化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (8): 1049-1057.DOI: 10.6023/A21050194 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 分子探针、纳米生物学与生命分析化学
研究论文
投稿日期:2021-05-06
发布日期:2021-06-09
通讯作者:
李贞, 刘志洪
基金资助:
Ju Huanga, Zhen Lib( ), Zhihong Liua,b(
), Zhihong Liua,b( )
)
Received:2021-05-06
Published:2021-06-09
Contact:
Zhen Li, Zhihong Liu
Supported by:文章分享

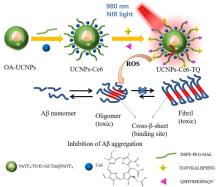
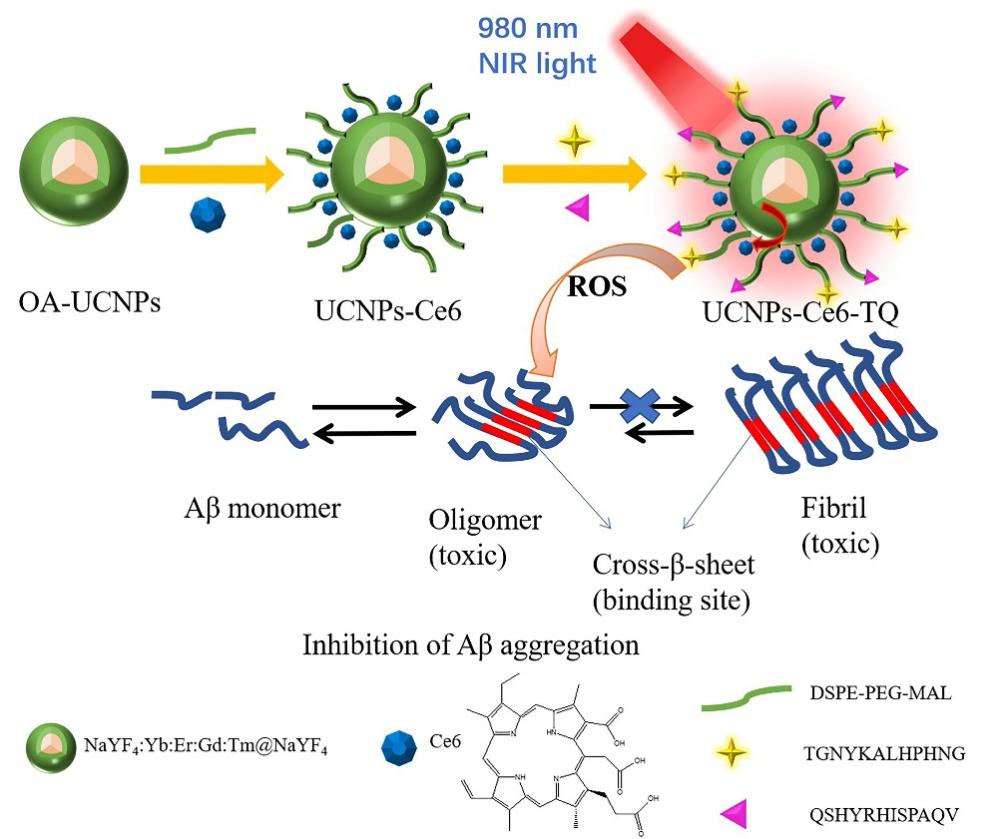
阿尔兹海默症(AD)是一种进行性神经退行性疾病, 其特征是记忆力减退、神志不清和各种认知障碍. β-淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)的自组装聚集是阿尔茨海默症患者大脑的主要特征之一, 其加剧了AD患者的神经病变和认知障碍, 因此抑制Aβ聚集是一种潜在的治疗AD的策略. 光动力疗法是抑制Aβ聚集和解聚Aβ聚集体的有效方法. 然而, 大多数光敏剂为紫外和可见光激发, 在生物组织中的渗透深度低, 并引起严重的组织损伤, 这限制了其在生物医学中的应用. 本工作构建了一种近红外光激发的双靶向上转换纳米体系应用于抑制Aβ聚集过程. 以核壳结构的上转换纳米颗粒(UCNPs)作为光转换器, 通过两亲聚合物二硬脂酰基磷脂酰乙醇胺-聚乙二醇-马来酰亚胺(DSPE-PEG-MAL)的疏水包覆作用负载光敏剂二氢卟吩e6 (Ce6), 在纳米颗粒表面通过马来酰亚胺与巯基的特异性反应修饰了可跨越血脑屏障的肽链TGN和靶向Aβ42的肽链QSH. 实验结果表明在近红外光激发下UCNPs通过发光共振能量转移(LRET)将能量转移至光敏剂Ce6, 使其跃迁至激发态后与周围的氧气分子作用产生单线态氧(1O2), 不可逆地氧化Aβ, 从而有效解聚了Aβ聚集体, 降低了Aβ聚集体的神经毒性. 此外, 该体系不仅具有良好的生物相容性, 而且可以有效穿过血脑屏障靶向作用于Aβ42, 显示出其在活体水平治疗AD的潜力.
黄菊, 李贞, 刘志洪. 近红外光激发功能化上转换纳米颗粒用于解聚Aβ聚集体[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1049-1057.
Ju Huang, Zhen Li, Zhihong Liu. Functionalized Upconversion Nanoparticles for Disassembly of β‑Amyloid Aggregation with Near-Infrared Excitation[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(8): 1049-1057.
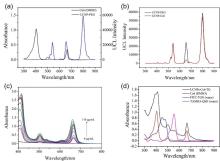
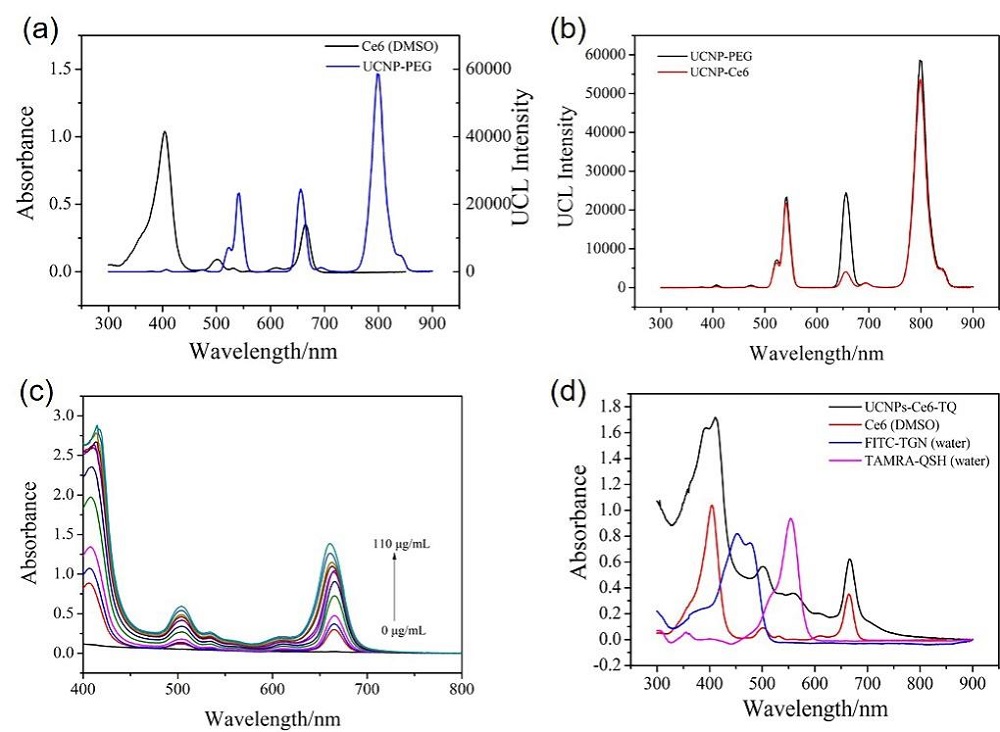
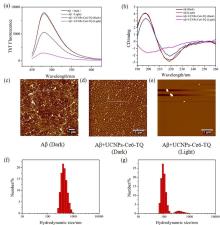
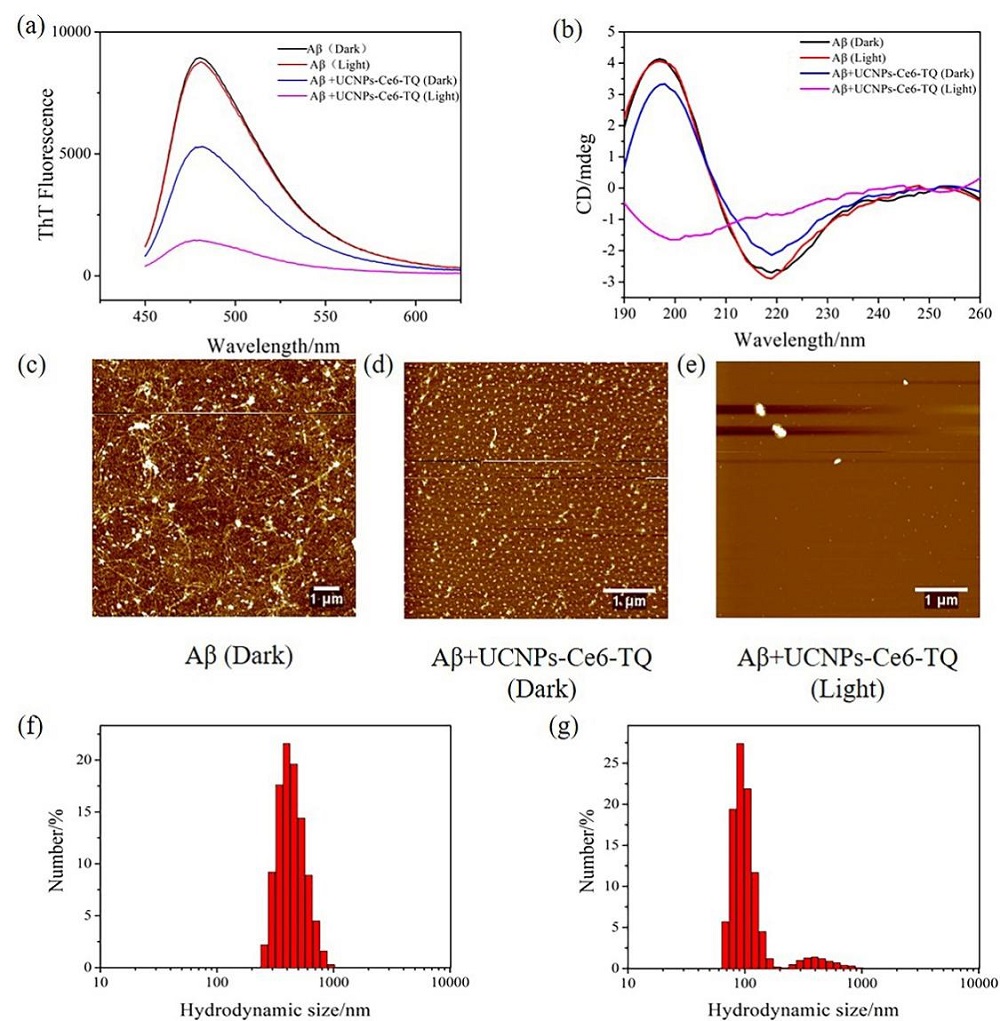

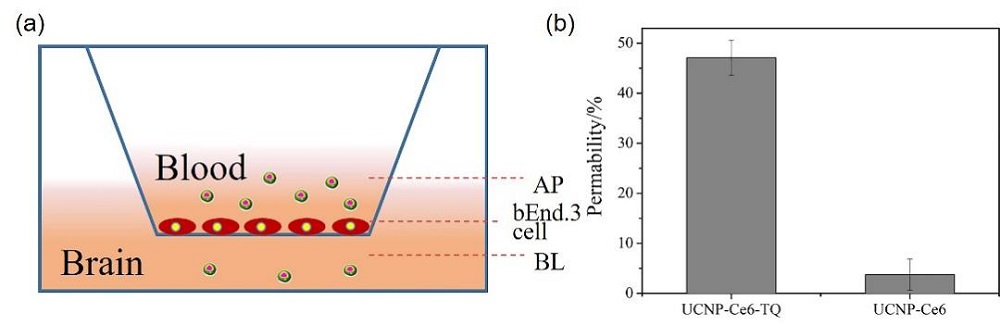
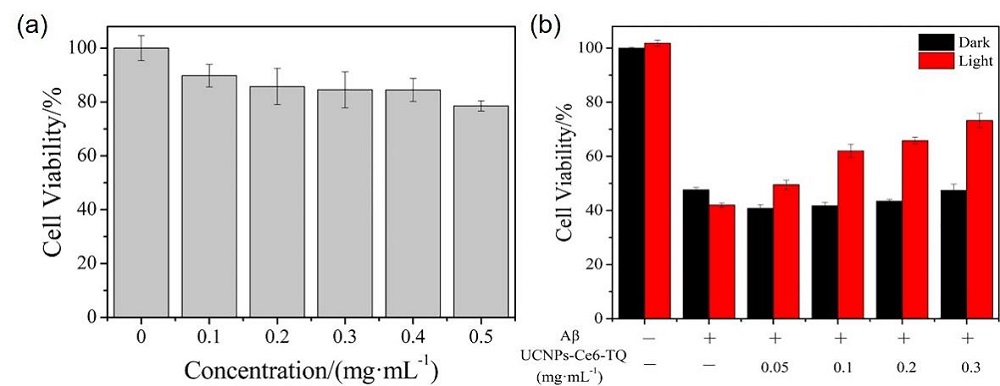
| [1] |
Alzheimer's, association, Alzheimer's Dementia 2016, 12, 459.
doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.03.001 |
| [2] |
Savelieff, M. G.; Nam, G.; Kang, J.; Lee, H. J.; Lee, M.; Lim, M. H. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1221.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00138 pmid: 30095897 |
| [3] |
Iadanza, M. G.; Jackson, M. P.; Hewitt, E. W.; Ranson, N. A.; Radford, S. E. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2018, 19, 755.
doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0060-8 |
| [4] |
Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D. J. Science 2002, 297, 353.
pmid: 12130773 |
| [5] |
Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Li, S. -L.; Zhou, L. -Y.; Wang, J. -W.; Liu, L. -B.; Lv, F. -T.; Gu, Q.; Hu, B. -Y.; Ma, Y. -G.; Wang, S. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5988.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.18 |
| [6] |
Fan, L. -Y.; Mao, C. -Y.; Hu, X. -C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z. -H.; Hu, Z. -H.; Sun, H. -F.; Fan, Y.; Dong, Y. -L.; Yang, J.; Shi, C. -H.; Xu, Y. -M. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1312.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01312 |
| [7] |
De Strooper,, B.; Vassar,, R.; Golde,, T. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 99.
doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2009.218 pmid: 20139999 |
| [8] |
Wilquet, V.; De Strooper, B. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 582.
doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.08.001 |
| [9] |
Haass, C.; Selkoe, D. J. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2007, 8, 101.
doi: 10.1038/nrm2101 |
| [10] |
Lee, S. J.C.; Nam, E.; Lee, H. J.; Savelieff, M. G.; Lim, M. H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 310.
doi: 10.1039/C6CS00731G |
| [11] |
Ehrnhoefer, D. E.; Bieschke, J.; Boeddrich, A.; Herbst, M.; Masino, L.; Lurz, R.; Engemann, S.; Pastore, A.; Wanker, E. E. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 558.
doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1437 pmid: 18511942 |
| [12] |
Taniguchi, A.; Sasaki, D.; Shiohara, A.; Iwatsubo, T.; Tomita, T.; Sohma, Y.; Kanai, M. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1382.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v53.5 |
| [13] |
Lee, B. I.; Lee, S.; Suh, Y. S.; Lee, J. S.; Kim, A. -k.; Kwon, O. Y.; Yu, K.; Park, C. B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11472.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v54.39 |
| [14] |
Suh, J. -M.; Kim, G.; Kang, J.; Lim, M. H. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 8.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b02813 |
| [15] |
Guan, Y. -J.; Du, Z.; Gao, N.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X. -H.; Scott, P.; Song, H. -L.; Ren, J. -S.; Qu, X. -G. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao6718.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aao6718 |
| [16] |
Goyal, D.; Shuaib, S.; Mann, S.; Goyal, B. ACS Comb. Sci. 2017, 19, 55.
doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.6b00116 |
| [17] |
Xiong, N.; Dong, X. -Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, F. -F.; Sun, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 5650.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b00915 |
| [18] |
Niu, L.; Liu, L.; Xi, W. -H.; Han, Q. -S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Q. -X.; Qu, F. -Y.; Xu, M.; Li, Y. -B.; Du, H. -W.; Yang, R.; Cramer, J.; Gothelf, K. V.; Dong, M. -D.; Besenbacher, F.; Zeng, Q. -D.; Wang, C.; Wei, G-H.; G-H., Y. -L. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4143.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07396 |
| [19] |
Han, Q. -S.; Cai, S. -F.; Yang, L.; Wang, X. -H.; Qi, C.; Yang, R.; Wang, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 21116.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b03816 |
| [20] |
Zhang, Z. -M.; Wang, J.; Song, Y. -X.; Wang, Z. -K.; Dong, M. -D.; Liu, L. Colloid. Surface. B 2019, 181, 341.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.053 |
| [21] |
Zhang, J. -Y.; Liu, J. -P.; Zhu, Y. -Y.; Xu, Z. -A.; Xu, J.; Wang, T. -T.; Yu, H. -J.; Zhang, W. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12044.
doi: 10.1039/C6CC06175C |
| [22] |
Ke, P. C.; Pilkington, E. H.; Sun, Y.; Javed, I.; Kakinen, A.; Peng, G.; Ding, F.; Davis, T. P. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901690.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.18 |
| [23] |
Yu, D. -Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H. -C.; Ren, J. -S.; Qu, X. -G. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 4963.
doi: 10.1039/D0SC07067J |
| [24] |
Du, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, J. -S.; Qu, X. -G. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2172.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00055 |
| [25] |
Furtado, D.; Björnmalm, M.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A. I.; Kempe, K.; Caruso, F. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801362.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.46 |
| [26] |
Ali, I. U.; Chen, X. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9470.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b05341 |
| [27] |
Yan, T.; Liu, Z. -H.; Song, X. -Y.; Zhang, S. -S. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 657 (in Chinese.)
doi: 10.6023/A20040132 |
|
( 闫涛, 刘振华, 宋昕玥, 张书圣 化学学报 2020, 78, 657.)
doi: 10.6023/A20040132 |
|
| [28] |
Li, M. -L.; Peng, X. -J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 959 (in Chinese.)
doi: 10.6023/A16100553 |
|
( 李明乐, 彭孝军, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 959.)
doi: 10.6023/A16100553 |
|
| [29] |
Liu, W.; Dong, X. -Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y. Acta Biomater. 2021, 123, 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.01.018 |
| [30] |
Lee, B. I.; Chung, Y. J.; Park, C. B. Biomaterials 2019, 190-191, 121.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.10.043 |
| [31] |
Tang, Y. -F.; Pei, F.; Lu, X. -M.; Fan, Q. -L.; Huang, W. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1900917.
doi: 10.1002/adom.v7.21 |
| [32] |
Liu, H. -W.; Zhu, L. -M.; Lou, X. -F.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X. -B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1240 (in Chinese.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070323 |
|
( 刘红文, 朱隆民, 娄霄峰, 袁林, 张晓兵, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1240.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070323 |
|
| [33] |
Yang, Y.; Liu, H. -L.; Han, M. -J.; Sun, B. -B.; Li, J. -B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13538.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201605905 |
| [34] |
Dong, H.; Du, S. -R.; Zheng, X. -Y.; Lyu, G. -M.; Sun, L. -D.; Li, L. -D.; Zhang, P. -Z.; Zhang, C.; Yan, C. -H. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10725.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00091 pmid: 26151155 |
| [35] |
Chen, G. -Y.; Qiu, H. -L.; Prasad, P. N.; Chen, X. -Y. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5161.
doi: 10.1021/cr400425h |
| [36] |
Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, F. -Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1323.
doi: 10.1039/C1CS15187H |
| [37] |
Zheng, W.; Huang, P.; Tu, D. -T.; Ma, E.; Zhu, H. -M.; Chen, X. -Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1379.
doi: 10.1039/c4cs00178h pmid: 25093303 |
| [38] |
Wang, P. -P.; Liang, T.; Zuo, M. -M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. -H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 797 (in Chinese.)
doi: 10.6023/A20050146 |
|
( 王培培, 梁涛, 左苗苗, 李贞, 刘志洪, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 797.)
doi: 10.6023/A20050146 |
|
| [39] |
Idris, N. M.; Jayakumar, M. K.G.; Bansal, A.; Zhang, Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1449.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00158C |
| [40] |
Yang, D. -M.; Ma, P. A.; Hou, Z. -Y.; Cheng, Z. -Y.; Li, C. -X.; Lin, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1416.
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00155A |
| [41] |
Hao, C. -L.; Wu, X. -L.; Sun, M. -Z.; Zhang, H. -Y.; Yuan, A. -M.; Xu, L. -G.; Xu, C. -L.; Kuang, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19373.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b09360 |
| [42] |
Zhu, X. -J.; Li, J. -C.; Qiu, X. -C.; Liu, Y.; Feng, W.; Li, F. -Y. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2176.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04571-4 |
| [43] |
Zhao, J.; Chu, H. -Q.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, L. -L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7056.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01931 |
| [44] |
Xu, J.; Xu, L. -G.; Wang, C. -Y.; Yang, R.; Zhuang, Q.; Han, X.; Dong, Z. -L.; Zhu, W. -W.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4463.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b00715 |
| [45] |
Zhou, Y. -Q.; Peng, Z. -L.; Seven, E. S.; Leblanc, R. M. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 290.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.015 |
| [46] |
Li, J. -W.; Feng, L.; Fan, L.; Zha, Y.; Guo, L-R.; Zhang, Q. -Z.; Chen, J.; Pang, Z. -Q.; Wang, Y. -C.; Jiang, X. -G.; Yang, V. C.; Wen, L. -P.. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4943.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.03.031 |
| [47] |
Yang, L. -C.; Sun, J.; Xie, W. -J.; Liu, Y. -N.; Liu, J. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5954.
doi: 10.1039/C6TB02952C |
| [48] |
Wiesehan, K.; Buder, K.; Linke, R. P.; Patt, S.; Stoldt, M.; Unger, E.; Schmitt, B.; Bucci, E.; Willbold, D. ChemBioChem 2003, 4, 748.
pmid: 12898626 |
| [49] |
Zhang, C.; Zheng, X. -Y.; Wan, X.; Shao, X. -Y.; Liu, Q. -F.; Zhang, Z. -M.; Zhang, Q. -Z. J. Control. Release 2014, 192, 317.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.07.050 |
| [50] |
Zhang, C.; Wan, X.; Zheng, X. -Y.; Shao, X. -Y.; Liu, Q. -F.; Zhang, Q. -Z.; Qian, Y. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 456.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.063 pmid: 24099709 |
| [51] |
Biancalana, M.; Koide, S. BBA-Proteins Proteomics 2010, 1804, 1405.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.04.001 |
| [52] |
Younan, N. D.; Viles, J. H. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 4297.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00309 |
| [53] |
Bartolini, M.; Bertucci, C.; Bolognesi, M. L.; Cavalli, A.; Melchiorre, C.; Andrisano, V. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 2152.
pmid: 17939148 |
| [54] |
Abbott, N. J.; Patabendige, A. A.; Dolman, D. E.; Yusof, S. R.; Begley, D. J. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13.
doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030 pmid: 19664713 |
| [55] |
Srinivasan, B.; Kolli, A. R.; Esch, M. B.; Abaci, H. E.; Shuler, M. L.; Hickman, J. J. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 107.
doi: 10.1177/2211068214561025 pmid: 25586998 |
| [56] |
Wei, Y.; Lu, F. -Q.; Zhang, X. -R.; Chen, D. -P. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5733.
doi: 10.1021/cm0606171 |
| [1] | 王海朋, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 抗冻剂抗冻机制的近红外光谱与分子模拟研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1167-1174. |
| [2] | 张媛, 郑贝宁, 符美春, 冯守华. 尖晶石氧化物在肿瘤诊疗应用领域研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 949-954. |
| [3] | 吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜. 过氧化氢激活型近红外氟硼二吡咯光敏剂的设计、合成及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 359-370. |
| [4] | 闫英红, 梁平兆, 邹杨, 袁林, 彭孝军, 樊江莉, 张晓兵. 有机光敏剂结构与性能调控及其光诊疗应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1642-1662. |
| [5] | 刘巴蒂, 王承俊, 钱鹰. 噻吩基氟硼二吡咯近红外光敏染料的合成、双光子荧光成像及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1071-1083. |
| [6] | 刘若湄, 冯艳辉, 李卓, 卢珊, 关天用, 李幸俊, 刘䶮, 陈卓, 陈学元. 基于cypate光裂解的新型近红外光响应稀土上转换纳米载药系统※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 423-427. |
| [7] | 王其, 夏辉, 熊炎威, 张新敏, 蔡杰, 陈冲, 高逸聪, 陆峰, 范曲立. 调控供电子策略简易制备近红外二区有机小分子光学诊疗试剂[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1485-1493. |
| [8] | 潘立祥, 黄艳琴, 盛况, 张瑞, 范曲立, 黄维. 透明质酸纳米材料在荧光/光声成像和光疗中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1097-1106. |
| [9] | 闫涛, 刘振华, 宋昕玥, 张书圣. 肿瘤微环境刺激响应型上转换光动力诊疗体系的构建和发展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(7): 657-669. |
| [10] | 汪明圆, 崔晓宇, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 温控近红外光谱用于葡萄糖的高灵敏检测[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 125-129. |
| [11] | 焦阳, 张希. 超分子自由基:构筑、调控与功能[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(9): 659-665. |
| [12] | 朱雪薇, 崔晓宇, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 温控近红外光谱用于胺类化合物氢键相互作用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(4): 298-302. |
| [13] | 祁丽华, 蔡文生, 邵学广. 直链烷烃近红外光谱的温度效应与应用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(2): 172-178. |
| [14] | 邵学广, 宁宇, 刘凤霞, 李积慧, 蔡文生. 近红外光谱在无机微量成分分析中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(20): 2109-2114. |
| [15] | 吴晓静,许晓娜. MgCl2/甲醇溶液的近红外光谱研究及量子计算[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(6): 535-540. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||