Acta Chimica Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (12): 1481-1485.DOI: 10.6023/A21080405 Previous Articles Next Articles
Article
投稿日期:2021-08-27
发布日期:2021-10-21
通讯作者:
姚建林
基金资助:
Hongyu Yuan, Minmin Xu, Jianlin Yao( )
)
Received:2021-08-27
Published:2021-10-21
Contact:
Jianlin Yao
Supported by:Share
Hongyu Yuan, Minmin Xu, Jianlin Yao. SERS Studies on the Electrochemical and SPR Synergistic Catalytic Interfacial Reaction of 4-Chlorothiophenol[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1481-1485.
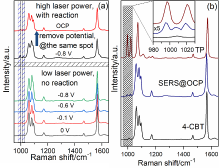
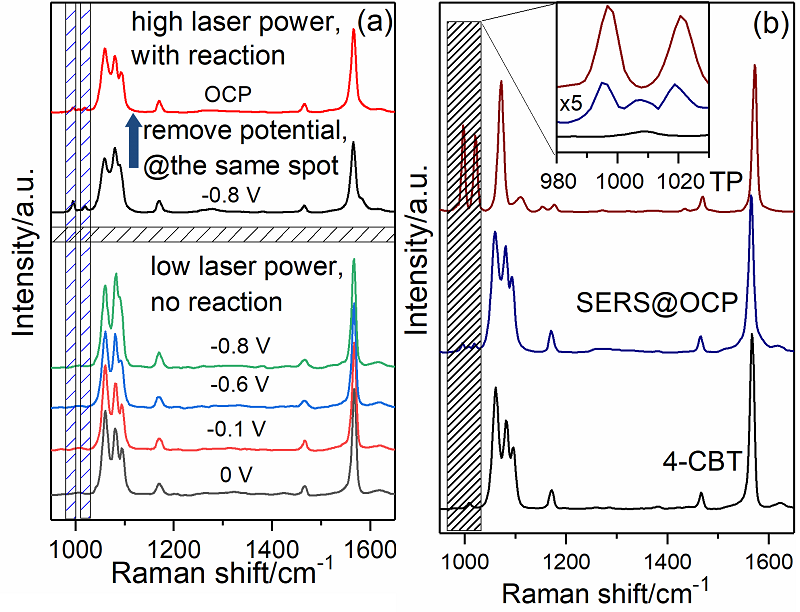
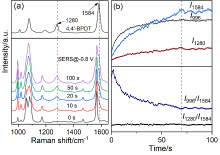

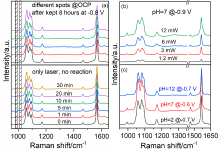
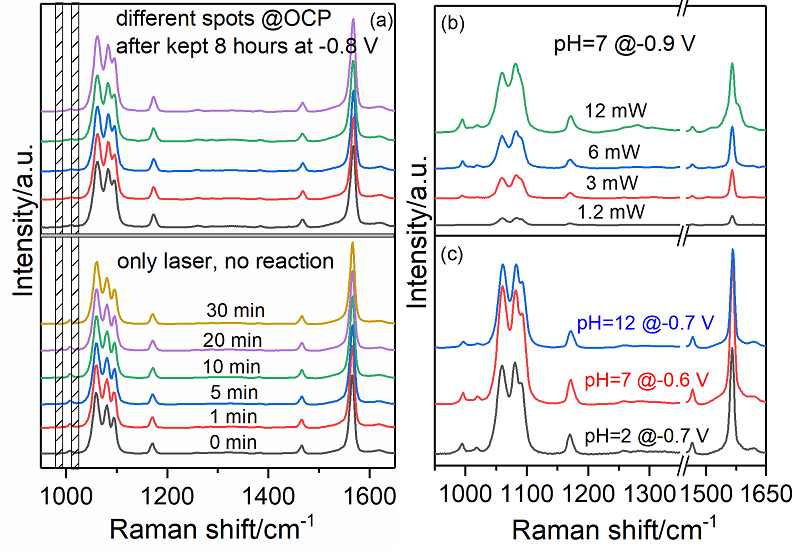
| [1] |
Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P. J.; McQuillan, A. J. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163.
doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(74)85388-1 |
| [2] |
Yi, R.-N.; Wu, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 694 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21010017 |
|
( 易荣楠, 吴燕, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 694.)
doi: 10.6023/A21010017 |
|
| [3] |
He, H.; Zhou, L.-L.; Liu, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 45 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20080364 |
|
( 贺晖, 周玲俐, 刘震, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 45.)
doi: 10.6023/A20080364 |
|
| [4] |
Perez-Jimenez, A. I.; Lyu, D.; Lu, Z.-X.; Liu, G.-K.; Ren, B. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4563.
doi: 10.1039/D0SC00809E |
| [5] |
Cheng, J.; Wang, P.-L.; Su, X.-O. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 977 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A19040139 |
|
( 程劼, 王培龙, 苏晓鸥, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 977.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040139 |
|
| [6] |
Homola, J.; Yee, S. S.; Gauglitz, G. Sens. Actuators, B 1999, 54, 3.
doi: 10.1016/S0925-4005(98)00321-9 |
| [7] |
Haes, A. J.; Haynes, C. L.; McFarland, A. D.; Schatz, G. C.; Van Duyne, R. P.; Zou, S.-L. MRS Bull. 2005, 30, 368.
doi: 10.1557/mrs2005.100 |
| [8] |
Knobloch, H.; Brunner, H.; Leitner, A.; Aussenegg, F.; Knoll, W. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10093.
doi: 10.1063/1.464398 |
| [9] |
Wark, A. W.; Lee, H. J.; Corn, R. M. Anat. Chem. 2005, 77, 3904.
doi: 10.1021/ac050402v |
| [10] |
Brockman, J. M.; Nelson, B. P.; Corn, R. M. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2000, 51, 41.
pmid: 11031275 |
| [11] |
Cui, Y.-X.; He, S.-L. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 16.
doi: 10.1364/OL.34.000016 |
| [12] |
Zhao, L.-B.; Huang, Y.-F.; Wu, D.-Y.; Ren, B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 1125 ( in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A14080602 |
|
( 赵刘斌, 黄逸凡, 吴德印, 任斌, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 1125.)
doi: 10.6023/A14080602 |
|
| [13] |
Halas, N. J.; Lal, S.; Chang, W.-S.; Link, S.; Nordlander, P. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3913.
doi: 10.1021/cr200061k |
| [14] |
Jahn, M.; Patze, S.; Hidi, I. J.; Knipper, R.; Radu, A. I.; Mühlig, A.; Yüksel, S.; Peksa, V.; Weber, K.; Mayerhöfer, T.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J. Analyst 2016, 141, 756.
doi: 10.1039/C5AN02057C |
| [15] |
Schlücker, S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4756.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201205748 |
| [16] |
Liebermann, T.; Knoll, W. Colloids Surf. 2000, 171, 115.
doi: 10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00550-6 |
| [17] |
Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Zheng, H.-R.; Sun, M.-T. Nanophotonics 2015, 4, 472.
doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2015-0028 |
| [18] |
Lindstrom, C. D.; Zhu, X.-Y. Chem. Rev. 2002, 106, 4281.
doi: 10.1021/cr0501689 |
| [19] |
Kamat, P. V. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7729.
doi: 10.1021/jp0209289 |
| [20] |
Kamat, P. V. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 2834.
doi: 10.1021/jp066952u |
| [21] |
Wu, D.-Y.; Li, J.-F.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z.-Q. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1025.
doi: 10.1039/b707872m |
| [22] |
Wu, D.-Y.; Ren, B.; Xu, X.; Liu, G.-K.; Yang, Z.-L.; Tian, Z.-Q. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 1701.
|
| [23] |
Wu, D.-Y.; Ren, B.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Xu, X.; Tian, Z.-Q. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 9042.
doi: 10.1021/jp025970i |
| [24] |
Zhao, L.-L.; Jensen, L.; Schatz, G. C. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1229.
pmid: 16771585 |
| [25] |
Zhang, X.; Wang, P.-J.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Fang, Y.-R.; Sun, M.-T. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5407.
doi: 10.1038/srep05407 pmid: 24958029 |
| [26] |
Li, X.; Zhang, C.-J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, M.-M.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Yao, J.-L. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 1928.
doi: 10.1002/jrs.v49.12 |
| [27] |
Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.-J.; Lu, Y.-H.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Xu, M.-M.; Yao, J.-L. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2020, 51, 2199.
doi: 10.1002/jrs.v51.11 |
| [28] |
Xiao, F.-X.; Liu, B. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1701098.
doi: 10.1002/admi.v5.6 |
| [29] |
Ding, C.-M.; Shi, J.-Y.; Wang, Z.-L.; Li, C. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 675.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b03107 |
| [30] |
Yao, T.-T.; An, X.-R.; Han, H.-X.; Chen, J.-Q.; Li, C. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800210.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.21 |
| [31] |
Liu, B.; Wen, L.; Zhao, X. Prog. Org. Coat. 2009, 64, 120.
doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2008.09.014 |
| [32] |
Ferraz, E. R. A.; Oliveira, G. A. R.; Grando, M. D.; Lizier, T. M.; Zanoni, M. V. B.; Oliveira, D. P. J. Environ. Manage. 2013, 124, 108.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.03.033 pmid: 23624428 |
| [33] |
Li, Y.-L.; Hu, Y.-F.; Shi, F.-X.; Li, H.-X.; Xie, W.; Chen, J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9049.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.27 |
| [34] |
Frens, G. Nature Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20.
doi: 10.1038/physci241020a0 |
| [35] |
Guo, Q.-H.; Xu, M.-M.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Gu, R.-A.; Yao, J.-L. Langmuir 2016, 32, 4530.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b04393 |
| [36] |
Zhang, C.-J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.-R.; Jin, Q.; Xu, M.-M.; Yao, J.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2017, 75, 860 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A17050198 |
|
( 张晨杰, 张婧, 林洁茹, 金琦, 徐敏敏, 姚建林, 化学学报, 2017, 75, 860.)
doi: 10.6023/A17050198 |
| [1] | Zeng Chongyang, Hu Ping, Wang Biqin, Fang Wenyan, Zhao Keqing, Donnio Bertrand. Star-shaped Triphenylene-triazine Multi-stimuli Responsive Discotic Liquid Crystals: Synthesis, Properties and Applications [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 469-479. |
| [2] | Yuan Fangyan, Li Chao, Luo Meiming, Zeng Xiaoming. Chromium-Catalyzed Carbonyl-Carbonyl Deoxygenative Couplings of Ketones to Tetrasubstituted Olefins★ [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 456-460. |
| [3] | Mingliang Han, Lihua Xu. Progress on the Transition Metal-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reaction of Thioesters [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(4): 381-392. |
| [4] | Xingyu Ma, Hui Sun, Jiang Li, Zhiyang Liu, Hongjun Zhou. “Continuous” Nitrogen Reduction Synthesis of Ammonia Based on Li-N2 Battery System [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 861-866. |
| [5] | Guanglu Yue, Jingyao Wei, Di Qiu, Fanyang Mo. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Arylstannanes [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(7): 956-969. |
| [6] | Yiding Wang, Fuhai Li, Qingle Zeng. Advances in Formation of C—X Bonds via Cleavage of C—N Bond of Quaternary Ammonium Salts [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 386-394. |
| [7] | Jinyue Ma, Lufei Huang, Baowen Zhou, Lin Yao. Construction and Catalysis Advances of Inorganic Chiral Nanostructures [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(11): 1507-1523. |
| [8] | Yao Zhai, Guoxiang Xin, Jiaqi Wang, Bangwen Zhang, Jinling Song, Xiaoxu Liu. Microwave-assisted Synthesis of rGO/CeO2 Supercapacitor Electrode Materials with Excellent Electrochemical Properties [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(9): 1129-1137. |
| [9] | Yang Shang, Jian Xiao, Yawen Wang, Yu Peng. Advances on Asymmetric Construction of Diarylmethine Stereocenters [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(11): 1303-1319. |
| [10] | Liu Ji-Lin, Yu Kai, Zhang Hong, Jiang Jie. Progress in the Study of Electrochemical Reaction by Mass Spectrometric Ionization Sources [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(6): 504-515. |
| [11] | Liu, Yu-Cheng, Zheng, Xiao, Huang, Pei-Qiang. Photoredox Catalysis for the Coupling Reaction of Nitrones with Aromatic Tertiary Amines [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2019, 77(9): 850-855. |
| [12] | Xu Shuya, Liu Zhihong, Zhang Huai, Yu Jinran. Preparation and Properties of Piezotronics Enhanced Plasmonic Photocatalytic Material by Ag/BaTiO3 [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(5): 427-433. |
| [13] | Zuo Fangtao, Xu Wei, Zhao Aiwu. A SERS Approach for Rapid Detection of Hg2+ Based on Functionalized Fe3O4@Ag Nanoparticles [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(4): 379-386. |
| [14] | Liu Jiao, Sun Hailong, Yin Lu, Yuan Yaxian, Xu Minmin, Yao Jianlin. On-line Monitoring on the Micro-synthesis of α-Phenylethanol by Microfluidic Chip Combined with Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(3): 257-262. |
| [15] | Wang Meng, Yan Xin, Wei Dequan, Liang Lanju, Wang Yueping. Application of Au/Ag Composite Nanocages in Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy [J]. Acta Chim. Sinica, 2019, 77(2): 184-188. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||