化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (8): 937-946.DOI: 10.6023/A25050149 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2025-05-09
发布日期:2025-06-18
通讯作者:
窦传冬
作者简介: |
袁刘忠, 2020年本科毕业于重庆师范大学, 然后进入吉林大学化学学院超分子结构与材料全国重点实验室攻读博士研究生.目前主要围绕杂化纳米分子碳及其光电功能开展研究工作. |
 |
孙文婷, 2020年本科毕业于曲阜师范大学, 然后进入吉林大学化学学院超分子结构与材料全国重点实验室攻读博士研究生. 目前主要从事含硼有机超分子光电功能材料研究. |
 |
窦传冬, 2011年博士毕业于吉林大学, 现为吉林大学化学学院超分子结构与材料全国重点实验室教授, 博士生导师. 围绕含硼有机功能材料为研究主题, 专心于含硼共轭分子和高分子的合成化学与功能调控研究, 推动形成了“含硼功能分子碳”特色方向. |
★ “中国青年化学家”专辑.
基金资助:
Liuzhong Yuan, Wenting Sun, Chuandong Dou*( )
)
Received:2025-05-09
Published:2025-06-18
Contact:
Chuandong Dou
About author:†These authors contributed equally to this work
★ For the VSI “Rising Stars in Chemistry”.
Supported by:文章分享
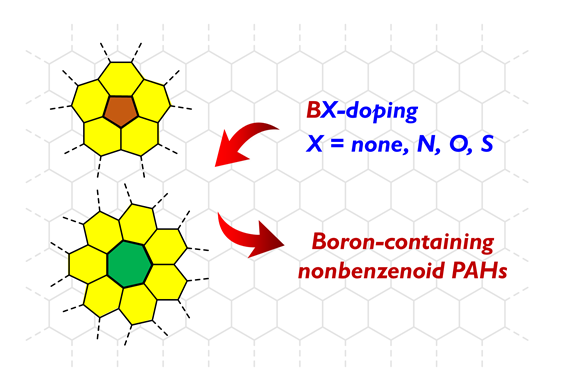
含硼非苯稠环芳烃是一类结合了硼原子和非苯基元的共轭多环芳烃体系, 其展现出与经典碳基稠环芳烃明显不同的电子结构和物化性质, 被广泛应用于有机发光二极管、有机场效应晶体管等器件技术领域. 近年来, 通过引入大位阻基团或采用结构约束的设计策略提升硼原子稳定性, 以及采用高效可控的有机合成方法, 已发展出一系列新颖的含硼非苯稠环芳烃, 包括硼氮型、硼氧型、硼硫型、以及纯硼掺杂的非苯稠环芳烃. 这些分子不仅具有优美的拓扑结构和良好的稳定性, 还展现出独特的光电性质和优良器件性能. 此外, 它们还具有路易斯酸性, 能够与路易斯碱配位形成路易斯酸碱加合物, 进而表现出刺激响应功能. 尽管该领域取得了诸多进展, 但仍然缺乏含硼非苯稠环芳烃研究进展的系统总结. 在这篇综述中, 旨在重点介绍含硼非苯稠环芳烃的设计与合成策略, 概述其独特的物理性质和功能特性, 并对含硼非苯稠环芳烃面临的合成挑战与未来发展方向进行了分析和展望.
袁刘忠, 孙文婷, 窦传冬. 含硼非苯稠环芳烃★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(8): 937-946.
Liuzhong Yuan, Wenting Sun, Chuandong Dou. Boron-Containing Nonbenzenoid Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(8): 937-946.











| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.201912213 pmid: 31613416 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.201807004 pmid: 30006951 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.201904934 pmid: 31342599 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b09556 pmid: 31746597 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00637 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1039/c8qo01368c |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1039/c1cs15165g pmid: 21850355 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1021/ja4092769 pmid: 24279901 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
doi: 10.1002/anie.201205265 pmid: 22930589 |
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b08197 pmid: 30251839 |
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
|
(段超, 张建伟, 向焌钧, 杨笑迪, 高希珂, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 29.)
|
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
|
(王一诺, 邵世洋, 王利祥, 化学学报, 2023, 81, 1202.)
doi: 10.6023/A23040186 |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
|
(张祎, 杜呈卓, 李继坤, 王小野, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 1645.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202212037 |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b00268 pmid: 28125773 |
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [1] | 孙满鑫, 张卫, 姬梦圆, 张延华. 常温常压下金纳米线催化芳基炔烃与NaBH4的还原氢化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(6): 563-568. |
| [2] | 彭小改, 胡竹斌, 孙海涛. 双氢键作用主导的十二硼烷-溶剂分子团簇理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(5): 510-517. |
| [3] | 马莹, 陈维希, 刘羽辰, 刘子义, 吴涛, 陆安慧, 王东琪. 六方氮化硼氧化模式的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 52-59. |
| [4] | 陈蕾, 张瀚月, 卿青, 宋芳, 李莉萍, 冷稚华. CsZn2B3O7:Eu2+宽带绿色荧光粉的发光性质及其在白光发光二极管上的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 894-902. |
| [5] | 高琦, 陈丽蓉, 钱金一, 樊瑞峰, 孙蔚青, 郭亚飞, 樊保敏. 手性噁唑硼烷催化芳基磷氧对α,β-双功能不饱和化合物的不对称膦氢化反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(7): 742-747. |
| [6] | 周何鑫, 崔青云, 胡雪敏, 杨文秀, 田肖, 王硕. 金属有机框架衍生氮掺杂碳限域钴原子簇催化硝基化合物转移加氢[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 503-510. |
| [7] | 李珺卿, 宋千禧, 刘子义, 王东琪. 机器学习方法预测含硼材料能隙[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 387-395. |
| [8] | 刘雨涵, 高盼. 使用机械化学生成的钙基重格氏试剂(R-CaX)对有机卤化物进行直接硼化[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(11): 1114-1119. |
| [9] | 甘绍艳, 钟晟昱, 王力廷, 史雷. 有机高价溴试剂的合成及其应用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1030-1042. |
| [10] | 李飞, 丁汇丽, 李超忠. 基于氟仿衍生的三氟甲基硼络合物参与的烯烃氢三氟甲基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 577-581. |
| [11] | 吕鑫, 吴仪, 张勃然, 郭炜. 过氧化氢激活型近红外氟硼二吡咯光敏剂的设计、合成及光动力治疗研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 359-370. |
| [12] | 魏颖, 周平, 陈鑫, 包秋景, 解令海. 有机纳米环/格的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 289-308. |
| [13] | 殷雪旸, 顾恺, 邵正中. 载药蛋白质/聚苯硼酸复合纳米微球制备及其释药性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 116-123. |
| [14] | 陈俊畅, 张明星, 王殳凹. 晶态多孔材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [15] | 杨贯文, 伍广朋. 模块化双功能有机硼氮和硼磷催化体系的设计及其催化转化★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1551-1565. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||