化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (1): 52-59.DOI: 10.6023/A24100324 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
马莹†, 陈维希†, 刘羽辰, 刘子义, 吴涛, 陆安慧, 王东琪*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-10-27
发布日期:2024-12-17
作者简介:基金资助:
Ying Ma†, Weixi Chen†, Yuchen Liu, Ziyi Liu, Tao Wu, An-Hui Lu, Dongqi Wang( )
)
Received:2024-10-27
Published:2024-12-17
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
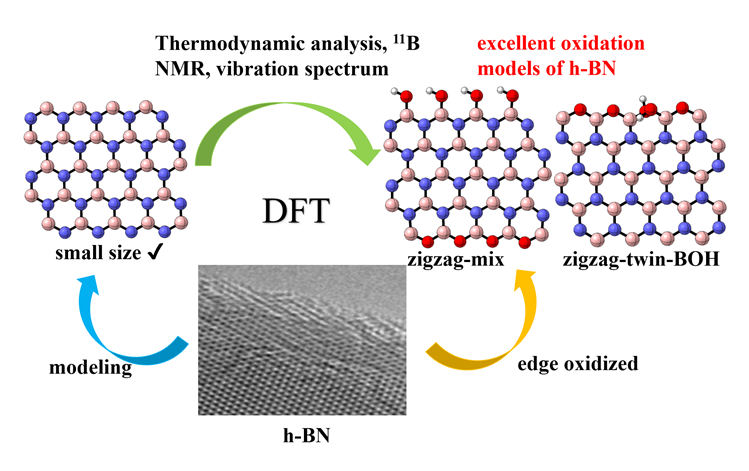
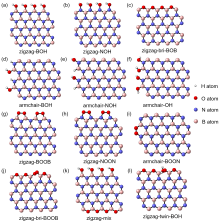
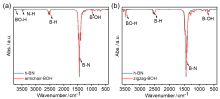
六方氮化硼(h-BN)因其在催化轻质烷烃氧化脱氢(ODH)反应中表现出高反应活性、高烯烃选择性而受到越来越多的关注. 之前对反应机理的研究表明, 含氧硼物种(如>BOH、>BOOB<)与催化剂活性密切相关, 但对h-BN可能的氧化模式和氧化模型的合理构建缺少系统研究和分析. 本项工作建立了多种可能的含氧硼物种的模型, 这些模型的区别在于氧化物种的类型(单氧与过氧)、氧化的位置(zigzag边或armchair边上的B或N位点)以及含氧基团的数量(氧化程度)等方面. 研究从热力学角度评估了它们的稳定性, 并计算了含氧硼物种的11B固体核磁位移和谐振频率, 提出了h-BN的zigzag边缘官能团化是其主要的氧化物种. 为了解决量子化学谐振频率被高估的问题, 研究进而采用硼基小分子拟合了含硼化合物的谐振频率校正因子, 数值为0.9658 (B3LYP/6-311G(d,p)). 这项工作明确了氮化硼及其含氧物种的模型简化思路, 为应用简化模型计算其热力学和核磁、振动光谱等性质提供了可行方案, 有助于采用理论手段研究硼基催化反应的机理和各驻点的性质, 为硼基催化体系的优化和理性设计提供理论依据.
马莹, 陈维希, 刘羽辰, 刘子义, 吴涛, 陆安慧, 王东琪. 六方氮化硼氧化模式的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(1): 52-59.
Ying Ma, Weixi Chen, Yuchen Liu, Ziyi Liu, Tao Wu, An-Hui Lu, Dongqi Wang. Density Functional Theory Study of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Oxidation Mode[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(1): 52-59.
| No. | Reaction | Reaction site |
|---|---|---|
| Eq. 2a | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→zigzag-BOH | zigzag-BH |
| Eq. 2b | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→zigzag-NOH | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 2c | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→armchair-BOH | armchair-BH |
| Eq. 2d | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→armchair-NOH | armchair-NH |
| Eq. 2e | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→armchair-OH | armchair-BH&NH |
| Eq. 3a | pristine_h-BN+3/2O2→zigzag-BOOB+H2O | zigzag-BH |
| Eq. 3b | pristine_h-BN+3/2O2→zigzag-NOON+H2O | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 3c | pristine_h-BN+3/2O2→armchair-BOON+H2O | armchair-BH&NH |
| Eq. 4a | pristine_h-BN+5/4O2→zigzag-bri-O+NO+1/2H2O | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 4b | pristine_h-BN+3/4O2→zigzag-bri-O+1/2N2+1/2H2O | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 4c | pristine_h-BN+H2O→zigzag-bri-O+NH3 | zigzag-NH |
| No. | Reaction | Reaction site |
|---|---|---|
| Eq. 2a | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→zigzag-BOH | zigzag-BH |
| Eq. 2b | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→zigzag-NOH | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 2c | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→armchair-BOH | armchair-BH |
| Eq. 2d | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→armchair-NOH | armchair-NH |
| Eq. 2e | pristine_h-BN+1/2O2→armchair-OH | armchair-BH&NH |
| Eq. 3a | pristine_h-BN+3/2O2→zigzag-BOOB+H2O | zigzag-BH |
| Eq. 3b | pristine_h-BN+3/2O2→zigzag-NOON+H2O | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 3c | pristine_h-BN+3/2O2→armchair-BOON+H2O | armchair-BH&NH |
| Eq. 4a | pristine_h-BN+5/4O2→zigzag-bri-O+NO+1/2H2O | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 4b | pristine_h-BN+3/4O2→zigzag-bri-O+1/2N2+1/2H2O | zigzag-NH |
| Eq. 4c | pristine_h-BN+H2O→zigzag-bri-O+NH3 | zigzag-NH |


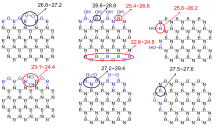
| Type of B | Chemical shift | Exp.[ |
|---|---|---|
| bridging-BOOB | 26.8~27.2 | — |
| bridging-B-O | 22.6~24.8 | 24.4 — |
| twin-BOH | 23.1~24.4 | |
| zigzag-BOH | 28.6~28.8 (middle) | — |
| 25.4~26.6 (corner) | 26.0 — | |
| armchair-BOH | 25.6~26.2 | |
| zigzag-BOOB | 27.2~29.4 | — |
| armchair-BOON | 27.5~27.6 | — |
| Type of B | Chemical shift | Exp.[ |
|---|---|---|
| bridging-BOOB | 26.8~27.2 | — |
| bridging-B-O | 22.6~24.8 | 24.4 — |
| twin-BOH | 23.1~24.4 | |
| zigzag-BOH | 28.6~28.8 (middle) | — |
| 25.4~26.6 (corner) | 26.0 — | |
| armchair-BOH | 25.6~26.2 | |
| zigzag-BOOB | 27.2~29.4 | — |
| armchair-BOON | 27.5~27.6 | — |

| Calc. | Exp. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ν/cm−1 | Mode | Group | ν/cm−1 | mode |
| B-N | 1496 | βB-N | B-N | 1325[ | βB-N |
| 819~874 | γB-N | 815[ | γB-N | ||
| B-OH (zigzag) | 3484 | νBO-H | B-OH | 3400[ | νBO-H |
| 729 | δBO-H | ||||
| B-OH (armchair) | 3715 994 | νBO-H δBO-H | B(OH)xO3-x | 1100~1200[ | δB-O |
| B-OH (twin) | 3484 | νBO-H | |||
| 1024 | δBO-H | ||||
| B-OH (mix) | 3484 | νBO-H | |||
| 753 | δBO-H | ||||
| O-O | 903~1305 | δO-O | O-O | 927, 1033[ | δO-O |
| B-O-B | 552~702 | δB-O | B-O-B | 561, 665[ | δB-O |
| Calc. | Exp. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ν/cm−1 | Mode | Group | ν/cm−1 | mode |
| B-N | 1496 | βB-N | B-N | 1325[ | βB-N |
| 819~874 | γB-N | 815[ | γB-N | ||
| B-OH (zigzag) | 3484 | νBO-H | B-OH | 3400[ | νBO-H |
| 729 | δBO-H | ||||
| B-OH (armchair) | 3715 994 | νBO-H δBO-H | B(OH)xO3-x | 1100~1200[ | δB-O |
| B-OH (twin) | 3484 | νBO-H | |||
| 1024 | δBO-H | ||||
| B-OH (mix) | 3484 | νBO-H | |||
| 753 | δBO-H | ||||
| O-O | 903~1305 | δO-O | O-O | 927, 1033[ | δO-O |
| B-O-B | 552~702 | δB-O | B-O-B | 561, 665[ | δB-O |

| [1] |
Sattler, J.; Ruiz-Martinez, J.; Santillan-Jimenez, E.; Weckhuysen, B. M. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10613.
doi: 10.1021/cr5002436 pmid: 25163050 |
| [2] |
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, G.-W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4359.
|
| [3] |
Cavani, F.; Ballarini, N.; Cericola, A. Catal. Today 2007, 127, 113.
|
| [4] |
Vajda, S.; Pellin, M. J.; Greeley, J. P.; Marshall, C. L.; Curtiss, L. A.; Ballentine, G. A.; Elam, J. W.; Catillon-Mucherie, S.; Redfern, P. C.; Mehmood, F.; Zapol, P. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 213.
|
| [5] |
Sheng, J.; Yan, B.; Lu, W.-D.; Qiu, B.; Gao, X.-Q.; Wang, D.-Q.; Lu, A.-H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1438.
doi: 10.1039/d0cs01174f pmid: 33300532 |
| [6] |
Klisinska, A.; Samson, K.; Gressel, I.; Grzybowska, B. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2006, 309, 10.
|
| [7] |
Petit, S.; Gode, T.; Thomas, C.; Dzwigaj, S.; Millot, Y.; Brouri, D.; Krafft, J. M.; Rousse, G.; Laberty-Robert, C.; Costentin, G. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 9630.
|
| [8] |
Zhou, H.; Yi, X.-F.; Hui, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Qin, Y.-C.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.-B.; Chu, X.-F.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Hong, X.; Chen, Z.-F.; Meng, X.-J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Song, L.-J.; Zheng, A.-M.; Xiao, F.-S. Science 2021, 372, 76.
|
| [9] |
Wang, T.-C.; Yin, J.-L.; Guo, X.-J.; Chen, Y.; Lang, W.-Z.; Guo, Y.-J. J. Catal. 2021, 393, 149.
|
| [10] |
Grant, J. T.; McDermott, W. P.; Venegas, J. M.; Bur, S. P.; Micka, J.; Phivilay, S. P.; Carrero, C. A.; Hermans, I. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3623.
|
| [11] |
Li, P.; Zheng, Y.-N.; Liu, Z.-K.; Lu, A.-H. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2024, 2406012 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 李佩, 郑跃楠, 刘占凯, 陆安慧, 物理化学学报, 2024, 2406012.)
|
|
| [12] |
Li, S.; Wang, Y. Chem. Propellants Polym. Mater. 2020, 18, 1 (in Chinese).
|
|
( 李师, 王毅, 化学推进剂与高分子材料, 2020, 18, 1.)
|
|
| [13] |
Grant, J. T.; Carrero, C. A.; Goeltl, F.; Venegas, J.; Mueller, P.; Burt, S. P.; Specht, S. E.; McDermott, W. P.; Chieregato, A.; Hermans, I. Science 2016, 354, 1570.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaf7885 pmid: 27934702 |
| [14] |
Shi, L.; Wang, D.-Q.; Song, W.; Sha, D.; Zhang, W.-P.; Lu, A.-H. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1788.
|
| [15] |
Shi, L.; Wang, D.-Q.; Lu, A.-H. Chinese J. Catal. 2018, 39, 908.
|
| [16] |
Zhou, Y.-L.; Lin, J.; Li, L.; Pan, X.-L.; Sun, X.-C.; Wang, X.-D. J. Catal. 2018, 365, 14.
|
| [17] |
Lu, W.-D.; Wang, D.-Q.; Zhao, Z.; Song, W.; Li, W.-C.; Lu, A.-H. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 8263.
|
| [18] |
Liu, Y.-C.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, D.-Q.; Lu, A.-H. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 21263.
|
| [19] |
Liu, Z.-Y.; Lu, W.-D.; Wang, D.-Q.; Lu, A.-H. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 24930.
|
| [20] |
Liu, Z.-Y.; Xu, D.-T.; Xia, M.-R.; Lu, W.-D.; Lu, A.-H.; Wang, D.-Q. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 8770.
|
| [21] |
Love, A. M.; Thomas, B.; Specht, S. E.; Hanrahan, M. P.; Venegas, J. M.; Burt, S. P.; Grant, J. T.; Cendejas, M. C.; McDermott, W. P.; Rossini, A. J.; Hermans, I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 182.
|
| [22] |
Venegas, J. M.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Agbi, T. O.; McDermott, W. P.; Alexandrova, A.; Hermans, I. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 16527.
|
| [23] |
Lu, W.-D.; Gao, X.-Q.; Wang, Q.-G.; Li, W.-C.; Zhao, Z.-C.; Wang, D.-Q.; Lu, A.-H. Chinese J. Catal. 2020, 41, 1837.
|
| [24] |
Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chai, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X.; Zheng, N.; Yao, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5930.
|
| [25] |
Love, A. M.; Cendejas, M. C.; Thomas, B.; McDermott, W. P.; Uchupalanun, P.; Kruszynski, C.; Burt, S. P.; Agbi, T.; Rossini, A. J.; Hermans, I. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27000.
|
| [26] |
Huang, R.; Zhang, B.-S.; Wang, J.; Wu, K.-H.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zheng, A.-M.; Schlogl, R.; Su, D.-S. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3293.
|
| [27] |
Yan, B.; Li, W.-C.; Lu, A.-H. J. Catal. 2019, 369, 296.
|
| [28] |
Liu, Y.-C.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Lu, W.-D.; Wang, D.-Q.; Lu, A.-H. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 11729.
|
| [29] |
Liu, Z.-K.; Yan, B.; Meng, S.-Y.; Liu, R.; Lu, W.-D.; Sheng, J.; Yi, Y.-H.; Lu, A.-H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19691.
|
| [30] |
Zhang, X.-Y.; You, R.; Wei, Z.-Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.-Z.; Pan, Y.; Wu, P.-W.; Jia, Q.-D.; Bao, Z.-H.; Bai, L.; Jin, M.-Z.; Sumpter, B.; Fung, V.; Huang, W.-X.; Wu, Z. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8042.
|
| [31] |
Torii, S.; Jimura, K.; Hayashi, S.; Kikuchi, R.; Takagaki, A. J. Catal. 2017, 335, 176.
|
| [32] |
Gao, X.; Zhu, L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Song, H.; Lin, L.; Wen, X.; Ma, D.; Yao, S. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1478.
|
| [33] |
Song, Y.; Duan, X.; Jiang, Y.-N.; Ma, Y. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 6890.
|
| [34] |
Lee, C. T.; Yang, W.-T.; Parr, R. G. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785.
doi: 10.1103/physrevb.37.785 pmid: 9944570 |
| [35] |
Becke, A. D. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098.
|
| [36] |
Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104.
|
| [37] |
Krishnan, R.; Binkley, J. S.; Seeger, R.; Pople, J. A. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 650.
|
| [38] |
Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Hratchian, H. P.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Montgomery, Jr. J. A.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Millam, N. J.; Klene, M.; Knox, J. E.; Cross, J. B.; Bakken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R. E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A. J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Voth, G. A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A. D.; Farkas, Ö.; Foresman, J. B.; Ortiz, J. V.; Cioslowski, J.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 09, Revision C01, 2010.
|
| [1] | 陈铭晖, 张博心, 魏滔, 孙兆雪, 冯亚青, 张宝. 三嗪共价骨架材料的层间位错行为及其光生载流子动力学理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(2): 93-100. |
| [2] | 赵雨晴, 梁栋, 贾吉慧, 余荣民, 卢灿忠. 具有双吸电子基团D-A型配体的Ag(I)发光配合物的合成与性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 486-492. |
| [3] | 王治业, 肖博怀. 利用平面σ-芳香性增强电子输运能力[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 520-526. |
| [4] | 赵玉强, 张霞, 杨芸如, 朱立平, 周莹. 聚集诱导发射光笼分子的设计合成及原位光激活成像研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 265-273. |
| [5] | 黄广龙, 薛小松. “陈试剂”作为三氟甲基源机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 132-137. |
| [6] | 黄伊晨, 聂长明, 王聪芝, 陈树森, 宋艳, 李昊, 石伟群. 羟基和氨基取代偕胺肟用于海水提铀的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(10): 1050-1057. |
| [7] | 梁雪峰, 荆剑, 冯昕, 赵勇泽, 唐新员, 何燕, 张立胜, 李慧芳. 共价有机框架COF66/COF366的电子结构: 从单体到二维平面聚合物[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 717-724. |
| [8] | 杨磊, 葛娇阳, 王访丽, 吴汪洋, 郑宗祥, 曹洪涛, 王洲, 冉雪芹, 解令海. 一种基于芴的大环结构的有效降低内重组能的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 613-619. |
| [9] | 张少秦, 李美清, 周中军, 曲泽星. 多共振热激活延迟荧光过程的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 124-130. |
| [10] | 王娟, 肖华敏, 谢丁, 郭元茹, 潘清江. 铜掺杂与氮化碳复合氧化锌材料结构和二氧化氮气体传感性质的密度泛函理论计算[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1493-1499. |
| [11] | 刘金晶, 杨娜, 李莉, 魏子栋. 铂活性位空间结构调控氧还原机理的理论研究★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1478-1485. |
| [12] | 栾雪菲, 王聪芝, 夏良树, 石伟群. 铀酰与羧酸和肟基类配体相互作用的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 708-713. |
| [13] | 王珞聪, 李哲伟, 岳彩巍, 张培焕, 雷鸣, 蒲敏. 电场下偶氮苯衍生物分子顺反异构化反应机理的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 781-787. |
| [14] | 熊昆, 陈伽瑶, 杨娜, 蒋尚坤, 李莉, 魏子栋. 理论探究水溶液条件对TMNxCy催化氮还原性能的增强机制[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1138-1145. |
| [15] | 王英辉, 魏思敏, 段金伟, 王康. 理论研究“受阻路易斯酸碱对”催化的烯醇硅醚氢化反应机理[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1164-1172. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||