化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (4): 458-470.DOI: 10.6023/A24020041 上一篇
综述
徐晗a,b, 王聪芝b,*( ), 刘峙嵘a,*(
), 刘峙嵘a,*( ), 石伟群b,*(
), 石伟群b,*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-02-01
发布日期:2024-03-21
作者简介: |
徐晗, 东华理工大学硕士研究生, 目前研究方向: 海水提铀理论计算. |
 |
王聪芝, 中国科学院高能物理研究所副研究员, 2012年博士毕业于北京理工大学. 长期专注于锕系元素计算与模拟方面的研究, 主要工作集中在海水提铀材料以及高放废液中新型锕系分离配体的理论设计方面. 目前以第一作者和通讯作者在ACS Cent. Sci.、Chem. Commun.、Inorg. Chem.等国内外知名期刊发表数十篇学术论文, 先后主持多项国家自然科学基金项目. |
 |
刘峙嵘, 本科毕业于青岛理工大学, 博士毕业于中国原子能科学研究院. 在国内外学术期刊上发表百余篇学术论文、专利12项; 获省部级奖6项. 先后主持国家自然科学基金面上/地区项目/江西省自然科学基金项目/江西省科技支撑计划项目多项. 国家自然科学基金函评专家、中国博士后科学基金评审专家、中国博士后科学基金特别资助评审专家、教育部留学归国人员科研启动基金评审专家. 中国辐射防护学会环境放射化学分会理事、中国核学会锕系元素物理与化学分会理事、中国核学会核化工分会理事. Journal of Hazardous Materials、Environmental Science & Technology、Applied Surface Science等国际学术刊物审稿专家. |
 |
石伟群, 中国科学院高能物理研究所研究员, 国家杰出青年科学基金获得者, 长期致力于核燃料循环化学相关基础研究. 在JACS、Angew. Chem、Chem.、Chem. Sci.、CCS Chem.、Nat. Commun、Adv. Mater.等国际知名期刊发表SCI 论文300余篇, 成果被国内外同行广泛关注和引用, 文章总引15000余次, H因子62 (Google Scholar), 2019~2022年每年均入选Elsevier中国高被引学者榜单(核科学技术). 分别担任期刊《Supramolecular Materials》副主编, 《Chinese Chemical Letters》、《Journal of Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Waste Technology》、《International Journal of Advanced Nuclear Reactor Design and Technology》和《Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology》的编委与国际顾问编委, 中文期刊《核化学与放射化学》编委. 现为中国核学会锕系物理与化学分会副理事长、中国有色金属学会熔盐化学与技术专业委员会副主任委员、中国化学会核化学与放射化学专业委员会委员、中国核学会核化工分会常务理事兼副秘书长. |
Han Xua,b, Congzhi Wangb,*( ), Zhirong Liua,*(
), Zhirong Liua,*( ), Weiqun Shib,*(
), Weiqun Shib,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-01
Published:2024-03-21
Contact:
* E-mail: 文章分享

铀是核工业发展中最重要的元素之一, 但陆地铀资源有限难以满足核工业的发展需求, 而海水中蕴含着丰富的铀资源, 因此如何从海水中提取铀备受关注. 然而由于海水条件复杂且铀浓度极低, 从海水中提取铀面临着很多挑战, 国内外诸多学者对此进行了大量研究, 目前已经开发出多种分离富集方法, 其中吸附法已被较广泛应用于海水提铀中. 本综述重点介绍了近年来开发的海水提铀吸附材料, 包括无机材料、有机材料、无机-有机杂化材料, 主要从材料的吸附能力、选择性、抗菌性、稳定性、可回收性以及制备成本等方面进行分析, 另外对偕胺肟和羧基等典型官能团以及近年来报道的其他代表性官能团与铀酰离子的配位机理进行总结分析, 同时对未来海水提铀材料的发展进行了展望.
徐晗, 王聪芝, 刘峙嵘, 石伟群. 海水提铀吸附材料及官能团配位机理研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 458-470.
Han Xu, Congzhi Wang, Zhirong Liu, Weiqun Shi. Advances in Adsorption Materials and Coordination Mechanism of Functional Groups for Uranium Extraction from Seawater[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(4): 458-470.
| 吸附剂类型 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 无机吸附材料 | 制备工艺简单、成本低、吸附率高、易于洗脱 | 选择性差、在海水中容易流失、不易回收、稳定性差 |
| 有机吸附材料 | 比表面积高、表面化学性质易调节、循环性高、选择性高 | 制备成本高、制备工艺复杂、易被污染 |
| 无机-有机杂化吸附材料 | 负载率高、比表面积大、稳定性高、选择性高 | 制备成本高、合成条件苛刻、不易回收 |
| 吸附剂类型 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 无机吸附材料 | 制备工艺简单、成本低、吸附率高、易于洗脱 | 选择性差、在海水中容易流失、不易回收、稳定性差 |
| 有机吸附材料 | 比表面积高、表面化学性质易调节、循环性高、选择性高 | 制备成本高、制备工艺复杂、易被污染 |
| 无机-有机杂化吸附材料 | 负载率高、比表面积大、稳定性高、选择性高 | 制备成本高、合成条件苛刻、不易回收 |

| Element | Concentration in seawater | |
|---|---|---|
| mg•kg-1 (ppm) | mol•L-1 | |
| Cl | 19400 | 0.546 |
| Na | 10800 | 0.468 |
| Mg | 1290 | 53×10-3 |
| Ca | 413 | 10.3×10-3 |
| K | 400 | 10.2×10-3 |
| Li | 0.18 | 26×10-6 |
| Ni | 0.005 | 8×10-9 |
| Fe | 0.0034 | 0.5×10-9 |
| U | 0.0033 | 14×10-9 |
| V | 0.00183 | 36×10-9 |
| Cu | 0.001 | 3×10-9 |
| S | 0.0009 | 28×10-3 |
| Pb | 0.00003 | 0.01×10-9 |
| TICa | 0.00029 | 24.2×10-3 |
| DIPb | 0.00071 | 2.3×10-6 |
| Element | Concentration in seawater | |
|---|---|---|
| mg•kg-1 (ppm) | mol•L-1 | |
| Cl | 19400 | 0.546 |
| Na | 10800 | 0.468 |
| Mg | 1290 | 53×10-3 |
| Ca | 413 | 10.3×10-3 |
| K | 400 | 10.2×10-3 |
| Li | 0.18 | 26×10-6 |
| Ni | 0.005 | 8×10-9 |
| Fe | 0.0034 | 0.5×10-9 |
| U | 0.0033 | 14×10-9 |
| V | 0.00183 | 36×10-9 |
| Cu | 0.001 | 3×10-9 |
| S | 0.0009 | 28×10-3 |
| Pb | 0.00003 | 0.01×10-9 |
| TICa | 0.00029 | 24.2×10-3 |
| DIPb | 0.00071 | 2.3×10-6 |
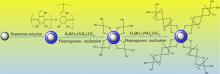





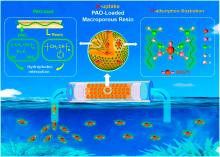

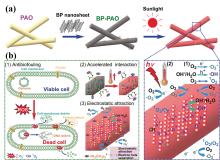

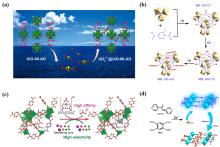





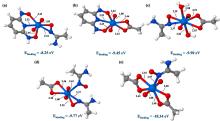


| 配体名称 | 配位机理 | 亲和力和选择性 |
|---|---|---|
| 偕胺肟 | η2双齿配位或单齿配位 | 与铀酰离子的亲和力较强, 但选择性较低 |
| 酰亚胺二肟 | 三齿配位 | 相比偕胺肟, 与铀酰离子的亲和力更强, 但选择性更差 |
| 双(羟基胺)-1,3,5-三嗪 | 三齿配位 | 相比酰亚胺二肟, 与铀酰离子的亲和力更强 |
| 羧基(与偕胺肟协同配位) | 单齿或双齿配位 | 与偕胺肟协同配位, 有利于络合铀酰离子 |
| 磷酸基(与偕胺肟协同配位) | 单齿或双齿配位 | 与偕胺肟协同配位, 有利于络合铀酰离子 |
| 1,10-菲罗啉-2,9-二羧酸 | 四齿螯合 | 与铀酰离子的结合能力强于钒离子, 对铀酰离子具有良好的选择性 |
| 五齿螯合配体H2saldian | 五齿螯合 | 与其他金属离子共存时, 对铀酰离子具有较高的选择性 |
| 配体名称 | 配位机理 | 亲和力和选择性 |
|---|---|---|
| 偕胺肟 | η2双齿配位或单齿配位 | 与铀酰离子的亲和力较强, 但选择性较低 |
| 酰亚胺二肟 | 三齿配位 | 相比偕胺肟, 与铀酰离子的亲和力更强, 但选择性更差 |
| 双(羟基胺)-1,3,5-三嗪 | 三齿配位 | 相比酰亚胺二肟, 与铀酰离子的亲和力更强 |
| 羧基(与偕胺肟协同配位) | 单齿或双齿配位 | 与偕胺肟协同配位, 有利于络合铀酰离子 |
| 磷酸基(与偕胺肟协同配位) | 单齿或双齿配位 | 与偕胺肟协同配位, 有利于络合铀酰离子 |
| 1,10-菲罗啉-2,9-二羧酸 | 四齿螯合 | 与铀酰离子的结合能力强于钒离子, 对铀酰离子具有良好的选择性 |
| 五齿螯合配体H2saldian | 五齿螯合 | 与其他金属离子共存时, 对铀酰离子具有较高的选择性 |
| [1] |
Wang, L.-L.; Luo, F.; Dang, L.-L.; Li, J. Q.; Wu, X.-L.; Liu, S.-J.; Luo, M.-B. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13724.
doi: 10.1039/C5TA01972A |
| [2] |
Fukaya, Y.; Goto, M. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2017, 99, 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.anucene.2016.09.029 |
| [3] |
Lindner, H.; Schneider, E. Energy Econ. 2015, 49, 9.
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2015.01.016 |
| [4] |
Endrizzi, F.; Rao, L.-F. Chem. - Eur. J. 2014, 20, 14499.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v20.44 |
| [5] |
Davies, R. V.; Kennedy, J.; McIlroy, R. W.; Spence, R.; Hill, K. M. Nature 1964, 203, 1110.
doi: 10.1038/2031110a0 |
| [6] |
Hu, B.-W.; Wang, H.-F.; Liu, R.-R.; Qiu, M.-Q. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129743.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129743 |
| [7] |
Li, S.-J.; Hu, Y.-Z.; Shen, Z.-W.; Cai, Y.-W.; Ji, Z.-Y.; Tan, X.-L.; Liu, Z.-X.; Zhao, G.-X.; Hu, S.-X.; Wang, X.-K. Sci. China: Chem. 2021, 64, 1323.
doi: 10.1007/s11426-021-9987-1 |
| [8] |
Zhang, Z.-C.; Parker, B. F.; Lohrey, T. D.; Teat, S. J.; Arnold, J.; Rao, L.-F. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8134.
doi: 10.1039/C8DT01191E |
| [9] |
Scanlan, J. P. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1977, 39, 635.
doi: 10.1016/0022-1902(77)80578-2 |
| [10] |
Endrizzi, F.; Leggett, C. J.; Rao, L.-F. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4249.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03679 |
| [11] |
Parker, B. F.; Hohloch, S.; Pankhurst, J. R.; Zhang, Z.; Love, J. B.; Arnold, J.; Rao, L. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5695.
doi: 10.1039/c7dt04069e pmid: 29632905 |
| [12] |
Choppin, G. R. Mar. Chem. 1989, 28, 19.
doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(89)90184-9 |
| [13] |
Gholap, H.; Warule, S.; Sangshetti, J.; Kulkarni, G.; Banpurkar, A.; Satpute, S.; Patil, R. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5849.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7391-1 |
| [14] |
Wang, Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Wang, J.; Liang, J.-J.; Pan, D.-Q.; Li, P.; Fan, Q.-H. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 113007.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113007 |
| [15] |
Yu, J.-Q.; Zhang, H.-S.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.-H.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.-H.; Li, R.-M.; Wang, J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129735.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129735 |
| [16] |
Donia, A. M.; Atia, A. A.; Moussa, E. M. M.; El-Sherif, A. M.; Abd El Magied, M. O. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 183.
doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2008.05.037 |
| [17] |
Luo, W.; Kelly, S. D.; Kemner, K. M.; Watson, D.; Zhou, J.; Jardine, P. M.; Gu, B. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7516.
doi: 10.1021/es900731a |
| [18] |
Gupta, S. K.; Rathore, N. S.; Sonawane, J. V.; Pabby, A. K.; Janardan, P.; Changrani, R. D.; Dey, P. K. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 131.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2007.05.018 |
| [19] |
Jalali, F.; Fakhari, J.; Zolfaghari, A. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 194.
doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.02.014 |
| [20] |
Kabay, N.; Demircioǧlu, M.; Yayli, S.; Günay, E.; Yüksel, M.; Saglam, M.; Streat, M. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 1983.
doi: 10.1021/ie970518k |
| [21] |
Lee, S.; Kang, U.; Piao, G.; Kim, S.; Han, D. S.; Park, H. Appl. Catal., B 2017, 207, 35.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.02.004 |
| [22] |
Liu, Z.-Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Hu, T.-Y.; Ye, G.; Chen, J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. & Technol.) 2021, 61, 23. (in Chinese)
|
|
(刘泽宇, 谢忆, 王一凡, 胡铜洋, 叶钢, 陈靖, 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 61, 23.)
|
|
| [23] |
Xiong, J.; Wen, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.-L. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2015, 37, 257. (in Chinese)
|
|
(熊洁, 文君, 胡胜, 汪小琳, 核化学与放射化学, 2015, 37, 257.)
doi: 10.7538/hhx.2015.37.05.0257 |
|
| [24] |
Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.-H.; Liu, X.-L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chen, Z.-S.; Yang, H.; Hu, B.-W.; Shen, C.; Tang, Z.-W.; Huang, Q.-F.; Wang, X.-K. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 483, 215097.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215097 |
| [25] |
Xin, Q.; Wang, Q.-L.; Gan, J.-L.; Lei, Z.-W.; Hu, E.-M.; Wang, H.-Q.; Wang, H.-Q. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120270.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120270 |
| [26] |
Abney, C. W.; Mayes, R. T.; Saito, T.; Dai, S. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13935.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00355 |
| [27] |
Wang, X.-L.; Wen, J. Uranium Extraction from Seawater, Science Press, Beijing, 2022, p. 163. (in Chinese)
|
|
(汪小琳, 文君, 海水提铀, 科学出版社, 北京, 2022, p. 163.)
|
|
| [28] |
Astheimer, L.; Schenk, H. J.; Witte, E. G.; Schwochau, K. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1983, 18, 307.
doi: 10.1080/01496398308068568 |
| [29] |
Wang, C.-Z.; Lan, J.-H.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-K.; Chai, Z.-F.; Shi, W.-Q. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9466.
doi: 10.1021/ic500202g |
| [30] |
Zhu, J.-H.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.-S.; Liu, J.-Y.; Zhang, H.-S.; Li, R.-M.; Wang, J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 353, 9.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.042 |
| [31] |
Zuo, L.-H.; Peng, W.; Xu, Z.-Z.; Guo, H.-Y.; Luo, M.-B. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 179, 105376.
doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2022.105376 |
| [32] |
Lan, F.-F.; Li, X.-H.; Yang, Y. J. Guangdong Univ. Technol. 2023, 40, 139. (in Chinese)
|
|
(蓝芳芳, 李贤辉, 杨阳, 广东工业大学学报, 2023, 40, 139.)
|
|
| [33] |
Tang, X.-R.; Huang, P.-L.; Ruan, H.-M.; Tang, L.; Gong, X.; Duan, T.; Chen, S.-S.; He, R.; Zhu, W.-K. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2023, 45, 267. (in Chinese)
|
|
(唐兴睿, 黄鹏玲, 阮昊明, 唐丽, 龚翔, 段涛, 陈树森, 何嵘, 竹文坤, 核化学与放射化学, 2023, 45, 267.)
doi: 10.7538/hhx.2023.YX.2021117 |
|
| [34] |
Tian, G.-X.; Liu, T.-T.; Yang, S.-L. At. Energy Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1. (in Chinese)
|
|
(田国新, 刘婷婷, 杨素亮, 原子能科学技术, 2023, 57, 1.)
doi: 10.7538/yzk.2022.youxian.0885 |
|
| [35] |
Ao, J.-X.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.-N.; Wu, G.-Z.; Li, Q.-N.; Ma, H.-J. J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process. 2019, 37, 3. (in Chinese)
|
|
(敖浚轩, 徐晓, 李玉娜, 吴国忠, 李晴暖, 马红娟, 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2019, 37, 3.)
|
|
| [36] |
Zhu, Y.-J.; Xu, Y.; Jian, M.-P.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-C. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2023, 42, 3029. (in Chinese)
|
|
(朱雅静, 徐岩, 简美鹏, 李海燕, 王崇臣, 化工进展, 2023, 42, 3029.)
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-1434 |
|
| [37] |
Li, L.-Y.; Wen, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.-L. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2022, 44, 15. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李璐琰, 文君, 胡胜, 汪小琳, 核化学与放射化学, 2022, 44, 15.)
|
|
| [38] |
Li, Z.-M.; Niu, Y.-Q.; Su, Y.-T.; Song, Y.; Wang, F.-J.; Gou, Y.-F.; Wang, H.-Z.; Chen, H.-S. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2022, 44, 233. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李子明, 牛玉清, 宿延涛, 宋艳, 王凤菊, 勾阳飞, 王海珍, 陈树森, 核化学与放射化学, 2022, 44, 233.)
|
|
| [39] |
Feng, J.; He, G.-Q.; Wei, Y.-X.; Duan, T.; Zhou, J. New Chem. Mater. 2022, 50, 7. (in Chinese)
|
|
(冯健, 何桂强, 魏艳霞, 段涛, 周建, 化工新型材料, 2022, 50, 7.)
|
|
| [40] |
Endrizzi, F.; Leggett, C. J.; Rao, L.-F. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4249.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03679 |
| [41] |
Denning, R. G. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 4125.
pmid: 17461564 |
| [42] |
Shi, W.-Q.; Yuan, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wang, L.; Mei, L.; Xiao, C.-L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.-J.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Chai, Z.-F. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7807.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.46 |
| [43] |
Pyykkö, P.; Li, J.; Runeberg, N. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 4809.
doi: 10.1021/j100069a007 |
| [44] |
Kim, J.; Tsouris, C.; Mayes, R. T.; Oyola, Y.; Saito, T.; Janke, C. J.; Dai, S.; Schneider, E.; Sachde, D. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 367.
doi: 10.1080/01496395.2012.712599 |
| [45] |
Li, B.; Zhou, J.-W.; Priest, C.; Jiang, D.-e. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 8171.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b04449 |
| [46] |
Kanno, M. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1984, 21, 1.
doi: 10.1080/18811248.1984.9731004 |
| [47] |
Zou, W.-H.; Zhao, L.; Han, R.-P. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 17, 585.
doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(08)60248-7 |
| [48] |
Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.-R.; Sui, Y.; Xue, J. H.; Ding, D.-X. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 317, 613.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-018-5923-0 |
| [49] |
Ma, S.-L.; Huang, L.; Ma, L.-J.; Shim, Y.; Islam, S. M.; Wang, P.-L.; Zhao, L.-D.; Wang, S.-C.; Sun, G.-B.; Yang, X.-J.; Kanatzidis, M. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3670.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00762 |
| [50] |
Wang, H.; Yao, H.-Q.; Chen, L.-H.; Yu, Z.-H.; Yang, L.-X.; Li, C.; Shi, K.-R.; Li, C.-Q.; Ma, S.-L. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143483.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143483 |
| [51] |
Wang, Q.; Yang, L.-X.; Yao, H.-Q.; Wu, Z.-L.; Liu, R.; Ma, S.-L. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 13046.
doi: 10.1039/D2DT02381D |
| [52] |
Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.-X.; Li, H.-P.; Chen, X.-J.; Wei, G.-Y.; Wu, T.; Maguire, D. J.; Ye, G.; Chen, J. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 282, 119523.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119523 |
| [53] |
Zeng, X.-K.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Uddin, M. H.; Xia, D.; McCarthy, D. T.; Deletic, A.; Yu, J.-G.; Zhang, X.-W. Appl. Catal., B 2020, 274, 119095.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119095 |
| [54] |
Koske, P. H.; Ohlrogge, K.; Peinemann, K. V. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1988, 23, 1929.
doi: 10.1080/01496398808075673 |
| [55] |
Das, S.; Oyola, Y.; Mayes, R. T.; Janke, C. J.; Kuo, L. J.; Gill, G.; Wood, J. R.; Dai, S. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4110.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03136 |
| [56] |
Das, S.; Brown, S.; Mayes, R. T.; Janke, C. J.; Tsouris, C.; Kuo, L. J.; Gill, G.; Dai, S. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 298, 125.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.013 |
| [57] |
Wang, D.; Song, J.-A.; Wen, J.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Liu, Z.-L.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, H.-L.; Zhao, S.-L.; Zhao, X.-M.; Fang, M.-H.; Lei, M.; Li, B.; Wang, N.; Wang, X.-L.; Wu, H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 12.
|
| [58] |
Yuan, Y.-H.; Zhao, S.-L.; Wen, J.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.-W.; Xu, L.-L.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, N. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 11.
|
| [59] |
Li, Z.; Yu, Z.-Q.; Wu, Y.-D.; Wu, X.-L.; Wan, Y.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Wang, N. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124648.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124648 |
| [60] |
Yan, B.-J.; Ma, C.-X.; Gao, J.-X.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Wang, N. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 8.
|
| [61] |
Gao, J.-X.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Yu, Q.-H.; Yan, B.-J.; Qian, Y.-X.; Wen, J.; Ma, C.-X.; Jiang, S.-H.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, N. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3935.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC09936K |
| [62] |
Yuan, Y.-H.; Guo, X.; Feng, L.-J.; Yu, Q.-H.; Lin, K.; Feng, T.-T.; Yan, B.-J.; Fedorovich, K. V.; Wang, N. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127878.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127878 |
| [63] |
Liu, R.-R.; Wen, S.-X.; Sun, Y.; Yan, B.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Chen, L.; Peng, S.-Y.; Ma, C.; Cao, X.-Y.; Ma, C.-X.; Duan, G.-G.; Shi, S.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Wang, N. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130060.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130060 |
| [64] |
Wen, S.-X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, R.-R.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.-W.; Peng, S.-Y.; Ma, C.-X.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Gong, W.-T.; Wang, N. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3246.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c21046 |
| [65] |
Xu, X.; Zhang, H.-J.; Ao, J.-X.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Guo, X.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.-N.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Ye, B.-J.; Wang, D.-L.; Shen, F.; Ma, H.-J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1979.
doi: 10.1039/C9EE00626E |
| [66] |
Ao, J.-X.; Zhang, H.-J.; Xu, X.; Yao, F.-J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Ye, B.-J.; Li, Q.-N.; Xu, L.; Ma, H.-J. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 28588.
doi: 10.1039/C9RA05440E |
| [67] |
Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Ao, J.-X.; Liang, Y.-L.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.-J.; Huang, C.; Ye, F.; Li, Q.-N.; Guo, X.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, H.-T.; Ma, S.-Q.; Ma, H.-J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 22032.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA07180C |
| [68] |
Huang, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Ma, L.; Bao, H.-L.; Liao, J.; Wang, J.-J.; Han, J.-G.; Xu, G.; Huang, D.-M.; Ye, B.-J.; Zhang, H.-J.; Wu, M.-H.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Ma, H.-J. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136312.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136312 |
| [69] |
Huang, C.; Fu, M.-T.; Ma, L.; Mao, C.-K.; Yao, Y.-Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Han, J.-G.; Xue, X.-G.; Xu, G.; Wu, M.-H.; Shao, H.-Y.; Ma, H.-J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145718.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.145718 |
| [70] |
Fu, M.-T.; Han, L.; Huang, C.; Ma, L.; Yao, Y.-Y.; Chen, K.; Sun, P.; Shao, H.-Y.; Wu, M.-H.; Zhang, B.-W.; Ma, H.-J. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147103.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.147103 |
| [71] |
Fu, M.-T.; Huang, C.; Ma, L.; Yao, Y.-Y.; Chen, J.; Han, L.; Chen, K.; Sun, P.; Wu, M.-H.; Ma, H.-J. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 332, 125803.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125803 |
| [72] |
Bai, Z.-H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.-S.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122555.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122555 |
| [73] |
Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.-W.; Yu, J.; Zhu, J.-H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.-R.; Liu, P.-L.; Wang, J. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109277.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.109277 |
| [74] |
Yu, Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.-R.; Yu, J.; Zhu, J.-H.; Wang, J. Desalination 2023, 565, 116828.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2023.116828 |
| [75] |
Zhao, Y.-S.; Liu, C.-X.; Feng, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.-Q.; Tian, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.-B.; Li, S.-J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 119.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.005 |
| [76] |
Kim, J. H.; Lee, H. I.; Yeon, J.-W.; Jung, Y.; Kim, J. M. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 286, 129.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-010-0624-3 |
| [77] |
Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Liu, Y.-H.; Cao, X.-H.; Liu, Y.-T.; Li, Q. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198-199, 246.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.112 |
| [78] |
Tian, G.; Geng, J.-X.; Jin, Y.-D.; Wang, C.-L.; Li, S.-Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.-S.; Li, S.-J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 442.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.066 pmid: 21497013 |
| [79] |
Schierz, A.; Zänker, H. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1088.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.09.045 pmid: 19010575 |
| [80] |
Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.-X.; Yang, J.-J.; Liao, J.-L.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Liu, N.; Tang, J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 10.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.182 |
| [81] |
Tian, K.; Wu, J.-L.; Wang, J.-L. Radiochim. Acta 2018, 106, 719.
doi: 10.1515/ract-2017-2913 |
| [82] |
Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhang, H.-S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.-R.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yu, J.; Jing, X.-Y.; Zhang, M.-L.; Wang, J. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 12984.
doi: 10.1039/C8DT02819B |
| [83] |
Huang, Z.-W.; Li, Z.-J.; Zheng, L.-R.; Zhou, L.-M.; Chai, Z.-F.; Wang, X.-L.; Shi, W.-Q. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 1066.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.067 |
| [84] |
Yuan, Y.-H.; Niu, B.-Y.; Yu, Q.-H.; Guo, X.; Guo, Z.-H.; Wen, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Wang, N. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1220.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.3 |
| [85] |
Zhou, H.-C.; Long, J. R.; Yaghi, O. M. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673.
doi: 10.1021/cr300014x |
| [86] |
Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K. E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
doi: 10.1126/science.1230444 |
| [87] |
Cohen, S. M. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 970.
doi: 10.1021/cr200179u pmid: 21916418 |
| [88] |
Liu, D.-H.; Zhong, C.-L. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10308.
doi: 10.1039/c0jm01045f |
| [89] |
Carboni, M.; Abney, C. W.; Liu, S.-B.; Lin, W.-B. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2396.
doi: 10.1039/c3sc50230a |
| [90] |
Chen, L.; Bai, Z.-L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.-J.; Cai, Y.-W.; Li, Y.-X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, L.-H.; Diwu, J.; Wang, J.-Q.; Chai, Z.-F.; Wang, S.-A. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32446.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b12396 |
| [91] |
Ma, L.; Gao, J.; Huang, C.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Ding, R.-H.; Bao, H.-L.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Xu, G.; Li, Q.-N.; Deng, P.-Y.; Ma, H.-J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 57831.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c18625 |
| [92] |
Ma, L.; Huang, C.; Yao, Y.-Y.; Fu, M.-T.; Han, F.; Li, Q.-N.; Wu, M.-H.; Zhang, H.-J.; Xu, L.; Ma, H.-J. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123526.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123526 |
| [93] |
Yuan, Y.-H.; Feng, S.-W.; Feng, L.-J.; Yu, Q.-H.; Liu, T.-T.; Wang, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4262.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v59.11 |
| [94] |
Wu, H.-Y.; Chi, F.-T.; Zhang, S.; Wen, J.; Xiong, J.; Hu, S. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109567.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109567 |
| [95] |
Zeng, Y.-Y.; Ni, Y.-R.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.-C.; Zhang, A.; Song, Y.-X.; Yang, L.; Pu, A.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Lv, L.-N.; Yuanli, L.; Chi, F.-T. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 343, 112123.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.112123 |
| [96] |
Qin, X.-F.; Yang, W.-T.; Yang, Y.-H.; Gu, D.-X.; Guo, D.-Y.; Pan, Q.-H. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 9857.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c01072 |
| [97] |
Li, N.; Yang, L.; Su, R.-D.; Shi, N.; Wu, J.-K.; Zhao, J.; Wen, L.-P.; Wang, Z.-N. Desalination 2023, 566, 116940.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2023.116940 |
| [98] |
Zhao, Z.-W.; Lei, R.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Cai, T.-T.; Han, B. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120514.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120514 |
| [99] |
Feng, L.-J.; Wang, H.; Feng, T.-T.; Yan, B.-J.; Yu, Q.-H.; Zhang, J.-C.; Guo, Z.-H.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Ma, C.-X.; Liu, T.; Wang, N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202101015.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v61.13 |
| [100] |
Bai, Z.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.-S.; Yu, J.; Chen, R.-R.; Liu, J.-Y.; Song, D.-L.; Li, R.-M.; Wang, J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18012.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c03007 |
| [101] |
Xie, Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Ren, X.-M.; Wang, X.-X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-K. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 180.
doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2019.01.005 |
| [102] |
Li, J.; Yang, X.-D.; Bai, C.-Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.-Y.; Ding, S.-D.; Xia, C.-Q.; Tan, X.-Y.; Ma, L.-J.; Li, S.-J. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 437, 211.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.09.046 |
| [103] |
Yu, J.-P.; Yuan, L.-Y.; Wang, S.; Lan, J.-H.; Zheng, L.-R.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.-W.; Tao, W.-Q.; Liu, Z.-R.; Chai, Z.-F.; Gibson, J. K.; Shi, W.-Q. CCS Chem. 2019, 1, 286.
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.019.20190005 |
| [104] |
Li, Z.-D.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Xiong, X.-H.; Luo, F. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 277, 484.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2019.06.044 |
| [105] |
Xiong, X.-H.; Yu, Z.-W.; Gong, L.-L.; Tao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Yin, W.-H.; Yang, L.-X.; Luo, F. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900547.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v6.16 |
| [106] |
Liang, Y.; Xia, M.; Yu, Q.-H.; Li, Y.-P.; Sui, Z.-Y.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Hu, X.-M.; Chen, Q.; Wang, N. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 184.
doi: 10.1007/s42114-021-00311-3 |
| [107] |
Li, Z.-Y.; Zhu, R.-M.; Zhang, P.-L.; Yang, M.; Zhao, R.-Q.; Wang, Y.-L.; Dai, X.; Liu, W. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134623.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.134623 |
| [108] |
Li, F.-F.; Cui, W.-R.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, C.-R.; Liang, R.-P.; Qiu, J.-D. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122333.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122333 |
| [109] |
Cui, W.-R.; Zhang, C.-R.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.-F.; Liang, R.-P.; Liu, J.-W.; Qiu, J.-D. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 436.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14289-x |
| [110] |
Eloy, F.; Lenaers, R. Chem. Rev. 1962, 62, 155.
doi: 10.1021/cr60216a003 |
| [111] |
Witte, E. G.; Schwochau, K. S.; Henkel, G.; Krebs, B. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1984, 94, 323.
doi: 10.1016/S0020-1693(00)84889-6 |
| [112] |
Hirotsu, T.; Katoh, S.; Sugasaka, K.; Senō, M.; Itagaki, T. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1986, 1609.
|
| [113] |
Park, Y.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Harada, M.; Tomiyasu, H.; Nogami, M.; Ikeda, Y. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2000, 37, 344.
doi: 10.1080/18811248.2000.9714904 |
| [114] |
Barber, P. S.; Kelley, S. P.; Rogers, R. D. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8526.
doi: 10.1039/c2ra21344c |
| [115] |
Vukovic, S.; Watson, L. A.; Kang, S. O.; Custelcean, R.; Hay, B. P. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 3855.
doi: 10.1021/ic300062s pmid: 22376298 |
| [116] |
Abney, C. W.; Liu, S.-B.; Lin, W.-B. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 11558.
doi: 10.1021/jp408460x |
| [117] |
Zhang, L.-J.; Su, J.; Yang, S.-T.; Guo, X.-J.; Jia, Y.-P.; Chen, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.-A.; Li, J.; Li, J.-Y.; Wu, G.-Z.; Wang, J.-Q. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4224.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03217 |
| [118] |
Guo, X.-J.; Wang, Y.-X.; Li, C.; Huai, P.; Wu, G.-Z. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 1327.
doi: 10.1080/00268976.2014.993732 |
| [119] |
Mehio, N.; Lashely, M. A.; Nugent, J. W.; Tucker, L.; Correia, B.; Do-Thanh, C.; Dai, S.; Hancock, R. D.; Bryantsev, V. S. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3567.
doi: 10.1021/jp512778x |
| [120] |
Lashley, M. A.; Mehio, N.; Nugent, J. W.; Holguin, E.; Do-Thanh, C.-L.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Dai, S.; Hancock, R. D. Polyhedron 2016, 109, 81.
doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2016.01.026 |
| [121] |
Abney, C. W.; Mayes, R. T.; Piechowicz, M.; Lin, Z.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Veith, G. M.; Dai, S.; Lin, W. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 448.
doi: 10.1039/C5EE02913A |
| [122] |
Kelley, S. P.; Barber, P. S.; Mullins, P. H. K.; Rogers, R. D. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12504.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC06370H |
| [123] |
Song, Y.-P.; Zhu, C.-J.; Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Abney, C. W.; Wojtas, L.; Ma, S.-Q. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1650.
doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c00906 |
| [124] |
Kobuke, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Ogoshi, H. Polym. J. 1990, 22, 179.
doi: 10.1295/polymj.22.179 |
| [125] |
Tian, G.-X.; Teat, S. J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Rao, L.-F. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 11579.
doi: 10.1039/c2dt30978e |
| [126] |
Tian, G.-X.; Teat, S. J.; Rao, L.-F. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 5690.
doi: 10.1039/c3dt32940b |
| [127] |
Kang, S. O.; Vuković, S.; Custelcean, R.; Hay, B. P. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6619.
doi: 10.1021/ie300492z |
| [128] |
Chatterjee, S.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Brown, S. S.; Johnson, J. C.; Grant, C. D.; Mayes, R. T.; Hay, B. P.; Dai, S.; Saito, T. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4161.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03212 |
| [129] |
Grant, C. D.; Kang, S. O.; Hay, B. P. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7735.
doi: 10.1021/jo4009386 |
| [130] |
Sun, X.-Q.; Tian, G.-X.; Xu, C.; Rao, L.-F.; Vukovic, S.; Kang, S. O.; Hay, B. P. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 551.
doi: 10.1039/C3DT52206G |
| [131] |
Ivanov, A. S.; Leggett, C. J.; Parker, B. F.; Zhang, Z.; Arnold, J.; Dai, S.; Abney, C. W.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Rao, L.-F. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1560.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01443-1 |
| [132] |
Meng, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-D.; Liu, L.-J.; Ma, F.-Q.; Zhang, C.-H.; Dong, H.-X. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 291, 120946.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120946 |
| [133] |
Li, Y.; Li, X.-X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Sha, L.-T.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.-Y. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122115.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122115 |
| [134] |
Xiao, F.; Cheng, Y.-X.; Zhou, P.-C.; Chen, S.-X.; Wang, X.-J.; He, P.; Nie, X.-Q.; Dong, F.-Q. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105681.
doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105681 |
| [135] |
Xiong, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Yu, H.-Z.; Xie, L.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.-L. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1924.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02663 |
| [136] |
Ahmad, Z.; Li, Y.; Ali, S.; Yang, J.-J.; Jan, F.; Fan, Y.; Gou, X.-Y.; Sun, Q.-Y.; Chen, J.-P. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 136076.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136076 |
| [137] |
Priest, C. W.; Li, B.; Jiang, D. e. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 12060.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b08345 |
| [138] |
Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.; Ivanov, A. S.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Earl, L. D.; Abney, C. W.; Wojtas, L.; Ma, S.-Q. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1644.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04032-y pmid: 29691403 |
| [139] |
Yu, B.-X.; Zhang, L.; Ye, G.; Liu, Q.-Z.; Li, J.-L.; Wang, X.-D.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.-M.; Ma, S.-Q. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 788.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-020-3217-7 |
| [140] |
Ivanov, A. S.; Bryantsev, V. S. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 10744.
doi: 10.1039/C6DT01752E |
| [141] |
Luan, X.-F.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Lan, J.-H.; Chai, Z.-F.; Xia, L.-S.; Shi, W.-Q. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126, 406.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c08072 |
| [142] |
Gan, J.-L.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wang, Q.-L.; Xin, Q.; Hu, E.-M.; Lei, Z.-W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Wang, H.-Q. Desalination 2023, 545, 116154.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2022.116154 |
| [143] |
Gan, J.-L.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wang, Q.-L.; Xin, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, E.-M.; Lei, Z.-W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Wang, H.-Q. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124074.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124074 |
| [144] |
Wen, D.; Dong, Z.; Ao, Y.-Y.; Xie, K.-J.; Zhai, M.-L.; Zhao, L. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117666.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117666 |
| [145] |
Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.-W.; Zhu, J.-H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.-R.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129407.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129407 |
| [146] |
Yang, H.-C.; Guo, X.-J.; Chen, R.-R.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yu, J.; Lin, C.-G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.-l. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146611.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146611 |
| [147] |
Melton, D. L.; VanDerveer, D. G.; Hancock, R. D. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 9306.
doi: 10.1021/ic061010p |
| [148] |
Ballance, D. G.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Ivanov, A. S.; Dai, S.; Hancock, R. D. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 488, 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2018.12.050 |
| [149] |
Chen, B.-H.; Liu, J.; Lv, L.-N.; Yang, L.; Luo, S.-Z.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Peng, S.-M. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 7416.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b00545 |
| [150] |
Lipin, R.; Ebenezer, C.; Solomon, R. V. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115819.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115819 |
| [151] |
Meng, R.-X.; Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Sun, M.-Z.; Xu, C.; Borisova, N. E.; Zhang, X.-W.; Lei, L.-C.; Xiao, C.-L. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 8754.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00715 |
| [152] |
Lashley, M. A.; Ivanov, A. S.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Dai, S.; Hancock, R. D. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 10818.
pmid: 27689540 |
| [153] |
Luan, X.-F.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Lan, J.-H.; Chai, Z.-F.; Xia, L.-S.; Shi, W.-Q. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 11381.
doi: 10.1039/D2DT01273A |
| [154] |
Luan, X.-F.; Wang, C.-Z.; Xia, L.-S.; Shi, W.-Q. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 708. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22010054 |
|
(栾雪菲, 王聪芝, 夏良树, 石伟群, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 708.)
doi: 10.6023/A22010054 |
|
| [155] |
Ivanov, A. S.; Parker, B. F.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Aguila, B.; Sun, Q.; Ma, S.-Q.; Jansone-Popova, S.; Arnold, J.; Mayes, R. T.; Dai, S.; Bryantsev, V. S.; Rao, L.-F.; Popovs, I. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 819.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08758-1 |
| [156] |
Mizumachi, T.; Sato, M.; Kaneko, M.; Takeyama, T.; Tsushima, S.; Takao, K. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 6175.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c00306 pmid: 35394284 |
| [157] |
Takao, K.; Kato, M.; Takao, S.; Nagasawa, A.; Bernhard, G.; Hennig, C.; Ikeda, Y. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 2349.
doi: 10.1021/ic902225f |
| [158] |
Xu, H.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Lan, J.-H.; Chai, Z.-F.; Liu, Z.-R.; Shi, W.-Q. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124411.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2024.124411 |
| [1] | 邓沈娜, 彭常春, 牛云宏, 许云, 张云霄, 陈祥, 王红敏, 刘珊珊, 沈晓. 自由基Brook重排调控的α-氟烷基-α-硅基甲醇参与的烯烃双官能团化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 119-125. |
| [2] | 黄涎廷, 韩洪亮, 肖婧, 王帆, 柳忠全. I2O5/KSCN介导的炔烃碘硫氰化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 5-8. |
| [3] | 杨地, 史潇凡, 张冀杰, 卜显和. 光热材料在海水淡化领域的近期研究进展与展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1052-1063. |
| [4] | 赵政嘉, 刘康, 郭燕, 于吉攀, 石伟群. 超铀金属有机化学研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1633-1641. |
| [5] | 温哥华, 温都日娜, 陈秀梅, 麻秀芳, 翁果果, 韦依凡, 鲍松松, 谢小吉, 胡淑贤, 郑丽敏. 层状铀酰膦酸配位聚合物作为双响应光致发光温度计★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1311-1317. |
| [6] | 栾雪菲, 王聪芝, 夏良树, 石伟群. 铀酰与羧酸和肟基类配体相互作用的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 708-713. |
| [7] | 蒋博龙, 崔艳艳, 史顺杰, 姜楠, 谭伟强. 双金属氮化物NiMoN析氢催化剂制备及其电解海水析氢性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1394-1400. |
| [8] | 滑熠龙, 李冬涵, 顾天航, 王伟, 李若繁, 杨建平, 张伟贤. 纳米零价铁富集水溶液中铀的表面化学及应用展望[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(8): 1008-1022. |
| [9] | 卢小彪, 肖茜, 万常峰, 汪志勇, 刘晋彪. 无金属条件下的肉桂酸类和酰胺的脱羧氧化偶联反应构建碳-碳键[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 751-754. |
| [10] | 刘毅川, 刘雅兰, 姜仕林, 李梅, 石伟群. 氯化物熔盐体系中铀的化学种态研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1425-1437. |
| [11] | 蒋成浩, 冯霄, 王博. 共价有机框架膜的制备及其在海水淡化和水处理领域的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 466-477. |
| [12] | 肖丽, 李嘉恒, 王挺. 可见光催化的氮自由基导向远程sp 3碳氢官能团化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 841-849. |
| [13] | 汤娜娜, 邵鑫, 王明扬, 吴新鑫, 朱晨. 磺酰氯参与的基于远端炔基迁移的非活化烯烃炔基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 922-926. |
| [14] | 杨俊航, 傅晓波, 卢增辉, 朱钢国. 可见光催化烯烃砜基化启动的远程醛基碳-氢键直接硫化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 901-905. |
| [15] | 张振, 龚莉, 周晓渝, 颜思顺, 李静, 余达刚. 二氧化碳参与的自由基型烯烃双官能团化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 783-793. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||