化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (1): 60-71.DOI: 10.6023/A24080248 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2024-08-21
发布日期:2024-11-08
作者简介: |
罗成璐, 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)在读硕士, 主要研究方向为纳米材料的合成、设计及其在生物医学领域上的应用. |
 |
田梦, 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)材料与化工在读博士, 主要从事新型纳米材料合成、精密生物传感方向的研究. |
 |
崔宇凡, 毕业于英国帝国理工学院, 目前于哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)攻读博士学位, 师从马兴毅教授, 从事纳米颗粒和等离子纳米孔的结合研究, 以改进单分子生物传感纳米材料的设计和合成. |
 |
马兴毅, 先后毕业于哈尔滨工业大学、成均馆大学和高丽大学, 现任哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)教授, 纳米医学与交叉科学课题组PI, 在生物医学工程、材料与化工、海洋科学等学科招收博士. 目前研究方向为: (1)生物技术→工程技术: 利用生物技术和生物分子设计制备高性能纳米材料, 将新材料用于生物芯片、传感系统等工程技术创新; (2)工程技术→医养健康: 利用纳米技术和纳米材料开展生物医学研究, 将新细胞用于生物发酵, 将新分子用于新药研发, 将新技术用于健康诊断和治疗. |
基金资助:
Chenglu Luoa, Meng Tiana, Yufan Cuia, Xingyi Maa,b,c( )
)
Received:2024-08-21
Published:2024-11-08
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享

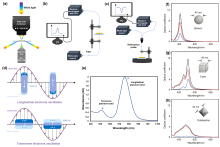
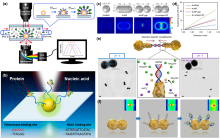
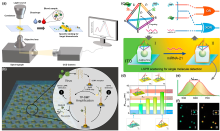
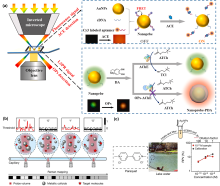
局域表面等离激元共振(LSPR), 是贵金属纳米材料产生的独特光学特性, 且备受广大研究者们关注. 将其与单分子识别检测策略结合, 可在分子水平上为光与物质之间的相互作用提供良好的研究体系. 因此, 本综述从LSPR传感策略出发, 介绍其基本原理并阐明了传感性能的影响因素, 进而探讨了高灵敏光学传感技术的设计方案, 综合分析了不同设计方案在单分子灵敏度检测中的前沿应用, 总结了技术发展趋势. 本综述可为研究者们开发和设计LSPR光学生物或化学传感器提供新思路, 并有效地提升单分子灵敏度检测的应用潜力.
罗成璐, 田梦, 崔宇凡, 马兴毅. 局域表面等离激元共振在单分子灵敏度检测中的应用及进展[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 60-71.
Chenglu Luo, Meng Tian, Yufan Cui, Xingyi Ma. Applications and Progress of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance in Detections with Single-molecule Sensitivity[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(1): 60-71.


| 检测物 | 分子量 | 使用材料 | 检测 光类型 | 检测时间 | 检测限 | 线性范围 | 发展潜力 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA1点突变DNA | 15~16 kDa | 金桥纳米颗粒 | 瑞利光散射 | 15 min | 8.63 nmol/L | 5~150 nmol/L | 依据亲和力大小建立识别图谱, 用以区分点突变类型[ |
| 外泌体PD-L1 | 33~45 kDa a | 金-银核壳纳米双锥体 | 散射光 | 38 min | 1.2×103~6.3×103 particles/μL | — | 检测限可降低至单个外泌体, 低样品消耗量, 可使用真实生物样品在单次测定中选择性鉴定、表征和测定外泌体亚 类[ |
| tau蛋白 | 55~62 kDa | 金纳米棒 | 瑞利光散射 | — | 153.17~179.85 fmol/L | 102~108 fmol/L | 可应用于创伤性小的样本, 如血液样本中的低含量目标物检测及相关临床试验[ |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 12 kDa | 金纳米岛 | 荧光 | ≤30 min | 直接检测: 0.1±0.04 pmol/L 扩增检测: 0.275±0.051 fmol/L | — | 实时病毒检测和预警[ |
| miRNA-21 | 6.65 kDa | Au@Ag核壳纳米立方体 | 散射光 | — | 0.1 amol/L | 1 amol/L~1 nmol/L | 对靶miRNA具有优异的选择性, 并且可用以区分miRNA中的单核苷酸突变, 以及异质样品的分析[ |
| 啶虫脒 | 208.65 Da | 纳米金 | 荧光 | — | 0.80 pmol/L | 2.40~479.27 nmol/L | 高选择性和可视化检测, 且可避免多农药检测的相互干 扰[ |
| 有机磷农药 | 483.15 Da | 散射光 | 0.35 fmol/L | 1.03~2.07×103 fmol/L | |||
| 卡那霉素 | 484.50 Da | SiO2-Au-ssDNA二维光子晶体 | 反射光 | — | 2.27 pmol/L | 10.32~10.32×106 pmol/L | 有一定的抗干扰能力, 可在复杂环境中快速测量[ |
| 抗PD1单克隆抗体 | 140~150 kDa | 金纳米盘阵列 | 反射光 | ≤20 min | 0.43 nmol/L | — | 仿生传感器, 研究新的免疫检查点靶点或可能的肿瘤耐药机制[ |
| 检测物 | 分子量 | 使用材料 | 检测 光类型 | 检测时间 | 检测限 | 线性范围 | 发展潜力 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA1点突变DNA | 15~16 kDa | 金桥纳米颗粒 | 瑞利光散射 | 15 min | 8.63 nmol/L | 5~150 nmol/L | 依据亲和力大小建立识别图谱, 用以区分点突变类型[ |
| 外泌体PD-L1 | 33~45 kDa a | 金-银核壳纳米双锥体 | 散射光 | 38 min | 1.2×103~6.3×103 particles/μL | — | 检测限可降低至单个外泌体, 低样品消耗量, 可使用真实生物样品在单次测定中选择性鉴定、表征和测定外泌体亚 类[ |
| tau蛋白 | 55~62 kDa | 金纳米棒 | 瑞利光散射 | — | 153.17~179.85 fmol/L | 102~108 fmol/L | 可应用于创伤性小的样本, 如血液样本中的低含量目标物检测及相关临床试验[ |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 12 kDa | 金纳米岛 | 荧光 | ≤30 min | 直接检测: 0.1±0.04 pmol/L 扩增检测: 0.275±0.051 fmol/L | — | 实时病毒检测和预警[ |
| miRNA-21 | 6.65 kDa | Au@Ag核壳纳米立方体 | 散射光 | — | 0.1 amol/L | 1 amol/L~1 nmol/L | 对靶miRNA具有优异的选择性, 并且可用以区分miRNA中的单核苷酸突变, 以及异质样品的分析[ |
| 啶虫脒 | 208.65 Da | 纳米金 | 荧光 | — | 0.80 pmol/L | 2.40~479.27 nmol/L | 高选择性和可视化检测, 且可避免多农药检测的相互干 扰[ |
| 有机磷农药 | 483.15 Da | 散射光 | 0.35 fmol/L | 1.03~2.07×103 fmol/L | |||
| 卡那霉素 | 484.50 Da | SiO2-Au-ssDNA二维光子晶体 | 反射光 | — | 2.27 pmol/L | 10.32~10.32×106 pmol/L | 有一定的抗干扰能力, 可在复杂环境中快速测量[ |
| 抗PD1单克隆抗体 | 140~150 kDa | 金纳米盘阵列 | 反射光 | ≤20 min | 0.43 nmol/L | — | 仿生传感器, 研究新的免疫检查点靶点或可能的肿瘤耐药机制[ |


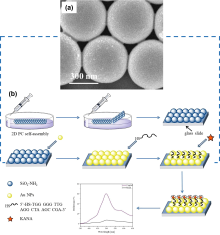

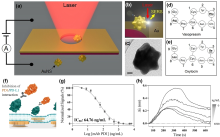

| [1] |
Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, J. J.; Xia, X. H.; Chen, H. Y. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108165.
|
| [2] |
Mayer, K. M.; Hafner, J. H. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3828.
|
| [3] |
Kim, S.; Kim, J. M.; Park, J. E.; Nam, J. M. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704528.
|
| [4] |
Jain, P. K.; Huang, X. H.; El-Sayed, I. H.; El-Sayed, M. A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1578.
|
| [5] |
Lee, S. E.; Lee, L. P. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2010, 21, 489.
|
| [6] |
Li, Y.; Jing, C.; Zhang, L.; Long, Y. T. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 632.
|
| [7] |
Shao, L.; Ruan, Q. F.; Wang, J. F.; Lin, H. Q. Physics 2014, 43, 290 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 邵磊, 阮琦锋, 王建方, 林海青, 物理, 2014, 43, 290.)
|
|
| [8] |
Zhou, W. C.; Li, Z. H.; Wu, J. Chin. Opt. 2022, 15, 878 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 周文超, 李政昊, 武杰, 中国光学(中英文), 2022, 15, 878.)
|
|
| [9] |
Cheng, L.; Jia, C. C.; Guo, X. F. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 2155 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 程丽, 贾传成, 郭雪峰, 科学通报, 2023, 68, 2155.)
|
|
| [10] |
Zhao, X.; Hao, Q.; Ni, Z. H.; Qiu, T. Acta Phys. Sinica 2021, 70, 148 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 赵星, 郝祺, 倪振华, 邱腾, 物理学报, 2021, 70, 148.)
|
|
| [11] |
Hu, J.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zhang, C. Y. Scientia Sinica Chim. 2017, 47, 1161 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 胡娟, 王子月, 张春阳, 中国科学:化学, 2017, 47, 1161.)
|
|
| [12] |
Ma, X. Y.; Song, S.; Kim, S.; Kwon, M. S.; Lee, H.; Park, W.; Sim, S. J. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 836.
|
| [13] |
Zhang, P. F.; Ma, G. Z.; Dong, W.; Wan, Z. J.; Wang, S. P.; Tao, N. J. Nat. Methods. 2020, 17, 1010.
|
| [14] |
Jia, H. X.; Li, Z. P.; Liu, C. H.; Cheng, Y. Q. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5498.
|
| [15] |
Sreekanth, K. V.; Alapan, Y.; ElKabbash, M.; Ilker, E.; Hinczewski, M.; Gurkan, U. A.; Luca, A. D.; Strangi, G. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 621.
|
| [16] |
Liu, L. H.; Zhang, X. J.; Zhu, Q.; Li, K. W.; Lu, Y; Zhou, X. H.; Guo, T. Light-Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 181.
|
| [17] |
Monroe, M. R.; Daaboul, G. G.; Tuysuzoglu, A.; Lopez, C. A.; Little, F. F.; Ünlü, M. S. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3698.
doi: 10.1021/ac4000514 pmid: 23469929 |
| [18] |
Liu, M. M.; Chao, J.; Deng, S.; Wang, K.; Li, K.; Fan, C. H. Colloid Surface B. 2014, 124, 111.
|
| [19] |
Hammami, I.; Alabdallah, N. M.; Al Jomaa, A.; Kamoun, M. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101560.
|
| [20] |
Li, J.; Lou, Z. Z.; Li, B. J. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1154.
|
| [21] |
Chen, C. Y.; Li, Y. F.; Qu, Y.; Chai, Z. F.; Zhao, Y. L. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8266.
|
| [22] |
Fan, J. N.; Cheng, Y. Q.; Sun, M. T. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 1474.
|
| [23] |
Lee, K. S.; El-Sayed, M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 19220.
|
| [24] |
Zhang, L.; Ma, X. Y.; Wang, G. Q.; Liang, X. G.; Mitomo, H.; Pike, A.; Houlton, A.; Ijiro, K. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101154.
|
| [25] |
Truong, P. L.; Ma, X. Y.; Sim, S. J. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2307.
doi: 10.1039/c3nr05211g pmid: 24413584 |
| [26] |
Agrawal, N.; Saxena, R.; Singh, L.; Saha, C.; Kumar, S. ISSS J. Micro Smart Syst. 2022, 11, 31.
|
| [27] |
Willets, K. A.; Van Duyne, R. P. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267.
|
| [28] |
Wang, K.; Cao, L. Sciencepaper online 2014 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 王康, 曹雷, 中国科技论文在线, 2014.)
|
|
| [29] |
Cao, J.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K. T. V. Sensor Actuators B-Chem. 2014, 195, 332.
|
| [30] |
Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U. J. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.08.020 pmid: 21995909 |
| [31] |
Anker, J. N.; Hall, W. P.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N. C.; Zhao, J.; Van Duyne, R. P. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 442.
|
| [32] |
Wiley, B. J.; Im, S. H.; Li, Z. Y.; Mclellan, J.; Siekkinen, A.; Xia, Y. N. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15666.
|
| [33] |
Zhu, S. L.; Zhou, W. J. Opt. 2011, 40, 65.
|
| [34] |
Yan, B. X.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Wei, Y.; Pei, H. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8391.
|
| [35] |
Ma, X. Y.; Sim, S. J. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6197.
|
| [36] |
Schatz, G. C.; Van Duyne, R. P. Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, 2006, pp. 759-774.
|
| [37] |
Lee, L. Understanding Biophotonics: Fundamentals, Advances, and Applications, Ed.: Tsia, K. K., CRC, Florida, 2015, Chapter 8.
|
| [38] |
Jia, B. L.; Chen, J. J.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Y. J.; Ho, H. P.; Shao, Y. H. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8367.
|
| [39] |
Ma, X. Y.; Huh, J.; Park, W.; Lee, L. P.; Kwon, Y. J.; Sim, S. J. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12873.
|
| [40] |
Hartland, G. V. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3858.
doi: 10.1021/cr1002547 pmid: 21434614 |
| [41] |
Shang, L.; Liu, C. J.; Chen, B.; Hayashi, K. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1531.
|
| [42] |
Sepúlveda, B.; Angelomé, P. C.; Lechuga, L. M.; Liz-Marzán, L. M. Nano Today 2009, 4, 244.
|
| [43] |
Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, X. L.; Dodson, S. L.; Dao, N. T.; Wong, L. M.; Wang, S. J.; Li, S. Z.; Phan, A. T.; Xiong, Q. H. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7583.
|
| [44] |
Ma, X. Y.; Truong, P. L.; Anh, N. H.; Sim, S. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 59.
|
| [45] |
Wang, Y.; Liu, X. L.; Wu, L. J.; Ding, L. H.; Effah, C. Y.; Wu, Y. J.; Xiong, Y. M.; He, L. L. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113661.
|
| [46] |
Qiu, G. Y.; Gai, Z. B.; Saleh, L.; Tang, J. K.; Gui, T.; Kullak-Ublick, G. A.; Wang, J. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7536.
|
| [47] |
Taylor, A. B.; Zijlstra, P. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1103.
|
| [48] |
Shu, F. Z.; Fan, R. H.; Wang, J. N.; Peng, R. W.; Wang, M. Acta Phys. Sin. 2019, 68, 133 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 束方洲, 范仁浩, 王嘉楠, 彭茹雯, 王牧, 物理学报, 2019, 68, 133.)
|
|
| [49] |
El Barghouti, M.; Haidar, O.; Akjouj, A.; Mir, A. Photonic. Nanostruct. 2022, 50, 101016.
|
| [50] |
Farka, Z.; Mickert, M. J.; Pastucha, M.; Mikusová, Z.; Skládal, P.; Gorris, H. H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10746.
|
| [51] |
Chauhan, N.; Saxena, K.; Jain, U. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1389.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.038 pmid: 35413320 |
| [52] |
Kim, H.; Lee, J. U.; Kim, S.; Song, S.; Sim, S. J. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 595.
|
| [53] |
Qiu, G. Y.; Gai, Z. B.; Tao, Y. L.; Schmitt, J.; Kullak-Ublick, G. A.; Wang, J. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5268.
|
| [54] |
Guo, K. Y.; Wustoni, S.; Koklu, A.; Díaz-Galicia, E.; Moser, M.; Hama, A.; Alqahtani, A. A.; Ahmad, A. N.; Alhamlan, F. S.; Shuaib, M.; Pain, A.; McCulloch, I.; Arold, S. T.; Grünberg, R.; Inal, S. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 666.
|
| [55] |
Zhang, Y.; Shuai, Z. H.; Zhou, H.; Luo, Z. M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y. N.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S. F.; Chao, J.; Weng, L. X.; Fan, Q. L.; Fan, C. H.; Huang, W.; Wang, L. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3988.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12772 pmid: 29504757 |
| [56] |
Behera, B. K.; Das, A.; Sarkar, D. J.; Weerathunge, P.; Parida, P. K.; Das, B. K.; Thavamani, P.; Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 212.
doi: S0269-7491(18)30649-3 pmid: 29807281 |
| [57] |
Borah, S. B. D.; Borah., T.; Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 1, 1.
|
| [58] |
Yang, Z. Y.; Sassa, F.; Hayashi, K. Sensors-Basel. 2023, 23, 9525.
|
| [59] |
Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z. W.; Liu, S. Q. Sensor Actuators B-Chem. 2022, 351, 130977.
|
| [60] |
Wang, X.; Wang, X. W.; Xiao, L. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1002 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A23040147 |
|
( 王晓, 王星文, 肖乐辉, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1002.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040147 |
|
| [61] |
Weng, R.; Lou, S. T.; Li, L. D.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Su, X.; Qian, Y. Z.; Walter, N. G. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1424.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04145 pmid: 30562003 |
| [62] |
Wei, H.; Abtahi, S. M. H.; Vikesland, P. J. Environ. Sci-Nano. 2015, 2, 120.
|
| [63] |
Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. C. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 835 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 杨犇, 张尧, 张杨, 董振超, 真空科学与技术学报, 2021, 41, 835.)
|
|
| [64] |
Bi, X. Y.; Czajkowsky, D. M.; Shao, Z. F.; Ye, J. Nature 2024, 628, 711.
|
| [65] |
Prigoda, K.; Ermina, A.; Bolshakov, V.; Tabarov, A.; Levitskii, V.; Andreeva, O.; Gazizulin, A.; Pavlov, S.; Danilenko, D.; Vitkin, V.; Zharova, Y. Opt. Mater. 2024, 149, 114977.
|
| [66] |
Su, Z. Q.; Li, T.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y. N.; Li, G. L. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 458.
|
| [67] |
Spitzberg, J. D.; Zrehen, A.; van Kooten, X. F.; Meller, A. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900422.
|
| [68] |
Yang, J. M.; Feng, J. D. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2452 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 杨金梅, 冯建东, 科学通报, 2022, 67, 2452.)
|
|
| [69] |
Li, X. X.; Jia, M. D.; Yu, L. C.; Li, Y. J.; He, X. W.; Chen, L. X.; Zhang, Y. K. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134239.
|
| [70] |
Zhang, Y. Y.; Li, G. L.; Wu, D.; Li, X. T.; Yu, Y. X.; Luo, P. J.; Chen, J.; Dai, C. J.; Wu, Y. N. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2019, 121, 115669.
|
| [71] |
Cappi, G.; Spiga, F. M.; Moncada, Y.; Ferretti, A.; Beyeler, M.; Bianchessi, M.; Decosterd, L.; Buclin, T.; Guiducci, C. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5278.
|
| [72] |
Huang, J. A.; Mousavi, M. Z.; Giovannini, G.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Hubarevich, A.; Soler, M. A.; Rocchia, W.; Garoli, D.; Angelis, F. D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11423.
|
| [73] |
Zhao, Q. L.; Yang, L.; Xie, R. X. China Pharm. 2020, 31, 2294 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 赵秋玲, 杨琳, 谢瑞祥, 中国药房, 2020, 31, 2294.)
|
|
| [74] |
Zinn, S.; Vazquez-Lombardi, R.; Zimmermann, C.; Sapra, P.; Jermutus, L.; Christ, D. Nat. Cancer. 2023, 4, 165.
|
| [75] |
Batool, R.; Soler, M.; Singh, R.; Lechuga, L. M. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, DOI: 10.1007/s00216-024-05398-3.
|
| [76] |
Batool, R.; Soler, M.; Colavita, F.; Fabeni, L.; Matusali, G.; Lechuga, L. M. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 226, 115137.
|
| [77] |
Fan, H. L.; Huang, L. P.; Li, R.; Chen, M. Q.; Huang, J. J.; Xu, H.; Hu, W. J.; Liu, G. L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203635.
|
| [78] |
Zeng, Q.; Zhou, X. Y.; Yang, Y. T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. A.; Zhai, C. H.; Li, J. H.; Yu, H. PNAS 2020, 119, e2120379119.
|
| [79] |
Wang, C. Y.; Huang, C. H.; Gao, Z. Q.; Shen, J. L.; He, J. C.; MacLachlan, A.; Ma, C.; Chang, Y.; Yang, W.; Cai, Y. X.; Lou, Y.; Dai, S. Y.; Chen, W. Q.; Li, F.; Chen, P. Y. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3308.
|
| [80] |
Li, C. W.; Lim, S. O.; Xia, W. Y.; Lee, H. H.; Chan, L. C.; Kuo, C. W.; Khoo, K. H.; Chang, S. S.; Cha, J. H.; Kim, T. W.; Hsu, J. L.; Wu, Y.; Hsu, J. M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ding, Q. Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Lee, C. C.; Wu, H. J.; Sahin, A. A.; Allison, J. P.; Yu, D. H.; Hortobagyi, G. N.; Hung, M. C. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12632.
|
| [81] |
Shu, Z.; Dwivedi, B.; Switchenko, J. M.; Yu, D. S.; Deng, X. M. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6830.
|
| [1] | 谷琪, 刘夏夏, 周鑫宇, 李江, 林秀婧, 马延文. 用于锂金属电池的聚合物固态电解质的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 449-457. |
| [2] | 崔国庆, 胡溢玚, 娄颖洁, 周明霞, 李宇明, 王雅君, 姜桂元, 徐春明. CO2加氢制醇类催化剂的设计制备及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1081-1100. |
| [3] | 宋云霞, 梁飞, 田皓天, 吴燕, 罗敏. 基于分子工程的方法设计首例具有Sr2Be2B2O7 (SBBO)结构的深紫外氟碳酸盐双折射晶体AMgLi2(CO3)2F (A=K, Rb)※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 105-109. |
| [4] | 李泽洋, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 二氧化碳还原电催化剂的结构设计及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 199-213. |
| [5] | 王静, 王锦. 气凝胶维度结构设计与功能化应用的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 430-442. |
| [6] | 林祖金, 曹荣. 多孔氢键有机框架(HOFs):现状与挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1309-1335. |
| [7] | 王亚锋, 杨倩, 苏彬. 基于纳米多孔薄膜光学干涉的光学传感器[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(11): 1071-1081. |
| [8] | 刘浩富, 孔凡娟, 饶艳英, 董健, 钱卫平. Ag@SiO2纳米颗粒的制备及其在H2O2检测上的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(9): 865-869. |
| [9] | 贯军,汤中佳,吴国庆. 新型混价稀土氟化物KEuLaF~6: 结构设计和碱金属还原法相结合的新产品[J]. 化学学报, 1995, 53(5): 468-472. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||