钠金属活性高、形成的固体电解质界面膜(SEI膜)不稳定、金属钠体积膨胀大等问题, 限制了其应用. 本工作利用离子液体与sp2碳间的非共价作用, 诱导碳纳米管和还原氧化石墨烯进行自组装, 制备得到了碳纳米管支撑的石墨烯高导电三维多孔碳(3D-GC)集流体. 制备得到的3D-GC具有三维多孔结构, 可以为金属钠提供较大的储存空间. 另外, 复合材料具有较高的导电性, 得到了较低的金属钠的沉积过电位(5.6 mV). 3D-GC@Na负极具有良好的电化学性能, 在电流密度为1 mA•cm−2, 沉积容量为1 mAh•cm−2时, 在240次充放电循环过程中始终保持了较高的库伦效率(CE), 平均CE为99.6%. 与Na3V2(PO4)2F3组装全电池也表现出优异的电化学性能.
刘稳, 王昱捷, 杨慧琴, 李成杰, 吴娜, 颜洋. 离子液体非共价诱导制备碳纳米管/石墨烯集流体用于钠金属负极[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1379-1386.
Wen Liu, Yujie Wang, Huiqin Yang, Chengjie Li, Na Wu, Yang Yan. The Preparation of Carbon Nanotubes/Reduced Graphene Oxide Current Collector by Non-covalent Induction of Ionic Liquid for Sodium Metal Anode[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(10): 1379-1386.









| [1] |
Wahid, M.; Puthusseri, D.; Gawli, Y.; Sharma, N.; Ogale, S. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 506.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v11.3 |
| [2] |
Kang, S. S.; Fan, S. C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y. C.; Li, Y.; Fang, J. G.; Meng, C. Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 647 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A19040119 |
|
(康树森, 范少聪, 刘岩, 魏彦存, 李营, 房金刚, 孟垂舟, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 647.)
|
|
| [3] |
Liang, S. S.; Kang, S. S.; Yang, D.; Hu, J. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1264 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A22040144 |
|
(梁世硕, 康树森, 杨东, 胡建华, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1264.)
|
|
| [4] |
Chen, Q. L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Xie, Q. S.; Zhang, Y. G.; Lin, J.; Qu, B. H.; Wang, L. S.; Sa, B. S.; Peng, D. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126469.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126469 |
| [5] |
Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Z.; Lei, Y. Y.; Zhou, D. L.; Wu, W. W.; Wu, X. H. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 926, 166850.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166850 |
| [6] |
Shi, H.; Zhang, Y. M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, C. Z. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, 202200112.
|
| [7] |
Liu, T. F.; Yang, X. K.; Nai, J. W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. J.; Liu, C. T.; Tao, X. Y. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 127943.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127943 |
| [8] |
Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Feng, X.; Chen, W.; Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. Chem 2019, 5, 2547.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.05.026 |
| [9] |
Xu, X. Y.; Li, Y. Y.; Cheng, J.; Hou, G. M.; Nie, X. K.; Ai, Q.; Dai, L. N.; Feng, J. K.; Ci, L. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 41, 73.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.05.003 |
| [10] |
Xie, D.; Li, H. H.; Diao, W. Y.; Jiang, R.; Tao, F. Y.; Sun, H. Z.; Wu, X. L.; Zhang, J. P. Energy Stor. Mater. 2021, 36, 504.
|
| [11] |
Wu, W.; Hou, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27300.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c07407 |
| [12] |
Eshetu, G. G.; Elia, G. A.; Armand, M.; Forsyth, M.; Komaba, S.; Rojo, T.; Passerini, S. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000093.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.20 |
| [13] |
Yan, J.; Zhi, G.; Kong, D. Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, T. T.; Zang, J. T.; Shen, W. X.; Xu, J. M.; Shi, Y. M.; Dai, S. G.; Li, X. J.; Wang, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 19843.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA05817C |
| [14] |
Zhao, C.; Lu, Y.; Yue, J.; Pan, D.; Qi, Y.; Hu, Y.-S.; Chen, L. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1584.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2018.03.004 |
| [15] |
Ma, C. Y.; Xu, T. T.; Wang, Y. Energy Stor. Mater. 2020, 25, 811.
|
| [16] |
Miao, R. Q.; Wang, C. Z.; Li, D. L.; Sun, C.; Li, J. B.; Jin, H. B. Small 2022, 18, 2204487.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v18.45 |
| [17] |
Fang, W.; Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C. H.; Xiang, H. F. J. Power Sources 2020, 455, 227956.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.227956 |
| [18] |
Seh, Z. W.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y. M.; Cui, Y. ACS Cent. Sci. 2015, 1, 449.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.5b00328 |
| [19] |
Zhao, L. F.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Z. Y.; Tao, Y.; Lai, W. H.; Zhao, A. L.; Liu, Q. N.; Peng, J.; Lei, Y. J.; Wang, Y. X.; Cao, Y. L.; Wu, C.; Chou, S. L.; Liu, H. K.; Dou, S. X. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200990.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v12.32 |
| [20] |
Zhu, M.; Wang, G. Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, B. K.; Xu, G.; Huang, Z. Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, H. K.; Dou, S. X.; Wu, C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6596.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.16 |
| [21] |
Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liang, J.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 864.
doi: 10.1039/C7QI00802C |
| [22] |
Xiong, W. S.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Qi, Y. Y.; Sun, W. W.; He, D.; Liu, Y. M.; Zhao, X. Z. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9406.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC03996H |
| [23] |
Xu, Y. L.; Menon, A. S.; Harks, P. P. R. M. L.; Hermes, D. C.; Haverkate, L. A.; Unnikrishnan, S.; Mulder, F. M. Energy Stor. Mater. 2018, 12, 69.
|
| [24] |
Chu, C. X.; Wang, N. N.; Li, L. L.; Lin, L. D.; Tian, F.; Li, Y. L.; Yang, J.; Dou, S. X.; Qian, Y. T. Energy Stor. Mater. 2019, 23, 137.
|
| [25] |
Park, B.; Oh, S. M.; Jin, X.; Adpakpang, K.; Lee, N. S.; Hwang, S. J. Chem 2017, 23, 6544.
|
| [26] |
Liu, H. J.; Osenberg, M.; Ni, L.; Hilger, A.; Chen, L. B.; Zhou, D.; Dong, K.; Arlt, T.; Yao, X. Y.; Wang, X. G.; Manke, I.; Sun, F. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 61, 61.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.03.004 |
| [27] |
Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. F.; Kuo, L. Y.; Kaghazchi, P.; Sun, Q.; Liang, J. N.; Wang, B. Q.; Lushington, A.; Li, R. Y.; Zhang, H. M.; Sun, X. L. Small 2018, 14, 1703717.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v14.20 |
| [28] |
Zheng, Z.; Zeng, X. X.; Ye, H.; Cao, F. F.; Wang, Z. B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30417.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b10292 |
| [29] |
Sui, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 382.
doi: 10.6023/A13080884 |
| [30] |
Olsson, E.; Chai, G.; Dove, M.; Cai, Q. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5274.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR10383F |
| [31] |
Wang, A. X.; Hu, X. F.; Tang, H. Q.; Zhang, C. Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y. W.; Yang, Q. H.; Luo, J. Y. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 11921.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v56.39 |
| [32] |
Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Kou, Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Zhuang, Q. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2457.
doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2007.07.017 |
| [33] |
Yan, Y.; Li, P. Q.; Gu, Z. Y.; Liu, W.; Cao, J. M.; Wu, X. L. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134195.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.134195 |
| [34] |
Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Niu, Z. Y.; Yan, Y.; Qiao, L. Z.; Wu, N. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200752.
doi: 10.1002/admi.v9.24 |
| [35] |
Li, P. Q. M.S. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, 2022 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 李培权, 硕士论文,大连理工大学,大连, 2022.)
|
| [1] | 曾少娟, 孙雪琦, 白银鸽, 白璐, 郑爽, 张香平, 张锁江. CO2捕集分离的功能离子液体及材料研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 627-645. |
| [2] | 赵天成, 蒋鸿宇, 张琨, 徐一帆, 康欣悦, 胥鉴宸, 周旭峰, 陈培宁, 彭慧胜. 基于环烷烃/乙醇混合碳源高性能碳纳米管纤维的连续化制备[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 565-571. |
| [3] | 成受明, 周波. 基于超高分辨质谱的溶解性有机质分子转化机理分析[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1106-1114. |
| [4] | 李晓倩, 张靖, 苏芳芳, 王德超, 姚东东, 郑亚萍. 多孔离子液体的构筑及应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 848-860. |
| [5] | 王超峰, 郑国栋, 王悦, 宋慧佳, 陈小艺, 高瑞霞. 金属卟啉-Sn网络可控非共价功能化碳纳米管的制备及蛋白吸附应用[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 126-132. |
| [6] | 武文俊, 李玉婷, 冯茜, 丁文星. 钙钛矿双功能钝化剂: 室温离子液体的机械化学制备[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1469-1475. |
| [7] | 王赫男, 张安歌, 张仲, 田洪瑞, 岳倩, 赵雪, 鹿颖, 刘术侠. 基于稀土阳离子和多酸阴离子的系列纯无机离子液体的合成及性质[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 920-924. |
| [8] | 张欣欣, 刘荣, 王蕾, 付宏刚. 细菌纤维素基柔性锌离子电池正极的构筑及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 670-677. |
| [9] | 吕玉苗, 陈伟, 王艳磊, 霍锋, 董依慧, 魏莉, 何宏艳. 离子液体二维结构制备及其特性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 443-458. |
| [10] | 宋光捷, 武调弟, 刘福鑫, 张彬雁, 刘秀辉. 壳聚糖/氮掺杂还原氧化石墨烯修饰电极对黄嘌呤的检测及尿酸抑制的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(1): 82-88. |
| [11] | 崔丽瑞, 张劲, 孙一焱, 卢善富, 相艳. 碳纳米管添加剂对质子交换膜燃料电池低铂载量膜电极性能的影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 47-53. |
| [12] | 朱明晶, 彭娟, 唐萍, 邱枫. 高稳定性和水溶性的共轭聚电解质/单壁碳纳米管复合物的制备和表征[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(6): 453-459. |
| [13] | 王引航, 李伟, 罗沙, 刘守新, 马春慧, 李坚. 离子液体固载型功能材料的应用研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(2): 85-94. |
| [14] | 邱华玉, 赵井文, 周新红, 崔光磊. 离子液体-无机颗粒杂化电解质在二次电池中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 749-756. |
| [15] | 李磊, 贾桂霄, 王晓霞, 吴铜伟, 宋希文, 安胜利. 基于缺陷曲率对含有V1~V4空位(5,5)单壁碳纳米管[1+1]和[2+1]加成反应的第一性原理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(3): 284-292. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||