化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (3): 310-316.DOI: 10.6023/A21120570 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
研究论文
投稿日期:2021-12-17
发布日期:2022-02-15
通讯作者:
李久盛
作者简介:基金资助:Received:2021-12-17
Published:2022-02-15
Contact:
Jiusheng Li
About author:Supported by:文章分享

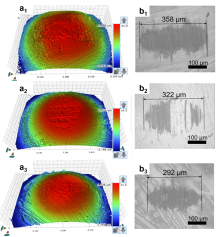
现代汽车工业的发展以及环保法规的日益严格对车用润滑油的性能提出了更高要求, 摩擦改进剂在提高发动机油减摩性能及燃油经济性方面发挥着重要作用. 有机钼化合物作为目前使用最为广泛的摩擦改进剂, 会增加油品热氧化沉积物的生成, 且油品氧化会导致其减摩性能下降. 针对摩擦改进剂所存在的诸如有害元素、灰分及活性吸附位点有限等问题, 设计并合成了两种双/三氮杂冠醚化合物, 将活性氮原子及长链烷基引入冠醚结构中以提高吸附性能和油溶性, 并研究其作为摩擦改进剂的减摩和抗磨性能. 结果表明, 所合成双/三氮杂冠醚能有效降低油品的摩擦系数和磨损率, 其中含有吡啶结构的三氮杂冠醚表现出更优的摩擦学性能, 可使摩擦系数和磨损率相对于基础油分别降低8.8%和42%. 机理分析表明, 所合成的双/三氮杂冠醚化合物能够在钢表面发生不同程度的吸附, 并进一步发生摩擦化学反应形成润滑保护膜, 防止滑动表面微凸体的直接接触进而改善摩擦学性能.
胡文敬, 李久盛. 双/三氮杂冠醚化合物的合成及其作为摩擦改进剂的性能研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 310-316.
Wenjing Hu, Jiusheng Li. Synthesis of Bis/triaza Crown Ethers and Study of Their Properties as Friction Modifiers※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(3): 310-316.
| 理化性质 | |
|---|---|
| 粗糙度 | 钢球(直径8 mm): 0.12 μm 钢板: 0.1 μm |
| 压力粘度系数 | 2.097×10–8 Pa–1 |
| 杨氏模量 | 2.10×1011 Pa |
| 泊松比 | 0.3 |
| hmin λ值 | 12.332 nm 0.079 |
| 理化性质 | |
|---|---|
| 粗糙度 | 钢球(直径8 mm): 0.12 μm 钢板: 0.1 μm |
| 压力粘度系数 | 2.097×10–8 Pa–1 |
| 杨氏模量 | 2.10×1011 Pa |
| 泊松比 | 0.3 |
| hmin λ值 | 12.332 nm 0.079 |

| 理化性质 | |
|---|---|
| 运动粘度@20 ℃ (mm2/s) | 44.910 |
| 运动粘度@40 ℃ (mm2/s) 运动粘度@100 ℃ (mm2/s) | 19.545 3.934 |
| 密度@20 ℃ (g/cm3) | 0.922 |
| 倾点/℃ | –41 |
| 闪点/℃ | 204 |
| 理化性质 | |
|---|---|
| 运动粘度@20 ℃ (mm2/s) | 44.910 |
| 运动粘度@40 ℃ (mm2/s) 运动粘度@100 ℃ (mm2/s) | 19.545 3.934 |
| 密度@20 ℃ (g/cm3) | 0.922 |
| 倾点/℃ | –41 |
| 闪点/℃ | 204 |
| [1] |
Cyriac, F.; Tee, X. Y.; Poornachary, S. K.; Chow, P. S. Friction 2021, 9, 380.
doi: 10.1007/s40544-020-0385-0 |
| [2] |
Spikes, H. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 60, 5.
doi: 10.1007/s11249-015-0589-z |
| [3] |
Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Erdemir, A. Tribol. Int. 2012, 47, 221.
doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2011.11.022 |
| [4] |
Wong, V. W.; Tung, S. C. Friction 2016, 4, 1.
doi: 10.1007/s40544-016-0107-9 |
| [5] |
Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Espejo, C.; Wang, J.; Neville, A.; Morina, A. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13523.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02329 |
| [6] |
De Barros Bouchet, M. I.; Martin, J. M.; Oumahi, C.; Gorbatchev, O.; Afanasiev, P.; Geantet, C.; Iovine, R.; Thiebaut, B.; Heau, C. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 600.
doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2017.11.039 |
| [7] |
Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 64.
doi: 10.1007/s11249-017-0847-3 |
| [8] |
Lundgren, S. M.; Eriksson, K.; Rossenaar, B. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2015, 8, 27.
doi: 10.4271/2015-01-0684 |
| [9] |
De Feo, M.; Minfray, C.; De Barros Bouchet, M. I.; Thiebaut, B.; Martin, J. M. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 93786.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA15250J |
| [10] |
Shu, Z. Y.; Xia, Y. Q.; Ge, X. Y. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 645, 137.
|
| [11] |
Kotia, A.; Chowdary, K.; Srivastava, I.; Ghosh, S. K.; Ali, M. K. A. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113200.
doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113200 |
| [12] |
Guimarey, M. J. G.; Comunas, M. J. P.; Lopez, E. R.; Amigo, A.; Fernandez, J. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 192.
doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2018.10.035 |
| [13] |
Brittain, W. J.; Minko, S. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 3505.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-0518 |
| [14] |
Robinson, J. W.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, J.; Bays, J. T.; Cosimbescu, L. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 109, 52.
doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2016.10.003 |
| [15] |
Zhang, S. M.; Gao, Y. J.; Zhang, Z. J.; Dang, H. X.; Liu, W. M.; Xue, Q. J. Acta Chim. Sinica 2002, 60, 1497. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张晟卯, 高永建, 张治军, 党鸿辛, 刘维民, 薛群基, 化学学报, 2002, 60, 1497.)
|
|
| [16] |
Chen, W. X.; Xu, J. P.; Ma, X. C.; Xu, Z. D.; Chen, W. L.; Wang, J. G.; Cheng, D. H.; Xia, J. B.; Gan, H. Y.; Jin, Y. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2002, 60, 1722. (in Chinese)
|
|
(陈卫祥, 涂江平, 马晓春, 徐铸德, 陈文录, 汪久根, 成旦红, 夏军保, 甘海洋, 金亚旭, 化学学报, 2002, 60, 1722.)
|
|
| [17] |
Ratoi, M.; Niste, V. B.; Alghawel, H.; Suen, Y. F.; Nelson, K. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4278.
doi: 10.1039/C3RA46403B |
| [18] |
Fry, B. M.; Moody, G.; Spikes, H. A.; Wong, J. S. S. Langmuir 2020, 36, 1147.
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03668 |
| [19] |
Desanker, M.; He, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, P.; Pickens, D. B.; Delferro, M.; Marks, T. J.; Chung, Y. W.; Wang, Q. J. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 9118.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b15608 |
| [20] |
Desanker, M.; He, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, P.; Pickens, D. B.; Delferro, M.; Marks, T. J.; Chung, Y. W.; Wang, Q. J. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 50.
doi: 10.1007/s11249-018-0996-z |
| [21] |
Nalam, P. C.; Pham, A.; Castillo, R. V.; Espinosa-Marzal, R. M. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 13672.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b02097 |
| [22] |
Pond, S. J. K.; Tsutsumi, O.; Rumi, M.; Kwon, O.; Zojer, E.; Bredas, J. L.; Marder, S. R.; Perry, J. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9291.
doi: 10.1021/ja049013t |
| [23] |
Dong, Z.; Jane, W. Q. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 041001.
doi: 10.1115/1.4004457 |
| [24] |
Zhang, W. F.; Ying, Z. N.; Wen, S. Z. Tribology 1988, 6, 39. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张文法, 应自能, 温诗铸, 摩擦学, 1988, 6, 39.)
|
|
| [25] |
Wilson, D.; Langell, M. A. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 303, 6.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.006 |
| [26] |
Wu, X. J.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Liang, Q. S.; Meng, J. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 340, 74.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2011.12.041 |
| [27] |
Kurtz, R. L.; Henrich, V. E. Surf. Sci. 1983, 129, 345.
doi: 10.1016/0039-6028(83)90185-1 |
| [28] |
Paparazzo, E. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1987, 43, 97.
doi: 10.1016/0368-2048(87)80022-1 |
| [29] |
Normand, F. L.; Hommet, J.; Szorenyi, T.; Fuchs, C.; Fogarassy, E. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 235416.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.64.235416 |
| [30] |
Hasik, M.; Bernasik, A.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Kowalski, K.; Wenda, E.; Camra, J. Surf. Sci. 2002, 507, 916.
|
| [31] |
De Faria, D. L. A.; Venancio Silva, S.; de Oliveira, M. T. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 873.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4555 |
| [32] |
Soler, M. A. G.; Qu, F. Raman Spectroscopy for Nanomaterials Characterization, Eds.: Kumar, C. S. S. R., Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012, p. 379.
|
| [33] |
Johnson, B.; Wu, H.; Desanker, M.; Pickens, D.; Chung, Y. W.; Wang, Q. J. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 2.
doi: 10.1007/s11249-017-0945-2 |
| [34] |
Hu, W. J.; Zhang, Z. J.; Zeng X. Q.; Li, J. S. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 59, 215.
doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05333 |
| [35] |
Uluçcam, G.; Beynek, N.; Seller, Z.; Akalın, G.; Turan, G.; Benkli, K. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2008, 183, 2237.
doi: 10.1080/10426500801907589 |
| [1] | 杨铃悦, 李赟婷, 舒超. 亚磺酸内酯研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 171-189. |
| [2] | 万义, 何江华, 张越涛. Lewis酸碱对催化极性烯烃单体精准聚合的研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1215-1230. |
| [3] | 洪梅, 高金强, 李彤, 杨世和. 原位刻蚀调控多级孔分子筛策略及其应用进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 937-948. |
| [4] | 甘绍艳, 钟晟昱, 王力廷, 史雷. 有机高价溴试剂的合成及其应用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1030-1042. |
| [5] | 郑文山, 高冠斌, 邓浩, 孙涛垒. Ag2Se@Ag2S核壳量子点的室温合成及其近红外荧光性能优化[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 763-770. |
| [6] | 张艳东, 朱守非. 环丙烷骨架膦配体的研究展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 777-783. |
| [7] | 刘坜, 郑刚, 范国强, 杜洪光, 谭嘉靖. 4-酰基/氨基羰基/烷氧羰基取代汉斯酯参与的有机反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 657-668. |
| [8] | 坎比努尔•努尔买买提, 王超, 罗时玮, 阿布都热西提•阿布力克木. 电化学条件下α,α,α-三卤(氯, 溴)甲基酮类化合物的选择性脱卤反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 582-587. |
| [9] | 王俊, 许晓梅, 周姣龙, 赵雅男, 孙秀丽, 唐勇, 何素芳, 杨红梅. 新型无硫无磷醚-酯化合物的合成及其作为无灰摩擦改进剂的性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 461-468. |
| [10] | 齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| [11] | 魏颖, 周平, 陈鑫, 包秋景, 解令海. 有机纳米环/格的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 289-308. |
| [12] | 陈俊畅, 张明星, 王殳凹. 晶态多孔材料合成方法的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 146-157. |
| [13] | 高杨, 张学鑫, 余金生, 周剑. α-手性三级叠氮化合物的不对称催化合成新进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1590-1608. |
| [14] | 王晓晨, 季泽尧, 刘健, 王炳福, 金辉, 张立新. 硫酯参与的有机催化不对称反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 64-83. |
| [15] | 张红丹, 兰欣雨, 程鹏. 羟基自由基辅助沸石分子筛合成的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 100-110. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
