化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (4): 369-377.DOI: 10.6023/A20110540 上一篇 下一篇
综述
投稿日期:2020-11-25
发布日期:2021-01-14
通讯作者:
施润, 张铁锐
作者简介: |
马一宁, 中国科学院理化技术研究所硕士研究生, 本科毕业于山东大学化学与化工学院化学基地班, 2020年进入中国科学院大学攻读材料学硕士学位. 目前在理化所张铁锐课题组从事电催化二氧化碳还原催化剂的设计与合成方面研究. |
 |
施润, 中国科学院理化技术研究所项目副研究员, 本科毕业于天津工业大学材料科学与工程学院, 2018年在中国科学院大学取得材料学博士学位. 目前在理化所张铁锐课题组从事能源催化相关研究, 致力于新型光、电催化材料界面特性及反应体系的设计制备, 并将其用于高性能分解水产氢及二氧化碳还原等重要的催化反应之中. |
 |
张铁锐, 中国科学院理化技术研究所研究员、博士生导师, 中国科学院光化学转化与功能材料重点实验室主任. 吉林大学化学学士, 吉林大学有机化学博士. 之后, 在德国、加拿大和美国进行博士后研究. 2009年底回国受聘于中国科学院理化技术研究所. 主要从事能量转换纳米催化材料方面的研究, 在Nat. Commun., Adv. Mater., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., JACS, Chem. Soc. Rev.等期刊上发表SCI论文200余篇, 被引用17000多次, H指数71, 并入选2018~2020科睿唯安“全球高被引科学家”; 申请国家发明专利42项(已授权33项). 2017年当选英国皇家化学会会士. |
基金资助:
Yining Maa, Run Shia,*( ), Tierui Zhanga,b,*(
), Tierui Zhanga,b,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-25
Published:2021-01-14
Contact:
Run Shi, Tierui Zhang
About author:Supported by:文章分享

电催化二氧化碳还原是能源化学及催化科学的研究重点与难点. 气-固-液三相界面模型作为物理化学中的基本概念, 近年来被越来越多地应用于电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究, 其相比于传统固-液两相体系表现出了诸多优点. 本综述阐述了三相界面电催化二氧化碳还原研究进展, 对三相界面电催化体系进行分类及原理探究. 再具体到二氧化碳还原反应, 讨论其水下超亲气体系以及气体扩散层体系的结构特性及电催化性质, 并对包括反应物界面扩散及界面浸润性等影响因素进行了系统分析. 最后对当前研究存在的问题及今后电催化二氧化碳还原领域的发展方向进行了总结与展望.
马一宁, 施润, 张铁锐. 三相界面电催化二氧化碳还原研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 369-377.
Yining Ma, Run Shi, Tierui Zhang. Research Progress on Triphase Interface Electrocatalytic Carbon Dioxide Reduction[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(4): 369-377.
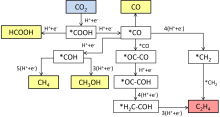
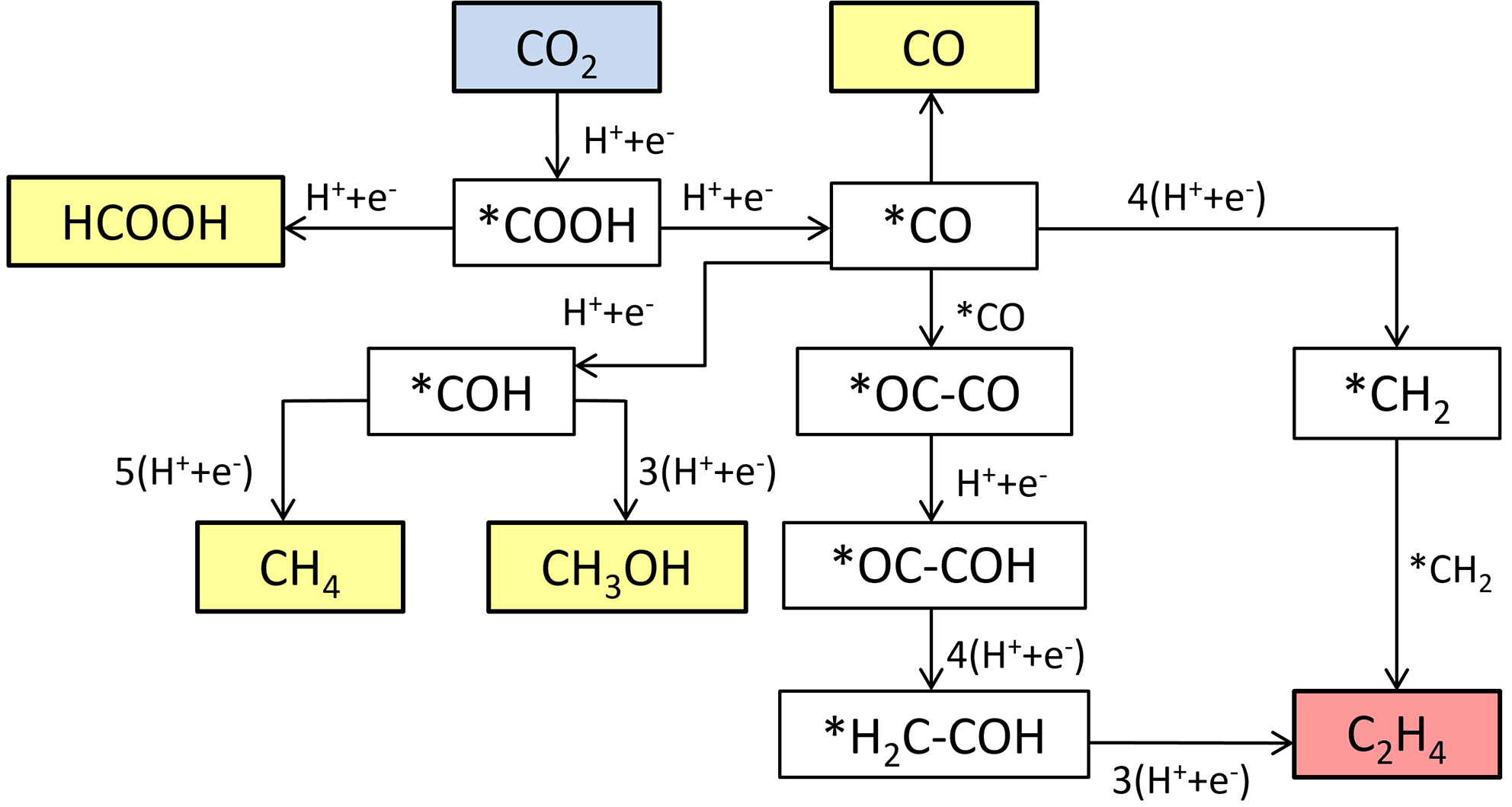


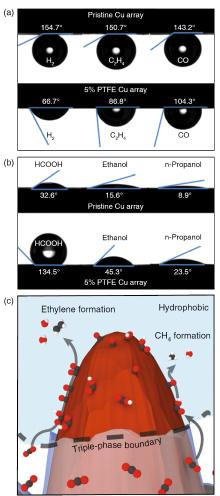

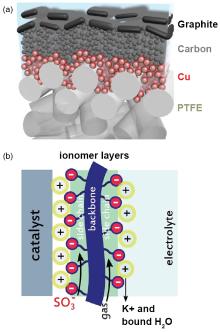


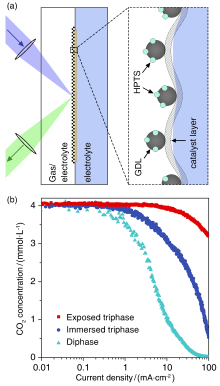

| [1] |
Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Nature 2012, 488,294.
|
| [2] |
Windle, C.D.; Perutz, R.N. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256,2562.
|
| [3] |
Liu, C.; Colon, B.C.; Ziesack, M.; Silver, P.A.; Nocera, D.G. Science 2016, 352,1210.
|
| [4] |
Li, Z.J.; Li, G.; Chen, X.L.; Xia, Z.; Yang, B.; Yao, J.N.; Lei, L.C.; Hou, Y. ChemSusChem 2018, 11,2382.
|
| [5] |
Choi, K.M.; Kim, D.; Rungtaweevoranit, B.; Trickett, C.A.; Barmanbek, J.T. D.; Alshammari, A.S.; Yang, P.D.; Yaghi, O.M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139,356.
|
| [6] |
Hori, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Murata, A.; Suzuki, S. Chem. Lett. 1986, 6,897.
|
| [7] |
Hori, Y.; Murata, A.; Takahashi, R. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1989, 85,2309.
|
| [8] |
Saveant, J.M. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3,1967.
|
| [9] |
Dufek, E.J.; Lister, T.E.; Stone, S.G.; Mcllwain, M.E. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159,F514.
|
| [10] |
Carroll, J.J.; Slupsky, J.D.; Mather, A.E. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1991, 20,1201.
|
| [11] |
Tackett, B.M.; Gomez, E.; Chen, J.G. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2,381.
|
| [12] |
Chi, C.; Juliet, F.K. K.; Stafford, W.S. Chem 2018, 4,2571.
|
| [13] |
Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Bond, A.M.; Zhang, J. Nano Today 2020, 31,100835.
|
| [14] |
Hori, Y.; Wakebe, H.; Tsukamoto, T.; Koga, O. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39,1833.
|
| [15] |
Schreier, M.; Yoon, Y.; Jackson, M.N.; Surendranath, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57,10221.
|
| [16] |
Hori, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Suzuki, S. Chem. Lett. 1985, 11,1695.
|
| [17] |
Cheng, T.; Xiao, H.; Goddard, W.A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138,133802.
|
| [18] |
Jones, J.; Prakash, G.K. S.; Olah, G.A. Isr. J. Chem. 2014, 54,1451.
|
| [19] |
Gao, S.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, X.C.; Sun, Y.F.; Luo, Q.Q.; Zhang, W.H.; Li, D.Q.; Yang, J.L.; Xie, Y. Nature 2016, 529,68.
|
| [20] |
Habisreutinger, S.N.; Schmidt-Mende, L.; Stolarczyk, J.K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52,7372.
|
| [21] |
Ting, L.R. L.; Yeo, B.S. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 8,126.
|
| [22] |
Albo, J.; Sáez, A.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Montiel, V.; Irabien, A. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2015, 176,709.
|
| [23] |
Li, J.; Chen, G.X.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Liang, Z.; Pei, A.; Wu, C.L.; Wang, H.X.; Lee, H.R.; Liu, K.; Chu, S.; Cui, Y. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1,592.
|
| [24] |
Xu, W.W.; Lu, Z.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Jiang, L.; Duan, X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51,1590.
|
| [25] |
Lu, Z.Y.; Zhu, W.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Li, Y.J.; Sun, X.M.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.M.; Luo, J.; Lei, X.D.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26,2683.
|
| [26] |
Wen, L.P.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54,3387.
|
| [27] |
Wang, J.M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Nie, F.Q.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Langmuir 2009, 25,14129.
|
| [28] |
Cai, Z,; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wu, Y.S.; Xu, W.W.; Wen, X.M.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.L.; Kuang, Y.; Sun, X.M. Nano Res. 2019, 12,345.
|
| [29] |
Schouten, K.J. P.; Kwon, Y.; Van der Ham, C.J. M.; Qin, Z.; Koper, M.T. M. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2,1902.
|
| [30] |
Wakerley, D.; Lamaison, S.; Ozanam, F.; Menguy, N.; Mercier, D.; Marcus, P.; Fontecave, M.; Mougel, V. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18,1222.
|
| [31] |
Dinh, C.T.; Burdyny, T.; Kibria, M.G.; Selfitokaldani, A.; Gabardo, C.M.; de Arquer, F.P. G.; Kiani, A.; Edwards, J.P.; De Luna, P.; Bushuyev, O.S.; Zou, C.Q.; Quintero-Bermudez, R.; Pang, Y.J.; Sinton, D.; Sargent, E.H. Science 2018, 360,783.
|
| [32] |
Zheng, T.T.; Jiang, K.; Ta, N.; Hu, Y.F.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, H.T. Joule 2019, 3,265.
|
| [33] |
de Arquer, F.P. G.; Dinh, C.T.; Ozden, A.; Wicks, J.; McCallum, C.; Kirmani, A.R.; Nam, D.H.; Gabardo, C.; Seifitokaldani, A.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.C.; Li, F.W.; Edwards, J.; Richter, L.J.; Thorpe, S.J.; Sinton, D.; Sargent, E.H. Science 2020, 367,661.
|
| [34] |
Kaczur, J.J.; Yang, H.Z.; Liu, Z.C.; Sajjad, S.A.; Masel, R.I. Front. Chem. 2018, 6,263.
|
| [35] |
Yin, Z.L.; Peng, H.Q.; Wei, X.; Zhou, H.; Gong, J.; Huai, M.M.; Xiao, L.; Wang, G.W.; Lu, J.T.; Zhuang, L. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12,2455.
|
| [36] |
Xiong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.H.; Shi, R.; Zhang, T.R. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 264,118518.
|
| [37] |
Burdyny, T.; Graham, P.J.; Pang, Y.J.; Dinh, C.T.; Min, L.; Sargent, E.H.; Sinton, D. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5,4031.
|
| [38] |
Shi, R.; Guo, J.H.; Zhang, Y.R.; Waterhouse, G.I. N.; Han, Z.J.; Zhao, Y.X.; Shang, L.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, T.R. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11,3028.
|
| [39] |
Nesbitt, N.T.; Burdyny, T.; Simonson, H.; Salvatore, D.; Bohra, D.; Kas, R.; Smith, W.A. ACS Catal. 2020, 10,14093.
|
| [40] |
Liu, Z.; Sheng, X.; Wang, D.D.; Feng, X.J. iScience 2019, 17,67.
|
| [41] |
Giorgi, L.; Antilini, E.; Pozio, A.; Passalacqua, E. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43,3675.
|
| [42] |
Martínez-Rodríguez, M.J.; Cui, T.; Shipalee, S.; Seraphin, S.; Duong, B.; Van Zee, J.W. J. Power Sources 2012, 207,91.
|
| [43] |
Jhong, H.-R. M.; Brushett, F.R.; Yin, L.L.; Stevenson, D.M.; Kenis, P.J. A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159,B292.
|
| [44] |
Kim, B.; Hillman, F.; Arioshi, M.; Fujikawa, S.; Kenis, P.J. A. J. Power Sources 2016, 312,192.
|
| [45] |
Jhong, H.-R. M.; Brushett, F.R.; Kenis, P.J. A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3,589.
|
| [46] |
Gabado, C.M.; Seifitokaldani, A.; Edwards, J.P.; Dinh, C.-T.; Burdyny, T.; Kibria, M.G.; O’Brien, C.P.; Sargent, E.H.; Sinton, D. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11,2531.
|
| [47] |
Thorson, M.R.; Siil, K.I.; Kenis, P.J. A. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160,F69.
|
| [48] |
Kim, B.; Ma, S.; Jhong, H.-R. M.; Kenis, P.J. A. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 166,271.
|
| [49] |
Verma, S.; Lu, X.; Ma, S.; Masel, R.I.; Kenis, P.J. A. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18,7075.
|
| [50] |
Chen, K.H.; Li, H.R.; He, L.N. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40,2195. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 陈凯宏, 李红茹, 何良年, 有机化学, 2020, 40,2195.)
|
|
| [51] |
Jhong, H.-R. M.; Tornow, C.E.; Kim, C.; Verma, S.; Oberst, J.L.; Anderson, P.S.; Gewirth, A.A.; Fujigaya, T.; Nakashima, N.; Kenis, P.J. A. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18,3274.
|
| [52] |
Wang, Y.J.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, J.J. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111,7625.
|
| [53] |
Liu, M.M.; Zhang, R.Z.; Chen, W. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114,5117.
|
| [54] |
Wang, Z.L.; Xu, D.; Xu, J.J.; Zhang, X.B. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43,7746.
|
| [55] |
Li, Y.G.; Gong, M.; Liang, Y.Y.; Feng, J.; Kim, J.E.; Wang, H.L.; Hong, G.S.; Zhang, B.; Dai, H.J. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4,1805.
|
| [56] |
Lu, Z.Y.; Xu, W.W.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.J.; Sun, X.M.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28,7155.
|
| [57] |
Lei, Y.J.; Sun, R.Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Feng, X.J.; Jiang, L. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28,1477.
|
| [58] |
Wang, Y.L.; Shi, R.; Shang, L.; Waterhouse, G.I. N.; Zhao, J.Q.; Zhang, Q.H.; Gu, L.; Zhang, T.R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59,13057.
|
| [59] |
Chen, S.L.; Patil, S.A.; Schroeder, U. Appl. Mater. 2018, 211,1089.
|
| [60] |
Li, J.; Chang, K.; Zhang, H.C.; He, M.; Goddard, W.A.; Chen, J.G. G.; Cheng, M.J.; Lu, Q. ACS Catal. 2019, 9,4709.
|
| [61] |
Chen, R.X.; Su, H.Y.; Liu, D.Y.; Huang, R.; Meng, X.G.; Cui, X.J.; Tian, Z.Q.; Zhang, D.H.; Deng, D.H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 59,154.
|
| [62] |
Jouny, M.; Luc, W.; Jiao, F. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1,1002.
|
| [63] |
Li, Y.J.; Zhang, H.C.; Xu, T.H.; Lu, Z.Y.; Wu, X.C.; Wan, P.B.; Sun, X.M.; Jiang, L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25,1737.
|
| [64] |
Hao, M.; Chanbonneau, V.; Fomena, N.N.; Gaudet, J.; Bruce, D.R.; Garbarino, S.; Harrington, D.A.; Gauy, D. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2,5734.
|
| [65] |
Yuan, J.X.; Cheng, X.D.; Wang, H.Q.; Lei, C.J.; Pardiwala, S.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.H.; Lei, L.C.; Wang, S.B.; Hou, Y. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12,104.
|
| [1] | 李珊, 路俊欣, 刘杰, 蒋绿齐, 易文斌. 氟烷基亚磺酸钠盐电化学合成α-氟烷基酮[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 110-114. |
| [2] | 刘建川, 李翠艳, 刘耀祖, 王钰杰, 方千荣. 高稳定二维联咔唑sp2碳共轭共价有机框架材料用于高效电催化氧还原★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 884-890. |
| [3] | 杨镇鸿, 干晓娟, 王书哲, 段君元, 翟天佑, 刘友文. 金属性Ni3N纳米粒子的制备与乙二醇电氧化性能★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1471-1477. |
| [4] | 闫绍兵, 焦龙, 何传新, 江海龙. ZIF-67/石墨烯复合物衍生的氮掺杂碳限域Co纳米颗粒用于高效电催化氧还原[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(8): 1084-1090. |
| [5] | 何家伟, 焦柳, 程雪怡, 陈光海, 吴强, 王喜章, 杨立军, 胡征. 金属有机框架衍生的空心碳纳米笼的结构调控与锂硫电池性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 896-902. |
| [6] | 蒋银龙, 李国超, 陈青松, 徐忠宁, 林姗姗, 郭国聪. 富晶格位错的多孔铋纳米花高效电还原二氧化碳制甲酸盐※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 703-707. |
| [7] | 王丹, 封波, 张晓昕, 刘亚楠, 裴燕, 乔明华, 宗保宁. 基于热解ZIF-8的氮掺杂碳电化学氧还原合成过氧化氢催化剂[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 772-780. |
| [8] | 应霞薇, 浮建军, 曾敏, 刘文, 张天宇, 沈培康, 张信义. 基于BiOCl-Fe2O3@TiO2介孔复合材料的光电化学合成氨性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 503-509. |
| [9] | 李泽洋, 杨宇森, 卫敏. 二氧化碳还原电催化剂的结构设计及性能研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(2): 199-213. |
| [10] | 安攀, 张庆慧, 杨状, 武佳星, 张佳颖, 王雅君, 李宇明, 姜桂元. 双碳目标下太阳能制氢技术的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(12): 1629-1642. |
| [11] | 王金格, 周伟, 李佳轶, 丁雅妮, 高继慧. 脉冲电催化的研究进展及性能强化机制[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(11): 1555-1568. |
| [12] | 王旭生, 杨胥, 陈春辉, 李红芳, 黄远标, 曹荣. 石墨烯量子点/铁基金属-有机骨架复合材料高效光催化二氧化碳还原※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 22-28. |
| [13] | 王瑞兆, 邹云杰, 洪晟, 徐铭楷, 凌岚. Pt0.01Fe0.05-g-C3N4催化剂高效光热催化二氧化碳还原[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 932-940. |
| [14] | 穆春辉, 张艺馨, 寇伟, 徐联宾. 镍氮掺杂有序大孔/介孔碳负载银纳米颗粒用于高效电催化CO2还原[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(7): 925-931. |
| [15] | 詹溯, 章福祥. 常温常压电催化合成氨的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 146-157. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||