化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (3): 282-290.DOI: 10.6023/A21120556 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
张璐璐a, 王媛媛a, 朱贵楠b, 戴文博b, 赵紫璇a, 赵盈a, 支俊格a,*( ), 董宇平b
), 董宇平b
投稿日期:2021-12-12
发布日期:2022-01-22
通讯作者:
支俊格
基金资助:
Lulu Zhanga, Yuanyuan Wanga, Guinan Zhub, Wenbo Daib, Zixuan Zhaoa, Ying Zhaoa, Junge Zhia( ), Yuping Dongb
), Yuping Dongb
Received:2021-12-12
Published:2022-01-22
Contact:
Junge Zhi
Supported by:文章分享
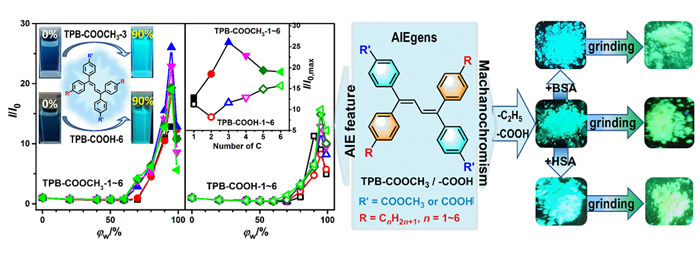
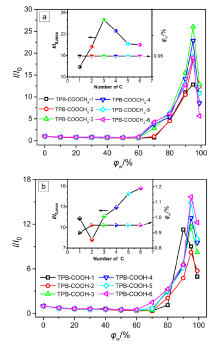
设计合成了带有不同长度烷基链、不同极性取代基的四苯基丁二烯(TPB)衍生物TPB-COOCH3-1~6和TPB-COOH-1~6, 目标化合物均具有显著的聚集诱导发光(AIE)特性及较高的固态荧光量子效率. 烷基链长及取代基极性都会影响目标化合物在聚集时分子排列及分子运动的受限程度, 从而调控其AIE行为. 带有羧酸甲酯的TPB-COOCH3-1~6中, 丙基取代的TPB-COOCH3-3在四氢呋喃/水(THF/H2O)体系中荧光发射增强最为显著; 而羧基取代的TPB-COOH-1~6中, 因亲水性增加, 己基取代的TPB-COOH-6荧光强度增加的倍数最大; 并且, TPB-COOH系列化合物荧光增强的倍数明显低于相同烷基取代的甲酯衍生物TPB-COOCH3. 此外, 牛血清白蛋白、人血清白蛋白和带有羧基的AIE化合物掺杂时明显影响其固态时的发光及其力致变色性质, 尤其是研磨后会明显提高其荧光强度.
张璐璐, 王媛媛, 朱贵楠, 戴文博, 赵紫璇, 赵盈, 支俊格, 董宇平. 含不同烷基链四苯基丁二烯衍生物的聚集诱导发光及力致变色性能[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 282-290.
Lulu Zhang, Yuanyuan Wang, Guinan Zhu, Wenbo Dai, Zixuan Zhao, Ying Zhao, Junge Zhi, Yuping Dong. Aggregation-Induced Emission and Mechanochromism of the Tetraphenylbutadiene Derivatives Containing Different Alkyl Chains[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 282-290.
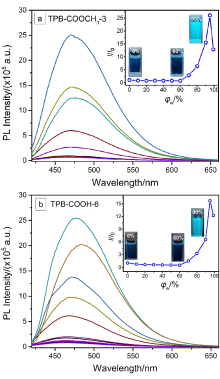

| 样品 | 溶液a | 固体 | αAIEd | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λabs/nm | λem/nm | Δλb/nm | Δνstb/cm-1 | ΦPLc/% | I/I0 | λem/nm | ΦPLc/% | |||||||
| TPB-COOCH3-1 | 368 | 470 | 102 | 5934 | 3.7 | 12.8 | 462 | 76.5 | 20.5 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-2 | 368 | 470 | 102 | 5934 | 3.8 | 18.5 | 460 | 80.1 | 20.6 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-3 | 370 | 472 | 102 | 5840 | 1.8 | 26.0 | 472 | 87.3 | 49.6 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-4 | 373 | 471 | 98 | 5614 | 1. 9 | 22.9 | 470 | 89.1 | 47.1 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-5 | 370 | 471 | 101 | 5796 | 2.1 | 19.3 | 470 | 87.5 | 41.9 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-6 | 370 | 471 | 101 | 5796 | 2.2 | 19.0 | 470 | 71.3 | 32.4 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-1 | 365 | 471 | 106 | 6166 | 3.9 | 11.3 | 496 | 55.6 | 14.4 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-2 | 365 | 470 | 105 | 6120 | 2.4 | 8.2 | 480 | 34.5 | 14.5 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-3 | 368 | 471 | 103 | 5979 | 2.1 | 11.6 | 500 | 42.8 | 20.8 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-4 | 368 | 472 | 104 | 6024 | 2.4 | 12.9 | 490 | 52.3 | 22.2 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-5 | 368 | 475 | 107 | 6158 | 2.3 | 14.9 | 492 | 60.9 | 26.3 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-6 | 368 | 475 | 107 | 6158 | 3.0 | 15.7 | 493 | 73.2 | 24.7 | |||||
| 样品 | 溶液a | 固体 | αAIEd | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λabs/nm | λem/nm | Δλb/nm | Δνstb/cm-1 | ΦPLc/% | I/I0 | λem/nm | ΦPLc/% | |||||||
| TPB-COOCH3-1 | 368 | 470 | 102 | 5934 | 3.7 | 12.8 | 462 | 76.5 | 20.5 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-2 | 368 | 470 | 102 | 5934 | 3.8 | 18.5 | 460 | 80.1 | 20.6 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-3 | 370 | 472 | 102 | 5840 | 1.8 | 26.0 | 472 | 87.3 | 49.6 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-4 | 373 | 471 | 98 | 5614 | 1. 9 | 22.9 | 470 | 89.1 | 47.1 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-5 | 370 | 471 | 101 | 5796 | 2.1 | 19.3 | 470 | 87.5 | 41.9 | |||||
| TPB-COOCH3-6 | 370 | 471 | 101 | 5796 | 2.2 | 19.0 | 470 | 71.3 | 32.4 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-1 | 365 | 471 | 106 | 6166 | 3.9 | 11.3 | 496 | 55.6 | 14.4 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-2 | 365 | 470 | 105 | 6120 | 2.4 | 8.2 | 480 | 34.5 | 14.5 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-3 | 368 | 471 | 103 | 5979 | 2.1 | 11.6 | 500 | 42.8 | 20.8 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-4 | 368 | 472 | 104 | 6024 | 2.4 | 12.9 | 490 | 52.3 | 22.2 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-5 | 368 | 475 | 107 | 6158 | 2.3 | 14.9 | 492 | 60.9 | 26.3 | |||||
| TPB-COOH-6 | 368 | 475 | 107 | 6158 | 3.0 | 15.7 | 493 | 73.2 | 24.7 | |||||

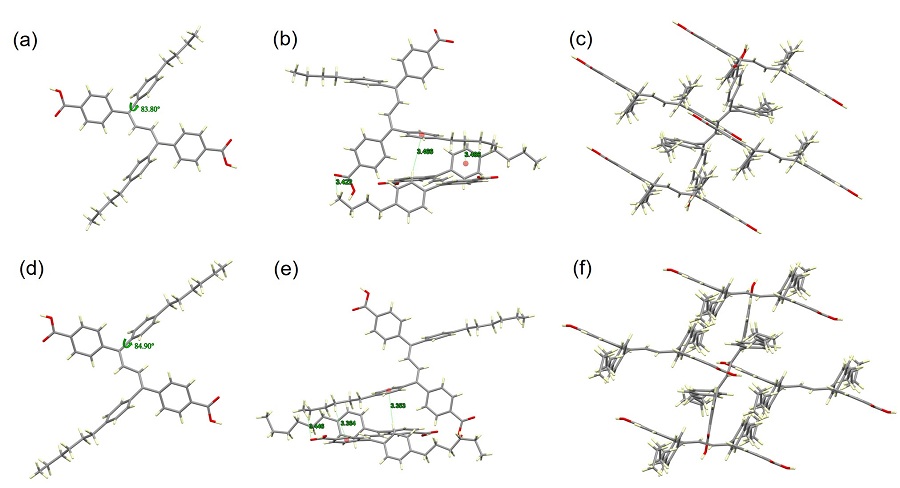
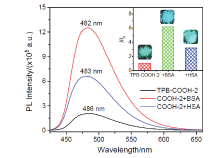
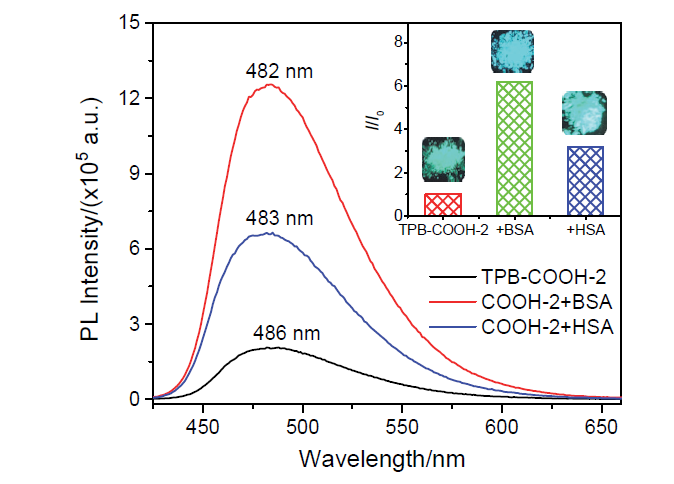
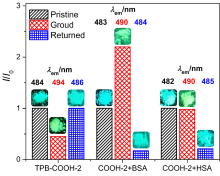

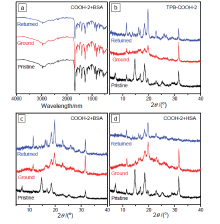
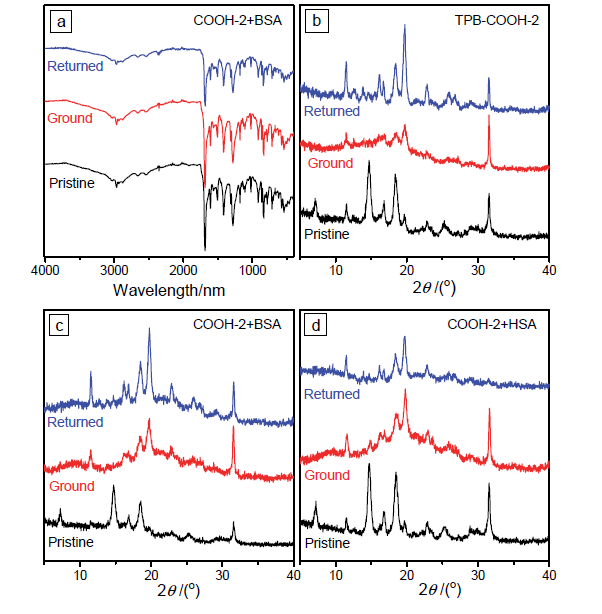
| [1] |
Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Cheng, L.; Tang, B. Z.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H. S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D. Chem. Commun. 2001, (18), 1740.
|
| [2] |
Chen, Y.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B. Z. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428.
doi: 10.1039/C8MH01331D |
| [3] |
Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Xu, W.; Shi, J.; Cai, Z.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15965.
doi: 10.1002/chem.201802114 |
| [4] |
Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.-J.; Xu, S.; Liu, B. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1862.
doi: 10.1039/C5SC03583J |
| [5] |
Gao, H.; Jiao, D.; Ou, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, D. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 319. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20100501 |
|
(高贺麟, 焦迪, 欧翰林, 章经天, 丁丹, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 319.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100501 |
|
| [6] |
Shao, L.; Sun, J.; Hua, B.; Huang, F. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4866.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC02077A |
| [7] |
Han, T.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Lin, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7049.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc42644k |
| [8] |
Zhang, Y.; Han, T.; Gu, S.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Bing, J.; Shi, J.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 8856.
|
| [9] |
Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Cai, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Dong, Y. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2018, 267, 351.
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.056 |
| [10] |
Guo, Y.; Feng, X.; Han, T.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15485.
doi: 10.1021/ja508962m |
| [11] |
Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Gao, W.-J.; Yu, H.-J.; Zhong, J.-X.; Jia, C.; Qin, Y.-S.; She, Z.; Kuang, D.-B.; Shao, G. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21088.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c02751 |
| [12] |
Guo, Y.; Gu, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Han, T.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, X.; James, T. D.; Wang, B. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4388.
doi: 10.1039/C4SC01611D |
| [13] |
He, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, M.; Cai, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3834.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.12 |
| [14] |
Liu, P.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 536.
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.064 |
| [15] |
Bera, M. K.; Chakraborty, C.; Malik, S. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 6872.
doi: 10.1039/C6TC04906K |
| [16] |
Xu, Z.; Gu, J.; Qiao, X.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z.; Ma, D. ACS Photonics 2019, 6, 767.
doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.8b01724 |
| [17] |
Zheng, K.; Ni, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, C.; Yang, C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9972.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.25 |
| [18] |
Huang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, B. S.; Tang, B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900516.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v29.16 |
| [19] |
Li, W.; Huang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Xie, Z.; Xu, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Aldred, M. P.; Chi, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12727.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201806861 |
| [20] |
Liu, M.; Wu, Q.; Shi, H.; An, Z.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 246. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A17110504 |
|
(刘明丽, 吴琪, 史慧芳, 安众福, 黄维, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 246.)
doi: 10.6023/A17110504 |
|
| [21] |
Hu, M.; Feng, H.-T.; Yuan, Y.-X.; Zheng, Y.-S.; Tang, B. Z. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2020, 416, 213329.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213329 |
| [22] |
Huang, Y.; You, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Gui, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10042.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.25 |
| [23] |
Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Han, M.; Liao, Q.; Huang, A.; Lin, P.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Li, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17297.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v58.48 |
| [24] |
Li, Q.; Li, Z. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 962.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00060 |
| [25] |
Wang, J.; Li, Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 575. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21010029 |
|
(王金凤, 李振, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 575.)
doi: 10.6023/A21010029 |
|
| [26] |
Zhou, T.; Qian, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, Q.; Xie, L.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 557. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A21010009 |
|
(周涛, 钱越, 王宏健, 冯全友, 解令海, 黄维, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 557.)
doi: 10.6023/A21010009 |
|
| [27] |
Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Ji, S.; Liu, Q.; Ding, D.; Zhao, D.; Liu, B. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2782.
doi: 10.1039/C6SC04384D |
| [28] |
Qu, J.; Ren, F.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Cai, Z.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14947.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v26.65 |
| [29] |
Li, N.; Liu, Y. Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, J. B.; Cui, R. R.; Gong, Q.; Zhao, N.; Tang, B. Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24249.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b04113 |
| [30] |
Qiu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, W.-C.; Xing, L.; Hu, S.; Ji, S.; Yang, Q.; Cai, N.; Ouyang, X.; Huo, Y. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 4139.
doi: 10.1039/C9TC05864H |
| [31] |
Li, J.-H.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Y.-X. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 8125.
doi: 10.1021/jo0486645 |
| [32] |
Li, Y.; Lei, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhi, J.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 573.
|
| [33] |
Yu, H.-X.; Zhi, J.; Wang, J.-L. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 3882.
doi: 10.1039/D0TC05994C |
| [34] |
Zhang, L.; Liang, K.; Dong, L.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhi, J.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 8877.
doi: 10.1039/C7NJ00583K |
| [35] |
Dong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Gong, J.; He, B.; Xu, S.; Yin, J.; Liu, S. H.; Tang, B. Z. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 894.
doi: 10.1039/C9TC06297A |
| [36] |
Xia, Z.; Shao, A.; Li, Q.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 351. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A16010001 |
|
(夏志清, 邵安东, 李强, 朱世琴, 朱为宏, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 351.)
doi: 10.6023/A16010001 |
|
| [37] |
Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Quan, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, S. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 439.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03620 |
| [38] |
Peng, Z.; Ji, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tong, B.; Shi, J.; Dong, Y. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1175.
doi: 10.1039/C8QM00096D |
| [39] |
Feng, X.; Tong, B.; Shen, J.; Shi, J.; Han, T.; Chen, L.; Zhi, J.; Lu, P.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Y. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16731.
doi: 10.1021/jp108254g |
| [40] |
Gao, H.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, A.; Wang, Y. Dyes Pigments 2018, 150, 165.
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.12.016 |
| [41] |
Lei, Y.; Lai, Y.; Dong, L.; Shang, G.; Cai, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhi, J.; Li, P.; Huang, X.; Tong, B.; Dong, Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 434.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.2 |
| [42] |
Song, W.; Zhi, J.; Wang, T.; Li, B.; Ni, S.; Ye, Y.; Wang, J. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 3875.
doi: 10.1002/asia.v14.21 |
| [43] |
Ràfols, C.; Amézqueta, S.; Fuguet, E.; Bosch, E. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 452.
doi: S0731-7085(17)32363-4 pmid: 29291587 |
| [44] |
Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Chem. J. Chinese Univ. 2021, 42, 731. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李梦硕, 张静, 刘丹, 朱亚先, 张勇, 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42, 731.)
|
| [1] | 刘斌, 陈磅宽. 基于联萘酚骨架的新型圆偏振发光材料的合成及性能探究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 929-935. |
| [2] | 王金凤, 李振. 聚集态分子排列对光电性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 575-587. |
| [3] | 高贺麒, 焦迪, 欧翰林, 章经天, 丁丹. 高性能聚集诱导发光纳米探针用于肿瘤切除手术导航[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 319-325. |
| [4] | 关晓琳, 李志飞, 王林, 刘美娜, 王凯龙, 杨学琴, 李亚丽, 胡丽丽, 赵小龙, 来守军, 雷自强. 具有AIE效应的Eu (III)-聚(N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮)配位聚合物Pdots的制备及双色肿瘤细胞成像[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(12): 1268-1278. |
| [5] | 夏志清, 邵安东, 李强, 朱世琴, 朱为宏. 取代基效应对喹啉腈AIE荧光性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(4): 351-355. |
| [6] | 彭喆, 季迎春, 王智, 佟斌, 石建兵, 董宇平. 具有聚集诱导发光性能的并吡咯衍生物的多晶性和酸响应行为研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 942-948. |
| [7] | 白玮, 史杨, 宋忱, 贺杰, 秦安军, 孙景志, 唐本忠. 荧蒽修饰的四苯基乙烯衍生物:分子合成、聚集增强荧光特性及其对苦味酸的高灵敏度检测[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 893-901. |
| [8] | 管伟江, 周文娟, 吕超. 基于聚集诱导发光金纳米簇构筑发光超薄膜[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 929-934. |
| [9] | 纪光, 闫路林, 王慧, 马莲, 徐斌, 田文晶. 高效近红外聚集诱导发光纳米粒子用于生物成像的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 917-922. |
| [10] | 黄玉章, 雷洛奇, 郑超, 危博, 赵祖金, 秦安军, 胡蓉蓉, 唐本忠. 含四苯基乙烯的炔酮衍生物的设计合成、聚集诱导发光性质及其对Pd2+的选择性荧光检测[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 885-892. |
| [11] | 段雨欣, 向雪琴, 董永强. 高对比度多色力致发光变色二苯并富烯衍生物的设计合成及性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 923-928. |
| [12] | 杨阳, 黄嫣嫣, 张关心, 赵睿, 张德清. 新型四苯乙烯衍生物的设计合成及其在羧酸酯酶活性分析中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 871-876. |
| [13] | 宾鑫, 罗卫剑, 袁望章, 张永明. 聚甲基丙烯酸(N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺)酯的簇聚诱导发光研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 935-941. |
| [14] | 韩婷, 詹嘉慧, 林荣业, 唐本忠. 具有聚集诱导发光效应的聚炔材料的合成及光学性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 877-884. |
| [15] | 余韵, 杨杰, 任子淳, 谢国华, 李倩倩, 李振. 可溶液加工蓝色聚集诱导发光小分子的合成及其器件性能[J]. 化学学报, 2016, 74(11): 865-870. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||