化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (5): 493-502.DOI: 10.6023/A23100474 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
薛冰a, 关伟鑫a, 王鹏a, 侯少文a, 陈欣辉a, 王奕星a, 苟焕其a, 郭锋浩a, 王梦闯a, 王天姿a, 刘金德a, 郑洲b, 柴寿根b, 陈家锐b, 张建林c, 棘云飞c, 倪珺a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-10-28
发布日期:2024-04-02
基金资助:
Bing Xuea, Weixin Guana, Peng Wanga, Shaowen Houa, Xinhui Chena, Yixing Wanga, Huanqi Goua, Fenghao Guoa, Mengchuang Wanga, Tianzi Wanga, Jinde Liua, Zhou Zhengb, Shougen Chaib, Jiarui Chenb, Jianlin Zhangc, Yunfei Jic, Jun Nia( )
)
Received:2023-10-28
Published:2024-04-02
Contact:
*E-mail: junni@zjut.edu.cn
Supported by:文章分享

1,3-丁二烯(以下简称丁二烯)作为化工的重要有机中间体, 在石油以及橡胶工业有着广泛的用途. 以乙醇为原料生产丁二烯能够解决生产原料不可再生的问题, 所以受到越来越多的关注. 本工作采用SBA-15为载体, 硝酸盐为氧化物前驱体, 含氮有机物为助剂, 通过水热合成法制备了催化剂, 并探究了乙醇合成丁二烯反应过程中, 乙醇转化率、丁二烯收率与催化剂酸碱性的关系. 具体来说, 使用三聚氰胺(M)、三聚氰酸(Ma)、1,10-菲啰啉(Pm)、咪唑(Im)和1,3,5-三嗪(St)为含氮助剂, 制备了Zn-Zr/SBA-15+X催化剂. 通过对催化剂的活性评价, 计算得到乙醇脱氢和脱水、乙醛缩合、Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley (MPV)反应的活性. 根据反应活性和丁二烯收率与催化剂酸碱性(酸碱强度和含量)的变化关系, 发现适当数量的弱酸(0.022 mmol·g−1)、中酸(0.078 mmol·g−1)、中碱(0.055 mmol·g−1)和强碱(0.056 mmol·g−1)有助于乙醇脱氢反应的发生, 过量的弱酸和中酸将导致乙醇的脱水反应. 中等数量的中酸(0.078 mmol·g−1)和中碱(0.055 mmol·g−1)有利于乙醛缩合和MPV反应的发生. 丁二烯收率与乙醛缩合活性和MPV活性关联较大. 三聚氰胺改性的催化剂(Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M)的弱酸、中酸、中碱和强碱含量符合以上的最优数量, 因此催化性能最优异: 乙醇转化率为99.5%, 丁二烯选择性为65.5%, 丁二烯产能达到了0.45 gBD·gcat−1·h−1.
薛冰, 关伟鑫, 王鹏, 侯少文, 陈欣辉, 王奕星, 苟焕其, 郭锋浩, 王梦闯, 王天姿, 刘金德, 郑洲, 柴寿根, 陈家锐, 张建林, 棘云飞, 倪珺. 氮改性ZnO-ZrO2/SBA-15催化剂的酸碱性与其催化乙醇合成1,3-丁二烯反应性能的关系[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 493-502.
Bing Xue, Weixin Guan, Peng Wang, Shaowen Hou, Xinhui Chen, Yixing Wang, Huanqi Gou, Fenghao Guo, Mengchuang Wang, Tianzi Wang, Jinde Liu, Zhou Zheng, Shougen Chai, Jiarui Chen, Jianlin Zhang, Yunfei Ji, Jun Ni. Relationship between the Acid-base Properties of Nitrogen-modified ZnO-ZrO2/SBA-15 Catalysts and Their Catalytic Performance in the Synthesis of 1,3-Butadiene from Ethanol[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(5): 493-502.
| 催化剂a | 转化率/% | 选择性/% | 丁二烯收率/% | 产能c/ (gBD·gcat−1·h−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丁二烯 | 乙烯 | 乙醛 | 乙醚 | 丁醇 | 其他b | ||||
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 90.9 | 50.0 | 4.72 | 9.73 | 0.79 | 2.90 | 31.9 | 45.5 | 0.32 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 99.5 | 65.5 | 8.42 | 5.47 | 0.54 | 1.07 | 18.9 | 65.2 | 0.45 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 98.5 | 63.7 | 10.4 | 4.84 | 0.63 | 0.96 | 19.5 | 62.7 | 0.44 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 99.4 | 61.4 | 13.2 | 2.60 | 0.63 | 0.96 | 21.2 | 61.0 | 0.42 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 96.8 | 60.7 | 13.5 | 3.81 | 0.62 | 0.90 | 20.5 | 58.8 | 0.41 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 97.1 | 59.8 | 12.5 | 4.55 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 21.5 | 58.1 | 0.40 |
| 催化剂a | 转化率/% | 选择性/% | 丁二烯收率/% | 产能c/ (gBD·gcat−1·h−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丁二烯 | 乙烯 | 乙醛 | 乙醚 | 丁醇 | 其他b | ||||
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 90.9 | 50.0 | 4.72 | 9.73 | 0.79 | 2.90 | 31.9 | 45.5 | 0.32 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 99.5 | 65.5 | 8.42 | 5.47 | 0.54 | 1.07 | 18.9 | 65.2 | 0.45 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 98.5 | 63.7 | 10.4 | 4.84 | 0.63 | 0.96 | 19.5 | 62.7 | 0.44 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 99.4 | 61.4 | 13.2 | 2.60 | 0.63 | 0.96 | 21.2 | 61.0 | 0.42 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 96.8 | 60.7 | 13.5 | 3.81 | 0.62 | 0.90 | 20.5 | 58.8 | 0.41 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 97.1 | 59.8 | 12.5 | 4.55 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 21.5 | 58.1 | 0.40 |
| 催化剂 | 关键反应步骤活性/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脱氢a | 脱水b | 缩合c | MPVd | |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 94.49 | 5.51 | 54.50 | 50.00 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 90.94 | 8.96 | 67.53 | 65.50 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 88.97 | 11.03 | 65.38 | 63.70 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 86.17 | 13.83 | 62.96 | 61.40 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 85.88 | 14.12 | 62.30 | 60.70 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 86.87 | 13.13 | 61.51 | 59.80 |
| 催化剂 | 关键反应步骤活性/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脱氢a | 脱水b | 缩合c | MPVd | |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 94.49 | 5.51 | 54.50 | 50.00 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 90.94 | 8.96 | 67.53 | 65.50 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 88.97 | 11.03 | 65.38 | 63.70 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 86.17 | 13.83 | 62.96 | 61.40 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 85.88 | 14.12 | 62.30 | 60.70 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 86.87 | 13.13 | 61.51 | 59.80 |
| 催化剂 | 比表面积a/ (m2·g−1) | 孔容b/ (cm3·g−1) | 平均孔径c/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 385.1 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 346.6 | 1.02 | 1.17 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 360.7 | 1.02 | 1.04 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 354.4 | 0.95 | 1.05 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 361.4 | 1.00 | 1.07 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 351.1 | 0.96 | 1.07 |
| 催化剂 | 比表面积a/ (m2·g−1) | 孔容b/ (cm3·g−1) | 平均孔径c/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 385.1 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 346.6 | 1.02 | 1.17 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 360.7 | 1.02 | 1.04 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 354.4 | 0.95 | 1.05 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 361.4 | 1.00 | 1.07 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 351.1 | 0.96 | 1.07 |
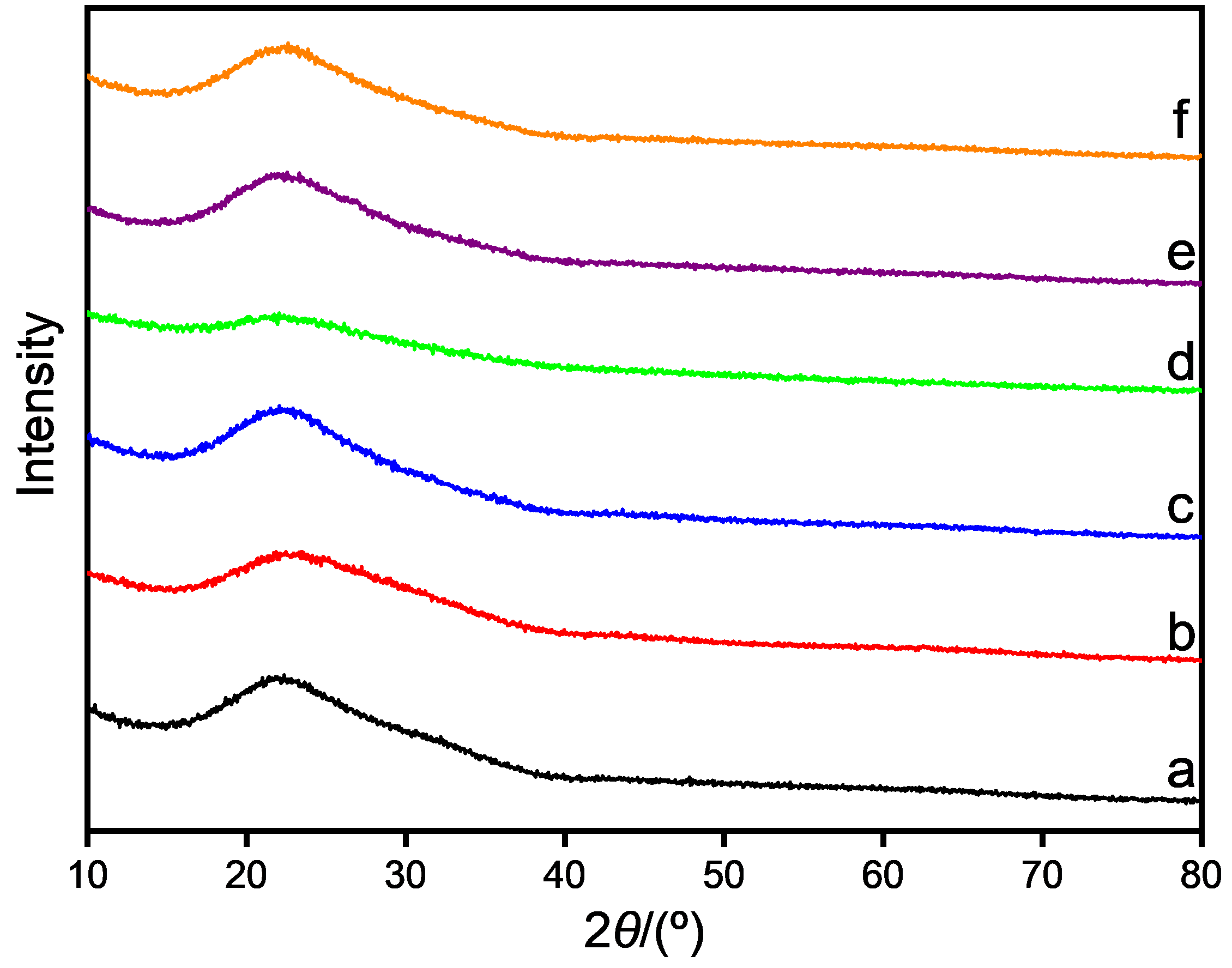
| Catalyst | Acid sites concentrationa/ (mmol·g−1), [T c/℃] | Basic sites concentrationb/ (mmol·g−1), [T c/℃] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak | Moderate | Total | Weak | Moderate | Strong | Total | |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 0.026 [181] | 0.070 [368] | 0.096 | 0.001 [102] | 0.052 [323] | 0.052 [400] | 0.105 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 0.022 [181] | 0.078 [320] | 0.100 | 0.0008 [98] | 0.055 [347] | 0.056 [400] | 0.112 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 0.030 [184] | 0.091 [348] | 0.121 | 0.0006 [105] | 0.054 [331] | 0.058 [400] | 0.113 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 0.028 [187] | 0.089 [360] | 0.117 | 0.0009 [103] | 0.058 [375] | 0.063 [400] | 0.122 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 0.027 [179] | 0.115 [345] | 0.142 | 0.0009 [95] | 0.056 [367] | 0.060 [400] | 0.117 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 0.029 [191] | 0.086 [368] | 0.115 | 0.0012 [116] | 0.061 [362] | 0.052 [400] | 0.114 |
| Catalyst | Acid sites concentrationa/ (mmol·g−1), [T c/℃] | Basic sites concentrationb/ (mmol·g−1), [T c/℃] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak | Moderate | Total | Weak | Moderate | Strong | Total | |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15 | 0.026 [181] | 0.070 [368] | 0.096 | 0.001 [102] | 0.052 [323] | 0.052 [400] | 0.105 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+M | 0.022 [181] | 0.078 [320] | 0.100 | 0.0008 [98] | 0.055 [347] | 0.056 [400] | 0.112 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Ma | 0.030 [184] | 0.091 [348] | 0.121 | 0.0006 [105] | 0.054 [331] | 0.058 [400] | 0.113 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Pm | 0.028 [187] | 0.089 [360] | 0.117 | 0.0009 [103] | 0.058 [375] | 0.063 [400] | 0.122 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+Im | 0.027 [179] | 0.115 [345] | 0.142 | 0.0009 [95] | 0.056 [367] | 0.060 [400] | 0.117 |
| Zn-Zr/SBA-15+St | 0.029 [191] | 0.086 [368] | 0.115 | 0.0012 [116] | 0.061 [362] | 0.052 [400] | 0.114 |

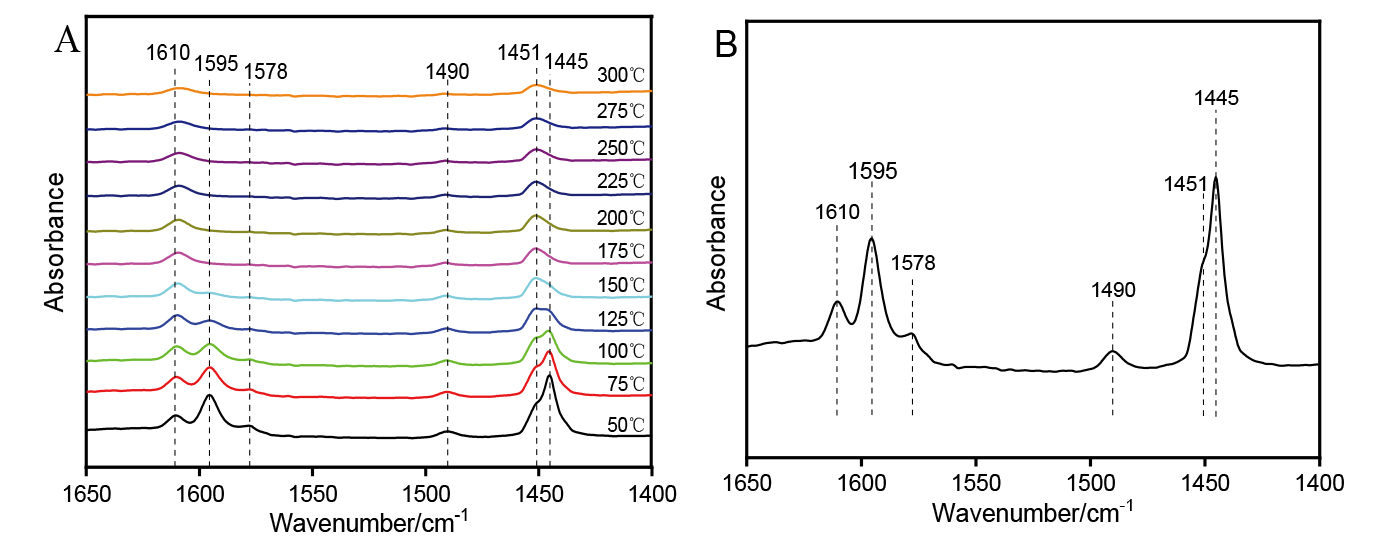
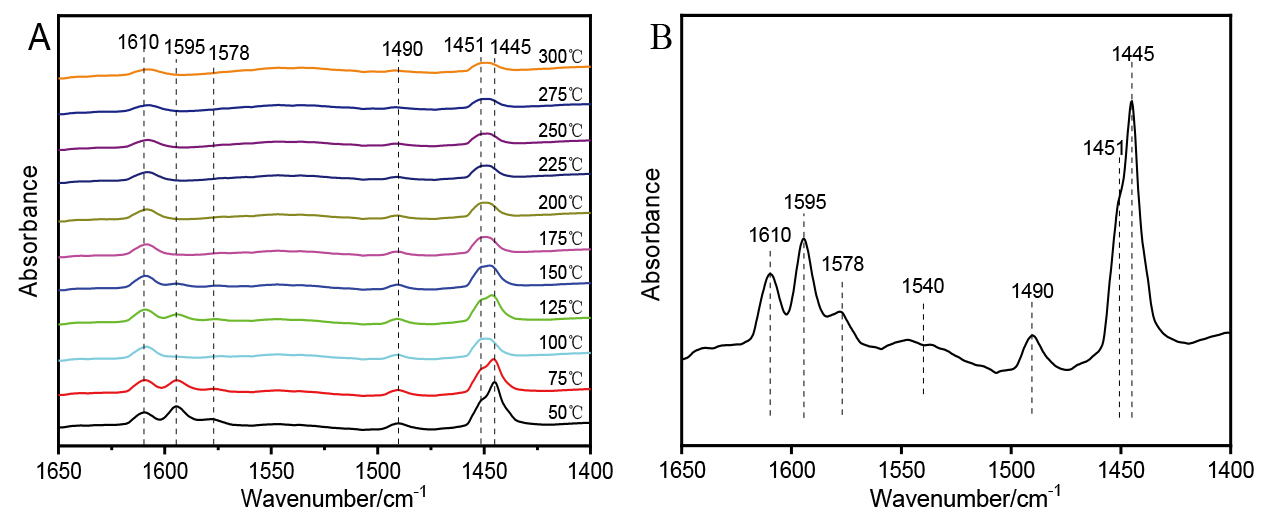
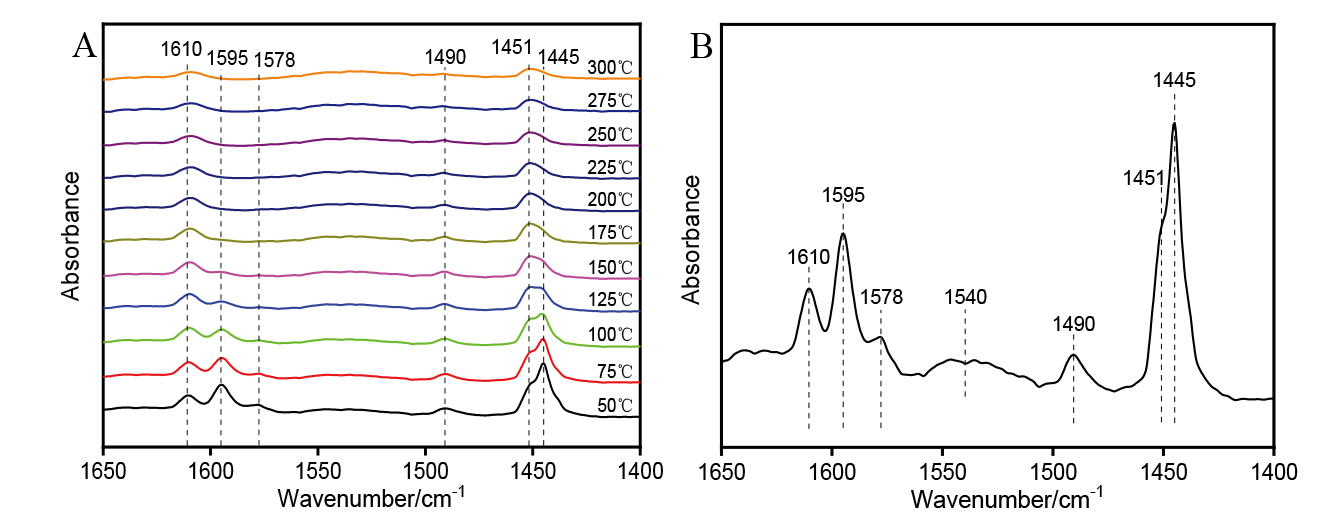
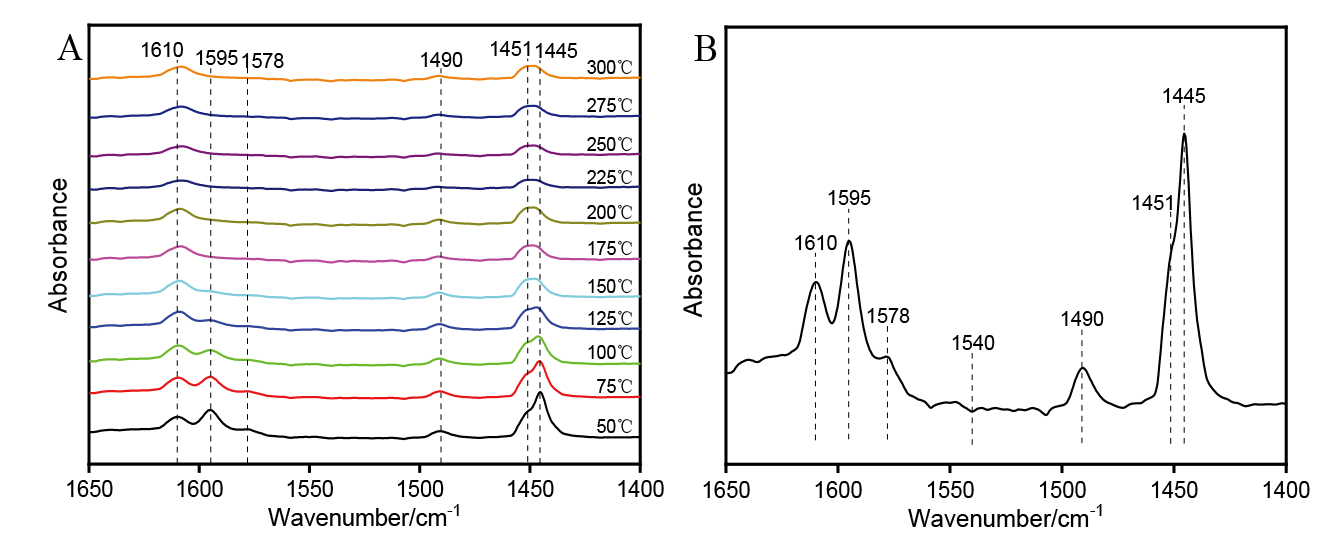
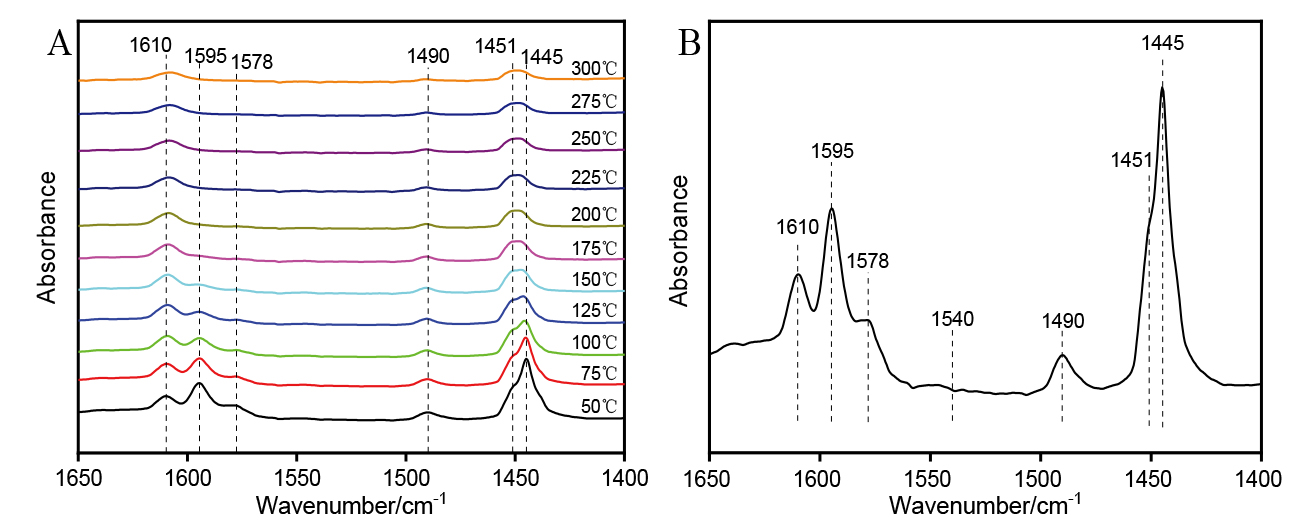
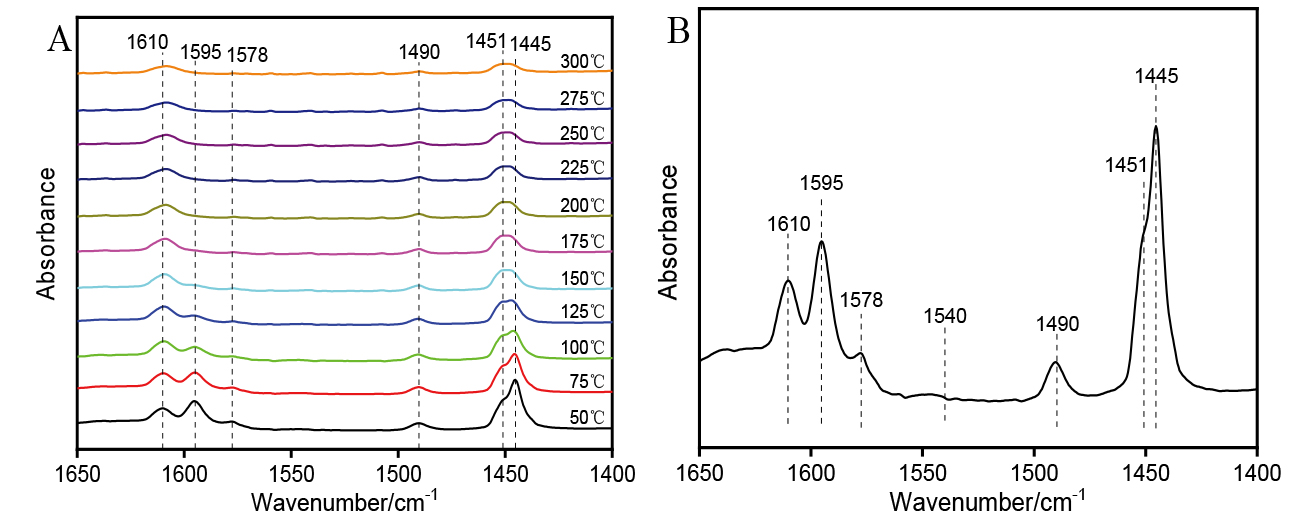
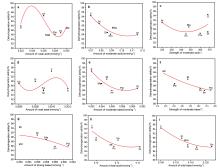

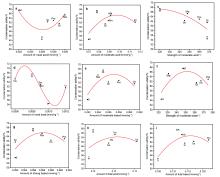

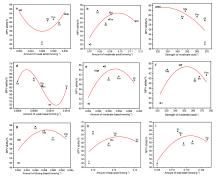



| [1] |
Corson, B. B.; Stahly, E. E.; Jones, H. E.; Bishop, H. D. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1949, 41, 1012.
|
| [2] |
Bruijnincx, P. C. A.; Weckhuysen, B. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11980.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201305058 pmid: 24136811 |
| [3] |
(a) Cespi, D.; Passarini, F.; Vassura, I.; Cavani, F. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1625.
|
|
(b) Shylesh, S.; Gokhale, A. A.; Scown, C. D.; Kim, D.; Ho, C. R.; Bell, A. T. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1462.
|
|
| [4] |
Pomalaza, G.; Arango Ponton, P.; Capron, M.; Dumeignil, F. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 4860.
|
| [5] |
(a) Li, H.; Riisager, A.; Saravanamurugan, S.; Pandey, A.; Sangwan, R. S.; Yang, S.; Luque, R. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 148.
|
|
(b) Bin Samsudin, I.; Zhang, H.; Jaenicke, S.; Chuah, G.-K. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 4199.
|
|
| [6] |
Sushkevich, V. L.; Ivanova, I. I.; Ordomsky, V. V.; Taarning, E. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2527.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.201402346 pmid: 25123990 |
| [7] |
Makshina, E. V.; Janssens, W.; Sels, B. F.; Jacobs, P. A. Catal. Today 2012, 198, 338.
|
| [8] |
Zhou, B.-X.; Ding, S.-S.; Zhang, B.-J.; Xu, L.; Chen, R.-S.; Luo, L.; Huang, W.-Q.; Xie, Z.; Pan, A.; Huang, G.-F. Appl. Catal., B 2019, 254, 321.
|
| [9] |
Osuga, R.; Fang, P.; Nishiyama, H.; Takizawa, K.; Yagihashi, N.; Yokoi, T.; Kondo, J. N. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 346, 112278.
|
| [10] |
Tu, P.-X.; Xue, B.; Tong, Y.-Q.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.-H.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Ni, J.; Li, X.-N. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 7258.
|
| [11] |
Damyanova, S.; Grange, P.; Delmon, B. J. Catal. 1997, 168, 421.
|
| [12] |
(a) Larina, O. V.; Kyriienko, P. I.; Balakin, D. Y.; Vorokhta, M.; Khalakhan, I.; Nychiporuk, Y. M.; Matolín, V.; Soloviev, S. O.; Orlyk, S. M. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 3964.
doi: 10.1039/c9cy00991d |
|
(b) Connell, G.; Dumesic, J. A. J. Catal. 1987, 105, 285.
|
|
|
(c) Larina, O. V.; Kyriienko, P. I.; Soloviev, S. O. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1162.
|
|
| [13] |
Ordomsky, V. V.; Sushkevich, V. L.; Ivanova, I. I. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2010, 333, 85.
|
| [14] |
(a) Jiang, D.-H.; Fang, G.-Q.; Tong, Y.-Q.; Wu, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Hong, D.-S.; Leng, W.-H.; Liang, Z.; Tu, P.-X.; Liu, L.; Xu, K.-Y.; Ni, J.; Li, X.-N. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11973.
|
|
(b) Wu, X.-Y.; Fang, G.-Q.; Liang, Z.; Leng, W.-H.; Xu, K.-Y.; Jiang, D.-H.; Ni, J.; Li, X.-N. Catal. Commun. 2017, 100, 15.
|
|
| [15] |
(a) Urbano, F. J.; Aramendía, M. A.; Marinas, A.; Marinas, J. M.. J. Catal. 2009, 268, 79.
|
|
(b) Liang, Z.; Jiang, D.-H.; Fang, G.-Q.; Leng, W.-H.; Tu, P.-X.; Tong, Y.-Q.; Liu, L.; Ni, J.; Li, X.-N. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 4364.
doi: 10.1002/slct.201900712 |
| [1] | 张璐璐, 王媛媛, 朱贵楠, 戴文博, 赵紫璇, 赵盈, 支俊格, 董宇平. 含不同烷基链四苯基丁二烯衍生物的聚集诱导发光及力致变色性能[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 282-290. |
| [2] | 杨磊, 吴宇静, 吴选军, 蔡卫权. 面向C4烯烃混合物吸附分离的真实金属-有机骨架材料高通量筛选[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 520-529. |
| [3] | 武艳, 庞爱民, 胡磊, 何根升, 张莹莹, 张利雄, 李明海, 马振叶. 纳米α-Fe2O3/(IPDI-HTPB)复合粒子的制备及其催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(4): 337-343. |
| [4] | 王永胜, 赵云鹭, 赵珍珍, 兰小林, 徐金霞徐伟祥, 段正康. 氮掺杂碳包覆Cu-ZrO2催化剂的制备及其催化脱氢性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(7): 661-668. |
| [5] | 付雯雯, 李严, 梁长海. 乙醇在Co(111)表面脱氢反应机理的第一性原理研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(6): 559-568. |
| [6] | 刘娇, 孙海龙, 印璐, 袁亚仙, 徐敏敏, 姚建林. 微流控芯片结合表面增强拉曼光谱实时监测α-苯乙醇的微量合成反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(3): 257-262. |
| [7] | 贾臻龙, 涂云宝, 王建强, Frenkel Anatoly I., 杨为民, 刘仲能, 许中强. X-射线吸收谱原位表征Cu-Zn/SiO2催化剂Cu价态[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(8): 639-643. |
| [8] | 吴匡衡, 周亚威, 马宪印, 丁辰, 蔡文斌. Au-Pt催化剂的控制合成及其对乙醇电氧化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(4): 292-297. |
| [9] | 朱婵, 海洋, 赵志刚, 阳耀月. Ni和P微量掺杂的Pd基催化剂对碱性介质中乙醇电氧化性能的增强效应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(1): 30-34. |
| [10] | 蔡跃进, 刘晨霞, 卓欧, 吴强, 杨立军, 陈强, 王喜章, 胡征. 温和条件下钌/氮掺杂碳纳米笼的苯乙酮选择性催化加氢性能[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(7): 686-691. |
| [11] | 孟超, 王华, 吴煜斌, 付贤智, 员汝胜. 二氧化钛光解水过程中乙醇选择性光催化氧化反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(5): 508-513. |
| [12] | 杨翠莲, 皇甫立霞, 粟航, 郭开华. 离子液体水溶液pH值测定及酸碱特性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(4): 495-501. |
| [13] | 付东, 王兰芬, 吴湘铖. DEA-CO2 水溶液的表面张力研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(03): 339-344. |
| [14] | 郑精武, 周杰, 郑飚, 乔梁, 姜力强, 张诚. 三乙醇胺对羟基亚乙基二膦酸镀铜液的影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(24): 2921-2928. |
| [15] | 范迎菊, 李加智, 孙中溪. 六方纳米氧化铟的制备及其气敏性质和表面酸碱性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(14): 1667-1672. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||