化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (8): 962-980.DOI: 10.6023/A25040117 上一篇
综述
投稿日期:2025-04-12
发布日期:2025-06-18
通讯作者:
张松涛, 庞欢
作者简介: |
高春, 江苏商贸职业学院继续教育学院副院长, 副教授, 长期从事化学教育研究和高校继续教育工作. |
 |
张松涛, 扬州大学测试中心助理研究员. 2016年毕业于南京航空航天大学, 获材料物理与化学博士学位. 近年来主要从事开发应用于电化学储能的MOF基功能材料和介孔基纳米复合材料. |
 |
庞欢, 男, 扬州大学化学化工学院院长, 二级教授, 博士生导师. 于2011年获得南京大学理学博士学位. 为教育部青年长江学者、新世纪优秀人才、江苏省杰出青年、英国皇家化学学会会士及全球高被引学者, 兼任《国家科学评论》学科编辑组成员及Nano Res.、Rare Met.等期刊编委. 主要从事纳米配合物及其衍生物的合成、功能应用研究, 尤其是纳米金属有机框架(MOF)的电化学研究. |
★ “中国青年化学家”专辑.
基金资助:
Chun Gaoa, Songtao Zhangb,*( ), Huan Pangb,c,*(
), Huan Pangb,c,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-12
Published:2025-06-18
Contact:
Songtao Zhang, Huan Pang
About author:★ For the VSI “Rising Stars in Chemistry”.
Supported by:文章分享

由于环境问题日益加剧, 能源需求持续增长, 传统材料已难以满足这些领域的进一步需求. 金属有机框架(MOFs)材料因其多孔结构、大比表面积和多功能的特性, 在这些领域中展现出巨大的潜力. 然而, 纯MOFs固有的不稳定性和低导电性限制了其实际应用. 基于MOFs的复合材料在保留单纯MOFs优点的同时, 整合了客体材料(包括无机碳材料、金属氧化物和聚合物等)的功能, 在未来能源和环境等科学领域展现出重要的研究价值. 全面综述了MOF复合材料在电化学储能和吸附领域的应用, 并从维度角度分析了基于MOFs的各种复合材料的物理和化学性质. 在此背景下, 不仅强调了MOF复合材料的优势, 还对其应用效果进行了详细分析和客观概述.
高春, 张松涛, 庞欢. 金属有机框架复合材料★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 962-980.
Chun Gao, Songtao Zhang, Huan Pang. Metal-Organic Framework Composites★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(8): 962-980.
| MOF复合物类型 | 结构调控的核心策略 | 电化学性能提升机制 | 合成工艺 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 金属氧化物@MOFs | 通过金属价态调控与异质界面设计优化电子结构 | 法拉第赝电容与协同电子传导 | 溶剂热、电化学沉积 |
| 无机碳材料@MOFs | 以MOF为前驱体, 通过热解与孔结构设计实现碳基功能化 | 双电层电容与表面赝电容 | 高温热解、模板法中空化 |
| 聚合物@MOFs | 引入多种官能团, 实现氧化还原活性、离子传导和 界面稳定化的协同 | 增强柔性、离子通透性与稳定性 | 原位聚合、一锅法 |
| MOF复合物类型 | 结构调控的核心策略 | 电化学性能提升机制 | 合成工艺 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 金属氧化物@MOFs | 通过金属价态调控与异质界面设计优化电子结构 | 法拉第赝电容与协同电子传导 | 溶剂热、电化学沉积 |
| 无机碳材料@MOFs | 以MOF为前驱体, 通过热解与孔结构设计实现碳基功能化 | 双电层电容与表面赝电容 | 高温热解、模板法中空化 |
| 聚合物@MOFs | 引入多种官能团, 实现氧化还原活性、离子传导和 界面稳定化的协同 | 增强柔性、离子通透性与稳定性 | 原位聚合、一锅法 |



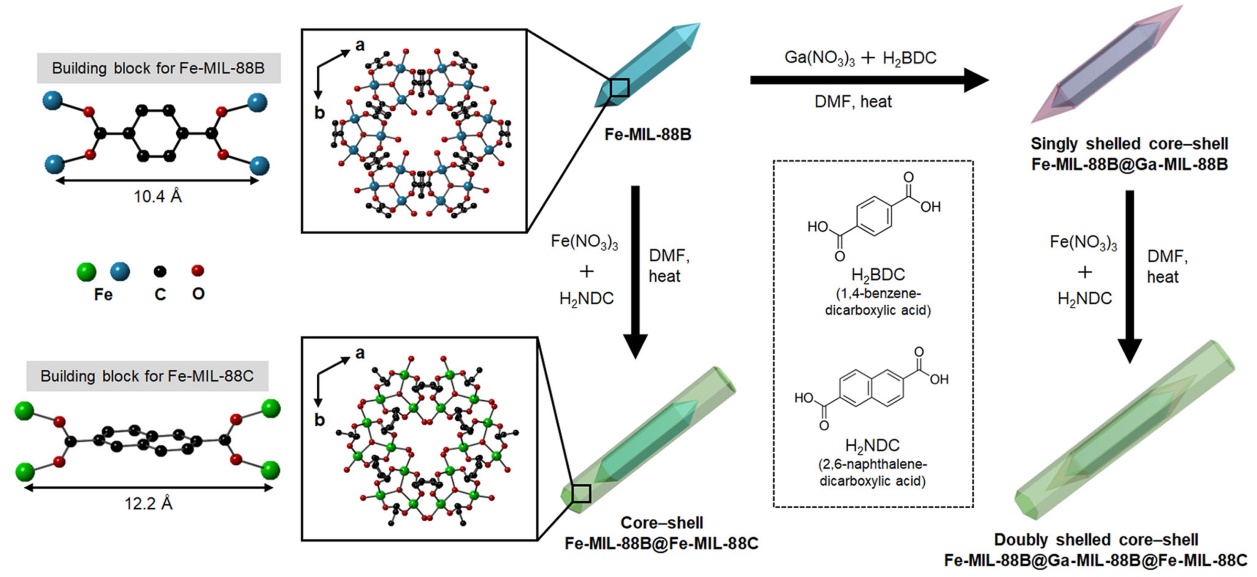






| MOF复合物 | 客体材料 | 应用 | 比容量 | 容量保持率 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPHK | 聚吡咯 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 147.2 mAh•g-1 at 1 C | 86.7% after 800 cycles | [ |
| Si/CNTs@ZIF-800N | 硅, 碳纳米管 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 1223 mAh•g-1 at 0.1 A•g-1 | 98.4% after 100 cycles | [ |
| Porous ZnCo2O4/C | 碳纤维 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 1707 mAh•g-1 at 0.1 A•g-1 | 67.1% after 100 cycles | [ |
| Co-TCPP MOF/rGO | 还原氧化石墨烯 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 2317 mAh•g-1 at 0.1 A•g-1 | ≈45.3% after 100 cycles | [ |
| PPy@Cu-MOFs | 聚吡咯 | 锂离子电池隔膜 | 150.2 mAh•g-1 at 0.5 C | ≈100% after 200 cycles | [ |
| PP@MIL-101-COOH | 聚偏二氟乙烯 | 锂离子电池隔膜 | — | 95.9% after 150 cycles | [ |
| PH-SSE | 聚偏二氟乙烯 | 锂离子电池电解质 | — | 85.1% after 300 cycles | [ |
| BMOF@HF/H-ZIF-8 | 聚丙烯腈中空纤维 | 锂离子电池电解质 | — | 90.45% after 200 cycles | [ |
| MOF复合物 | 客体材料 | 应用 | 比容量 | 容量保持率 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPHK | 聚吡咯 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 147.2 mAh•g-1 at 1 C | 86.7% after 800 cycles | [ |
| Si/CNTs@ZIF-800N | 硅, 碳纳米管 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 1223 mAh•g-1 at 0.1 A•g-1 | 98.4% after 100 cycles | [ |
| Porous ZnCo2O4/C | 碳纤维 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 1707 mAh•g-1 at 0.1 A•g-1 | 67.1% after 100 cycles | [ |
| Co-TCPP MOF/rGO | 还原氧化石墨烯 | 锂离子电池阳极 | 2317 mAh•g-1 at 0.1 A•g-1 | ≈45.3% after 100 cycles | [ |
| PPy@Cu-MOFs | 聚吡咯 | 锂离子电池隔膜 | 150.2 mAh•g-1 at 0.5 C | ≈100% after 200 cycles | [ |
| PP@MIL-101-COOH | 聚偏二氟乙烯 | 锂离子电池隔膜 | — | 95.9% after 150 cycles | [ |
| PH-SSE | 聚偏二氟乙烯 | 锂离子电池电解质 | — | 85.1% after 300 cycles | [ |
| BMOF@HF/H-ZIF-8 | 聚丙烯腈中空纤维 | 锂离子电池电解质 | — | 90.45% after 200 cycles | [ |




| MOF复合物 | 客体材料 | 应用 | 比容量 | 容量保持率 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-BTC/CNTs | 碳纳米管 | 锂硫电池阴极 | 805.28 mAh•g−1 at 1 C | 60.34% after 200 cycles | [ |
| ZIF@T-PVDF | 聚偏二氟乙烯 | 锂硫电池隔膜 | 1324.2 mAh•g−1 at 2 C | — | [ |
| CSUST-1/CNT | CNT | 锂硫电池隔膜 | 1468 mAh•g−1 at 0.1 C | — | [ |
| UiO-66/ACNT | 酸处理碳纳米管 | 锂硫电池隔膜 | 4.01 mAh•cm-2 at 0.2C | — | [ |
| MOF复合物 | 客体材料 | 应用 | 比容量 | 容量保持率 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-BTC/CNTs | 碳纳米管 | 锂硫电池阴极 | 805.28 mAh•g−1 at 1 C | 60.34% after 200 cycles | [ |
| ZIF@T-PVDF | 聚偏二氟乙烯 | 锂硫电池隔膜 | 1324.2 mAh•g−1 at 2 C | — | [ |
| CSUST-1/CNT | CNT | 锂硫电池隔膜 | 1468 mAh•g−1 at 0.1 C | — | [ |
| UiO-66/ACNT | 酸处理碳纳米管 | 锂硫电池隔膜 | 4.01 mAh•cm-2 at 0.2C | — | [ |

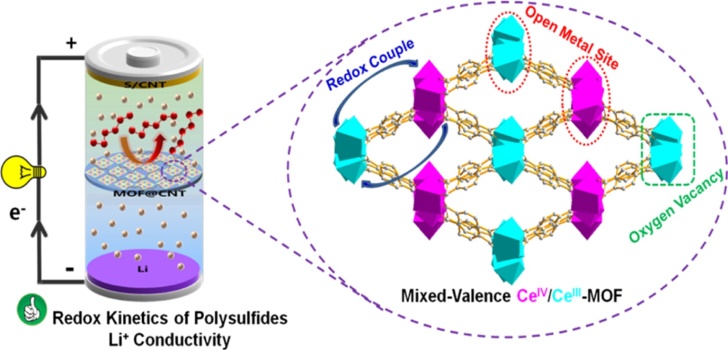
| MOF复合物 | 客体材料 | 应用 | 比容量 | 容量保持率 | 文献. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-88B(V)@rGO | 氧化石墨烯 | 锌离子电池阴极 | 480 mAh•g-1 at 0.05 A•g-1 | 80.3% after 400 cycles | [ |
| Mn-MOF/CNT | 碳纳米管 | 锌离子电池阴极 | 260 mAh•g-1 at 0.05 A•g-1 | ≈100% after 900 cycles | [ |
| V-MOF@graphene | 石墨烯 | 锌离子电池阴极 | 342 mAh•g-1 at 0.1A•g-1 | ≈89% after 100 cycles | [ |
| MXene/Cu-THBQ | MXene | 锌离子电池阳极 | 235.4 mAh•g-1 at 0.2 A•g-1 | 98.7% after 400 cycles | [ |
| MOF复合物 | 客体材料 | 应用 | 比容量 | 容量保持率 | 文献. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIL-88B(V)@rGO | 氧化石墨烯 | 锌离子电池阴极 | 480 mAh•g-1 at 0.05 A•g-1 | 80.3% after 400 cycles | [ |
| Mn-MOF/CNT | 碳纳米管 | 锌离子电池阴极 | 260 mAh•g-1 at 0.05 A•g-1 | ≈100% after 900 cycles | [ |
| V-MOF@graphene | 石墨烯 | 锌离子电池阴极 | 342 mAh•g-1 at 0.1A•g-1 | ≈89% after 100 cycles | [ |
| MXene/Cu-THBQ | MXene | 锌离子电池阳极 | 235.4 mAh•g-1 at 0.2 A•g-1 | 98.7% after 400 cycles | [ |










| [1] |
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
(何燕萍, 谭衍曦, 张健, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 1228.)
doi: 10.6023/A14090632 |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
(郭彩霞, 马小杰, 王博, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 967.)
doi: 10.6023/A21040173 |
|
| [13] |
|
|
(张晋维, 李平, 张馨凝, 马小杰, 王博, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 597.)
doi: 10.6023/A20050153 |
|
| [14] |
|
|
(代迷迷, 王健, 李麟阁, 王琪, 刘美男, 张跃钢, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 355.)
doi: 10.6023/A20010017 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c00972 pmid: 38579304 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.6023/A15080547 |
|
(黄刚, 陈玉贞, 江海龙, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 113.)
doi: 10.6023/A15080547 |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
(吕露茜, 赵娅俐, 魏嫣莹, 王海辉, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 869.)
doi: 10.6023/A21030099 |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
|
(于越, 张新波, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1434.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070290 |
|
| [56] |
doi: 10.6023/A20090442 |
|
(常智, 乔羽, 杨慧军, 邓瀚, 朱星宇, 何平, 周豪慎, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 139.)
doi: 10.6023/A20090442 |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
|
(吕天天, 马文, 詹冬笋, 邹燕敏, 李继龙, 冯美玲, 黄小荥, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 640.)
doi: 10.6023/A21120614 |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
|
(杨文远, 梁红, 乔智威, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 785.)
doi: 10.6023/A18070293 |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [1] | 吴子林, 张璐, 陈杨, 李晋平, 李立博. 乙烷选择性金属有机框架材料的结构设计与分离应用★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 917-936. |
| [2] | 朱永朝, 刘冰洁, 梁文杰, 徐海. 多功能MOFs隔离膜用于锂硫电池的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 861-867. |
| [3] | 杨天宇, 代佳楠, 张玉洁, 薛娟琴, 马晶. 层间阴离子可调控LiAl-LDHs的制备及锂吸附性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(6): 569-578. |
| [4] | 赵梦飞, 韩赫兴, 杨幼明, 李庭刚. 离子吸附型稀土矿生物浸出技术研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(4): 415-427. |
| [5] | 王跃, 邹莹, 张元, 郑舒婕, 王恒宇, 刘天赋, 李仁富. 锆基金属有机框架材料在氧传感器上的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 45-51. |
| [6] | 康健, 石梓煊, 李景梅. 高抗菌性光催化材料的制备及LED光驱动其抗菌性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 962-970. |
| [7] | 王馨雨, 许雄文. SnCl2敏化的TiO2表面对PbI2粒子的诱导吸附[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 865-870. |
| [8] | 王南南, 陈玉贞. CoNi-MOF-74/泡沫镍衍生的CoNi@C/NF复合物用于高效有机电合成[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 621-628. |
| [9] | 周何鑫, 崔青云, 胡雪敏, 杨文秀, 田肖, 王硕. 金属有机框架衍生氮掺杂碳限域钴原子簇催化硝基化合物转移加氢[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 503-510. |
| [10] | 徐晗, 王聪芝, 刘峙嵘, 石伟群. 海水提铀吸附材料及官能团配位机理研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 458-470. |
| [11] | 刘洋, 高丰琴, 马占营, 张引莉, 李午戊, 侯磊, 张小娟, 王尧宇. 一例钴基金属有机框架化合物活化过氧单硫酸盐高效降解水中亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| [12] | 林航青, 马若茹, 江怡蓝, 许木榕, 林洋彭, 杜克钊. 用于卤素捕获的材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 62-74. |
| [13] | 韩玉淳, 王毅琳. 长效抗菌材料的研究现状与展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1196-1201. |
| [14] | 王华高, 程群峰. 冰模板技术仿生构筑层状高分子纳米复合材料的研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1231-1239. |
| [15] | 孙博, 琚雯雯, 王涛, 孙晓军, 赵婷, 卢晓梅, 陆峰, 范曲立. 高分散共轭聚合物-金属有机框架纳米立方体的制备及抗肿瘤应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 757-762. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||