化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (12): 1526-1533.DOI: 10.6023/A21070324 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
梁其梅a, 郭昱娇b, 郭俊明a,*( ), 向明武a,*(
), 向明武a,*( ), 刘晓芳a, 白玮a, 宁平b
), 刘晓芳a, 白玮a, 宁平b
投稿日期:2021-07-13
发布日期:2021-11-02
通讯作者:
郭俊明, 向明武
基金资助:
Qimei Lianga, Yujiao Guob, Junming Guoa( ), Mingwu Xianga(
), Mingwu Xianga( ), Xiaofang Liua, Wei Baia, Ping Ningb
), Xiaofang Liua, Wei Baia, Ping Ningb
Received:2021-07-13
Published:2021-11-02
Contact:
Junming Guo, Mingwu Xiang
Supported by:文章分享

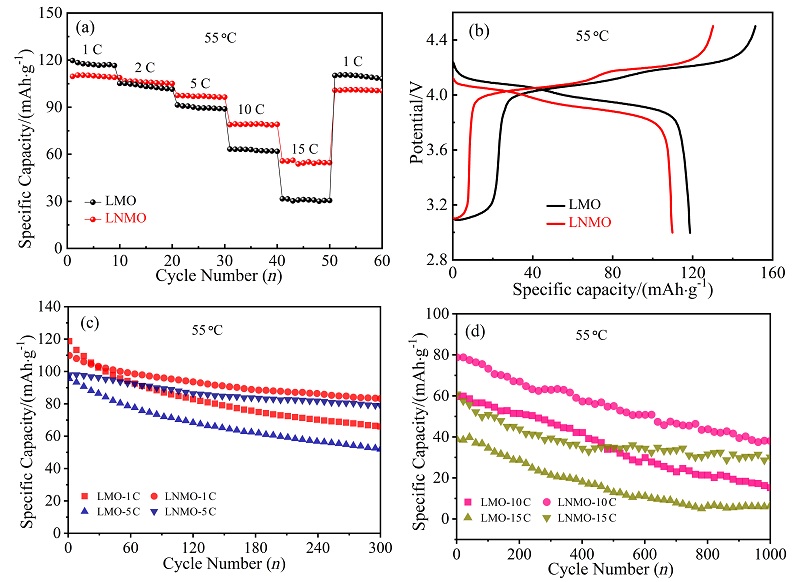
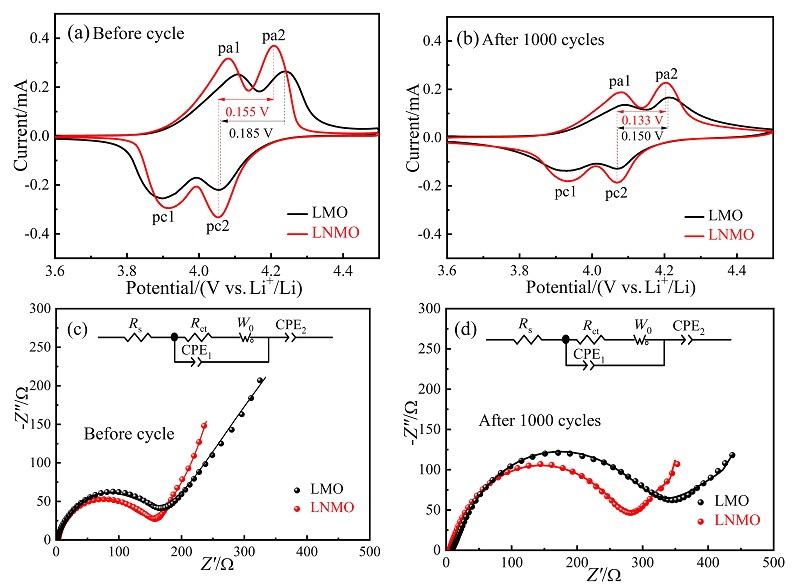
采用低温固相燃烧法快速制备了一种具有{111}、{110}和{100}晶面的去顶角八面体LiNi0.08Mn1.92O4 (LNMO)正极材料, 其高暴露{111}晶面可以减少充放电过程中Mn的溶解, 面积相对较小的{110}和{100}晶面可增加Li+快速扩散的通道. 测试结果表明, 所合成的LNMO具有LiMn2O4特有的立方晶系结构, 其颗粒尺寸为亚微米级. LNMO的高温电化学性能优异, 在55 ℃, 1和5 C的首次放电比容量分别为109.9和98.0 mAh/g, 分别循环300次后容量保持率为75.8%和80.5%; 即使在55 ℃, 10和15 C下分别循环1000次后仍具有48.4%和49.4%的容量保持率, 而未掺杂的LiMn2O4于15 C循环1000次后容量损失高达98%. LNMO在55 ℃有较高的Li+扩散系数(D=3.86×10-15 cm2/s)和较小的电荷转移阻抗(循环前、后Rct=158.0和279.8 Ω)以及较低的表观活化能(Ea=17.63 kJ/mol), 说明Ni掺杂能够提高Li+在尖晶石型LiMn2O4内的扩散速率及减小锂离子在脱嵌过程中的能垒, 从而提高锂离子的扩散速率和倍率性能. 对LNMO于55 ℃循环1000次后的极片进行X射线衍射(XRD)分析, 发现LNMO电极材料的晶体结构基本保持不变, 表明Ni掺杂提高了锰酸锂材料在55 ℃长循环过程中的晶体结构稳定性, 有效抑制了Jahn-Teller效应及Mn的溶解, 显著提升了其高温电化学性能. 本工作为尖晶石LiMn2O4电极材料在高温方面的应用提供了借鉴.
梁其梅, 郭昱娇, 郭俊明, 向明武, 刘晓芳, 白玮, 宁平. 亚微米去顶角八面体LiNi0.08Mn1.92O4正极材料制备及高温电化学性能[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1526-1533.
Qimei Liang, Yujiao Guo, Junming Guo, Mingwu Xiang, Xiaofang Liu, Wei Bai, Ping Ning. Preparation and High Temperature Electrochemical Performance of LiNi0.08Mn1.92O4 Cathode Material of Submicron Truncated Octahedron[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1526-1533.




| [1] |
Chen, S.; He, T.; Su, Y.-F.; Lu, Y.; Bao, L.-L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.-J.; Wu, F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29732.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b08006 |
| [2] |
Liu, J.-D.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Liu, J.-X.; Li, J.-H.; Qiu, X.-G.; Cheng, F.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1426 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20070330 |
|
( 刘九鼎, 张宇栋, 刘俊祥, 李金翰, 邱晓光, 程方益, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1426.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070330 |
|
| [3] |
Zhan, C.; Wu, T.-P.; Lu, J.; Amine, K. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 243.
doi: 10.1039/C7EE03122J |
| [4] |
Duan, Y.-Z.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Guo, J.-M.; Xiang, M.-W.; Liu, X.-F.; Bai, H.-L.; Su, C.-W. Chem. J. Chinese Universities 2019, 40, 2574 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 段玉珍, 朱金玉, 郭俊明, 向明武, 刘晓芳, 白红丽, 苏长伟, 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40, 2574.)
|
|
| [5] |
Lu, D.; Zheng, C.-M.; Chen, Y.-F.; Li, Y.-J.; Zhang, H.-M. Chem. J. Chinese Universities 2020, 41, 16844 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 陆地, 郑春满, 陈宇方, 李宇杰, 张红梅, 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41, 16844.)
|
|
| [6] |
Luo, X.-Y.; Xiang, M.-W.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.-M.; Liu, X.-F.; Bai, H.-L.; Bai, W.; Su, C.-W. Vacuum 2020, 179, 109505.
doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109505 |
| [7] |
Song, H.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, Y.; Hou, H. Solid State Ionics 2019, 331, 49.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2018.12.015 |
| [8] |
Ni, J.-F.; Zhou, H.-H.; Chen, J.-T.; Su, G.-Y. Prog. Chem. 2004, 16, 335 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 倪江锋, 周恒辉, 陈继涛, 苏光耀, 化学进展, 2004, 16, 335.)
|
|
| [9] |
Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, Y.; Khan, A.-M.; Ahmed, S. Ionics 2017, 23, 1995.
doi: 10.1007/s11581-017-2062-5 |
| [10] |
Liu, H.-Q.; Tian, R.-Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, X.-H.; Chen, J.-K.; Zhang, L.-N.; Guo, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-F.; Sun, L.-F.; Chu, W.-G. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 138.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.08.123 |
| [11] |
Yang, S.-Q.; Zhang, T.-R.; Tao, Z.-L.; Chen, J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 1029 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A13030294 |
|
( 杨思七, 张天然, 陶占良, 陈军, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1029.)
doi: 10.6023/A13030294 |
|
| [12] |
Liu, Q.; Liang, Q.-M.; Guo, J.-M.; Xiang, M.-W.; Bai, W.; Bai, H.-L.; Liu, X.-F. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2441.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.086 |
| [13] |
Liu, W.-H.; Xu, H.-H.; Zhou, Q.-H.; Dai, Y.-W.; Hu, W.; Li, H.-L. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 5523.
doi: 10.1007/s11664-020-08298-1 |
| [14] |
Jiang, J.-B.; Liang, L.-W.; Li, D.; Xiao, J.; Peng, Z.-D.; Du, K.; Cao, Y.-B.; Hu, G.-R.; Jiang, F. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 9182.
doi: 10.1166/jnn.2017.13919 |
| [15] |
Bai, H.-L.; Xu, W.-Q.; Guo, J.-M.; Su, C.-W.; Xiang, M.-W.; Liu, X.-F.; Wang, R. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. M. 2018, 29, 14668.
|
| [16] |
Raju, K.; Nkosi, F.-P.; Viswanathan, E.; Mathe, M.-K.; Damodaran, K.; Ozoemena, K.-I. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 13074.
doi: 10.1039/C6CP01873D |
| [17] |
Deepi, A.-S.; Srikesh, G.; Nesaraj, S.-A. Matéria 2021, 26, 1.
|
| [18] |
Ta, T.-A.; Nguyen, H.-S.; Nguyen, O.-T.-T.; Dang, C.-T.; Hoang, L.-A.; Pham, L.-D. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 065505.
doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab0ab2 |
| [19] |
Wei, Q.-L.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yang, X.-K.; Ju, B.-W.; Hu, B.-N.; Shu, H.-B.; Wen, W.-C.; Zhou, M.; Song, Y.-F.; Wu, H.; Hu, H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4010.
doi: 10.1039/c3ta01698f |
| [20] |
Gu, X.; Li, X.-W.; Xu, L.-Q.; Xu, H.-Y.; Yang, J.; Qian, Y.-T. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 2504.
|
| [21] |
Duan, Y.-Z.; Guo, J.-M.; Xiang, M.-W.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Su, C.-W.; Bai, H.-L.; Liu, X.-F.; Bai, W.; Wang, R. Solid State Ionics 2018, 326, 100.
doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2018.09.014 |
| [22] |
Kunjuzwa, N.; Kebede, M.; Ozoemena, K.-I.; Mathe, M.-K. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111882.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA23052K |
| [23] |
Wang, F.-X.; Xiao, S.-Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhu, Y.-S.; Wu, Y.-P.; Wang, J.-Z.; Holze, R. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 93, 301.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.01.106 |
| [24] |
Zhao, C.-H.; Kang, W.-P.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Shen, Q. Micro Nano Lett. 2012, 7, 558.
doi: 10.1049/mnl.2012.0020 |
| [25] |
Benedek, R.; Thackeray, M.-M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4050.
doi: 10.1021/jp208793k |
| [26] |
Kim, J.-S.; Kim, K. S.; Cho, W.; Shin, W.-H.; Kanno, R. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6358.
doi: 10.1021/nl303619s |
| [27] |
Huang, S.-S.; Wu, H.; Chen, P.-H.; Guo, Y.; Nie, B.; Chen, B.-J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3633.
doi: 10.1039/C4TA06522K |
| [28] |
Zhou, S.-Y.; Mei, T.; Wang, X.-B.; Qian, Y.-T. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17435.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR04842H |
| [29] |
Jiang, C.-H.; Tang, Z.-L.; Wang, S.-T.; Zhang, Z.-T. J. Power Sources 2017, 357, 144.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.04.079 |
| [30] |
Wang, F.-X.; Xiao, S.-Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhu, Y.-S.; Wu, Y.-P.; Wang, J.-Z.; Holze, R. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 93, 301.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.01.106 |
| [31] |
Wang, Q.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.-L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, C.-J. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 474.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.130 |
| [32] |
Zhu, C.-Y.; Liu, J.-X.; Yu, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Dong, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.-N. Ceram Int. 2019, 45, 19351.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.187 |
| [33] |
Cai, Y.-J.; Huang, Y.-D.; Wang, X.-C.; Jia, D.-Z.; Pang, W.-K.; Guo, Z.-P.; Du, Y.-P.; Tang, X.-C. J. Power Sources 2015, 278, 574.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.12.082 |
| [34] |
Tabassam, L.; Nazir, T.; Manzoor, U.; Mehmood, S.; Hassan, M.-U.; Bhatti, A.-S. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115550.
doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab3970 |
| [35] |
Yu, Y.; Xiang, M.-W.; Guo, J.-M.; Su, C.-W.; Liu, X.-F.; Bai, H.-L.; Bai, W.; Duan, K.-J. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 555, 64.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.07.078 |
| [36] |
Huang, X.-H.; Li, G.-H.; Cao, B.-Q.; Wang, M.; Hao, C.-Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 113, 4381.
doi: 10.1021/jp810790h |
| [37] |
Chen, M.-F.; Chen, P.; Yang, F.; Song, H.-Y.; Liao, S.-J. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 206, 356.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.04.148 |
| [38] |
Huang, Y.-D.; Jiang, R.-R.; Jia, D.-Z.; Guo, Z.-P. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3486.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.07.091 |
| [39] |
Eriksson, T.; Hjelm, A.-K.; Lindbergh, G.; Gustafsson, T. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A1164.
doi: 10.1149/1.1497170 |
| [40] |
Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Nakamura, H.; Noguchi, H.; Yoshio, M. J. Power Sources 2007, 166, 485.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.01.023 |
| [41] |
Yoshio, M.; Noguchi, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. J. Power Sources 2006, 154, 273.
doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.03.232 |
| [42] |
Wu, Y.; Cao, C.-B.; Zhang, J.-T.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.-L.; Xu, X.-Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19567.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b06820 |
| [43] |
Li, Y.-L.; Yu, D.-D.; Lin, S.; Sun, D.-F.; Lei, Z.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 200 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A20090428 |
|
( 李燕丽, 于丹丹, 林森, 孙东飞, 雷自强, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 200.)
doi: 10.6023/A20090428 |
|
| [44] |
Rangarajan, S.-P.; Barsukov, Y.; Mukherjee, P.-P. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2131.
doi: 10.1149/2.1191910jes |
| [1] | 何家伟, 焦柳, 程雪怡, 陈光海, 吴强, 王喜章, 杨立军, 胡征. 金属有机框架衍生的空心碳纳米笼的结构调控与锂硫电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 896-902. |
| [2] | 黄擎, 丁瑞, 陈来, 卢赟, 石奇, 张其雨, 聂启军, 苏岳锋, 吴锋. Na2PO3F对LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2材料的复合改性及机理分析[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 150-158. |
| [3] | 薛晓兰, 张洋, 石美瑜, 李天琳, 黄天龙, 戚继球, 委福祥, 隋艳伟, 金钟. 有机电极材料在非水系金属镁二次电池中的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1618-1628. |
| [4] | 邱凯, 严铭霞, 赵守旺, 安胜利, 王玮, 贾桂霄. Al掺杂的锂离子电池层状正极材料Li(Li0.17Ni0.17Al0.04Fe0.13Mn0.49)O2结构稳定性及氧离子氧化的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1146-1153. |
| [5] | 陆远, 王继芬, 谢华清. LiMn2O4尖晶石氧化物的低指数表面结构优化及表面能的第一性原理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1058-1064. |
| [6] | 李童心, 李东林, 张清波, 高建行, 孔祥泽, 樊小勇, 苟蕾. 大孔高镍LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2正极材料的制备及其电化学性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 678-684. |
| [7] | 林碧霞, 黄颖珊, 陈帅, 邢震宇. 钠硒电池关键材料的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 641-648. |
| [8] | 张璐, 王文凤, 张洪明, 韩树民, 王利民. 水系锌离子电池研究进展和挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 158-175. |
| [9] | 李燕丽, 于丹丹, 林森, 孙东飞, 雷自强. α-MnO2纳米棒/多孔碳正极材料的制备及水系锌离子电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 200-207. |
| [10] | 谢佶晟, 肖竹梅, 左文华, 杨勇. 钠离子电池钴酸钠正极材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1232-1243. |
| [11] | 汤功奥, 毛鲲, 张静, 吕品, 程雪怡, 吴强, 杨立军, 王喜章, 胡征. 分级结构氮掺杂碳纳米笼:高倍率长寿命可充电镁电池正极材料[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(5): 444-450. |
| [12] | 刘九鼎, 张宇栋, 刘俊祥, 李金翰, 邱晓光, 程方益. 磷酸锂原位包覆富锂锰基锂离子电池正极材料[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1426-1433. |
| [13] | 任旭强, 李东林, 赵珍珍, 陈光琦, 赵坤, 孔祥泽, 李童心. 铝掺杂及钨酸锂表面包覆双效提升富锂锰基正极材料的循环稳定性[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(11): 1268-1274. |
| [14] | 宋学霞, 李继成, 李朝晖, 李喜飞, 丁燕怀, 肖启振, 雷钢铁. 钾掺杂对钒酸钠纳米片储钠性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(7): 625-633. |
| [15] | 李钊, 王忠, 班丽卿, 王建涛, 卢世刚. 富锂锰基正极材料的表面改性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1115-1128. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||