化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (4): 535-541.DOI: 10.6023/A21120584 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
研究评论
投稿日期:2021-12-25
发布日期:2022-04-28
通讯作者:
田善喜
作者简介: |
胡婕, 中国科学技术大学合肥微尺度物质科学国家研究中心副研究员, 2012、2018年在中国科学技术大学化学物理系获得学士、博士学位. 2019年1月至2021年12月在中国科技大学从事博士后研究, 2022年1月起任副研究员, 研究方向为低能离子-分子反应动力学. |
 |
田善喜, 中国科学技术大学化学物理系教授, 合肥微尺度物质科学国家研究中心兼职研究员. 2000年于中国科技大学近代物理系获得博士学位, 2000~2004年先后在日本东北大学、美国加州大学戴维斯分校做博士后研究, 2004年起在中国科技大学工作. 2006年入选教育部新世纪人才计划, 中科院青年促进会会员, 2016年获得国家自然基金委杰出青年项目资助. 目前的研究兴趣为: 气相、液相及气液界面的微观化学动力学机制与电子(电荷)诱导的化学反应. |
基金资助:Received:2021-12-25
Published:2022-04-28
Contact:
Shanxi Tian
About author:Supported by:文章分享
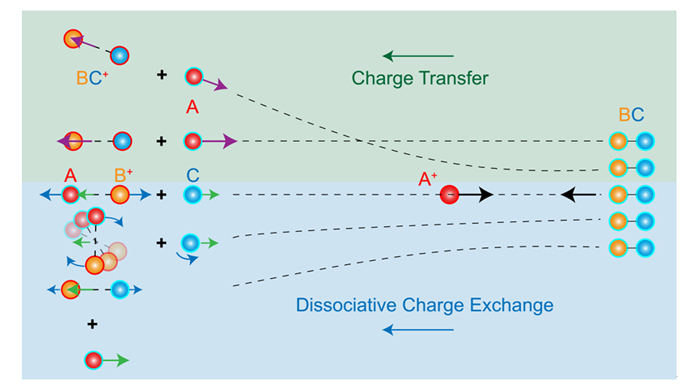
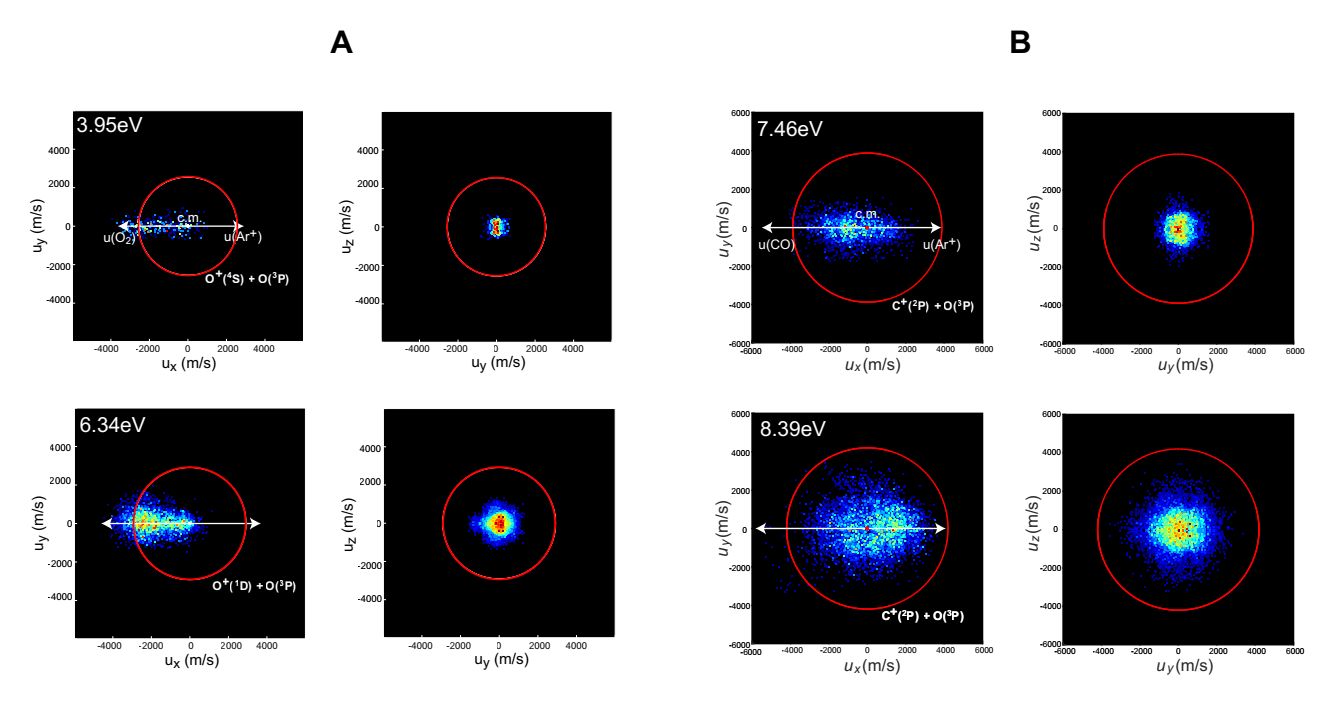
离子-分子反应是星际空间、地球大气、燃烧火焰和等离子体等各类环境中物质演化的关键步骤之一, 而且此类反应还涉及到电荷转移、能量传递等基本物理化学过程. 近十几年来, 离子速度成像技术的引入推动了低能离子-分子反应动力学的实验研究, 但仍有很多微观动力学机制有待深入探索. 基于自制的交叉束离子速度成像装置, 本研究组最近利用延迟线阳极探测器实现了多通道产物的三维离子速度影像的高效测量. 对Ar+和小分子的电荷转移研究中, 作者发现了此过程与光电离、Marcus理论模型之间的差异; 通过研究Ar+与O2、CO的解离性电荷转移反应, 揭示了奇特的立体动力学特征, 分析了解离性电荷转移与纯电荷转移的动力学差异. 结合国际上相关研究, 作者对未来的实验技术发展与研究内容作了展望.
胡婕, 田善喜. 低能离子-分子反应动力学的研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 535-541.
Jie Hu, Shanxi Tian. Progresses in the Study of Low-Energy Ion-molecule Reaction Dynamics※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(4): 535-541.

| [1] |
Larsson, M.; Geppert, W. D.; Nyman, G. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 066901.
doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/75/6/066901 |
| [2] |
Semo, N. M.; Koski, W. S. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 5320.
doi: 10.1021/j150666a042 |
| [3] |
Williams, K. L.; Martin, I. T.; Fisher, E. R. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 13, 518.
doi: 10.1016/S1044-0305(02)00371-9 |
| [4] |
Ng, C.-Y.; Baer, M. State-selected and State-to-State Ion-Molecule Reaction Dynamics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1992.
|
| [5] |
Marcus, R.; Sutin, N. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 811, 265.
|
| [6] |
McDaniel, E. W.; Barnes, W. S.; Martin, D. W. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1962, 33, 2.
doi: 10.1063/1.1717656 |
| [7] |
Baldeschwieler, J. D.; Woodgate, S. S. Acc. Chem. Res. 1971, 4, 114.
doi: 10.1021/ar50039a006 |
| [8] |
Teloy, E.; Gerlich, D. Chem. Phys. 1974, 4, 417.
doi: 10.1016/0301-0104(74)85008-1 |
| [9] |
Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Xie, J. C.; He, M. M.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1346.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c03601 |
| [10] |
Hu, J.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Xie, J. C.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 7127.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c01980 |
| [11] |
Xie, J.; Otto, R.; Mikosch, J.; Zhang, J.; Wester, R.; Hase, W. L. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2960.
doi: 10.1021/ar5001764 |
| [12] |
Meyer, J.; Wester, R. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2017, 68, 333.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-052516-044918 |
| [13] |
Wester, R. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 1.
|
| [14] |
Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 6122.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.6b05699 |
| [15] |
Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Ma, Y. S.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 9171.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.8b08005 |
| [16] |
Wu, C. X.; Hu, J.; He, M. M.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 8536.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.9b06607 |
| [17] |
Wu, C. X.; Hu, J.; He, M. M.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Tian, S. X. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4640.
doi: 10.1039/C9CP06289K |
| [18] |
He, M. M.; Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Zhi, Y. Y.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 3358.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.0c02047 |
| [19] |
Hu, J.; Xie, J. C.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, S. X. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 234303.
doi: 10.1063/5.0055002 |
| [20] |
Zhi, Y. Y.; Hu, J.; Xie, J. C.; Tian, S. X. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 2573.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c00754 |
| [21] |
Trippel, S.; Stei, M.; Cox, J. A.; Wester, R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 163201
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.163201 |
| [22] |
Michaelsen, T.; Bastian, B.; Carrascosa, E.; Meyer, J.; Parker, D. H.; Wester, R. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 013940.
doi: 10.1063/1.4983305 |
| [23] |
Michaelsen, T.; Gstir, T.; Bastian, B.; Carrascosa, E.; Ayasli, A.; Meyer, J.; Wester, R. Mol. Phys. 2021, 119, e1815885.
doi: 10.1080/00268976.2020.1815885 |
| [24] |
Carrascosa, E.; Kainz, M. A.; Stei, M.; Wester, R. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2742.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b01028 pmid: 27352138 |
| [25] |
Bastian, B.; Carrascosa, E.; Kaiser, A.; Meyer, J.; Michaelsen, T.; Czakó, G.; Hase, W. L.; Wester, R. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 438, 175.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2018.12.004 |
| [26] |
Vera, M. H.; Wester, R.; Gianturco, F. A. J. Phys. B 2017, 51, 014004.
doi: 10.1088/1361-6455/aa97b0 |
| [27] |
Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 204305.
doi: 10.1063/1.4719808 |
| [28] |
Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 154312.
doi: 10.1063/1.4759265 |
| [29] |
Pei, L. S.; Carrascosa, E.; Yang, N.; Falcinelli, S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1684.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00517 |
| [30] |
Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 377, 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2014.07.007 |
| [31] |
Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 084304.
doi: 10.1063/1.4929389 |
| [32] |
Pei, L. S.; Farrar, J. M. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 227.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00227 |
| [33] |
Herman, Z. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 212, 413.
doi: 10.1016/S1387-3806(01)00493-6 |
| [34] |
Reichert, E. L.; Thurau, G.; Weisshaar, J. C. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 653.
doi: 10.1063/1.1482369 |
| [35] |
Mikosch, J.; Fruhling, U.; Trippel, S.; Schwalm, D.; Weidemuller, M.; Wester, R. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 2990.
pmid: 16880912 |
| [36] |
Hu, J.; Wu, C. X.; Tian, S. X. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 066104.
doi: 10.1063/1.5026822 |
| [37] |
Azriel, V. M.; Rusin, L.Y.; Sevryuk, M. B. Theor. Chim. Acta 1993, 87, 195.
doi: 10.1007/BF01112933 |
| [38] |
Filsinger, F.; Meijer, G.; Stapelfeldt, H.; Chapman, H. N.; Küpper, J. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2076.
doi: 10.1039/c0cp01585g pmid: 21165481 |
| [39] |
Zhang, G.; Guan, L.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, M.; Gao, H. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 34, 71.
doi: 10.1063/1674-0068/cjcp2012219 |
| [40] |
Kilaj, A.; Wang, J.; Straňák, P.; Schwilk, M.; Rivero, U.; Xu, L.; Lilienfeld, O. A.; Küpper, J.; Willitsch, S. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6047.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26309-5 |
| [1] | 许宁, 乔庆龙, 刘晓刚, 徐兆超. 基于抑制扭转的分子内电荷转移(TICT)提升有机小分子荧光染料亮度及光稳定性※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 553-562. |
| [2] | 朱青青, 宋晓君, 邓兆祥. 金/铜纳米异质界面的电荷转移等离激元调控[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(7): 675-679. |
| [3] | 倪宇欣, 张晨杰, 袁亚仙, 徐敏敏, 姚建林. 纳米ZnO的表面增强拉曼散射效应来源研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(7): 641-646. |
| [4] | 刘胜伟, 赵建军, 许宜铭. 锐钛矿光催化降解苯酚:氟离子吸附的影响大于磷酸根[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(4): 351-357. |
| [5] | 王少静, 李长伟, 李锦, 陈邦, 郭媛. 新型香豆素类氟离子荧光探针的合成及细胞成像研究[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(4): 383-390. |
| [6] | 秦天依, 曾毅, 陈金平, 于天君, 李嫕. 有机荧光温度传感体系研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2017, 75(12): 1164-1172. |
| [7] | 沈成, 张菁, 时东霞, 张广宇. 退火对单层二硫化钼荧光特性的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(9): 954-958. |
| [8] | 宋晔, 吕惠玲, 胡颂伟, 杨春艳, 朱绪飞. 聚苯胺在高pH值溶液中的电化学活性[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(07): 999-1006. |
| [9] | 叶素玉, 彭亮, 宋柯晟, 顾凤龙. 卤素掺杂聚甲基苯基硅烷的电子结构的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(02): 271-278. |
| [10] | 董江舟, 赵峻岩, 巢晖, 曹亚安. 表面敏化TiO2基复合薄膜的能带结构与光致电荷转移的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(23): 2781-2786. |
| [11] | 杨永梅, 尹世伟, 李兰兰, 杨家瑜. 孤立轨道法评估不同并五苯分子堆积的电荷转移积分[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(17): 1991-1996. |
| [12] | 易平贵, 周继明, 汪朝旭, 于贤勇, 李筱芳, 陈建, 刘峥军. 含不同质子供体的2-苯基苯并三唑衍生物激发态质子转移的理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(14): 1645-1653. |
| [13] | 王素凡, 周涛, 黄玉成, 叶世勇, 沈伟丽. LDS751激发态电荷转移和光致异构化的量子化学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2011, 69(02): 176-182. |
| [14] | 钱妍, 蔡敏敏, 解令海, 黄维. 基于2-(2 -羟基苯基)苯并噻唑的激发态分子内质子转移化合物的光物理行为研究[J]. 化学学报, 2010, 68(22): 2285-2289. |
| [15] | 张首才,王嵩,周欣,张红星,邵琛,李传碧. 双核Pt(II)配合物的光谱结构和激发态性质的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2008, 66(8): 841-846. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
