化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 83 ›› Issue (12): 1472-1479.DOI: 10.6023/A25110372 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: “中国青年化学家”合辑
研究论文
孟凡荣†, 李国锋†, 赵杰, 肖文精, 石德清*( ), 陈加荣*(
), 陈加荣*( )
)
投稿日期:2025-11-16
发布日期:2025-12-16
作者简介:★ “中国青年化学家”专辑.
基金资助:
Fanrong Meng, Guofeng Li, Jie Zhao, Wenjing Xiao, Deqing Shi*( ), Jiarong Chen*(
), Jiarong Chen*( )
)
Received:2025-11-16
Published:2025-12-16
Contact:
* E-mail: chshidq@mail.ccnu.edu.cn;chenjiarong@mail.ccnu.edu.cn; Fax: (+)86(27)67862041
About author:★For the VSI "Rising Stars in Chemistry".
Supported by:文章分享
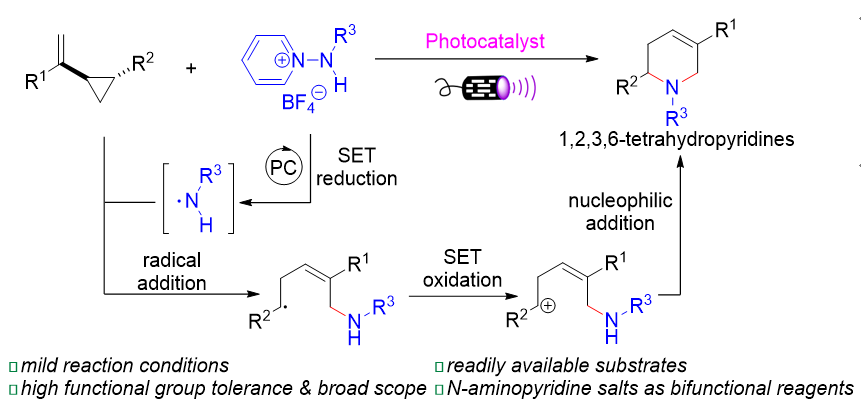
本工作报道了一类通过可见光催化活化N-氨基吡啶盐产生氮自由基, 并与乙烯基环丙烷的加成/环化反应. 该反应不仅扩展了氮自由基作为双功能试剂参与的反应类型的范围, 还为构建四氢吡啶类化合物提供了一种有效的合成策略. 在该反应中, N-氨基吡啶盐表现出双功能特性, 既作为氮自由基的前体, 又作为氮亲核试剂; 乙烯基环丙烷作为四原子组分的自由基受体和亲电试剂. 经过一系列条件优化, 确定了最优反应条件: 使用10-苯基吩噻嗪(Ph-PTZ)作为光催化剂, 1,2-二氯乙烷(DCE)作为溶剂, 并以波长为390 nm的紫光作为可见光的光源. 在此条件下, 对N-氨基吡啶盐和乙烯基环丙烷的底物适用范围进行了广泛考察, 以中等到较好的分离收率成功合成了42种1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶类化合物. 该方法可以放大至克级规模, 同时产物也能发生官能团的各种转化.
孟凡荣, 李国锋, 赵杰, 肖文精, 石德清, 陈加荣. 光催化氮自由基参与的乙烯基环丙烷加成/环化反应合成四氢吡啶★[J]. 化学学报, 2025, 83(12): 1472-1479.
Fanrong Meng, Guofeng Li, Jie Zhao, Wenjing Xiao, Deqing Shi, Jiarong Chen. Photocatalytic N-Radical-Mediated Addition/Cyclization Reaction of Vinylcyclopropanes for Tetrahydropyridine Synthesis★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2025, 83(12): 1472-1479.

| Entrya | Variation | Yieldb/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | 77 (74) |
| 2 | fac-Ir(ppy)3c | 69 |
| 3 | Eosin-Yc | N.D. |
| 4 | Ru(bpy)3Cl2c | trace |
| 5 | DCM instead of DCE | 68 |
| 6 | MeCN instead of DCE | 52 |
| 7 | 1a/2a (1∶1) instead of 1a/2a (1∶3) | 14 |
| 8 | no light | N.R. |
| 9 | no Ph-PTZ | 14 |
| Entrya | Variation | Yieldb/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | 77 (74) |
| 2 | fac-Ir(ppy)3c | 69 |
| 3 | Eosin-Yc | N.D. |
| 4 | Ru(bpy)3Cl2c | trace |
| 5 | DCM instead of DCE | 68 |
| 6 | MeCN instead of DCE | 52 |
| 7 | 1a/2a (1∶1) instead of 1a/2a (1∶3) | 14 |
| 8 | no light | N.R. |
| 9 | no Ph-PTZ | 14 |
| [11] |
(c)
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00281 |
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00712 |
|
|
(e)
|
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c07082 |
|
| [12] |
(a)
doi: 10.1039/D0QO00343C |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00820 |
|
| [13] |
(a)
pmid: 35285636 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/d3qo00190c pmid: 35285636 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1039/D2CC00369D pmid: 35285636 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00831 pmid: 35285636 |
|
| [1] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/jm501100b pmid: 25602368 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.11.062 pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1002/ajoc.v1.1 pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/cb500893q pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)75003-9 pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1002/jps.2600650736 pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202505018 pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(刘艺琦, 陈文婕, 赵泽艳, 王苏棋, 唐圣松, 何卫民, 彭俊梅, 有机化学, 2025, 45, 3546.)
pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(h)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202311019 pmid: 25602368 |
|
|
(裴鸿艳, 叶家麟, 王锋, 刘东东, 余裕奎, 张静, 张立新, 有机化学, 2024, 44, 1592.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202311019 pmid: 25602368 |
|
| [13] |
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03084 pmid: 35285636 |
|
(f)
doi: 10.1039/C7QO00836H pmid: 35285636 |
|
|
(g)
pmid: 35285636 |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1021/ol503338b pmid: 25541887 |
| [15] |
(a)
doi: 10.1007/s11426-023-1589-7 |
| [2] |
(a)
pmid: 15777212 |
|
(b)
pmid: 15777212 |
|
|
(c)
pmid: 15777212 |
|
| [3] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/ja0344009 pmid: 24063643 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2011.02.047 pmid: 24063643 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/ol402141d pmid: 24063643 |
|
| [15] |
(b)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202207019 |
|
(杨少慧, 宋敬城, 董道青, 杨昊, 周梦宇, 张会淑, 王祖利, 有机化学, 2022, 42, 4099.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202207019 |
|
| [16] |
For selected examples, see: (a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b02989 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/C7CC09151F |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b02377 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1007/s11426-020-9852-8 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c01565 |
|
| [3] |
(d)
doi: 10.1039/C7SC04515H pmid: 24063643 |
| [4] |
For selected examples, see: (a)
doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)01714-2 pmid: 32202807 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/ol200709h pmid: 32202807 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00027a pmid: 32202807 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01344 pmid: 32202807 |
|
| [16] |
(f)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c14169 |
|
(g)
|
|
| [17] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00090 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00638 |
|
| [18] |
CCDC 2302357 contains the supplementary crystallographic data of product 3aa and it can be downloaded for free (https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk†)
|
| [19] |
(a)
doi: 10.1186/s43094-021-00335-y |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.10.018 |
|
| [4] |
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00918 pmid: 32202807 |
|
(f)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c08420 pmid: 32202807 |
|
| [5] |
For selected examples, see: (a)
pmid: 20662502 |
|
(b)
pmid: 20662502 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1021/ja104480g pmid: 20662502 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1002/anie.v52.20 pmid: 20662502 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1002/anie.v45:29 pmid: 20662502 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1055/s-00000084 pmid: 20662502 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c02558 pmid: 20662502 |
|
|
(h)
pmid: 20662502 |
|
| [6] |
For selected examples, see: (a)
doi: 10.1021/jo952088i pmid: 27409716 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1002/anie.200800823 pmid: 27409716 |
|
| [20] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03124 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/D0CC05167E |
|
| [6] |
(c)
doi: 10.1021/ja201204g pmid: 27409716 |
|
(d)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b01787 pmid: 27409716 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1039/D0QO00838A pmid: 27409716 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b02027 pmid: 27409716 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.1039/c2cc36941a pmid: 27409716 |
|
| [7] |
(a)
pmid: 12785763 |
|
(b)
pmid: 12785763 |
|
| [8] |
(a)
doi: 10.6023/A25020057 |
|
(赵瑜, 邢彤彤, 段玉荣, 赵全庆, 化学学报, 2025, 83, 773.)
doi: 10.6023/A25020057 |
|
|
(b)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202408001 |
|
|
(张艮红, 余若曦, 陈跃刚, 有机化学, 2025, 45, 1548.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202408001 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v43.24 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.31635/ccschem.025.202505512 |
|
|
(e)
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00057 |
|
|
(f)
doi: 10.6023/A25060202 |
|
|
(彭琼慧, 彭佳, 蔡迎丽, 王祖利, 易荣楠, 沈超, 何卫民, 化学学报, 2025, 83, 1013.)
doi: 10.6023/A25060202 |
|
|
(g)
doi: 10.6023/A25030064 |
|
|
(李文静, 杨黎燕, 关丽, 张雪娇, 尤静, 沈思语, 赵钰琦, 段琛, 化学学报, 2025, 83, 596.)
doi: 10.6023/A25030064 |
|
|
(h)
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v43.14 |
|
|
(i)
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v43.10 |
|
|
(j)
doi: 10.6023/A24100329 |
|
|
(辛翠, 蒋俊, 邓紫微, 欧丽娟, 何卫民, 化学学报, 2024, 82, 1109.)
doi: 10.6023/A24100329 |
|
|
(k)
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.01.021 |
|
|
(l)
doi: 10.1039/D3GC02575F |
|
| [9] |
(a)
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v42.19 pmid: 27116936 |
|
(b)
pmid: 27116936 |
|
|
(c)
doi: 10.1039/C5CS00655D pmid: 27116936 |
|
|
(d)
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00852b pmid: 27116936 |
|
| [10] |
(a)
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00160 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1039/D1OB00838B |
|
| [11] |
(a)
doi: 10.1038/nchem.1998 |
|
(b)
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00364 |
| [1] | 贾红绍, 乔保坤, 江智勇. 光氧化还原催化自由基偶联合成β-氟代-α-氨基酸衍生物[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(12): 1477-1480. |
| [2] | 张洪浩, 俞寿云. 过渡金属与光氧化还原协同催化的烯丙基取代反应的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 832-840. |
| [3] | 吴自俊, 汪舰. 可见光氧化还原催化下α-酮酸对对位亚甲基醌(p-QMs)脱羧/1,6-共轭加成反应[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(1): 74-79. |
| [4] | 周泉泉, 刘丹, 肖文精, 陆良秋. 可见光光氧化还原催化的三级胺α位C-H氰基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(1): 110-114. |
| [5] | 荣健, 倪传法, 王云泽, 匡翠文, 顾玉诚, 胡金波. 可见光促进下氟烷基砜对芳基烯烃的自由基氟烷基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(1): 105-109. |
| [6] | 谭芬, 肖文精. 可见光促进的氧化还原催化反应在天然产物全合成中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(2): 85-89. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||