化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (1): 20-28.DOI: 10.6023/A22090400 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
投稿日期:2022-09-25
发布日期:2022-12-12
基金资助:
Xiaomao Tian, Yuequn Lin, Han Zhu, Chao Huang( ), Bixue Zhu(
), Bixue Zhu( )
)
Received:2022-09-25
Published:2022-12-12
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
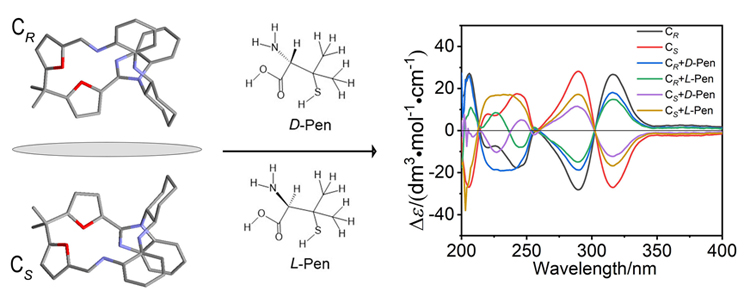
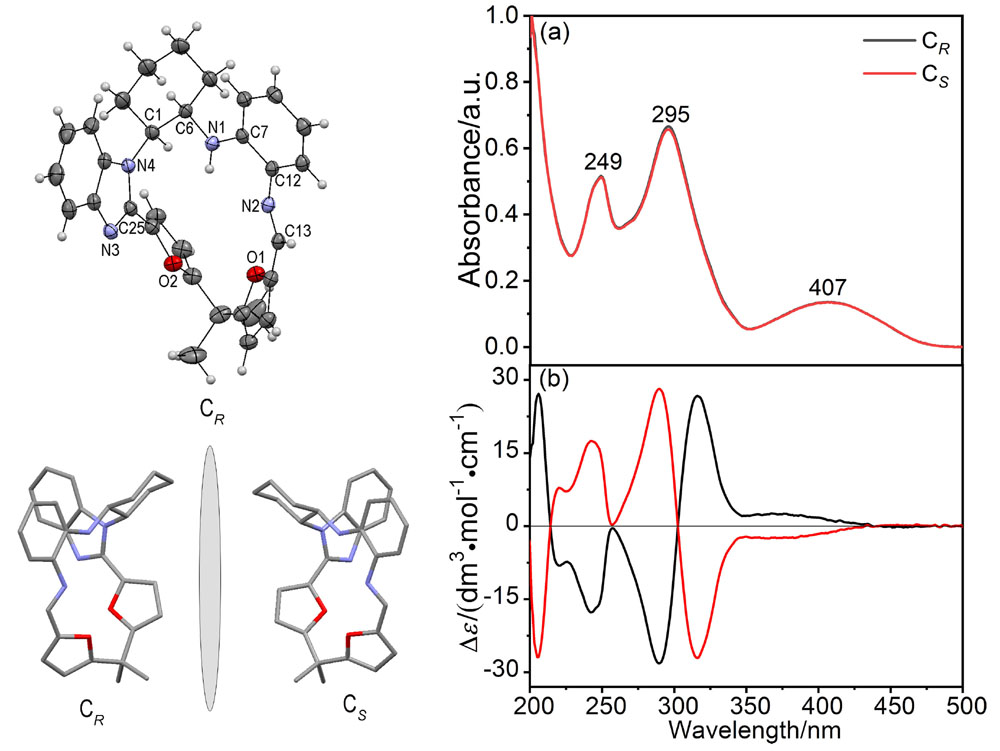
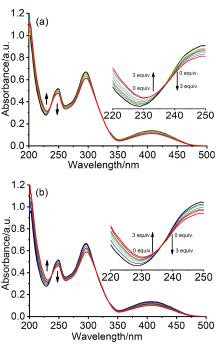
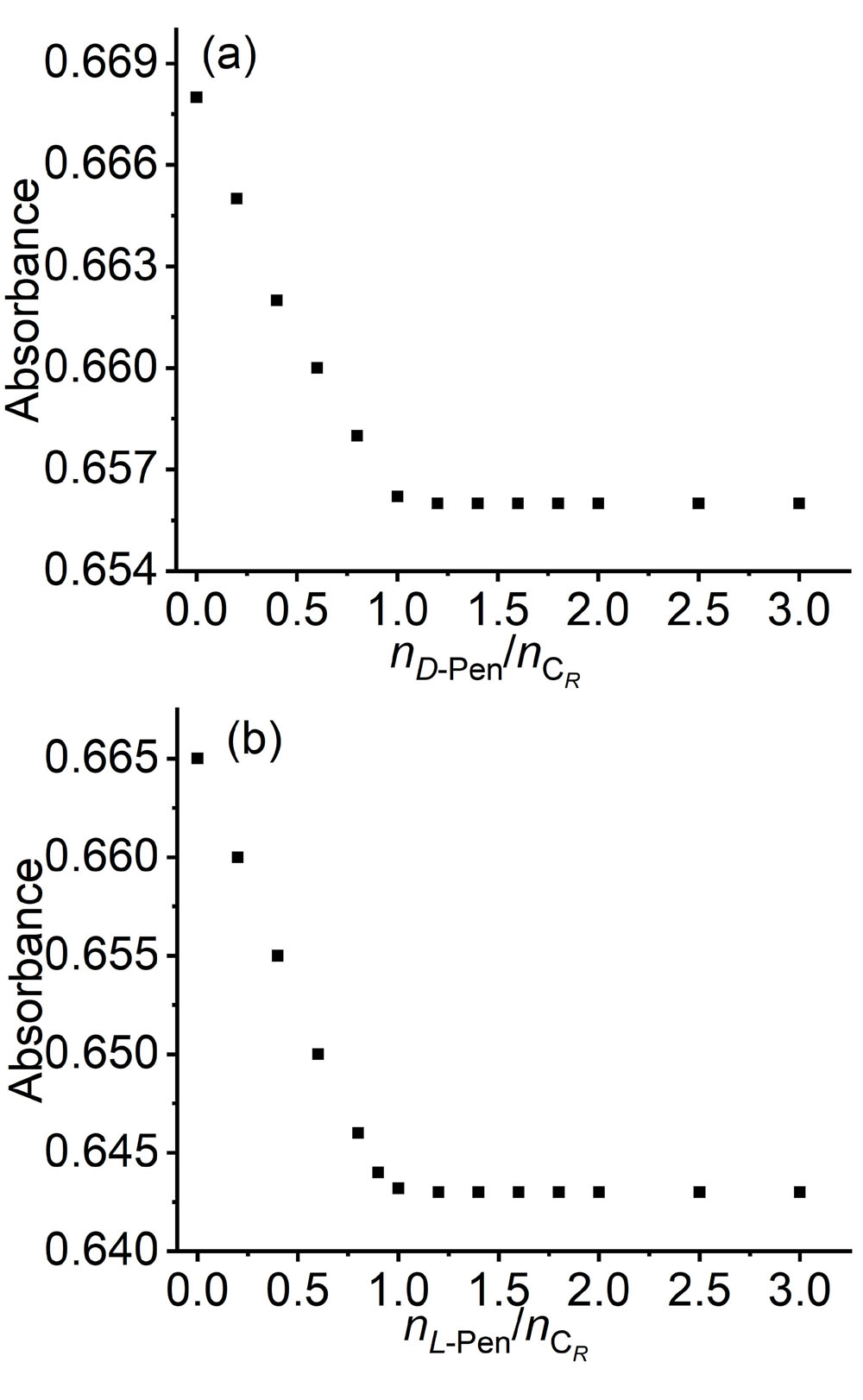
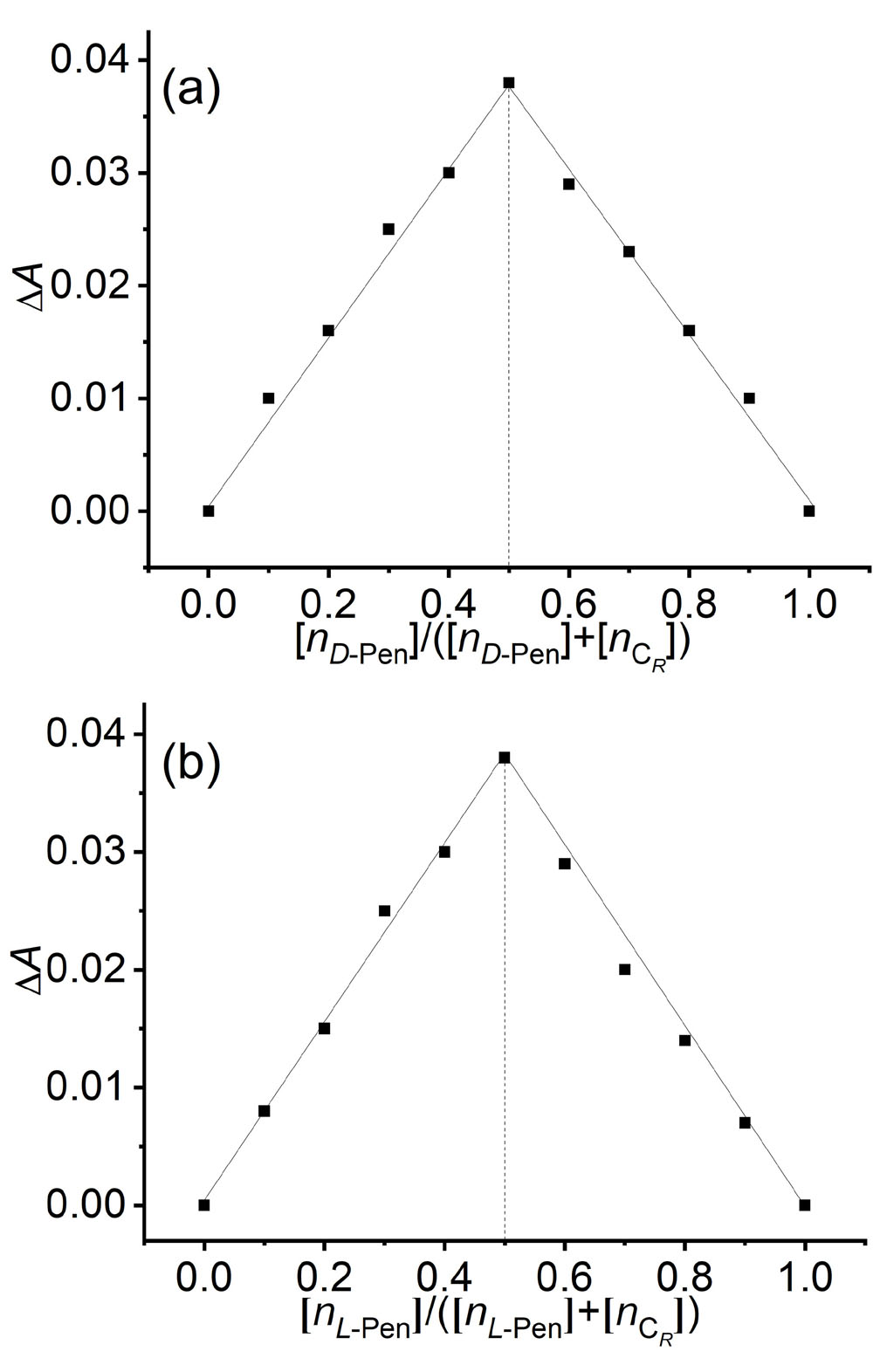
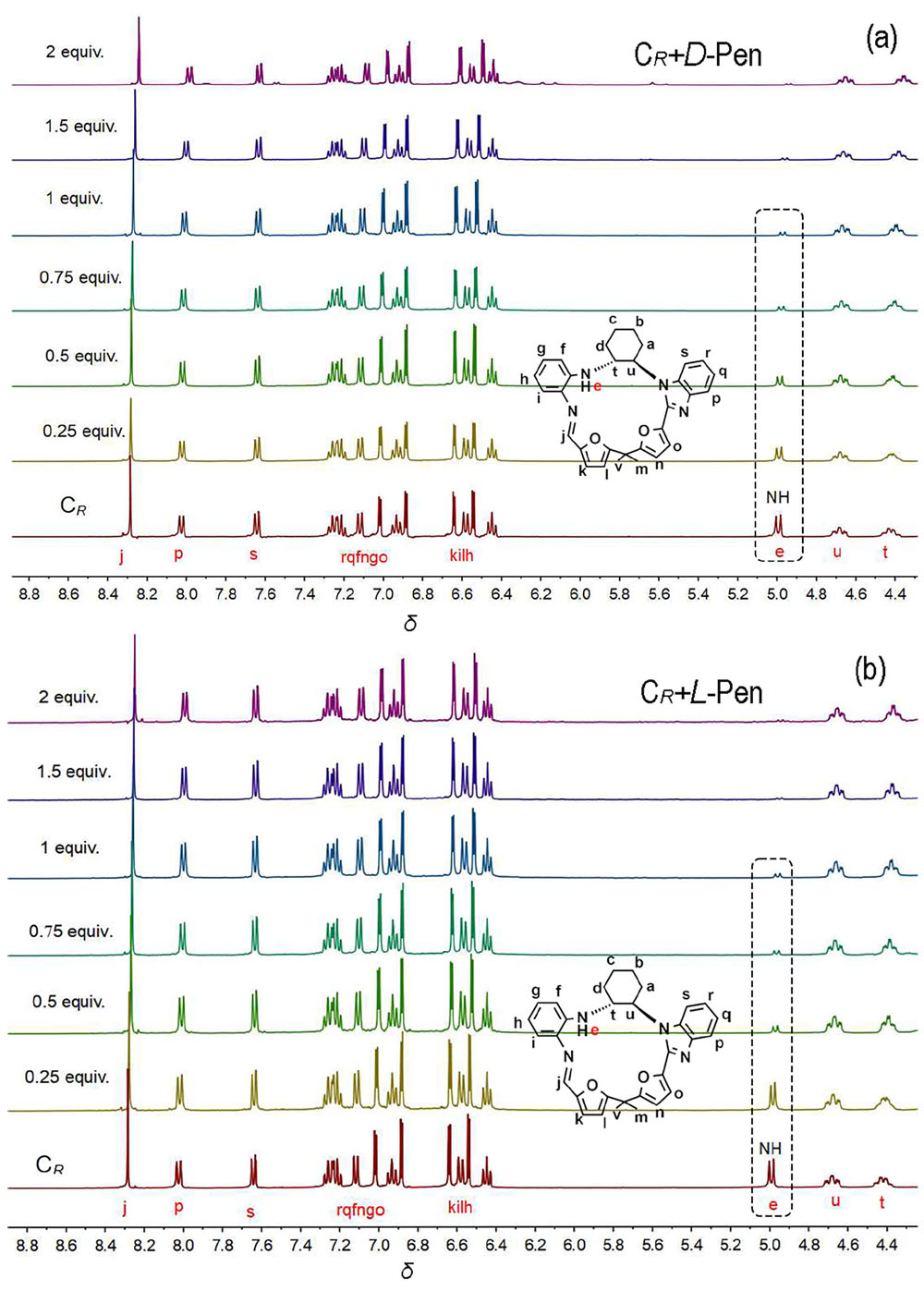
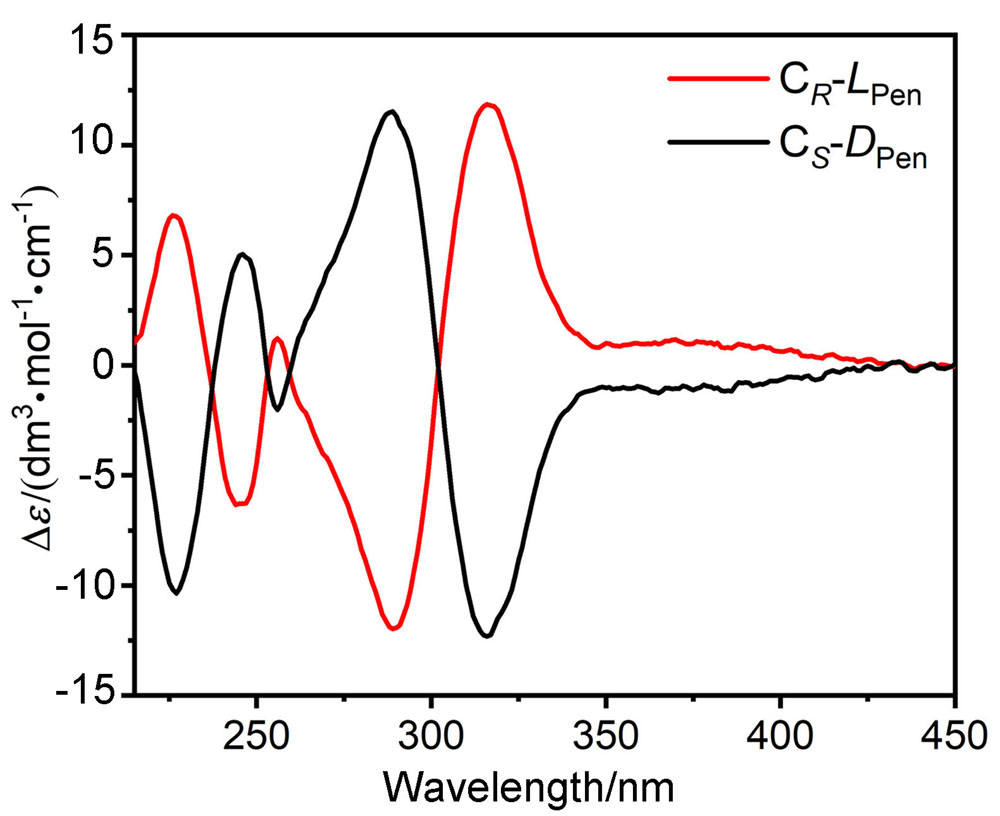
大量手性药物分子均具有D-和L-对映异构体, 呈镜像结构的对映体通常表现出截然不同的生理学反应. 青霉胺(Pen)是从青霉素中获取的一种常见的手性药物, 研究者为了实现这两种对映异构体严格区辨和分析一直在不断付出努力. 基于含有NH功能基的手性席夫碱大环化合物具有合成条件温和、结构收敛的优点, 本工作报道了含NH功能基的手性单Schiff碱大环对映异构体的合成(CR和CS)及其对小分子青霉胺对映体(D-Pen和L-Pen)的键合作用及对映体识别选择性. 通过X射线单晶衍射技术解析了单Schiff碱大环对映异构体的晶体结构, 结果表明这两个大环对映体均具有扭曲的非平面构型, 环状骨架中与环己基手性碳相连的亚胺(NH)质子均指向环腔内侧. 采用紫外可见光吸收光谱(UV-Vis)和核磁共振氢谱(1H NMR)滴定技术对手性大环与青霉胺对映体之间相互作用行为进行考察, 表明手性大环与青霉胺不同对映体键合比均为1∶1, 键合常数接近107 L•mol-1, 电喷雾电离质谱法(ESI-MS)表征观察到大环与青霉胺按1∶1键合的缔合物[C-Pen+H]+的分子离子峰. 1H NMR滴定表明手性大环与青霉胺对映体之间的缔合源于大环结构中不对称NH功能基与青霉胺对映体之间形成分子间氢键作用. 通过手性大环与青霉胺对映异构体之间的键合常数比较, 表明大环CR对L-Pen具有更高的选择性键合能力, 而CS则对D-Pen表现出更高的选择性键合能力, 选择性键合常数比均接近2倍. 进一步通过圆二色光谱(CD)滴定考察, 阐释了手性大环与青霉胺对映体选择性键合作用能力与两者之间对映体结构的手性匹配性质密切相关, 主体大环对与其手性相匹配青霉胺对映体表现出较高的键合作用能力, 而与手性不相匹配的青霉胺对映体键合作用则相对较弱.
田小茂, 林悦群, 朱菡, 黄超, 朱必学. 手性单Schiff碱大环对青霉胺对映体识别研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(1): 20-28.
Xiaomao Tian, Yuequn Lin, Han Zhu, Chao Huang, Bixue Zhu. Enantiomers Identification of Penicillamine by Chiral Mono-Schiff Base Macrocycles[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(1): 20-28.


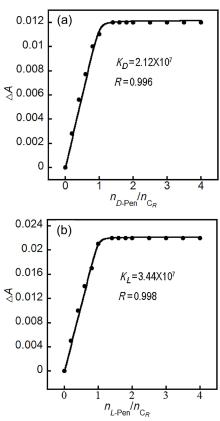

| Host-guest | KD (D-Pen) | KL (L-Pen) | KL/KD | KD/KL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR-pen | 2.12×107 | 3.44×107 | 1.62 | 0.61 |
| CS-pen | 3.20×107 | 1.77×107 | 0.55 | 1.81 |
| Host-guest | KD (D-Pen) | KL (L-Pen) | KL/KD | KD/KL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR-pen | 2.12×107 | 3.44×107 | 1.62 | 0.61 |
| CS-pen | 3.20×107 | 1.77×107 | 0.55 | 1.81 |



| [1] |
Xiao, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, C.; Wang, L. Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2013, 31, 627.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201300246 |
| [2] |
Geer, M. F.; Walla, M.; Solntsev, K.; Strassert, C.; Shimizu, L. S. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 5568.
doi: 10.1021/jo400685u |
| [3] |
Radujević, A.; Penavic, A.; Pavlović, R. Z.; Badjić, J. D.; Anzenbacher, P. Chem 2022, 8, 2228.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2022.05.010 |
| [4] |
Wang, D.; You, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z. T. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 6967.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2013.10.064 |
| [5] |
María, D.; Claramunt, R.; Torralba, M.; Torres, M.; Elguero, J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 1206.
doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.03.066 |
| [6] |
Wei, X. K.; Gu, J. C.; Liu, X. L.; Huang, C.; Zhu, B. X. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 38, 3386. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201805012 |
|
( 魏小康, 谷静池, 刘兴丽, 黄超, 朱必学, 有机化学, 2018, 38, 3386.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201805012 |
|
| [7] |
Xiong, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, H. J.; Yi, R.; Zhu, B. X.; Ni, X. L. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3522.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.04.060 |
| [8] |
Li, D. H.; Smith, B. D. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1086.
doi: 10.3762/bjoc.15.105 |
| [9] |
Barisic, D.; Lesic, F.; Vlasic, M. T.; Uzarevic, K.; Bregovic, N.; Tomisi, V. Tetrahedron 2022, 120, 132875.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2022.132875 |
| [10] |
Tromans, R. A.; Carter, T. S.; Chabanne, L.; Crump, M. P.; Li, H. Y.; Matlock, J. V.; Orchard, M. G.; Davis, A. P. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 52.
doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0155-z pmid: 30420776 |
| [11] |
Roth, J. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 285.
doi: 10.1021/cr000423j |
| [12] |
Glavin, D. P.; Burton, A. S.; Elsila, J. E.; Aponte, J. C.; Dworkin, J. P. Chem. Rev. 2019, 120, 4660.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00474 |
| [13] |
Lu, H. J.; Yu, C. T.; Guo, Y. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2002, 60, 882. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 陆豪杰, 余翀天, 郭寅龙, 化学学报, 2002, 60, 882.)
|
|
| [14] |
Li, D.; Gao, B. J.; Xu, W. M. Acta Chim. Sinica 2011, 69, 3019 (in Chinese)
|
|
( 李丁, 高保娇, 许文梅, 化学学报, 2011, 69, 3019.)
doi: 10.6023/A1106192 |
|
| [15] |
Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, M.; Yang, L.; Li, G.; Xu, W. W.; Qu, H. N.; Liang, F.; Cheng, J.; Li, H. B. Analyst 2022, 147, 1803.
doi: 10.1039/D2AN00310D |
| [16] |
Zhu, B. X.; Ruan, W. J.; Gao, F.; Hu, G. H.; Zhu, Z. A. Acta Chim. Sinica 2004, 62, 58. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 朱必学, 阮文娟, 高峰, 胡国航, 朱志昂, 化学学报, 2004, 62, 58.)
|
|
| [17] |
Liu, T.; Ruan, W. J.; Nan, J.; Zhu, Z. A. Chin. J. Chem. 2003, 21, 751.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.20030210709 |
| [18] |
Forte, G.; Sfrazzetto, G. T.; Pappalardo, A. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2015, 1068, 8.
doi: 10.1016/j.comptc.2015.06.007 |
| [19] |
Ikbal, S. A.; Sakata, Y.; Akine, S. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 4119.
doi: 10.1039/d1dt00218j pmid: 33662079 |
| [20] |
Peluso, P.; Chankvetadze, B. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 13235.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00846 pmid: 35917234 |
| [21] |
Rajasekar, P.; Jose, C.; Sarkar, M.; Boomishankar, R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4023.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202012392 |
| [22] |
Wang, S. Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 121, 115691.
doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.115691 |
| [23] |
Padovani, D.; Galardon, E. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 412.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00313 |
| [24] |
Durán, G. M.; Abellán, C.; Contento, A. M.; Ríos, Á. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 815.
doi: 10.1007/s00604-017-2074-x |
| [25] |
Mendes, J.; Almeida, K. J.; Neto, J. L.; Ramalho, T. C.; Duarte, H. A. J. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 184, 308.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.05.025 |
| [26] |
Yang, N.; Zhang, K.; Guan, Q. W.; Wang, Z. J.; Chen, K. N.; Mao, X. Y. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1602.
doi: 10.3390/antiox11081602 |
| [27] |
Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Y.; He, X. W.; Li, W. Y.; Zhang, Y. K. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125249.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125249 |
| [28] |
Sun, L.; Huang, F.; Liu, W. W.; Lin, L.; Hong, Y.; Kong, X. L. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 241, 118653.
doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118653 |
| [29] |
Li, Z. B.; Lin, J.; Pu, L. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1690.
doi: 10.1002/anie.200462471 |
| [30] |
Zhu, Y. Y.; Wu, X. D.; Gu, S. H.; Pu, L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 175.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b07803 |
| [31] |
Pu, L. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 8038.
doi: 10.1039/D2CC02363F |
| [32] |
Dong, J. Q.; Tan, C. X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Low, P. J.; Jiang, J. W.; Cui, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1554.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b11422 |
| [33] |
Gangemi, C. M. A.; Rimkaite, U.; Cipria, F.; Sfrazzetto, G. T.; Pappalardo, A. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 836.
doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00836 pmid: 31850322 |
| [34] |
Yang, S. T.; Wu, F. L.; Yu, F. Z.; Gu, L. C.; Wang, H. H.; Liu, Y. Y.; Chu, Y. Q.; Wang, F. Y.; Fang, X.; Ding, C. F. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339017.
doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339017 |
| [35] |
Ema, T.; Yamasaki, T.; Watanabe, S.; Hiyoshi, M.; Takaishi, K. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 10762.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b01327 |
| [36] |
Wen, J.; Feng, L.; Zhao, H. M.; Zheng, L.; Stavropoulos, P.; Ai, L.; Zhang, J. X. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 7934.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c00587 |
| [37] |
Ohishi, Y.; Chiba, J.; Inouye, M. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 10825.
doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c01095 pmid: 35938888 |
| [38] |
Thordarson, P. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1305.
doi: 10.1039/c0cs00062k pmid: 21125111 |
| [39] |
Shi, M.; Qian, H. X. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 4949.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2005.03.043 |
| [40] |
Chen, Z. H.; Wu, C. T. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 22, 582. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 陈展虹, 吴成泰, 有机化学, 2002, 22, 582.)
|
| [1] | 黄涎廷, 韩洪亮, 肖婧, 王帆, 柳忠全. I2O5/KSCN介导的炔烃碘硫氰化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 5-8. |
| [2] | 韩叶强, 史炳锋. 钯(II)催化不对称C(sp3)—H键官能团化研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1522-1540. |
| [3] | 刘传志, 李芬, 王静静, 赵晓璐, 张婷美, 黄鑫, 邬梦丽, 户志远, 刘新明, 黎占亭. 基于分子间卤键的超分子平面大环自组装[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1365-1368. |
| [4] | 杨普苏, 刘晨旭, 张文文, 游书力. 铱催化中氮茚衍生物的Friedel-Crafts类型不对称烯丙基取代反应[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 742-746. |
| [5] | 邓卓基, 欧阳溢凡, 敖运林, 蔡倩. 铜催化不对称去对称化分子内烯基C—N偶联反应[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 649-652. |
| [6] | 周波, 梁仁校, 曹中艳, 周平海, 贾义霞. 钯催化吡咯环内共轭双键的Heck反应[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(2): 176-179. |
| [7] | 廖港, 吴勇杰, 史炳锋. 非共价作用在过渡金属催化的选择性碳氢键活化中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(4): 289-298. |
| [8] | 张荣华, 许冰, 张展鸣, 张俊良. Ming-Phos/铜催化的亚甲胺叶立德与硝基烯烃的不对称[3+2]环加成反应[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(3): 245-249. |
| [9] | 林祖金, 曹荣. 多孔氢键有机框架(HOFs):现状与挑战[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12): 1309-1335. |
| [10] | 林凤闺蓉, 梁宇杰, 郦鑫耀, 宋颂, 焦宁. 氧气氧化铜催化的苯胺邻位叠氮化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 906-910. |
| [11] | 杨俊航, 傅晓波, 卢增辉, 朱钢国. 可见光催化烯烃砜基化启动的远程醛基碳-氢键直接硫化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 901-905. |
| [12] | 杨启亮, 王向阳, 翁信军, 杨祥, 徐学涛, 童晓峰, 方萍, 伍新燕, 梅天胜. 电氧化促进的钯催化的芳烃C(sp 2)—H键氯代反应[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(9): 866-873. |
| [13] | 李忠原, 景昆, 李祁利, 王官武. 钯催化的2-苯氧基吡啶导向的脱羧酯基化反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(8): 729-734. |
| [14] | 秦小转, 王新潮, 冯丹丹, 贺加贝, 郑丽萍, 王勇, 谢光辉, 李靖靖, 丁戈. 枝状含联苯胺基片段的有机生色团的激发态分子间质子转移性质研究[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(8): 751-757. |
| [15] | 王昱赟, 刘云云. 无金属催化的吡啶C2位碳-氢键胺甲酰化反应合成吡啶甲酰胺[J]. 化学学报, 2019, 77(5): 418-421. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||