化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 79 ›› Issue (6): 716-728.DOI: 10.6023/A21020074 上一篇 下一篇
综述
邵阳a,*( ), 杨国胜b, 张继龙c, 罗敏a, 马玲玲a, 徐殿斗a
), 杨国胜b, 张继龙c, 罗敏a, 马玲玲a, 徐殿斗a
投稿日期:2021-02-26
发布日期:2021-04-25
通讯作者:
邵阳
作者简介: |
邵阳, 助理研究员. 2019年毕业于中国科学院高能物理研究所, 获博士学位. 2018年以博士生身份在日本弘前大学辐射医疗综合研究所山田正俊课题组访问和学习一年. 主要研究方向为关键放射性核素分析方法开发与示踪应用研究. |
 |
杨国胜, 日本量子科学技术研究开发机构, 主任研究员. 主要从事环境和人体中痕量人工放射性核素的分析方法开发、示踪及剂量评估等研究(137Cs、Te、226Ra、236U、237Np、239Pu、240Pu、129I等). |
基金资助:
Yang Shaoa( ), Guosheng Yangb, Jilong Zhangc, Min Luoa, Lingling Maa, Diandou Xua
), Guosheng Yangb, Jilong Zhangc, Min Luoa, Lingling Maa, Diandou Xua
Received:2021-02-26
Published:2021-04-25
Contact:
Yang Shao
Supported by:文章分享

铀-236是一种重要的人工放射性核素, 是三种天然铀同位素之外可以应用在环境示踪、核应急、核取证以及核保障中的一种铀同位素. 人工236U主要是由核燃料235U经过中子照射后吸收中子产生, 因此, 不同“年龄”阶段核燃料中的236U和其他同位素的比值(指纹特征)截然不同. 同时不同反应堆类型中相应指纹特征也不尽相同. 通过监测核燃料、可疑核材料以及环境样品中不同236U/238U、236U/235U同位素比值等指纹特征即可确认反应堆运行状况、追溯核材料来源出处, 甚至可以开展放射性核污染物在环境中的迁移模拟等问题. 铀-236属于低丰度同位素, 其在核样品和环境样品中含量极低, 因此, 精确测定其同位素比值对236U在环境示踪、核应急、核取证以及核保障中的应用尤为重要. 本综述中, 作者总结了近年来痕量236U测定时样品前处理和检测分析技术的发展, 尤其着重于236U同位素比值的质谱检测技术的发展, 以及236U在核保障和环境中的示踪应用的研究进展. 最后, 对痕量236U检测和应用方面的研究提出展望.
邵阳, 杨国胜, 张继龙, 罗敏, 马玲玲, 徐殿斗. 人工放射性核素236U的分析方法进展及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 716-728.
Yang Shao, Guosheng Yang, Jilong Zhang, Min Luo, Lingling Ma, Diandou Xu. Progress and Application on the Analysis of Anthropogenic Radionuclide 236U[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(6): 716-728.
| 样品类型 | 检测核素 | 树脂色谱柱 | 铀回收率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珊瑚 | 236U、239,240Pu | AG 1-X8、UTEVA | — | [ |
| 海水 | 236U、239,240Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | 约60% | [ |
| 海水 | 236U、237Np、239,240Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | 82%~100% | [ |
| 水样 | 238,239,240Pu、237Np、228,232Th、234,235,236,238U、241Am、242,243,244Cm、147Pm、90Y、89,90Sr、55Fe | AG MP-1M、UTEVA、DGA、Sr、TRU | 100% | [ |
| 水样 | 238U、232Th、226Ra、210Po、210Pb | TRU、Sr、HRa | 93%±7% | [ |
| 环境擦拭样品 | 234,235,236,238U、239,240,241,242Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | >99% | [ |
| 土壤 | 234,235,238U、228,230,232Th | Microthene-TOPO | 79.8%±13.0% | [ |
| 土壤 | 235,238U、239,240,241Pu | UTEVA、DOWEXTM 1×8 | — | [ |
| 河水 | 234,235,236,238U、230,232Th、239,240Pu、237Np、241Am、90Sr | TEVA、DGA | 93%±6.2% | [ |
| 海水 | 99Tc、237Np、239,240Pu、238U | TEVA、AG MP-1M、UTEVA | 65% | [ |
| 海水 | 236U、237Np、239,240Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | 72.7%~112.1% | [ |
| 样品类型 | 检测核素 | 树脂色谱柱 | 铀回收率 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 珊瑚 | 236U、239,240Pu | AG 1-X8、UTEVA | — | [ |
| 海水 | 236U、239,240Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | 约60% | [ |
| 海水 | 236U、237Np、239,240Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | 82%~100% | [ |
| 水样 | 238,239,240Pu、237Np、228,232Th、234,235,236,238U、241Am、242,243,244Cm、147Pm、90Y、89,90Sr、55Fe | AG MP-1M、UTEVA、DGA、Sr、TRU | 100% | [ |
| 水样 | 238U、232Th、226Ra、210Po、210Pb | TRU、Sr、HRa | 93%±7% | [ |
| 环境擦拭样品 | 234,235,236,238U、239,240,241,242Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | >99% | [ |
| 土壤 | 234,235,238U、228,230,232Th | Microthene-TOPO | 79.8%±13.0% | [ |
| 土壤 | 235,238U、239,240,241Pu | UTEVA、DOWEXTM 1×8 | — | [ |
| 河水 | 234,235,236,238U、230,232Th、239,240Pu、237Np、241Am、90Sr | TEVA、DGA | 93%±6.2% | [ |
| 海水 | 99Tc、237Np、239,240Pu、238U | TEVA、AG MP-1M、UTEVA | 65% | [ |
| 海水 | 236U、237Np、239,240Pu | TEVA、UTEVA | 72.7%~112.1% | [ |
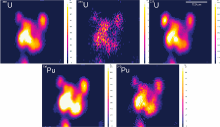

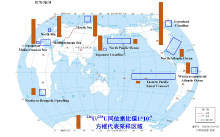

| 采样海域 | 采样时间 | 236U/238U同位素比值 | 236U/238U同位素比值平均值 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Atlantic | 2014 | 40×10-12~2350×10-12 | (1075±345)×10-12 | [ |
| Eastern Pacific Zonal Transect | 2013 | 0.2×10-12~727×10-12 | (179±247)×10-12 | [ |
| Greenland coastal line | 2012~2016 | 1.1×10-9~15.5×10-9 | 3.097×10-9 | [ |
| coast off Japan | 2013~2015 | 930×10-12~1300×10-12 | (1084±163)×10-12 | [ |
| North Sea | 2010 | 1.24×10-9~19.49×10-9 | (7.612±3.750)×10-9 | [ |
| Danish Seawater | 2014 | 5.4×10-9~24.0×10-9 | 13.40×10-9 | [ |
| western equatorial Atlantic Ocean | 2010 | 91×10-12~3567×10-12 | (808±1369)×10-12 | [ |
| North Pacific Ocean | 2012 | 0.09×10-10~14.1×10-10 | (3.441±4.14)×10-10 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: Barents Sea shelf | 2015 | 1380×10-12~3680×10-12 | 1550×10-12 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: West Spitsbergen | 2015 | 1340×10-12~1960×10-12 | 1560×10-12 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: Eurasian Basin | 2015 | 110×10-12~2980×10-12 | 1700×10-12 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: Makarov Basin | 2015 | 2.8×10-12~2810×10-12 | 1670×10-12 | [ |
| Fram Strait | 2016 | 367×10-12~2902×10-12 | (1845±654)×10-12 | [ |
| Mediterranean Sea | 2013 | 710×10-12~2220×10-12 | (1518±369)×10-12 | [ |
| northwest Mediterranean Sea | — | 1.4×10-9~2.13×10-9 | (1.78±0.33)×10-9 | [ |
| northern Benguela Upwelling | 2014 | 0.22×10-10~6.70×10-10 | (5.091±1.596)×10-10 | [ |
| Irish Sea | 1993 | — | (2.0±0.4)×10-6 | [ |
| 采样海域 | 采样时间 | 236U/238U同位素比值 | 236U/238U同位素比值平均值 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North Atlantic | 2014 | 40×10-12~2350×10-12 | (1075±345)×10-12 | [ |
| Eastern Pacific Zonal Transect | 2013 | 0.2×10-12~727×10-12 | (179±247)×10-12 | [ |
| Greenland coastal line | 2012~2016 | 1.1×10-9~15.5×10-9 | 3.097×10-9 | [ |
| coast off Japan | 2013~2015 | 930×10-12~1300×10-12 | (1084±163)×10-12 | [ |
| North Sea | 2010 | 1.24×10-9~19.49×10-9 | (7.612±3.750)×10-9 | [ |
| Danish Seawater | 2014 | 5.4×10-9~24.0×10-9 | 13.40×10-9 | [ |
| western equatorial Atlantic Ocean | 2010 | 91×10-12~3567×10-12 | (808±1369)×10-12 | [ |
| North Pacific Ocean | 2012 | 0.09×10-10~14.1×10-10 | (3.441±4.14)×10-10 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: Barents Sea shelf | 2015 | 1380×10-12~3680×10-12 | 1550×10-12 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: West Spitsbergen | 2015 | 1340×10-12~1960×10-12 | 1560×10-12 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: Eurasian Basin | 2015 | 110×10-12~2980×10-12 | 1700×10-12 | [ |
| Arctic Ocean: Makarov Basin | 2015 | 2.8×10-12~2810×10-12 | 1670×10-12 | [ |
| Fram Strait | 2016 | 367×10-12~2902×10-12 | (1845±654)×10-12 | [ |
| Mediterranean Sea | 2013 | 710×10-12~2220×10-12 | (1518±369)×10-12 | [ |
| northwest Mediterranean Sea | — | 1.4×10-9~2.13×10-9 | (1.78±0.33)×10-9 | [ |
| northern Benguela Upwelling | 2014 | 0.22×10-10~6.70×10-10 | (5.091±1.596)×10-10 | [ |
| Irish Sea | 1993 | — | (2.0±0.4)×10-6 | [ |
| [1] |
Brockman, J. D.; Brown, J. W.; Morrell, J. S.; Robertson, J. D. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8765.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02144 |
| [2] |
Purser, K. H.; Kilius, L. R.; Litherland, A. E.; Zhao, X. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 1996, 113, 445.
doi: 10.1016/0168-583X(95)01369-5 |
| [3] |
Christl, M.; Casacuberta, N.; Lachner, J.; Herrmann, J.; Synal, H. A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12146.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03168 |
| [4] |
Bu, W.; Zheng, J.; Ketterer, M. E.; Hu, S.; Uchida, S.; Wang, X. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 995, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.09.029 |
| [5] |
Sakaguchi, A.; Kawai, K.; Steier, P.; Quinto, F.; Mino, K.; Tomita, J.; Hoshi, M.; Whitehead, N.; Yamamoto, M. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4238.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.058 |
| [6] |
Quinto, F.; Hrnecek, E.; Krachler, M.; Shotyk, W.; Steier, P.; Winkler, S. R. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5243.
doi: 10.1021/es400026m |
| [7] |
Shao, Y.; Yang, G.; Luo, M.; Xu, D.; Tazoe, H.; Yamada, M.; Ma, L. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 127909.
doi: S0045-6535(20)32104-4 pmid: 32822937 |
| [8] |
Steier, P.; Bichler, M.; Keith Fifield, L.; Golser, R.; Kutschera, W.; Priller, A.; Quinto, F.; Richter, S.; Srncik, M.; Terrasi, P.; Wacker, L.; Wallner, A.; Wallner, G.; Wilcken, K. M.; Maria Wild, E. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2008, 266, 2246.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2008.03.002 |
| [9] |
Shao, Y.; Yang, G.; Xu, D.; Yamada, M.; Tazoe, H.; Luo, M.; Cheng, H.; Yang, K.; Ma, L. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 197, 1.
doi: S0265-931X(18)30596-4 pmid: 30463028 |
| [10] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Becker, J. S. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 1143.
doi: 10.1039/B202196J |
| [11] |
Sakaguchi, A.; Steier, P.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3691.
doi: 10.1021/es405294s |
| [12] |
Castrillejo, M.; Witbaard, R.; Casacuberta, N.; Richardson, C. A.; Dekker, R.; Synal, H. A.; Christl, M. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137094.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137094 |
| [13] |
Lee, S. H.; Povinec, P. P.; Wyse, E.; Hotchkis, M. A. C. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2008, 66, 823.
doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2008.02.020 |
| [14] |
Christl, M.; Lachner, J.; Vockenhuber, C.; Lechtenfeld, O.; Stimac, I.; van der Loeff, M. R.; Synal, H. A. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 77, 98.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.11.009 |
| [15] |
Martelat, B.; Isnard, H.; Vio, L.; Dupuis, E.; Cornet, T.; Nonell, A.; Chartier, F. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8622.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01884 |
| [16] |
Diez-Fernandez, S.; Jaegler, H.; Bresson, C.; Chartier, F.; Evrard, O.; Hubert, A.; Nonell, A.; Pointurier, F.; Isnard, H. Talanta 2020, 206, 120221.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120221 |
| [17] |
Lopez-Lora, M.; Chamizo, E.; Villa-Alfageme, M.; Hurtado- Bermudez, S.; Casacuberta, N.; Garcia-Leon, M. Talanta 2018, 178, 202.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.09.026 |
| [18] |
Wang, H.; Ni, Y.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, D.; Aono, T. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 71.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.065 |
| [19] |
Kolacinska, K.; DeVol, T. A.; Seliman, A. F.; Bliznyuk, V. N.; Dudek, J.; Dudek, M. K.; Piotrowski, P.; Trojanowicz, M. Talanta 2019, 205, 120099.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.099 |
| [20] |
Huang, Z.; Ni, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Yamazaki, S.; Sakaguchi, A.; Long, X.; Uchida, S. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 597.
doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2019.05.044 |
| [21] |
Lopez-Lora, M.; Levy, I.; Chamizo, E. Talanta 2019, 200, 22.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.036 |
| [22] |
Wang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Cao, L.; Tagami, K.; Uchida, S. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7387.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01934 |
| [23] |
Willberger, C.; Amayri, S.; Haussler, V.; Scholze, R.; Reich, T. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11537.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00997 |
| [24] |
Du, J.; Wang, L.; Xiong, P. Nuclear Electronics and Detection Technology 2017, 37, 335. (in Chinese)
|
|
(杜杰, 王丽萍, 熊鹏辉, 核电子学与探测技术, 2017, 37, 335.)
|
|
| [25] |
Yang, G.; Tazoe, H.; Yamada, M. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 944, 44.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.09.033 |
| [26] |
Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Zhai, L.; Shen, X.; Yuan, X.; Wei, G.; Fang, S.; Deng, H.; Li, Z. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society 2019, 40, 518. (in Chinese)
|
|
(汪伟, 徐江, 翟利华, 沈小攀, 袁祥龙, 韦冠一, 方随, 邓虎, 李志明, 质谱学报, 2019, 40, 518.)
|
|
| [27] |
Park, J. H.; Choi, E. J. Talanta 2016, 160, 600.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.006 |
| [28] |
Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Cole, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, D.; Tan, X. Uranium Geology 2019, 35, 38. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张继龙, 黎春, 王岚, 武朝辉, Cole, H, 周至波, 杨丽芳, 李多宏, 谭西早, 铀矿地质, 2019, 35, 38.)
|
|
| [29] |
Bellucci, J. J.; Whitehouse, M. J.; Aleshin, M.; Eriksson, M. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5599.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04809 |
| [30] |
Prášek, T.; Němec, M.; Steier, P.; Kern, M.; Honda, M.; Hain, K.; Zhang, X. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2020, 472, 64.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2020.03.029 |
| [31] |
Claverie, F.; Hubert, A.; Berail, S.; Donard, A.; Pointurier, F.; Pécheyran, C. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4375.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04802 |
| [32] |
Boulyga, S.; Konegger-Kappel, S.; Richter, S.; Sangély, L. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1469.
doi: 10.1039/C4JA00491D |
| [33] |
Fahey, A. J.; Groopman, E. E.; Grabowski, K. S.; Fazel, K. C. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7145.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01209 |
| [34] |
Jaegler, H.; Pointurier, F.; Diez-Fernandez, S.; Gourgiotis, A.; Isnard, H.; Hayashi, S.; Tsuji, H.; Onda, Y.; Hubert, A.; Laceby, J. P.; Evrard, O. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 849.
doi: S0045-6535(19)30500-4 pmid: 30904765 |
| [35] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Heumann, K. G. J. Environ. Radioact. 2006, 88, 1.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2005.12.007 |
| [36] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Matusevich, J. L.; Mironov, V. P.; Kudrjashov, V. P.; Halicz, L.; Segal, I.; McLean, J. A.; Montaser, A.; Sabine Becker, J. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 958.
doi: 10.1039/b201803a |
| [37] |
Marsden, O. J.; Livens, F. R.; Day, J. P.; Fifield, L. K.; Goodall, P. S. Analyst 2001, 126, 633.
pmid: 11394304 |
| [38] |
Maxwell, S. L.; Culligan, B. K.; Kelsey-Wall, A.; Shaw, P. J. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 701, 112.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.06.011 |
| [39] |
Maxwell, S. L.; Culligan, B. K.; Noyes, G. W. Radiochim. Acta 2010, 98, 793.
doi: 10.1524/ract.2010.1785 |
| [40] |
Zhang, W.; Hu, Z. Spectrochim. Acta B 2019, 160, 105690.
doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2019.105690 |
| [41] |
Qiao, J.; Hou, X.; Steier, P.; Golser, R. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11026.
doi: 10.1021/ac402673p |
| [42] |
Qiao, J.; Hou, X.; Steier, P.; Nielsen, S.; Golser, R. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7411.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01608 |
| [43] |
Michel, H.; Levent, D.; Barci, V.; Barci-Funel, G.; Hurel, C. Talanta 2008, 74, 1527.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.09.030 pmid: 18371813 |
| [44] |
Rovan, L.; Štrok, M. J. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1882.
doi: 10.1039/C9JA00144A |
| [45] |
Froehlich, M. B.; Chan, W. Y.; Tims, S. G.; Fallon, S. J.; Fifield, L. K. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 165, 197.
doi: S0265-931X(16)30429-5 pmid: 27764678 |
| [46] |
Dai, X.; Kramer-Tremblay, S. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5441.
doi: 10.1021/ac500572g |
| [47] |
Dalencourt, C.; Chabane, M. N.; Tremblay-Cantin, J. C.; Lariviere, D. Talanta 2020, 207, 120282.
doi: S0039-9140(19)30915-4 pmid: 31594595 |
| [48] |
Metzger, S. C.; Ticknor, B. W.; Rogers, K. T.; Bostick, D. A.; McBay, E. H.; Hexel, C. R. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9441.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02095 |
| [49] |
Jia, G. J. Radioan. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 311, 1007.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-016-4905-3 |
| [50] |
Shibahara, Y.; Kubota, T.; Fujii, T.; Fukutani, S.; Takamiya, K.; Konno, M.; Mizuno, S.; Yamana, H. J. Radioan. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 307, 2281.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-015-4551-1 |
| [51] |
Habibi, A.; Boulet, B.; Gleizes, M.; Lariviere, D.; Cote, G. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 883, 109.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.04.025 |
| [52] |
Qiao, J.; Shi, K.; Hou, X.; Nielsen, S.; Roos, P. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3935.
doi: 10.1021/es404584b |
| [53] |
Chamizo, E.; López-Lora, M.; Villa, M.; Casacuberta, N.; López-Gutiérrez, J. M.; Pham, M. K. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2015, 361, 535.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2015.02.066 |
| [54] |
De Cesare, M.; Fifield, L. K.; Sabbarese, C.; Tims, S. G.; De Cesare, N.; D’Onofrio, A.; D’Arco, A.; Esposito, A. M.; Petraglia, A.; Roca, V.; Terrasi, F. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2013, 294, 152.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2012.05.020 |
| [55] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Koepf, A.; Konegger-Kappel, S.; Macsik, Z.; Stadelmann, G. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2016, 31, 2272.
doi: 10.1039/C6JA00238B |
| [56] |
Buchholz, B. A.; Brown, T. A.; Hamilton, T. F.; Hutcheon, I. D.; Marchetti, A. A.; Martinelli, R. E.; Ramon, E. C.; Tumey, S. J.; Williams, R. W. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2007, 259, 733.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2007.01.248 |
| [57] |
Duffin, A. M.; Hart, G. L.; Hanlen, R. C.; Eiden, G. C. J. Radioan. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 296, 1031.
doi: 10.1007/s10967-012-2218-8 |
| [58] |
Craig, G.; Horstwood, M. S. A.; Reid, H. J.; Sharp, B. L. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1011.
doi: 10.1039/D0JA00066C |
| [59] |
Krachler, M.; Wallenius, M.; Nicholl, A.; Mayer, K. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 16629.
doi: 10.1039/D0RA02899A |
| [60] |
Krachler, M.; Varga, Z.; Nicholl, A.; Wallenius, M.; Mayer, K. Microchem. J. 2018, 140, 24.
doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2018.03.038 |
| [61] |
Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G.; Shen, X.; Zhai, L. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2015, 43, 703. (in Chinese)
|
|
(汪伟, 李志明, 徐江, 周国庆, 沈小攀, 翟利华, 分析化学, 2015, 43, 703.)
|
|
| [62] |
Jaegler, H.; Gourgiotis, A.; Steier, P.; Golser, R.; Diez, O.; Cazala, C. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7869.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01121 |
| [63] |
Xing, S.; Luo, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Dai, X. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 2027.
doi: 10.1039/C9JA00209J |
| [64] |
Tanimizu, M.; Sugiyama, N.; Ponzevera, E.; Bayon, G. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2013, 28, 1372.
doi: 10.1039/c3ja50145k |
| [65] |
Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y. Talanta 2021, 224, 121882.
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121882 |
| [66] |
Zhao, X.; Kilius, L. R.; Litherland, A. E.; Beasley, T. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 1997, 126, 297.
doi: 10.1016/S0168-583X(96)01034-8 |
| [67] |
Zhao, X.; Nadeau, M. J.; Kilius, L. R.; Litherland, A. E. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 1994, 92, 249.
doi: 10.1016/0168-583X(94)96014-3 |
| [68] |
Zhao, X.; Nadeau, M. J.; Kilius, L. R.; Litherland, A. E. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1994, 124, 241.
doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)00090-5 |
| [69] |
Quinto, F.; Golser, R.; Lagos, M.; Plaschke, M.; Schafer, T.; Steier, P.; Geckeis, H. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5766.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00980 |
| [70] |
Lopez-Lora, M.; Chamizo, E.; Rozmaric, M.; Louw, D. C. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135222.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135222 |
| [71] |
Hain, K.; Steier, P.; Froehlich, M. B.; Golser, R.; Hou, X.; Lachner, J.; Nomura, T.; Qiao, J.; Quinto, F.; Sakaguchi, A. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1275.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15008-2 pmid: 32152279 |
| [72] |
Zhao, X. L.; Francisco, B. B. A.; Kieser, W. E.; El-Jaby, A.; Cochrane, C.; Clark, I. D. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2019, 459, 98.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2019.08.012 |
| [73] |
Kazi, Z. H.; Charles, C. R. J.; Zhao, X. L.; Cornett, R. J.; Kieser, W. E. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2019, 456, 218.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2019.04.006 |
| [74] |
Wang, C.; Dong, K.; Zhao, X.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. Atomic Energy Science and Technology 2016, 50, 732. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王琛, 董克君, 赵兴红, 何明, 张燕, 姜山, 赵永刚, 李力力, 原子能科学技术, 2016, 50, 732.)
|
|
| [75] |
Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, J. Atomic Energy Science and Technology 2015, 49, 400. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王凡, 张燕, 王晓明, 赵永刚, 王琛, 刘宇昂, 朱建锐, 鹿捷, 原子能科学技术, 2015, 49, 400.)
|
|
| [76] |
Shen, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Atomic Energy Science and Technology 2019, 53, 585. (in Chinese)
|
|
(沈彦, 王同兴, 王琛, 张燕, 赵永刚, 原子能科学技术, 2019, 53, 585.)
|
|
| [77] |
Schneider, S.; Bister, S.; Christl, M.; Hori, M.; Shozugawa, K.; Synal, H. A.; Steinhauser, G.; Walther, C. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 85, 194.
doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.05.022 |
| [78] |
Yang, G.; Tazoe, H.; Hayano, K.; Okayama, K.; Yamada, M. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13619.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13998-6 |
| [79] |
Shinonaga, T.; Steier, P.; Lagos, M.; Ohkura, T. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3808.
doi: 10.1021/es404961w |
| [80] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Sabine Becker, J.; Matusevitch, J. L.; Dietze, H. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 203, 143.
doi: 10.1016/S1387-3806(00)00296-7 |
| [81] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Prohaska, T. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 531.
pmid: 17874079 |
| [82] |
Mironov, V. P.; Matusevich, J. L.; Kudrjashov, V. P.; Boulyga, S. F.; Becker, J. S. J. Environ. Monit. 2002, 4, 997.
doi: 10.1039/b207573c |
| [83] |
Boulyga, S. F.; Sabine Becker, J. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 370, 612.
pmid: 11496994 |
| [84] |
Qiao, J.; Hain, K.; Steier, P. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127185.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127185 |
| [85] |
Lopez-Lora, M.; Chamizo, E.; Levy, I.; Christl, M.; Casacuberta, N.; Kenna, T. C. Sci. Total Environ. 2020,142741.
|
| [86] |
Arnason, J. G.; Pellegri, C. N.; Moore, J. L.; Lewis-Michl, E. L.; Parsons, P. J. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 629.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.04.006 |
| [87] |
Casacuberta, N.; Christl, M.; Buesseler, K. O.; Lau, Y.; Vockenhuber, C.; Castrillejo, M.; Synal, H. A.; Masque, P. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9826.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03057 |
| [88] |
Tims, S. G.; Froehlich, M. B.; Fifield, L. K.; Wallner, A.; De Cesare, M. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 151, 563.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.06.020 |
| [89] |
Child, D. P.; Hotchkis, M. A. C. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2013, 294, 642.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2012.05.018 |
| [90] |
Sakaguchi, A.; Kawai, K.; Steier, P.; Imanaka, T.; Hoshi, M.; Endo, S.; Zhumadilov, K.; Yamamoto, M. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5392.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.07.073 |
| [91] |
Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Yamada, M.; Yang, G. Catena 2020, 193, 104605.
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104605 |
| [92] |
Wang, C.; Hou, S.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y.; GÄGgeler, H. W.; Christl, M.; Synal, H. A. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 929.
doi: 10.1017/jog.2017.59 |
| [93] |
Tortorello, R.; Widom, E.; Renwick, W. H. J. Environ. Radioact. 2013, 124, 287.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2013.06.007 pmid: 23871969 |
| [94] |
Sakaguchi, A.; Kadokura, A.; Steier, P.; Takahashi, Y.; Shizuma, K.; Hoshi, M.; Nakakuki, T.; Yamamoto, M. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 333-334, 165.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.04.004 |
| [95] |
Casacuberta, N.; Christl, M.; Lachner, J.; van der Loeff, M. R.; Masqué, P.; Synal, H. A. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 133, 34.
doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.012 |
| [96] |
Casacuberta, N.; Masqué, P.; Henderson, G.; Rutgers van-der-Loeff, M.; Bauch, D.; Vockenhuber, C.; Daraoui, A.; Walther, C.; Synal, H. A.; Christl, M. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 440, 127.
doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.02.020 |
| [97] |
Castrillejo, M.; Casacuberta, N.; Christl, M.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Vockenhuber, C.; Synal, H. A.; Masque, P. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593-594, 745.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.201 |
| [98] |
Chamizo, E.; Lopez-Lora, M.; Bressac, M.; Levy, I.; Pham, M. K. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 767.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.142 |
| [99] |
Christl, M.; Casacuberta, N.; Lachner, J.; Maxeiner, S.; Vockenhuber, C.; Synal, H.-A.; Goroncy, I.; Herrmann, J.; Daraoui, A.; Walther, C.; Michel, R. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2015, 361, 510.
doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2015.01.005 |
| [100] |
Casacuberta, N.; Christl, M.; Vockenhuber, C.; Wefing, A. M.; Wacker, L.; Masque, P.; Synal, H. A.; van der Loeff, M. R. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 6909.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014168 |
| [101] |
Castrillejo, M.; Casacuberta, N.; Christl, M.; Vockenhuber, C.; Synal, H.-A.; Garcia-Ibanez, M. I.; Lherminier, P.; Sarthou, G.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Masque, P. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 5545.
doi: 10.5194/bg-15-5545-2018 |
| [102] |
Qiao, J.; Steier, P.; Nielsen, S.; Hou, X.; Roos, P.; Golser, R. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6867.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b00504 |
| [103] |
Villa-Alfageme, M.; Chamizo, E.; Kenna, T. C.; López-Lora, M.; Casacuberta, N.; Chang, C.; Masqué, P.; Christl, M. Chem. Geol. 2019, 517, 44.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.04.003 |
| [104] |
Wefing, A. M.; Christl, M.; Vockenhuber, C.; van der Loeff, M. R.; Casacuberta, N. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 882.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014399 |
| [1] | 关松磊, 吕磊, 胡秀丽, 刘忠英, 宋凤瑞, 刘志强. 顺铂对卵巢癌COC1细胞总蛋白表达的影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(14): 1721-1724. |
| [2] | 戚苓,张诚,魏先文,吴鸣飞,徐正,周克瑜,曹亚澄. 中性富勒烯分子的直接电喷雾质谱分析[J]. 化学学报, 1997, 55(5): 498-502. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||