化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (12): 1415-1424.DOI: 10.6023/A21080380 上一篇 下一篇
综述
董雪a, 曹鸿a, 徐雷a,b, 王志鹏a,*( ), 陈靖a, 徐超a,*(
), 陈靖a, 徐超a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-08-13
发布日期:2021-10-08
通讯作者:
王志鹏, 徐超
作者简介: |
董雪, 男, 博士研究生. 2018年7月毕业于西南科技大学国防科技学院, 获学士学位. 目前就读于清华大学核能与新能源技术研究院, 主要从事核废物处理中超铀元素的化学行为和分离机制研究. |
 |
王志鹏, 男, 助理研究员. 2019年于四川大学获放射化学专业博士学位. 2019~2021年在清华大学核能与新能源技术研究院开展博士后研究. 2021年8月起任职助理研究员. 主要从事于核燃料循环相关的分离化学、氧化还原化学和配位化学研究. |
 |
徐超, 男, 清华大学核能与新能源技术研究院长聘副教授. 2009年于北京大学获理学博士学位, 同年进入清华大学核能与新能源技术研究院工作至今. 中国化学会核化学与放射化学分会理事会副秘书长, 中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会理事. 主要研究领域包括放射性废物高效分离和处理技术, 锕系及镧系离子配位化学等. |
基金资助:
Xue Donga, Hong Caoa, Lei Xua,b, Zhipeng Wanga( ), Jing Chena, Chao Xua(
), Jing Chena, Chao Xua( )
)
Received:2021-08-13
Published:2021-10-08
Contact:
Zhipeng Wang, Chao Xu
Supported by:文章分享

镎(Np)和钚(Pu)是核能领域两种重要的锕系元素, 其在水溶液中的配位化学对于了解和控制其在水环境中的种态分布和迁移行为具有重要意义. Review了近十几年来国内外Np和Pu与环境中常见无机阴离子在水溶液中的配位化学研究进展, 重点阐述了不同价态Np/Pu离子与OH–、 $CO_3^{2-}$、 $SO_4^{2-}$、Cl–、 $NO_3^-$、F–、 $PO_4^{3-}$等阴离子之间形成的配位物种和配位热力学信息, 并对该领域存在的关键科学问题和未来发展方向进行了分析和展望.
董雪, 曹鸿, 徐雷, 王志鹏, 陈靖, 徐超. 镎和钚与环境中无机阴离子的配位化学研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1415-1424.
Xue Dong, Hong Cao, Lei Xu, Zhipeng Wang, Jing Chen, Chao Xu. Advances in Environmental Coordination Chemistry of Np and Pu with Inorganic Anions in Aqueous Solution[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(12): 1415-1424.
| log β01 | log β02 | log β03 | log β04 | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np(IV) | 0.55±0.20 | 0.35±0.30 | –8.30±1.10 | [ | |
| 0.5±0.2 | 0.3±0.3 | –2.8±1.0 | –8.3±1.1 | [ | |
| Pu(IV) | 0.60±0.20 | 0.60±0.30 | –2.30±0.40 | –8.50±0.50 | [ |
| 0.0±0.2 | –1.2±0.6 | –3.1±0.9 | [ |
| log β01 | log β02 | log β03 | log β04 | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np(IV) | 0.55±0.20 | 0.35±0.30 | –8.30±1.10 | [ | |
| 0.5±0.2 | 0.3±0.3 | –2.8±1.0 | –8.3±1.1 | [ | |
| Pu(IV) | 0.60±0.20 | 0.60±0.30 | –2.30±0.40 | –8.50±0.50 | [ |
| 0.0±0.2 | –1.2±0.6 | –3.1±0.9 | [ |
| Species | I/(mol•L–1) | log β | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np(IV) | [Np(CO3)2(OH)2]2– | 0 | 46.4±0.5 | [ |
| [NpCO3(OH)4]2– | 0 | 50.5±0.5 | [ | |
| [Np(CO3)2(OH)4]4– | 0 | 47.4±0.5 | [ | |
| Pu(IV) | [Pu(CO3)2(OH)4]4– | 0.1 | 49.7±0.5 | [ |
| [Pu(CO3)2(OH)2]2– | 0 | 44.8 | [ | |
| 0.1 | 44.2±0.6 | [ |
| Species | I/(mol•L–1) | log β | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np(IV) | [Np(CO3)2(OH)2]2– | 0 | 46.4±0.5 | [ |
| [NpCO3(OH)4]2– | 0 | 50.5±0.5 | [ | |
| [Np(CO3)2(OH)4]4– | 0 | 47.4±0.5 | [ | |
| Pu(IV) | [Pu(CO3)2(OH)4]4– | 0.1 | 49.7±0.5 | [ |
| [Pu(CO3)2(OH)2]2– | 0 | 44.8 | [ | |
| 0.1 | 44.2±0.6 | [ |
| log β | ∆G0/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆H0/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆S0/(J•k–1•mol–1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PuSO4]2+ | 2.71±0.05 | –15.5 | 11.2 | 89.6 |
| Pu(SO4)2 | 4.59±0.04 | –26.2 | 5.1 | 104.8 |
| log β | ∆G0/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆H0/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆S0/(J•k–1•mol–1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PuSO4]2+ | 2.71±0.05 | –15.5 | 11.2 | 89.6 |
| Pu(SO4)2 | 4.59±0.04 | –26.2 | 5.1 | 104.8 |
| log *βn | ∆Gn0/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆Hnb/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆Snb/(J•K–1•mol–1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NpO2(OH) | –9.01±0.07 | 51.3±0.5 | 31.6±0.6 | –66±3 |
| [NpO2(OH)2]– | –18.95±0.07 | 28.6±0.3 | 39.7±0.5 | 47.5±0.5 |
| log *βn | ∆Gn0/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆Hnb/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆Snb/(J•K–1•mol–1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NpO2(OH) | –9.01±0.07 | 51.3±0.5 | 31.6±0.6 | –66±3 |
| [NpO2(OH)2]– | –18.95±0.07 | 28.6±0.3 | 39.7±0.5 | 47.5±0.5 |
| Method | log β01 | log β02 | log β03 | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np(V) | 光谱法 | 4.92±0.06 | 6.53±0.06 | 5.50±0.15 | [ |
| CE-ICP-MS | 4.88±0.12 | 6.27±0.11 | 5.64±0.15 | [ | |
| Pu(V) | 光谱法 | 4.95±0.10 | 5.03±0.95 | [ | |
| CE-ICP-MS | 4.95±0.01 | 6.34±0.10 | 5.61±0.16 | [ |
| Method | log β01 | log β02 | log β03 | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Np(V) | 光谱法 | 4.92±0.06 | 6.53±0.06 | 5.50±0.15 | [ |
| CE-ICP-MS | 4.88±0.12 | 6.27±0.11 | 5.64±0.15 | [ | |
| Pu(V) | 光谱法 | 4.95±0.10 | 5.03±0.95 | [ | |
| CE-ICP-MS | 4.95±0.01 | 6.34±0.10 | 5.61±0.16 | [ |
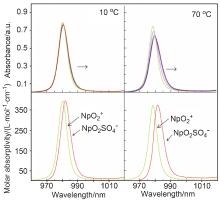
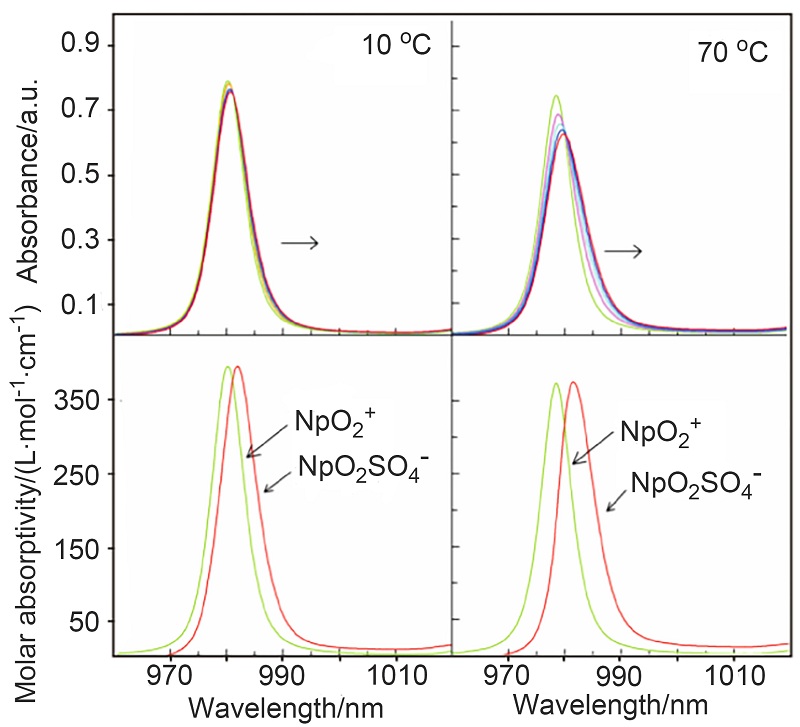
| log β | ∆H/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆S/(J•k–1•mol–1) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NpO2F | 1.42±0.10 | 20.8 | 96.9 | [ |
| 1.26±0.15 | 7.3±3.6 | 48±11 | [ | |
| 1.25±0.05 | 8.1±1.0 | 51±5 | [ | |
| [NpO2F2]– | 1.79±0.20 | 17.2±6.0 | 90±18 | [ |
| 1.77±0.09 | 14.2±3.1 | 82±12 | [ |
| log β | ∆H/(kJ•mol–1) | ∆S/(J•k–1•mol–1) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NpO2F | 1.42±0.10 | 20.8 | 96.9 | [ |
| 1.26±0.15 | 7.3±3.6 | 48±11 | [ | |
| 1.25±0.05 | 8.1±1.0 | 51±5 | [ | |
| [NpO2F2]– | 1.79±0.20 | 17.2±6.0 | 90±18 | [ |
| 1.77±0.09 | 14.2±3.1 | 82±12 | [ |


| [1] |
Altmaier, M.; Gaona, X.; Fanghaenel, T. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 901.
doi: 10.1021/cr300379w pmid: 23369090 |
| [2] |
Magill, J.; Berthou, V.; Haas, D.; Galy, J.; Schenkel, R. Nucl. Energy 2003, 42, 263.
|
| [3] |
Maher, K.; Bargar, J. R.; Brown, G. E. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 3510.
doi: 10.1021/ic301686d pmid: 23137032 |
| [4] |
Wang, Z. P.; Pu, N.; Tian, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. R.; Chen, J.; Ding, S. D. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 5457.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01635 |
| [5] |
Neck, V.; Altmaier, M.; Fanghänelab, T. C. R. Chim. 2007, 10, 959.
doi: 10.1016/j.crci.2007.02.011 |
| [6] |
Ikeda-Ohno, A.; Hennig, C.; Rossberg, A.; Funke, H.; Scheinost, A. C.; Bernhard, G.; Yaita, T. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 8294.
doi: 10.1021/ic8009095 pmid: 18698766 |
| [7] |
Knope, K. E.; Soderholm, L. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 944.
doi: 10.1021/cr300212f |
| [8] |
Altmaier, M.; Vercouter, T.; Poinssot, C.; Geckeis, H. Radionuclide Behaviour in the Natural Environment. Science, Implications and Lessons for the Nuclear Industry, Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2012.
|
| [9] |
Shilov, V. P.; Gogolev, A. V.; Fedoseev, A. M.; Ershov, B. G. Radiochemistry 2012, 54, 22.
|
| [10] |
Choppin, G. R. Radiochim. Acta 1983, 32, 43.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1983.32.13.43 |
| [11] |
Mefod'Eva, M. P.; Krot, N. N.; Afanas'Eva, T. V.; Gel'Man, A. D. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR, Div. Chem. Sci. 1974, 23, 2285.
doi: 10.1007/BF00921308 |
| [12] |
Cho, H. R.; Youn, Y. S.; Jung, E. C.; Cha, W. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 19449.
doi: 10.1039/C6DT03992H |
| [13] |
Thomas, V.; Vitorge, P.; Amekraz, B.; Giffaut, E.; Hubert, S.; Moulin, C. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 5833.
doi: 10.1021/ic050214n |
| [14] |
Lemire, R. J.; Fuger, J.; Nitsche, H.; Potter, P. E.; Rand, M. H.; Rydberg, J.; Spahiu, K.; Sullivan, J. C.; Ullman, W. J.; Vitorge, P.; Wanner, H. Chemical Thermodynamics of Neptunium and Plutonium, Elsevier, North Holland, Amsterdam, 2001.
|
| [15] |
Fujiwara, K.; Kohara, Y. Radiochim. Acta 2008, 96, 613.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2008.1544 |
| [16] |
Neck, V.; Kim, J. I.; Seidelc, B. S.; Marquardt, C. M.; Dardenne, K.; Jensen, M. P.; Hauser, W. Radiochim. Acta 2001, 89, 439.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2001.89.7.439 |
| [17] |
Guillaumont, R.; Mompean, F. J. Update on the Chemical Thermodynamics of Uranium, Neptunium, Plutonium, Americium and Technetium, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003.
|
| [18] |
Yun, J. I.; Cho, H. R.; Neck, V.; Altmaier, M.; Seibert, A.; Marquardt, C. M.; Walther, C.; Fanghänel, T. Radiochim. Acta 2007, 95, 89.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2007.95.2.89 |
| [19] |
Walther, C.; Cho, H. R.; Marquardt, C. M.; Neck, V.; Seibert, A.; Yun, J. I.; Fanghänel, T. Radiochim. Acta 2007, 95, 7.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2007.95.1.7 |
| [20] |
Silver, G. L. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2011, 288, 89.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-010-0953-2 |
| [21] |
Silver, G. L. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 291, 915.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-011-1401-7 |
| [22] |
Kitamura, A.; Kohara, Y. Radiochim. Acta 2004, 92, 583.
doi: 10.1524/ract.92.9.583.55002 |
| [23] |
Kitamura, A.; Kohara, Y. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2002, 39, 294.
doi: 10.1080/00223131.2002.10875466 |
| [24] |
Yamaguchi, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ohnuki, T. Radiochim. Acta 1994, 66, 9.
|
| [25] |
Clark, D. L.; Hecker, S. S.; Jarvinen, G. D.; Neu, M. P. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements, Springer, Dordrecht, 2006.
|
| [26] |
Xia, Y. X.; Friese, J. I.; Moore, D. A.; Bachelor, P. P.; Rao, L. F. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2007, 274, 79.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-006-6907-z |
| [27] |
Danesi, P. R.; Chiarizia, R.; Scibona, G.; D'Alessandro, G. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1971, 33, 3503.
doi: 10.1016/0022-1902(71)80672-3 |
| [28] |
Veirs, D. K.; Smith, C. A.; Berg, J. M.; Zwick, B. D.; Marsh, S. F.; Allen, P.; Conradson, S. D. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 213, 328.
|
| [29] |
Berg, J. M.; Veirs, D. K.; Vaughn, R. B.; Cisneros, M. R.; Smith, C. A. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 812.
doi: 10.1366/0003702001950436 |
| [30] |
Allen, P. G.; Veirs, D. K.; Conradson, S. D.; Smith, C. A.; Marsh, S. F. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 2841.
doi: 10.1021/ic9511231 |
| [31] |
Dacheux, N.; Thomas, A. C.; Brandel, V.; Genet, M. J. Nucl. Mater. 2000, 257, 108.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-3115(98)00443-7 |
| [32] |
Brandel, V.; Dacheux, N. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 4743.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2004.08.009 |
| [33] |
Topin, S.; Aupiais, J. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 153, 237.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.12.016 |
| [34] |
Topin, S.; Aupiais, J.; Moisy, P. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1747.
doi: 10.1002/elps.v30:10 |
| [35] |
Rao, L. F.; Srinivasan, T. G.; Garnov, A. Y.; Zanonato, P. L.; Bernardo, P. D. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 4821.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.06.007 |
| [36] |
Bennett, D. A.; Hoffman, D.; Nitsche, H.; Russo, R. E.; Torres, R. A.; Baisden, P. A.; Andrews, J. E.; Palmer, C. E. A.; Silva, R. J. Radiochim. Acta 1992, 56, 15.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1992.56.1.15 |
| [37] |
Oliver, J. H. Radiochim. Acta 1983, 33, 29.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1983.33.1.29 |
| [38] |
Xia, Y.; Friese, J. I.; Moore, D. A.; Rao, L. F. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 268, 445.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-006-0189-3 |
| [39] |
Inoue, Y.; Tochiyama, O. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 58, 2228.
doi: 10.1246/bcsj.58.2228 |
| [40] |
Rao, L. F.; Tian, G. X.; Xia, Y.; Friese, J. I. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 95, 409.
doi: 10.1007/s10973-008-9247-0 |
| [41] |
Topin, S.; Aupiais, J.; Baglan, N.; Vercouter, T.; Vitorge, P.; Moisy, P. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5354.
doi: 10.1021/ac900275d |
| [42] |
Gainar, I.; Sykes, K. W. J. Chem. Soc. 1964, 4452.
|
| [43] |
Rao, P. R. V.; Gudi, N. M.; Bagawde, S. V.; Patil, S. K. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1979, 41, 235.
doi: 10.1016/0022-1902(79)80520-5 |
| [44] |
Topin, S.; Aupiais, J.; Baglan, N. Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 71.
|
| [45] |
Maiwald, M. M.; Fellhauer, D.; Skerencak-Frech, A.; Panak, P. J. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 104, 10.
doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.03.004 |
| [46] |
Tian, G. X.; Rao, L. F.; Xia, Y.; Friese, J. I. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 95, 415.
doi: 10.1007/s10973-008-9248-z |
| [47] |
Gaona, X.; Tits, J.; Dardenne, K.; Liu, X.; Rothe, J.; Denecke, M. A.; Wieland, E.; Altmaier, M. Radiochim. Acta 2012, 100, 759.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2012.1948 |
| [48] |
Gaona, X.; Fellhauer, D.; Altmaier, M. Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 2027.
doi: 10.1351/pac-con-12-12-06 |
| [49] |
Reilly, S. D.; Neu, M. P. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 1839.
pmid: 16472001 |
| [50] |
Cho, H. R.; Jung, E. C.; Park, K. K.; Kim, W. H.; Song, K.; Yun, J. I. Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 765.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2010.1782 |
| [51] |
Cho, H. R.; Jung, E. C.; Park, K. K.; Song, K.; Yun, J. I. Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 555.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2010.1753 |
| [52] |
Rao, L. F.; Tian, G. X.; Bernardo, P. D.; Zanonato, P. L. Chem.-Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10985.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v17.39 |
| [53] |
Moriyama, H.; Kitamura, A.; Fujiwara, K.; Yamana, H. Radiochim. Acta 1999, 87, 97.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1999.87.34.97 |
| [54] |
Moriyama, H.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Takagi, I. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408, 1302.
|
| [55] |
Kato, Y.; Kimura, T.; Yoshida, Z.; Nitani, N. Radiochim. Acta 1996, 74, 21.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1996.74.special-issue.21 |
| [56] |
Maya, L. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 16, 3926.
|
| [57] |
Pashalidis, I.; Czerwinski, K. R.; Fanghanel, T.; Kim, J. I. Radiochim. Acta 1997, 76, 55.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1997.76.12.55 |
| [58] |
Matsika, S.; Pitzer, R. M. The Electronic Spectrum of the Neptunyl ion, NpO22+, Department of Chemistry, The Ohio State University, 1998.
|
| [59] |
Ahrland, S.; Brandt, L.; Magnéli, C.; Tolboe, O.; Paasivirta, J. Acta Chem. Scand. 1968, 22, 1579.
doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.22-1579 |
| [60] |
Gaunt, A. J.; May, I.; Neu, M. P.; Reilly, S. D.; Scott, B. L. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4244.
doi: 10.1021/ic200525u |
| [61] |
Mathur, J. N.; Choppin, G. R. Radiochim. Acta 1994, 64, 175.
doi: 10.1524/ract.1994.64.34.175 |
| [62] |
Gaunt, A. J.; May, I.; Neu, M. P.; Reilly, S. D.; Scott, B. L. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4244.
doi: 10.1021/ic200525u |
| [63] |
Sawant, R. M.; Chaudhuri, N. K.; Rizvi, G. H.; Patil, S. K. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1985, 91, 41.
doi: 10.1007/BF02036308 |
| [1] | 杨宇洁, 巩宇锈, 顾天航, 张伟贤. 冷冻电子显微镜技术进展及环境研究应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 990-1001. |
| [2] | 王娟, 肖华敏, 谢丁, 郭元茹, 潘清江. 铜掺杂与氮化碳复合氧化锌材料结构和二氧化氮气体传感性质的密度泛函理论计算[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1493-1499. |
| [3] | 韩逸之, 蓝建慧, 刘学, 石伟群. 基于机器学习势函数的熔盐体系分子动力学研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1663-1672. |
| [4] | 杨学志, 陆达伟, 王伟超, 杨航, 刘倩, 江桂斌. 辨微识源: 纳米颗粒物溯源技术的新进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(5): 652-658. |
| [5] | 刘康, 李斌, 于吉攀, 石伟群. 十四族卡本衍生物: 一类重要的活性中间体[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 373-385. |
| [6] | 李程桥, 王一波. 一种量子化学组合方法及其应用于汞对硫酸气溶胶形成影响的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1065-1072. |
| [7] | 蔡政, 张颖雯, 姜立萍, 朱俊杰. 基于类芬顿反应的Mn3O4/DOX@Lip纳米递药体系的构建及应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 481-489. |
| [8] | 闫涛, 刘振华, 宋昕玥, 张书圣. 肿瘤微环境刺激响应型上转换光动力诊疗体系的构建和发展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(7): 657-669. |
| [9] | 李海梅, 罗华健, 肖琦, 杨立云, 黄珊, 刘义. 手性石墨烯量子点与DNA相互作用及其机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 577-586. |
| [10] | 朱桂芬, 陈乐田, 程国浩, 赵娟, 杨灿, 张耀宗, 王醒, 樊静. UiO-66/CoSO4复合材料对环境中盐酸左氧氟沙星的高效去除[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(5): 434-441. |
| [11] | 王宁, 庞宏伟, 于淑君, 顾鹏程, 宋爽, 王宏青, 王祥科. 层状双金属氢氧化物及复合材料对放射性元素铀的吸附及机理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(2): 143-152. |
| [12] | 梁珊, 宗敏华, 娄文勇. 酶法催化二氧化碳制备高附加值化学品研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(11): 1099-1114. |
| [13] | 郭肖茹, 阴永光, 谭志强, 刘景富, 江桂斌. 纳米银对水中三价砷的催化氧化研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(5): 387-392. |
| [14] | 郭宇, 刘瑜, 戚娟娟, 李慧, 赫兰兰, 卢丽男, 刘翠, 宫利东, 赵东霞, 杨忠志. S4-S0转化期水结合至放氧复合体可能机制的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(9): 914-921. |
| [15] | 黄潇月, 王伟, 凌岚, 张伟贤. 纳米零价铁与重金属的反应:“核-壳”结构在重金属去除中的作用[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(6): 529-537. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||