化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (5): 548-558.DOI: 10.6023/A23020041 上一篇
综述
投稿日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2023-03-28
作者简介: |
齐学平, 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所无机化学专业在读硕士研究生, 师从王飞研究员. 目前主要研究方向为钛基金属有机框架材料的设计、合成及应用. |
 |
王飞, 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所研究员, 博士生导师. 2012年入选“中科院青年创新促进会”会员. 2014年获得卢嘉锡青年人才奖, 同年入选中国科学院福建物质结构研究所(海西研究院)“春苗”青年人才. 2019年获福建省自然科学二等奖(排名第二). 从事金属有机框架材料研究, 在钛基金属有机框架材料、手性金属有机框架材料、沸石型金属有机框架材料的设计合成及其在气体分离、催化/光电催化、手性识别拆分等领域取得系列进展, 已在Chem. Soc. Rev., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., ACS Materials Lett., J. Mater. Chem A.及ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces等期刊以第一和通讯作者发表论文100多篇. |
 |
张健, 中国科学院福建物质结构研究所研究员, 博士生导师. 现任中国科学院福建物质结构研究所副所长, 结构化学国家重点实验室副主任. 2014年获国家杰出青年基金资助. 主要研究方向为团簇和多孔催化材料. 目前作为课题负责人承担有国家杰出青年基金, 中国科学院“先导B”课题, 国家自然科学基金重点项目等多项研究课题. 已在系列国际知名期刊上发表论文300多篇, 论文被他人正面引用超过2万次, H因子82. |
基金资助:
Xueping Qi, Fei Wang( ), Jian Zhang
), Jian Zhang
Received:2023-02-20
Published:2023-03-28
Contact:
*E-mail: wangfei04@fjirsm.ac.cn
Supported by:文章分享
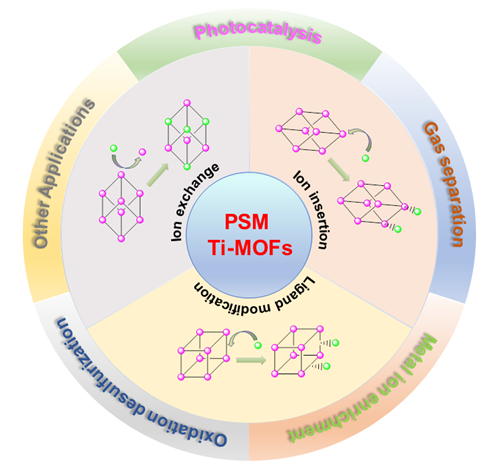
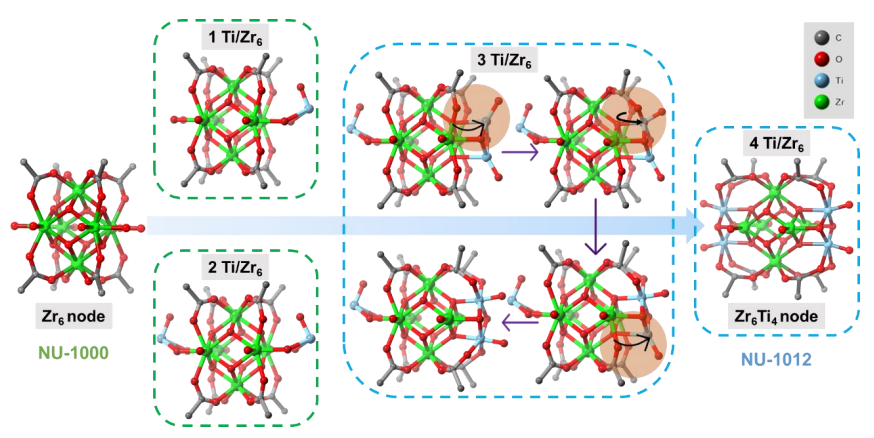
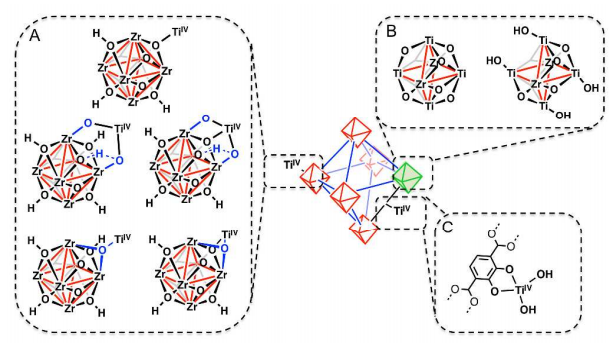
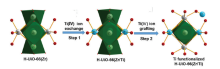
钛基金属有机框架(Ti-MOFs)因其优异的光催化活性成为当前材料研究领域的热点. 但由于Ti离子极高的反应活性和亲氧属性, 在反应过程中极易形成氧化物和其它竞争性的副产物, 使得Ti-MOFs的合成极具挑战性. 在MOFs发展的初期, 关于Ti-MOFs的研究便同步开展, 然而经过二十多年的发展, 已报道的Ti-MOFs只有数十种, 在上万种的MOFs中占比极其有限. 为了避免或减少钛离子副反应的发生, 通常在已知MOFs框架中引入金属Ti离子, 来定向合成Ti-MOFs, 该方法被称为后合成法(PSM), 也是构筑Ti-MOF框架的一种有效方法. 对PSM构筑Ti-MOFs的实例进行了系统的调研和总结. 首先, 依据钛离子引入方式和位置的不同, 分为离子交换、离子插入(金属节点或簇单元位置引入钛离子)和配体修饰(有机配体位置引入钛离子)三种途径, 并通过实例介绍了每种途径构筑的Ti-MOFs. 随后, 对PSM构筑的Ti-MOFs及其复合材料的设计与应用进行讨论. 最后, 对PSM构筑Ti-MOFs的现状进行总结并展望了未来的发展方向.
齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558.
Xueping Qi, Fei Wang, Jian Zhang. A Post-Synthetic Method for the Construction of Titanium-Based Metal Organic Frameworks and Their Applications[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(5): 548-558.
| Name | PSM | Ti source | Solvent | Ti percentage (max) | Condition | BET surface area/(m2•g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 TiCl4(THF)2 TiBr4 | DMF | w=12.0% w=37.9% w=1.4% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1259 1365 1291 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr/Ce) | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=20.2% | 120 ℃, 96 h | 1019 | [ |
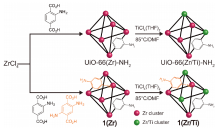
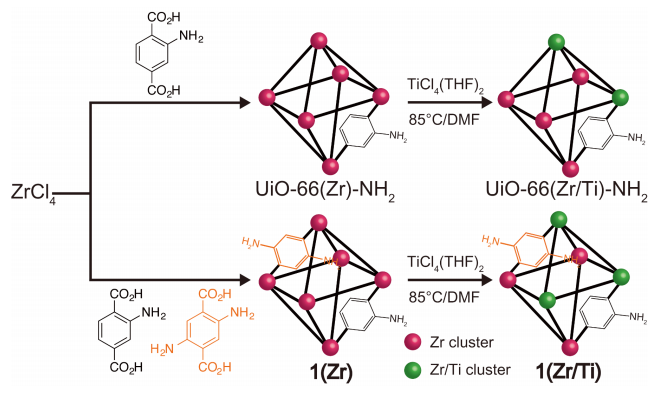
| UiO-66(Zr)-NH2,1(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=28.4% | 85 ℃, 120 h | — | [ |
| Zr-NDC | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=26.7% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1062.6 | [ |
| Zr-DNC-NH2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=28.3% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1026.7 | [ |
| UiO-66(Ce) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | — | 100 ℃, 3 h | 1032.9 | [ |
| (Ti/Ce)UiO-X@TiO2 (X=H, Br, NO2, NH2, N) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | — | 100 ℃, 3 h | — | [ |
| PCN-224 | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | x=38.6% | 120 ℃, 192 h | — | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | x≤60% | 120 ℃, 8 h, microwave | 965.8 | [ |
| MOF-5(Zn) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=2% | room temperature, 7 d, stir | about 650 | [ |
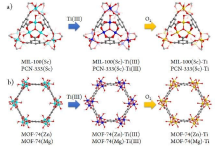
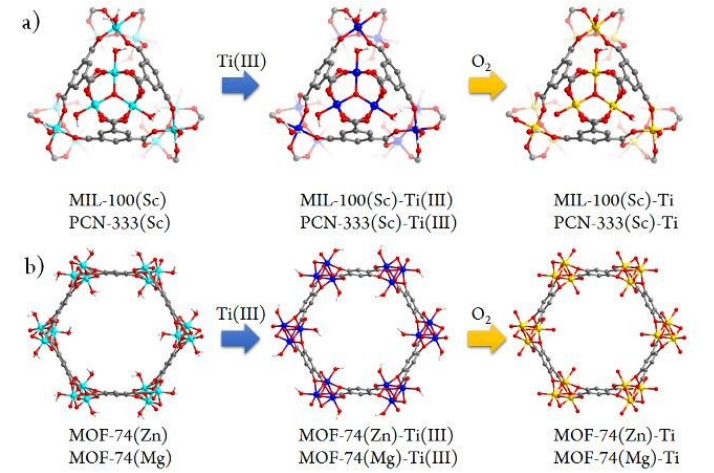
| MIL-100(Sc) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=88.0% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2, | — | [ |
| PCN-333(Sc) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=48.8% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2 | — | [ |
| MOF-74(Zn) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=94.7% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2 | — | [ |
| MOF-74(Mg) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=37.9% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2, | — | [ |
| NU-1200(Zr) | 离子插入 | Ti(OiPr)4 | CH2Cl2 | x=25% | 60 ℃, 24 h | — | [ |
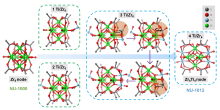
| NU-1000(Zr) | 离子插入 | Ti(OiPr)4 | Heptane | w=5.16% | overnight, N2 | 1930 | [ |
| NU-1008(Zr) | 离子插入 | Ti(OiPr)4 | Isopropanol | x=27.3% | 80 ℃, 40 h | — | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr) | 离子插入 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | X=21.3%~22.3% | 90 ℃, 120 h | 1200 | [ |
| 2D UiO-67(Hf)-NS | 离子插入 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=14.58% | 120 ℃, 120 h | — | [ |
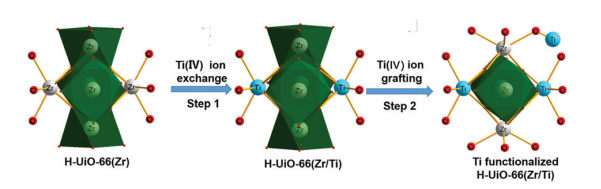
| H-UiO-66(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | x=3.83% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1220 | [ |
| H-UiO-66(Zr/Ti) | 离子插入 | TiCp2Cl2 TiO(acac)2 TiO(Bu)4 Ti-Citrate | MeOH; H2O | x=6.42% x=7.14% x=14.47% x=4.93% | 65 ℃, 12 h, backflow | 1031 1092 1588 859 | [ |
| IRMOF-3 | 配体修饰 | Ti(OiPr)4 | CHCl3 | w=4.3% | 25 ℃, 24 h, N2 | 870 | [ |
| MIL-47-NH2 | 配体修饰 | TiO(acac)2 | Toluene | — | 90 ℃, 40 h, Ar, stir | — | [ |
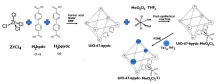
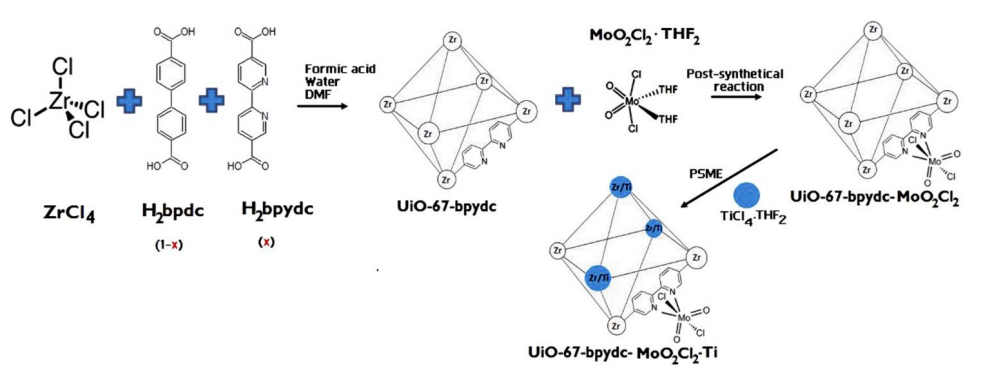
| UiO-67-bpydc-MoO2Cl2 | 配体修饰和离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=1.15% | 120 ℃, 144 h | — | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NH2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=57% | 120 ℃, 384 h | 787 | [ |
| MOF-525(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=90% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 2780 | [ |
| UiO-67(Zr)-Ru | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=54.5% | 120 ℃, 18 h | 1694 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NH2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=10.4% | 120 ℃, 96 h | 770 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NO2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=10.4% | 120 ℃, 96 h | 590 | [ |
| Name | PSM | Ti source | Solvent | Ti percentage (max) | Condition | BET surface area/(m2•g-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UiO-66(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 TiCl4(THF)2 TiBr4 | DMF | w=12.0% w=37.9% w=1.4% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1259 1365 1291 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr/Ce) | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=20.2% | 120 ℃, 96 h | 1019 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NH2,1(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=28.4% | 85 ℃, 120 h | — | [ |
| Zr-NDC | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=26.7% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1062.6 | [ |
| Zr-DNC-NH2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=28.3% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1026.7 | [ |
| UiO-66(Ce) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | — | 100 ℃, 3 h | 1032.9 | [ |
| (Ti/Ce)UiO-X@TiO2 (X=H, Br, NO2, NH2, N) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | — | 100 ℃, 3 h | — | [ |
| PCN-224 | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | x=38.6% | 120 ℃, 192 h | — | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | x≤60% | 120 ℃, 8 h, microwave | 965.8 | [ |
| MOF-5(Zn) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=2% | room temperature, 7 d, stir | about 650 | [ |
| MIL-100(Sc) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=88.0% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2, | — | [ |
| PCN-333(Sc) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=48.8% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2 | — | [ |
| MOF-74(Zn) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=94.7% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2 | — | [ |
| MOF-74(Mg) | 离子交换 | TiCl3(THF)3 | DMF | x=37.9% | 120 ℃, 24 h, N2, | — | [ |
| NU-1200(Zr) | 离子插入 | Ti(OiPr)4 | CH2Cl2 | x=25% | 60 ℃, 24 h | — | [ |
| NU-1000(Zr) | 离子插入 | Ti(OiPr)4 | Heptane | w=5.16% | overnight, N2 | 1930 | [ |
| NU-1008(Zr) | 离子插入 | Ti(OiPr)4 | Isopropanol | x=27.3% | 80 ℃, 40 h | — | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr) | 离子插入 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | X=21.3%~22.3% | 90 ℃, 120 h | 1200 | [ |
| 2D UiO-67(Hf)-NS | 离子插入 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=14.58% | 120 ℃, 120 h | — | [ |
| H-UiO-66(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCp2Cl2 | DMF | x=3.83% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 1220 | [ |
| H-UiO-66(Zr/Ti) | 离子插入 | TiCp2Cl2 TiO(acac)2 TiO(Bu)4 Ti-Citrate | MeOH; H2O | x=6.42% x=7.14% x=14.47% x=4.93% | 65 ℃, 12 h, backflow | 1031 1092 1588 859 | [ |
| IRMOF-3 | 配体修饰 | Ti(OiPr)4 | CHCl3 | w=4.3% | 25 ℃, 24 h, N2 | 870 | [ |
| MIL-47-NH2 | 配体修饰 | TiO(acac)2 | Toluene | — | 90 ℃, 40 h, Ar, stir | — | [ |
| UiO-67-bpydc-MoO2Cl2 | 配体修饰和离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=1.15% | 120 ℃, 144 h | — | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NH2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=57% | 120 ℃, 384 h | 787 | [ |
| MOF-525(Zr) | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=90% | 85 ℃, 120 h | 2780 | [ |
| UiO-67(Zr)-Ru | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=54.5% | 120 ℃, 18 h | 1694 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NH2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=10.4% | 120 ℃, 96 h | 770 | [ |
| UiO-66(Zr)-NO2 | 离子交换 | TiCl4(THF)2 | DMF | x=10.4% | 120 ℃, 96 h | 590 | [ |
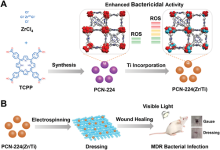
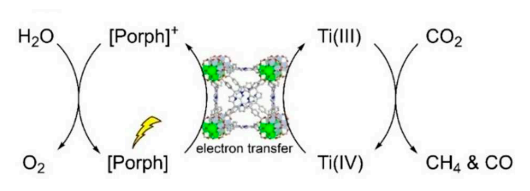
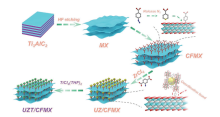
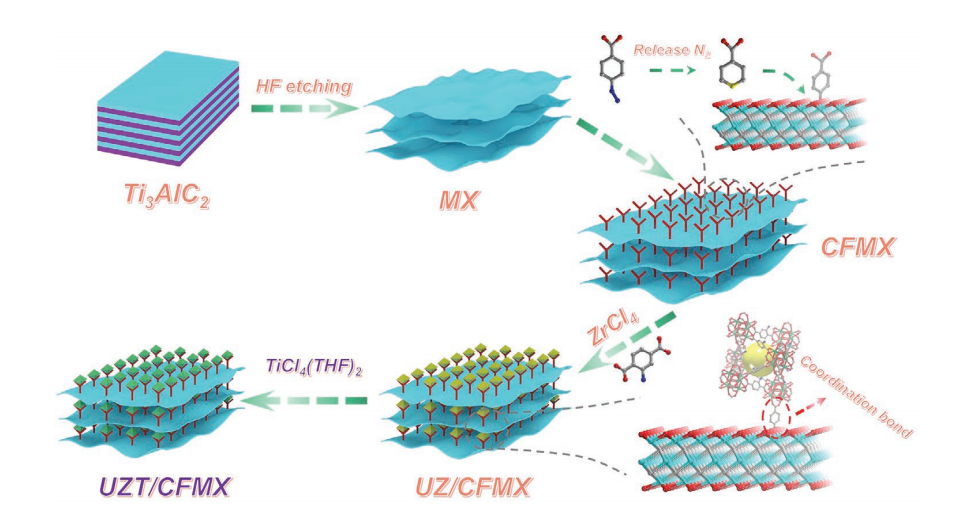
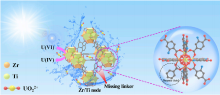
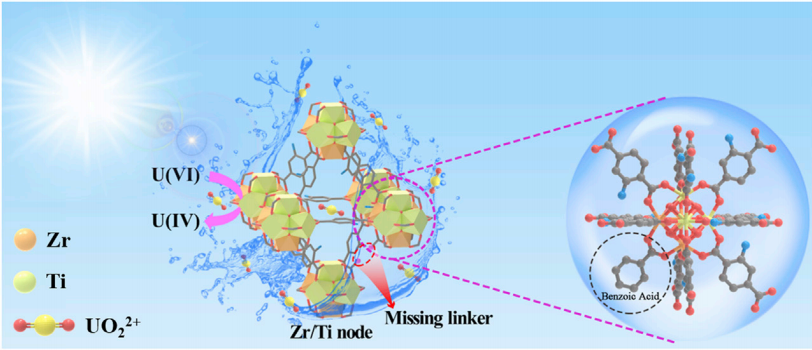
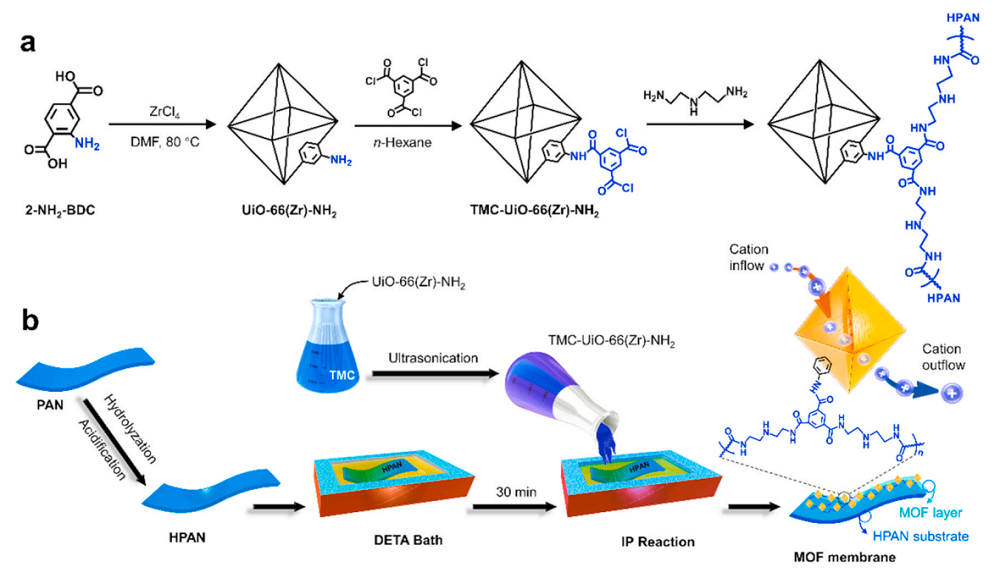
| [80] |
Navarro Amador, R.; Carboni, M.; Meyer, D. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 195.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA26552A |
| [81] |
Feng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Cao, M. J.; Ling, N.; Yao, J. F. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 5973.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b01403 |
| [82] |
Liu, T.; Tang, S.; Wei, T.; Chen, M. W.; Xie, Z. J.; Zhang, R. Q.; Liu, Y. J.; Wang, N. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100892.
|
| [83] |
Santiago Portillo, A.; Baldoví, H. G.; García Fernandez, M. T.; Navalón, S.; Atienzar, P.; Ferrer, B.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H.; Li, Z. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 7015.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b13068 |
| [84] |
Bahmani, M.; Mowla, D.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Ghaedi, M. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 286, 121304.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121304 |
| [85] |
Bahmani, M.; Dashtian, K.; Mowla, D.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Ghaedi, M. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129206.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129206 |
| [86] |
Smith, S. J. D.; Ladewig, B. P.; Hill, A. J.; Lau, C. H.; Hill, M. R. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7823.
doi: 10.1038/srep07823 |
| [87] |
Smith, S. J. D.; Lau, C. H.; Mardel, J. I.; Kitchin, M.; Konstas, K.; Ladewig, B. P.; Hill, M. R. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10627.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA02603F |
| [88] |
Avci, G.; Altintas, C.; Keskin, S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 17311.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c03630 |
| [89] |
Xu, T. T.; Sheng, F. M.; Wu, B.; Shehzad, M. A.; Yasmin, A.; Wang, X. X.; He, Y.; Ge, L.; Zheng, X. S.; Xu, T. W. J. Membrane Sci. 2020, 615, 118608.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118608 |
| [90] |
Ye, G.; Qi, H.; Li, X. L.; Leng, K. Y.; Sun, Y. Y.; Xu, W. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1903.
doi: 10.1002/cphc.v18.14 |
| [91] |
Piscopo, C. G.; Voellinger, L.; Schwarzer, M.; Polyzoidis, A.; Bošković, D.; Loebbecke, S. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 2806.
doi: 10.1002/slct.201900342 |
| [92] |
Nguyen, H. G. T.; Schweitzer, N. M.; Chang, C. Y.; Drake, T. L.; So, M. C.; Stair, P. C.; Farha, O. K.; Hupp, J. T.; Nguyen, S. T. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2496.
doi: 10.1021/cs5001448 |
| [93] |
Santiago-Portillo, A.; Navalón, S.; Álvaro, M.; García, H. J. Catal. 2018, 365, 450.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.07.032 |
| [94] |
Ye, J. Y.; Gagliardi, L.; Cramer, C. J.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Catal. 2018, 360, 160.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.12.007 |
| [95] |
Qin, M. H.; Shi, Y. M.; Lu, D. K.; Deng, J. J.; Shi, G. Y.; Zhou, T. S. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 595, 153494.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153494 |
| [96] |
Liu, Q. J.; Sun, N. R.; Gao, M. X.; Deng, C. H. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4382.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00023 |
| [1] |
Li, X. F.; Yan, B. Y.; Huang, W. Q.; Fu, L. P.; Sun, X. H.; Lǚ, A. H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 459. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20100494 |
|
(李旭飞, 闫保有, 黄维秋, 浮历沛, 孙宪航, 吕爱华, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 459.)
doi: 10.6023/A20100494 |
|
| [2] |
Liu, X. L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Y.; You, Z. F.; Li, J. L.; Ma, D. X.; Li, B. Y. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3462.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.12 |
| [3] |
Yan, X.; Qu, H. M.; Chang, Y.; Duan, X. X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1183. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22030134 |
|
(闫续, 屈贺幂, 常烨, 段学欣, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1183.)
doi: 10.6023/A22030134 |
|
| [4] |
Deng, H. L.; Luo, X. S.; Li, Z. H.; Zhao, J. Y.; Huang, M. H. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 624. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202005070 |
|
(邓汉林, 罗贤生, 李志华, 赵江颖, 黄木华, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 624.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202005070 |
|
| [5] |
Mo, G. L.; Wang, Q.; Lu, W. Y.; Wang, C.; Li, P. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 41, 335.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v41.3 |
| [6] |
Huang, H. L.; Sun, Y. X.; Jia, X. M.; Xue, W. J.; Geng, C. X.; Zhao, X.; Mei, D. H.; Zhong, C. L. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 39, 1538.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v39.6 |
| [7] |
Dou, J.; Chen, Q. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 695.
doi: 10.1002/cjoc.v41.6 |
| [8] |
Qi, Y.; Ren, S. S.; Che, Y.; Yen, J. W.; Ning, G. L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 613. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20040126 |
|
(齐野, 任双颂, 车颖, 叶俊伟, 宁桂玲, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 613.)
doi: 10.6023/A20040126 |
|
| [9] |
Assi, H.; Mouchaham, G.; Steunou, N.; Devic, T.; Serre, C. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3431.
doi: 10.1039/C7CS00001D |
| [10] |
Li, L.; Wang, X. S.; Liu, T. F.; Ye, J. H. Small Methods 2020, 4, 2000486.
doi: 10.1002/smtd.v4.12 |
| [11] |
Yan, Y.; Li, C. Q.; Wu, Y. H.; Gao, J. K.; Zhang, Q. C. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15245.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA03749D |
| [12] |
Zhu, J. J.; Li, P. Z.; Guo, W. H.; Zhao, Y. L.; Zou, R. Q. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2018, 359, 80.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.12.013 |
| [13] |
Serre, C.; Ferey, G. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 5370.
doi: 10.1021/ic990345m |
| [14] |
Serre, C.; Groves, J. A.; Lightfoot, P.; Slawin, A. M. Z.; Wright, P. A.; Stock, N.; Bein, T.; Haouas, M.; Taulelle, F.; Ferry, G. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1451.
doi: 10.1021/cm052149l |
| [15] |
Dan-Hardi, M.; Serre, C.; Frot, T.; Rozes, L.; Maurin, G.; Sanchez, C.; Ferey, G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10857.
doi: 10.1021/ja903726m |
| [16] |
Gao, J. K.; Miao, J. W.; Li, P. Z.; Teng, W. Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y. L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q. C. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3786.
doi: 10.1039/C3CC49440C |
| [17] |
Yuan, S.; Liu, T. F.; Feng, D. W.; Tian, J.; Wang, K. C.; Qin, J. S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. P.; Bosch, M.; Zou, L. F; Teat, S. J.; Dalgarno, S. J.; Zhou, H. C. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 3926.
doi: 10.1039/C5SC00916B |
| [18] |
Wang, S. J; Kitao, T.; Guillou, N.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Martineau Corcos, C.; Nouar, F.; Tissot, A.; Binet, L.; Ramsahye, N.; Devautour-Vinot, S.; Kitagawa, S.; Seki, S.; Tsutsui, Y.; Briois, V.; Steunou, N.; Maurin, G.; Uemura, T.; Serre, C. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1660.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04034-w |
| [19] |
Keum, Y.; Park, S.; Chen, Y. P.; Park, J. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2018, 57, 14852.
|
| [20] |
Castells-Gil, J.;
doi: 10.1039/c8sc05218b pmid: 31057758 |
| [21] |
Li, C. Q.; Xu, H.; Gao, J. K; Du, W. N.; Shangguan, L. Q.; Zhang, X.; Lin, R. B.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X. F.; Yao, J. M.; Chen, B. L. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11928.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA01942A |
| [22] |
Wang, S. J.; Reinsch, H.; Heymans, N.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Martineau-Corcos, C.; De Weireld, G.; Maurin, G.; Serre, C. Matter 2020, 2, 440.
doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2019.11.002 |
| [23] |
Li, H. Z.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q. H.; Lin, Q. P.; Lin, D. Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 965.
doi: 10.1039/D2TA08921A |
| [24] |
Sun, Y. Y.; Gao, M. Y.; Sun, Y. X.; Lu, D. F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 13955.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c02179 |
| [25] |
Sun, Y. Y.; Lu, D. F.; Sun, Y. X.; Gao, M. Y.; Zheng, N.; Gu, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 3, 64.
|
| [26] |
Salcedo-Abraira, P.; Babaryk, A. A.; Montero-Lanzuela, E.; Contreras-Almengor, O. R.; Cabrero-Antonino, M.; Grape, E. S.; Willhammar, T.; Navalon, S.; Elkaim, E.; Garcia, H.; Horcajada, P. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2106627.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v33.52 |
| [27] |
Yan, Y.; Li, C. Q; Wu, Y. H.; Gao, J. K.; Zhang, Q. C. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15245.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA03749D |
| [28] |
Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Yi, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3150.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00421 |
| [29] |
Mason, J. A.; Darago, L. E.; Lukens, W. W. Jr.; Long, J. R. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 10096.
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b02046 |
| [30] |
Nguyen, N. T.; Furukawa, H.; Gandara, F.; Trickett, C. A.; Jeong, H. M.; Cordova, K. E.; Yaghi, O. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15394.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10999 pmid: 26595681 |
| [31] |
Schaate, A.; Roy, P.; Godt, A.; Lippke, J.; Waltz, F.; Wiebcke, M.; Behrens, P. Chem.-Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6643.
doi: 10.1002/chem.v17.24 |
| [32] |
Lan, G. X.; Ni, K. Y.; Veroneau, S. S.; Feng, X. Y.; Nash, G. T.; Luo, T. K.; Xu, Z. W.; Lin, W. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4204.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b13804 |
| [33] |
Bueken, B.; Vermoortele, F.; Vanpoucke, D. E.; Reinsch, H.; Tsou, C. C.; Valvekens, P.; De Baerdemaeker, T.; Ameloot, R.; Kirschhock, C. E.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Mayer, J. M.; De Vos, D. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2015, 54, 13912.
|
| [34] |
Smolders, S.; Willhammar, T.; Krajnc, A.; Sentosun, K.; Wharmby, M. T.; Lomachenko, K. A.; Bals, S.; Mali, G.; Roeffaers, M. B. J.; De Vos, D. E.; Bueken, B. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2019, 58, 9160.
|
| [35] |
Padial, N. M.; Castells-Gil, J.; Almora-Barrios, N.; Romero-Angel, M.; da Silva, I.; Barawi, M.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.; de la Pena O'Shea, V. A.; Marti-Gastaldo, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 13124.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b04915 |
| [36] |
Nguyen, H. L.; Gándara, F.; Furukawa, H.; Doan, T. L. H.; Cordova, K. E.; Yaghi, O. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4330.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b01233 pmid: 26998612 |
| [37] |
Nguyen, H. L.; Vu, T. T.; Le, D.; Doan, T. L. H.; Nguyen, V. Q.; Phan, N. T. S. ACS Catal. 2016, 7, 338.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b02642 |
| [38] |
Chang, J. N.; Li, Q.; Yan, Y.; Shi, J. W.; Zhou, J.; Lu, M.; Zhang, M.; Ding, H. M.; Chen, Y. F.; Li, S. L.; Lan, Y. Q. Angew. Chem., nt. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209289.
|
| [39] |
Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Kan, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y. F.; Liu, J.; Li, S. L.; Lan, Y. Q. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4681.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32449-z pmid: 35948601 |
| [40] |
Cohen, S. M. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 970.
doi: 10.1021/cr200179u pmid: 21916418 |
| [41] |
Mi, L. W.; Hou, H. W.; Song, Z. Y.; Han, H. Y.; Xu, H.; Fan, Y. T.; Ng, S. W. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 7, 2553.
doi: 10.1021/cg070468e |
| [42] |
Xu, M. M.; Chen, Q.; Xie, L. H.; Li, J. R. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2020, 421, 213421.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213421 |
| [43] |
Kim, M.; Cahill, J. F.; Fei, H.; Prather, K. A.; Cohen, S. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18082.
doi: 10.1021/ja3079219 |
| [44] |
Lau, C. H.; Babarao, R.; Hill, M. R. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3634.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc40470f |
| [45] |
Yasin, A. S.; Li, J. T.; Wu, N. Q.; Musho, T. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 12748.
doi: 10.1039/C5CP08070C |
| [46] |
Pratik, S. M.; Cramer, C. J. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 19778.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b05693 |
| [47] |
Melillo, A.; Cabrero-Antonino, M.; Navalón, S.; Álvaro, M.; Ferrer, B.; García, H. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 278, 119345.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119345 |
| [48] |
Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, J. K.; Cohen, S. M. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5735.
doi: 10.1039/C5CC00686D |
| [49] |
Rasero-Almansa, A. M.; Iglesias, M.; Sánchez, F. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 106790.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA23143H |
| [50] |
Wu, X. P.; Gagliardi, L.; Truhlar, D. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7904.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b03613 |
| [51] |
Zhang, Y. J.; Chen, H. J.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, X. L.; Jiang, X. F.; Long, Z.; Hou, X. D. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13959.
doi: 10.1039/C9CC06562H |
| [52] |
Parnicka, P.; Lisowski, W.; Klimczuk, T.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2022, 310, 121349.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121349 |
| [53] |
He, J. H.; Zhang, Y. J.; He, J.; Zeng, X. L.; Hou, X. D.; Long, Z. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8610.
doi: 10.1039/C8CC04891F |
| [54] |
Chen, M.; Long, Z.; Dong, R. H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. J.; Li, S. X.; Zhao, X. H.; Hou, X. D.; Shao, H. W.; Jiang, X. Y. Small 2020, 16, 1906240.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v16.7 |
| [55] |
Tu, J. P.; Zeng, X. L.; Xu, F. J.; Wu, X.; Tian, Y. F.; Hou, X. D.; Long, Z. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3361.
doi: 10.1039/C7CC00076F |
| [56] |
Zhou, Y.; Liu, J. J.; Long, J. L. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 303, 122510.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2021.122510 |
| [57] |
Brozek, C. K.; Dinca, M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12886.
doi: 10.1021/ja4064475 pmid: 23902330 |
| [58] |
Zou, L. F.; Feng, D. W.; Liu, T. F.; Chen, Y. P.; Yuan, S.; Wang, K. C.; Wang, X.; Fordham, S.; Zhou, H. C. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1063.
doi: 10.1039/C5SC03620H |
| [59] |
Liu, T. F.; Vermeulen, N. A.; Howarth, A. J.; Li, P.; Sarjeant, A. A.; Hupp, J. T.; Farha, O. K. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4349.
doi: 10.1002/ejic.v2016.27 |
| [60] |
Li, Z. Y.; Peters, A. W.; Platero-Prats, A. E.; Liu, J.; Kung, C. W.; Noh, H.; DeStefano, M. R.; Schweitzer, N. M.; Chapman, K. W.; Hupp, J. T.; Farha, O. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15251.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b09365 |
| [61] |
Wang, X. J.; Ma, K. K.; Goh, T.; Mian, M. R.; Xie, H. M.; Mao, H.; Duan, J.; Kirlikovali, K. O.; Stone, A.; Ray, D.; Wasielewski, M. R.; Gagliardi, L.; Farha, O. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12192.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c03060 |
| [62] |
Katz, M. J.; Brown, Z. J.; Colon, Y. J.; Siu, P. W.; Scheidt, K. A.; Snurr, R. Q.; Hupp, J. T.; Farha, O. K. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9449.
doi: 10.1039/c3cc46105j |
| [63] |
Nguyen, H. G. T.; Mao, L.; Peters, A. W.; Audu, C. O.; Brown, Z. J.; Farha, O. K.; Hupp, J. T.; Nguyen, S. T. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4444.
doi: 10.1039/C5CY00825E |
| [64] |
Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Peh, S. B.; Zhai, L. Z.; Ying, Y. P.; Liu, G. L.; Cheng, Y. D.; Zhao, D. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 2, 298.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b01303 |
| [65] |
Jia, B. Y; Wu, M. J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, G. Y. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 16981.
doi: 10.1039/C9NJ04241E |
| [66] |
Wu, C. D.; Hu, A.; Zhang, L.; Lin, W. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8940.
doi: 10.1021/ja052431t |
| [67] |
Ma, L. Q.; Falkowski, J. M.; Abney, C.; Lin, W. B. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 838.
doi: 10.1038/nchem.738 |
| [68] |
Kim, J.; Kim, D. O.; Kim, D. W.; Park, J.; Jung, M. S. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 390, 22.
doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2012.04.020 |
| [69] |
Kim, J.; McNamara, N. D.; Her, T. H.; Hicks, J. C. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2013, 5, 11479.
doi: 10.1021/am404089v |
| [70] |
Kim, J.; Neumann, G. T.; McNamara, N. D.; Hicks, J. C. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14014.
doi: 10.1039/C4TA03050H |
| [71] |
Leus, K.; Vanhaelewyn, G.; Bogaerts, T.; Liu, Y. Y.; Esquivel, D.; Callens, F.; Marin, G. B.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Vrielinck, H.; Van Der Voort, P. Catal. Today 2013, 208, 97.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.09.037 |
| [72] |
Kim, J.; Ok Kim, D.; Wook Kim, D.; Sagong, K. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 230, 110.
doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2015.06.034 |
| [73] |
Huang, Z. Y.; Liu, D.; Camacho-Bunquin, J.; Zhang, G. H.; Yang, D. L.; López-Encarnación, J. M.; Xu, Y. J.; Ferrandon, M. S.; Niklas, J.; Poluektov, O. G.; Jellinek, J.; Lei, A.; Bunel, E. E.; Delferro, M. Organometallics 2017, 36, 3921.
doi: 10.1021/acs.organomet.7b00544 |
| [74] |
Bravo-Sanabria, C. A.; Solano-Delgado, L. C.; Ospina-Ospina, R.; Martínez-Ortega, F.; Ramírez-Caballero, G. E. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 305, 110359.
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110359 |
| [75] |
Sun, D.; Liu, W. J.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y. F.; Li, Z. H. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2056.
doi: 10.1039/C4CC09407G |
| [76] |
Zeama, M.; Morsy, M.; Abdel-Azeim, S.; Abdelnaby, M.; Alloush, A.; Yamani, Z. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 119287.
doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2019.119287 |
| [77] |
Gao, W. Y.; Ngo, H. T.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, W. J.; Pan, Y. X.; Yang, Z. Y.; Bhethanabotla, V. R.; Joseph, B.; Aguila, B.; Ma, S. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 6273.
|
| [78] |
Shi, L. T.; Wu, C. C.; Wang, Y.; Dou, Y. H.; Yuan, D.; Li, H.; Huang, H. W.; Zhang, Y.; Gates, I. D.; Sun, X. D.; Ma, T. Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202571.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.30 |
| [79] |
Wang, A.; Zhou, Y. J.; Wang, Z. L.; Chen, M.; Sun, L. Y.; Liu, X. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3671.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA24135A |
| [1] | 陈宇波, 郑德旭, 王楠, 刘吉双, 于凤阳, 吴飒建, 刘生忠, 李智鹏. 旋涂两步法甲脒铅基钙钛矿太阳能电池近期研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 987-1000. |
| [2] | 康健, 石梓煊, 李景梅. 高抗菌性光催化材料的制备及LED光驱动其抗菌性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 962-970. |
| [3] | 张林, 张慧, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. CsPbIBr2钙钛矿太阳能电池湿度稳定机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 971-978. |
| [4] | 王馨雨, 许雄文. SnCl2敏化的TiO2表面对PbI2粒子的诱导吸附[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 865-870. |
| [5] | 张帆帆, 蔡元韬, 陶剑波, 常国菊, 郭欣辰, 郝仕油. Zn, C引入量和煅烧温度对ZnO/C/CeO2光催化还原Cu2+效率的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 871-878. |
| [6] | 彭亚晶, 赵雨新, 杨金辉, 仉昕昕, 程佳玲. CsPbBrxI3-x全无机钙钛矿量子点的组分及浓度对电子结构及荧光性质影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 879-886. |
| [7] | 李康葵, 龙先扬, 黄岳, 祝诗发. 可见光介导炔烃的自由基1,2-官能团化反应新进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 658-676. |
| [8] | 王南南, 陈玉贞. CoNi-MOF-74/泡沫镍衍生的CoNi@C/NF复合物用于高效有机电合成[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(6): 621-628. |
| [9] | 周何鑫, 崔青云, 胡雪敏, 杨文秀, 田肖, 王硕. 金属有机框架衍生氮掺杂碳限域钴原子簇催化硝基化合物转移加氢[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 503-510. |
| [10] | 王国景, 陈永辉, 张秀芹, 张俊笙, 徐俊敏, 王静. 氧空位控制BiVO4晶面异质结的磁性和光电催化性能[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(4): 409-415. |
| [11] | 张强, 王欢, 王帅, 王园园, 张梅, 宋华. NiCe(x)/FLRC-TiO2催化剂的制备及其加氢脱氧性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 287-294. |
| [12] | 黄广峥, 李坤玮, 罗艳楠, 张强, 潘远龙, 高洪林. 水热后处理构建K掺杂和表面缺陷g-C3N4纳米片促进光催化制氢[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 314-322. |
| [13] | 鲍梦凡, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 邓慧娟, 冒爱琴, 檀杰. 低共熔溶剂辅助制备空心球状钙钛矿型高熵氧化物及高倍率储锂性能[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 303-313. |
| [14] | 刘雪朋, 李博桐, 韩明远, 张先付, 陈建林, 戴松元. 自组装单分子空穴传输层在反式钙钛矿太阳电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 348-366. |
| [15] | 刘洋, 高丰琴, 马占营, 张引莉, 李午戊, 侯磊, 张小娟, 王尧宇. 一例钴基金属有机框架化合物活化过氧单硫酸盐高效降解水中亚甲基蓝研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 152-159. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||