化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 80 ›› Issue (6): 734-740.DOI: 10.6023/A21120621 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 中国科学院青年创新促进会合辑
研究论文
王丹a, 郭香a,b, 李鹏飞a, 张昱临a,b, 徐彩虹a,b, 张宗波a,*( )
)
投稿日期:2021-12-31
发布日期:2022-07-07
通讯作者:
张宗波
作者简介:基金资助:
Dan Wanga, Xiang Guoa,b, Pengfei Lia, Yulin Zhanga,b, Caihong Xua,b, Zongbo Zhanga( )
)
Received:2021-12-31
Published:2022-07-07
Contact:
Zongbo Zhang
About author:Supported by:文章分享

利用全氢聚硅氮烷(PHPS)转化制备的氧化硅材料在存储芯片、柔性显示封装等领域展现出较高的应用价值. 本工作系统研究了PHPS在高温加热条件下的氧化硅形成过程, 考察了转化过程中化学组成和微观结构对体积收缩、折射率和力学性能的影响. 研究结果表明: 转化温度低于180 ℃时, PHPS的转化以Si—H和Si—N的水解缩合反应为主, 转化程度较低, 形成的是氧化硅为分散相、PHPS为连续相的海岛结构; 转化温度在180~300 ℃区间内, 转化以氧化反应为主, 氧化硅相逐渐生长, 形成双连续的相结构, 且在温度高于200 ℃时发生相反转, 氧化硅相成为连续相. 转化温度在300~600 ℃区间时, 氧化硅网络骨架基本形成, 在高温的作用下进一步致密化. PHPS转化样品的体积收缩、折光指数和力学性能与其转化程度和相分布有关.
王丹, 郭香, 李鹏飞, 张昱临, 徐彩虹, 张宗波. 全氢聚硅氮烷-氧化硅的转化过程研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 734-740.
Dan Wang, Xiang Guo, Pengfei Li, Yulin Zhang, Caihong Xu, Zongbo Zhang. Conversion Process of Perhydropolysilazane to Silica※[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2022, 80(6): 734-740.
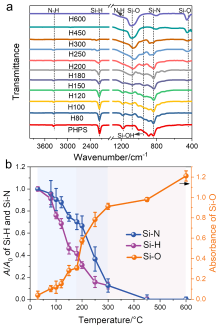
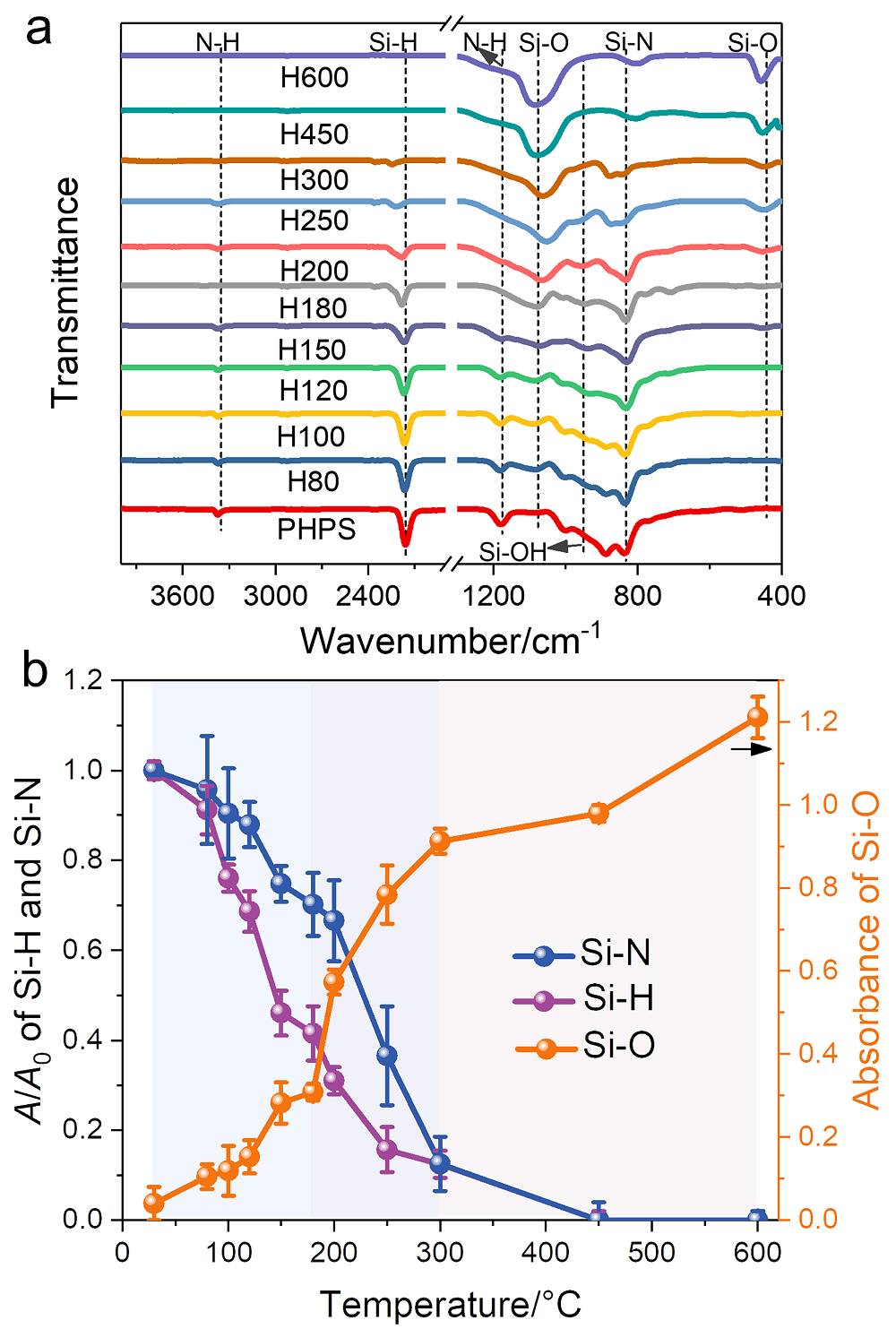
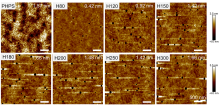



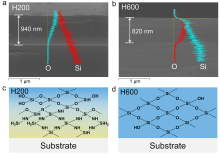

| 制备方法 | 折光指数a | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 热氧化 | 1.45~1.46 | [ |
| 离子束溅射 | 1.47 | [ |
| 化学气相沉积 | 1.45~1.46 | [ |
| PHPS转化法 | 1.447 | 本工作 |
| 制备方法 | 折光指数a | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 热氧化 | 1.45~1.46 | [ |
| 离子束溅射 | 1.47 | [ |
| 化学气相沉积 | 1.45~1.46 | [ |
| PHPS转化法 | 1.447 | 本工作 |
| [1] |
Khodakarami, S.; Zhao, H.; Rabbi, K. F.; Miljkovic, N. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4519.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c19683 |
| [2] |
Wu, Y. P.; Lei, X. Y.; Lu, Y. M.; Chen, H. N. CIESC Journal 2021, 72, 21. (in Chinese)
|
|
(吴延鹏, 雷晓宇, 陆禹名, 陈卉妮, 化工学报, 2021, 72, 21.)
|
|
| [3] |
Guo, J. Y.; Zhao, Y. M.; Li, W. J.; Yang, J. Y.; Wang, R. J.; Su, L. J. Mater. Rep. 2021, 35, 90. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郭建业, 赵英民, 李文静, 杨洁颖, 王瑞杰, 苏力军, 材料导报, 2021, 35, 90.)
|
|
| [4] |
He, T.; Yang, X. F.; Chen, Y. Z.; Tong, Z. H.; Wu, L. Z. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 41. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18090374 |
|
(何通, 杨晓峰, 陈玉哲, 佟振合, 吴骊珠, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 41.)
doi: 10.6023/A18090374 |
|
| [5] |
Wang, K. K.; He, J. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2018, 76, 807. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A18050201 |
|
(王凯凯, 贺军辉, 化学学报, 2018, 76, 807.)
doi: 10.6023/A18050201 |
|
| [6] |
Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Qiu, W.; Li, L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2017, 28, 2143.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.08.041 |
| [7] |
Wang, X.; Tan, L. L.; Yang, Y. W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2016, 74, 303. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A16010003 |
|
(王鑫, 谭丽丽, 杨英威, 化学学报, 2016, 74, 303.)
doi: 10.6023/A16010003 |
|
| [8] |
Liu, D. L.; Lu, D. F.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, C.; Qi, Z. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 41. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A14100734 |
|
(刘德龙, 逯丹凤, 赵乔, 陈晨, 祁志美, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 41.)
doi: 10.6023/A14100734 |
|
| [9] |
Ji, Y. J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, K.; Xu, L.; Peng, H. G.; Wu, P. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 371. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12110980 |
|
(纪永军, 张斌, 张坤, 徐乐, 彭洪根, 吴鹏, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 371.)
doi: 10.6023/A12110980 |
|
| [10] |
Huang, Z. Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, G. C. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 235. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A1107063 |
|
(黄紫洋, 张岚, 梁广超, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 235.)
doi: 10.6023/A1107063 |
|
| [11] |
Borisova, D.; Möhwald, H.; Shchukin, D. G. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1939.
doi: 10.1021/nn102871v |
| [12] |
Xu, L. G.; Li, X. Y.; He, J. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 2648. (in Chinese)
|
|
(许利刚, 李晓禹, 贺军辉, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 2648.)
|
|
| [13] |
Mattox, D. M. Met. Finish. 2000, 98, 410.
doi: 10.1016/S0026-0576(00)80350-5 |
| [14] |
Reichelt, K.; Jiang, X. Thin Solid Films 1990, 191, 91.
doi: 10.1016/0040-6090(90)90277-K |
| [15] |
Böke, F.; Giner, I.; Keller, A.; Grundmeier, G.; Fischer, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17805.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b04421 |
| [16] |
Mathur, S.; Shen, H.; Altmayer, J. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2007, 15, 16.
|
| [17] |
Jen, S.-H.; Bertrand, J. A.; George, S. M. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 084305.
doi: 10.1063/1.3567912 |
| [18] |
George, S. M. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 111.
doi: 10.1021/cr900056b |
| [19] |
Zhao, R. T.; Han, T. H.; Sun, D. Y.; Shan, D.; Liu, Z. P.; Liang, F. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 954. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20060208 |
|
(赵若彤, 韩天昊, 孙大吟, 山丹, 刘正平, 梁福鑫, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 954.)
doi: 10.6023/A20060208 |
|
| [20] |
Xiong, B. T.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Wang, C. R.; Chen, B. X.; Luo, J. Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 443. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12100794 |
|
(熊必涛, 朱志艳, 王长荣, 陈宝信, 骆钧炎, 化学学报, 2013, 71, 443.)
doi: 10.6023/A12100794 |
|
| [21] |
Wang, X, W.; Wei, Q.; Hong, Z. F.; Li, Q. Y.; Nie, Z. R. Acta Chim. Sinica 2012, 70, 2529. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A12080568 |
|
(王学伟, 韦奇, 洪志发, 李群艳, 聂祚仁, 化学学报, 2012, 70, 2529.)
doi: 10.6023/A12080568 |
|
| [22] |
Zhang, Z. B.; Xiao, F. Y.; Luo, Y. M.; Xu, C. H. Paint. Coat. Ind. 2013, 43, 74. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张宗波, 肖凤艳, 罗永明, 徐彩虹, 涂料工业, 2013, 43, 74.)
|
|
| [23] |
Zhang, Z. B.; Xiao, F. Y.; Luo, Y. M.; Xu, C. H. Fine and Specialty Chemicals 2013, 21, 25. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张宗波, 肖凤艳, 罗永明, 徐彩虹, 精细与专用化学品, 2013, 21, 25.)
|
|
| [24] |
Kozuka, H.; Nakajima, K.; Uchiyama, H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8329.
doi: 10.1021/am400845y |
| [25] |
Li, P.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56186.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c16556 |
| [26] |
Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Liang, Q.; Dong, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, F.; Hu, W. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 1237.
doi: 10.1007/s40843-017-9216-2 |
| [27] |
Wang, D.; Zhang, Z. B.; Wang, X. F.; Xue, J. X.; Xu, C. H. Micronanoelectron. Technol. 2017, 54, 514. (in Chinese)
|
|
(王丹, 张宗波, 王晓峰, 薛锦馨, 徐彩虹, 微纳电子技术, 2017, 54, 514.)
|
|
| [28] |
Seul, H. J.; Kim, H. G.; Park, M. Y.; Jeong, J. K. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 10486.
doi: 10.1039/C6TC03725A |
| [29] |
Jeong, Y.; Pearson, C.; Kim, H. G.; Park, M. Y.; Kim, H.; Do, L. M.; Petty, M. C. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 36083.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA02989A |
| [30] |
Channa, I. A.; Distler, A.; Zaiser, M.; Brabec, C. J.; Egelhaaf, H. J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900598.
|
| [31] |
Sun, L.; Uemura, K.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Suzuri, Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43425.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b14994 |
| [32] |
Zhang, Z. B.; Wang, D.; Xu, C. H. Paint. Coat. Ind. 2016, 46, 82.. (in Chinese)
|
|
(张宗波, 王丹, 徐彩虹, 涂料工业, 2016, 46, 82.)
|
|
| [33] |
Morlier, A.; Cros, S.; Garandet, J.-P.; Alberola, N. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 2013, 115, 93.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2013.03.033 |
| [34] |
Matsuo, H.; Yamada, K. Convertech. 1995, 23, 25.
|
| [35] |
Kamiya, K.; Tange, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Nasu, H.; Shimizu, Y. Res. Rep. Fac. Eng. 2001, 26, 23.
|
| [36] |
Bauer, F.; Decker, U.; Dierdorf, A.; Ernst, H.; Heller, R.; Liebe, H.; Mehnert, R. Prog. Org. Coat. 2005, 53, 183.
doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2005.02.006 |
| [37] |
Ohishi, T. J. Non·Cryst. Solids 2003, 330, 248.
|
| [38] |
Kozuka, H.; Fujita, M.; Tamoto, S. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2008, 48, 148.
doi: 10.1007/s10971-008-1793-1 |
| [39] |
Kubo, T.; Kozuka, H. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 114, 517.
doi: 10.2109/jcersj.114.517 |
| [40] |
Kubo, T.; Tadaoka, E.; Kozuka, H. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2004, 31, 257.
doi: 10.1023/B:JSST.0000047999.87439.c2 |
| [41] |
Kubo, T.; Tadaoka, E.; Kozuka, H. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 635.
doi: 10.1557/jmr.2004.19.2.635 |
| [42] |
Tanaka, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Shindo, T.; Kunzelmann, K.-H.; Teranaka, T. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 170.
doi: 10.4012/dmj.2010-113 |
| [43] |
Seifert, M.; Motz, G. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 3601.
doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.05.009 |
| [44] |
Je, S. Y.; Son, B. G.; Kim, H. G.; Park, M. Y.; Do, L. M.; Choi, R.; Jeong, J. K. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18693.
doi: 10.1021/am504231h |
| [45] |
Lebrun, J. J.; Porte, H. US 4,689,252, 1987.
|
| [46] |
Nakajima, K.; Uchiyama, H.; Kitano, T.; Kozuka, H. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 2806.
doi: 10.1111/jace.12513 |
| [47] |
Zhang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Luo, Y.; An, P.; Zhang, M.; Xu, C. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 971.
doi: 10.1002/pi.4871 |
| [48] |
Dargère, N.; Bounor-Legaré, V.; Boisson, F.; Cassagnau, P.; Martin, G.; Sonntag, P.; Garois, N. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 62, 389.
doi: 10.1007/s10971-012-2738-2 |
| [49] |
Morlier, A.; Cros, S.; Garandet, J.-P.; Alberola, N. Thin Solid Films. 2012, 524, 62.
doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2012.09.065 |
| [50] |
Awazu, K.; Kawazoe, H. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 6243.
doi: 10.1063/1.1618351 |
| [51] |
Günthner, M.; Wang, K.; Bordia, R. K.; Motz, G. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 1883.
doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.09.005 |
| [52] |
Blankenburg, L.; Schrödner, M. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 275, 193.
doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.05.019 |
| [53] |
Miller, K. S.; Krochta, J. M. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 228.
doi: 10.1016/S0924-2244(97)01051-0 |
| [54] |
Nikitin, T.; Velagapudi, R.; Sainio, J.; Lahtinen, J.; Räsänen, M.; Novikov, S.; Khriachtchev, L. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 094316.
doi: 10.1063/1.4764893 |
| [55] |
Jung, S.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Oh, J.-H.; Moon, S.-W.; Kim, S.-D. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 111505.
doi: 10.1143/JJAP.49.111505 |
| [56] |
Guo, C. L. M.S. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 2014. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郭春林, 硕士论文, 浙江大学, 杭州, 2014.)
|
|
| [57] |
Jiang, Y. G.; Wang, L. S.; Liu, H. S.; Liu, D. D.; Jiang, C. H.; Yang, Y. P.; Ji, Y. Q. Infrared and Laser Engineering 2014, 43, 3334. (in Chinese)
|
|
(姜玉刚, 王利栓, 刘华松, 刘丹丹, 姜承慧, 羊亚平, 季一勤, 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43, 3334.)
|
|
| [58] |
Li, P. M.S. Thesis, Xi’an Technological University, Xi’an, 2015. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李鹏, 硕士论文, 西安工业大学, 西安, 2015.)
|
|
| [59] |
Chowdhury, S. C.; Haque, B. Z.; Gillespie, J. W. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10139.
doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0242-8 |
| [60] |
Oliver, W. C.; Pharr, G. M. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564.
doi: 10.1557/JMR.1992.1564 |
| [1] | 曾杨, 姜兰, 张晓昕, 谢颂海, 裴燕, 乔明华, 李振华, 徐华龙, 范康年, 宗保宁. W掺杂多级孔SiO2纳米球负载Pt用于催化甘油氢解制1,3-丙二醇[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 903-912. |
| [2] | 吴峰, 苏倩倩, 周乐乐, 许鹏飞, 董傲, 钱卫平. 基于二氧化硅胶体晶体薄膜和反射干涉光谱的蛋白冠监测方法[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(3): 338-343. |
| [3] | 李勇, 王晓艳, 唐勇. α,ω-双烯烃的配位聚合: 催化剂对聚合物微观结构的调控[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1320-1330. |
| [4] | 何通, 杨晓峰, 陈玉哲, 佟振合, 吴骊珠. 基于二氧化硅纳米颗粒的三重态-三重态湮灭上转换研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(1): 41-46. |
| [5] | 王凯凯, 贺军辉. 基于季铵盐改性SiO2空心球的抗菌/减反增透双功能薄膜的制备和研究[J]. 化学学报, 2018, 76(10): 807-812. |
| [6] | 李媛, 刘文娜, 郑行望. 四(三羟甲基氨基甲烷)合铜(II)电催化联吡啶钌/二氧化硅复合纳米粒子电化学发光分析特性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(7): 749-754. |
| [7] | 秦咪咪, 李昕, 郑一平, 张焱, 李从举. PEDOT基光子晶体的制备及其电致变色性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(11): 1161-1166. |
| [8] | 刘德龙, 逯丹凤, 赵乔, 陈晨, 祁志美. 介孔SiO2薄膜与金银合金薄膜相结合的大面积、高性能SERS基底[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 73(1): 41-46. |
| [9] | 李相晔, 练成, 支东彦, 徐首红, 刘洪来. SiO2-HA/PNIPAm核壳温敏微凝胶的合成及其溶胀性能[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(6): 689-696. |
| [10] | 林洁华, 张慧慧, 邵美佳. 基于离子液体修饰介孔硅的免标记电化学免疫测定双组分肿瘤标志物[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(2): 241-245. |
| [11] | 纪永军, 张斌, 张坤, 徐乐, 彭洪根, 吴鹏. ZSM-5@Mesoporous Silica核壳复合结构分子筛的制备及其甲苯甲醇烷基化择形催化性能的研究[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(03): 371-380. |
| [12] | 胡争艳, 孙珍, 张轶, 吴仁安, 邹汉法. 纳米二氧化硅影响人肺癌细胞的定量糖蛋白质组学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(19): 2059-2065. |
| [13] | 徐淑芝, 董相廷, 盖广清, 王进贤, 刘桂霞, 鲁统晓. 三层同轴静电纺丝技术制备TiO2@SiO2同轴双壁亚微米管及光催化性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(15): 1660-1666. |
| [14] | 胡园园, 何建平, 王涛, 郭云霞, 薛海荣, 李国显. 有序介孔二氧化硅-碳纳米管复合材料载Pt 及其电催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(07): 822-830 . |
| [15] | 傅小勤, 郭明, 武嘉, 战胜鑫. 甲基丙烯酸/丙烯酰胺双单体共聚反蛋白石光子晶体的制备[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 0(05): 611-616 . |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||