化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (3): 348-366.DOI: 10.6023/A24010026 上一篇 下一篇
综述
刘雪朋, 李博桐, 韩明远, 张先付, 陈建林, 戴松元*( )
)
投稿日期:2024-01-22
发布日期:2024-02-18
作者简介: |
刘雪朋, 副教授. 主要从事新型太阳电池中有机光电材料的设计、合成及构效关系探索; 新型薄膜太阳电池中关键材料开发及界面修饰. 现工作于华北电力大学新能源学院. 主要研究方向: 钙钛矿太阳电池. |
 |
戴松元, 教授, “新型薄膜太阳电池”北京市重点实验室主任. 长期从事新型太阳电池的研究, 包括染料敏化太阳电池、钙钛矿太阳电池、量子点太阳电池及其他新兴纳米杂化有机/无机太阳电池的研究; 能源转换材料和储能材料的研究和纳米材料的制备和合成等. 现工作于华北电力大学新能源学院. 主要研究方向: 新型薄膜太阳电池. |
基金资助:
Xuepeng Liu, Botong Li, Mingyuan Han, Xianfu Zhang, Jianlin Chen, Songyuan Dai( )
)
Received:2024-01-22
Published:2024-02-18
Contact:
*E-mail: Supported by:文章分享
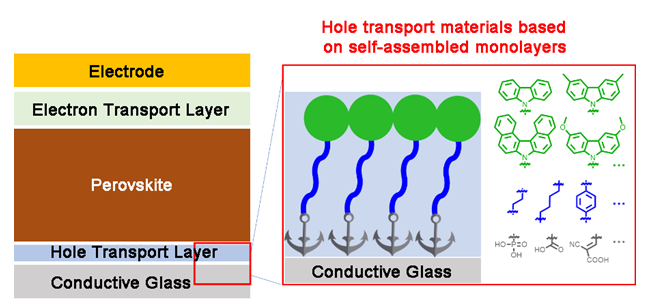
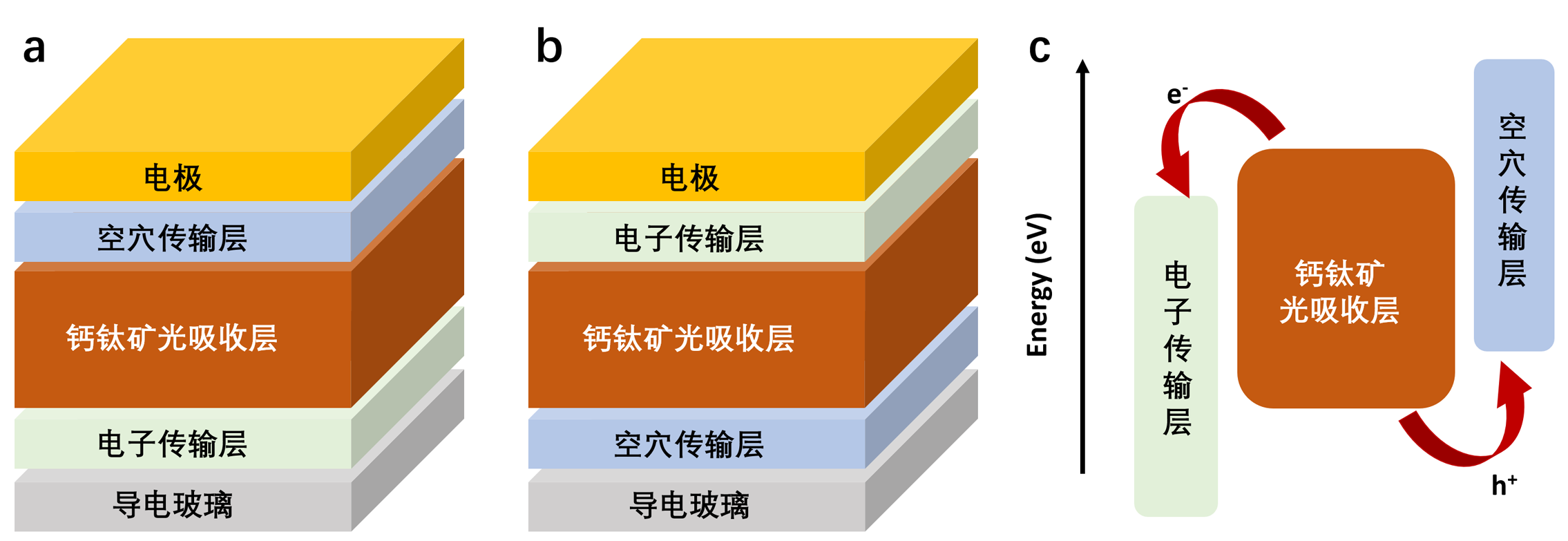
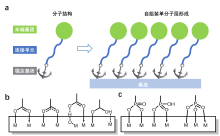
空穴传输层在钙钛矿太阳电池(Perovskite solar cell, PSC)中起着抽取和传输钙钛矿层产生的光生空穴、抑制电子回流等重要作用, 是构成高性能器件的重要组成部分. 经典的空穴传输材料, 如2,2',7,7'-四[N,N-二(4-甲氧基苯基)氨基]-9,9'-螺二芴(spiro-OMeTAD)、聚[双(4-苯基)(2,4,6-三甲基苯基)胺](PTAA)等, 空穴迁移率低、价格昂贵等缺点限制了其规模化应用. 近年来, 在反式PSC中自组装单分子层(self-assembled monolayers, SAM)作为空穴传输层广泛应用, 提升了器件性能. SAM分子结构中含有锚定官能团, 可以在衬底上形成单分子薄膜, 有着材料消耗小、无需添加剂、寄生吸收低、能够兼容叠层器件和有利于大面积制造等优点, 已成为PSC领域的研究热点. 本综述结合PSC发展, 按照SAM分子结构中锚定基团的不同, 对近年来基于SAM的空穴传输层的研究进行了分类和归纳, 结合分子骨架变化分析了结构变化对其特性及器件性能的影响. 最后, 对SAM作为空穴传输层的发展做了总结和展望.
刘雪朋, 李博桐, 韩明远, 张先付, 陈建林, 戴松元. 自组装单分子空穴传输层在反式钙钛矿太阳电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 348-366.
Xuepeng Liu, Botong Li, Mingyuan Han, Xianfu Zhang, Jianlin Chen, Songyuan Dai. Research Progress of Self-assembled Hole-transporting Monolayers in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(3): 348-366.


| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1036 | -4.7 | ITO/V1036+C4/Cs0.05(MA0.17FA0.83)0.95Pb(I0.83- Br0.17)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.63 | 1.09 | 21.4 | 76.5 | 17.8 | [ |
| MeO- 2PACz | -5.1 | ITO/MeO-2PACz/Cs0.05(MA0.17FA0.83)0.95Pb(I0.83- Br0.17)3/C60/BCP/Cu(Ag) | 1.63 | 1.144 | 22.2 | 80.5 | 20.2 | [ |
| 2PACz | -5.6 | ITO/2PACz/Cs0.05(MA0.17FA0.83)0.95Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3/ C60/BCP/Cu(Ag) | 1.60 | 1.188 | 21.9 | 80.2 | 20.8 | |
| 两端: silicon(Si)heterojunction bottom cell/ITO/2PACz/Cs0.22FA0.78Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3+5%MAPbCl3/LiF or PI+C60/SnO2/IZO/LiF/Ag | 顶电池: 1.68 底电池: Si | 1.98 | 20.24 | 81.81 | 32.5 | [ | ||
| DC-PA | -5.38 | ITO/DC-PA+IAHA/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.16 | 24.66 | 82.45 | 23.59 | [ |
| Ph-2PACz | -5.52 | ITO/Ph-2PACz/Cs0.15FA0.65MA0.2Pb(I0.8Br0.2)3/LiF/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.67 | 1.26 | 20.5 | 82.6 | 21.3 | [ |
| 两端: Ag/ITO/<p>a-Si:H/<i>a-Si:H/c-Si(n)/ <i>a-Si:H/<n>a-Si:H/ITO/Ph-2PACz/Cs0.15FA0.65- MA0.2Pb(I0.8Br0.2)3/LiF/C60/SnO2/Ag/ITO/ARC | 顶电池: 1.67 底电池: Si | 1.91 | 19.1 | 79.1 | 28.9 | |||
| Br-2PACz | -5.28 | ITO/Br-2PACz/Cs0.25FA0.75Sn0.5Pb0.5I3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.2~1.3 | 0.81 | 32.1 | 75 | 19.51 | [ |
| Br-2EPT | -5.47 | TCO/Br-2EPT/FA0.92MA0.08Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.56 | 1.09 | 25.11 | 82 | 22.44 | [ |
| Br-2EPO | -5.37 | FTO/Br-2EPO/Cs0.05(FA0.92MA0.08)Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/ C60/BCP/Cu | 1.04 | 24.25 | 80.74 | 21.02 | [ | |
| Br-2EPSe | -5.33 | FTO/Br-2EPSe/Cs0.05(FA0.92MA0.08)Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.12 | 24.49 | 82.86 | 22.73 | ||
| Me- 4PACz | -5.6 | ITO/Me-4PACz/Cs0.05(FA0.77MA0.23)0.95Pb(I0.77- Br0.23)3/(LiF)/C60/SnO2/Ag | 1.68 | 1.22 | 20.7 | 82 | 20.8 | [ |
| 两端: Ag/AZO/a-Si(p)/a-Si(i)/c-Si(n)/a-Si(i)/nc-SiOx(n)/ ITO/Me-4PACz/Cs0.05(FA0.77MA0.23)0.95Pb(I0.77- Br0.23)3/(LiF)/C60/SnO2/IZO/Ag/LiF | 顶电池: 1.68 底电池: Si | 1.90 | 19.26 | 79.52 | 29.15 | |||
| FTO/NiOx/Me-4PACz/Cs0.05MA0.05FA0.90PbI3/ DMDP/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 1.17 | 26.2 | 85.8 | 26.4 | [ | ||
| Poly- 4PACz | -5.28 | ITO/Poly-4PACz/MA0.7FA0.3PbI3 (1,000 nm)/C60/BCP/Cu | — | 1.17 | 24.8 | 83.9 | 24.4 | [ |
| Ph-4PACz | -5.52 | FTO/Al2O3-NPs/Ph-4PACz/Cs0.05(FA0.98MA0.02)0.95Pb(I0.98Br0.02)3/PDI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.55 | 1.207 | 25.18 | 84.23 | 25.6 | [ |
| Cbz2S | -5.45 | ITO/Cbz2S/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 0.997 | 24.15 | 80.20 | 19.23 | [ |
| Cbz2SMe | -5.37 | ITO/Cbz2SMe/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.172 | 25.16 | 82.82 | 24.42 | ||
| 3PATAT- C3 | -5.44 | TCO/3PATAT-C3/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.57 | 1.13 | 24.5 | 83 | 23.0 | [ |
| 2PATAT- C3 | -5.43 | TCO/2PATAT-C3/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.14 | 23.3 | 83 | 22.2 | ||
| 1PATAT- C3 | -5.45 | TCO/1PATAT-C3/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.06 | 24.0 | 82 | 21.1 | ||
| 3PATAT- C4 | -5.41 | TCO/3PATAT-C4/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.14 | 23.3 | 83 | 22.1 | ||
| 4dp3PACz | -5.77 | ITO/4dp3PACz/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2/GuBr/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.77 | 1.214 | 17.8 | 79.44 | 17.17 | [ |
| -5.77 | 两端: ITO/4dp3PACz/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2)/C60/ ALDSnO2/IZO/PEDOT:PSS/Cs0.025FA0.475MA0.5- Sn0.5Pb0.5I2.925Br0.075/C60/BCP/Ag | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 1.77 | 17.53 | 85.3 | 26.47 | ||
| 2BrCzPA | -6.15 | ITO/2BrCzPA/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95- Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.62 | 1.10 | 11.43 | 33.77 | 4.24 | [ |
| 2BrPTZPA | -5.77 | ITO/2BrPTZPA/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95- Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.18 | 22.29 | 80.02 | 22.06 | ||
| 2BrPXZPA | -5.59 | ITO/2BrPXZPA/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95Pb(I0.85- Br0.15)3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.19 | 22.51 | 81.69 | 22.93 | ||
| DMAcPA | -5.98 | ITO/(DMAcPA)Perovskite/PEABr/PCBM/BCP/ Ag | 1.56 | 1.187 | 25.69 | 84.73 | 25.86 | [ |
| MeO- BTBT | -5.39 | ITO/MeO-BTBT/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.16 | 24.87 | 85.28 | 24.53 | [ |
| 4PACz | -5.43 | ITO/4PACz/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.07 | 23.20 | 58.43 | 14.5 | [ |
| CbzPh | -5.36 | ITO/CbzPh/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.12 | 23.43 | 73.06 | 19.2 | ||
| CbzNaph | -5.24 | ITO/CbzNaph/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.17 | 24.69 | 83.39 | 24.1 | ||
| 4PADCB | -5.53 | ITO/4PADCB/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/ SnO2/Cu | 1.77 | 1.31 | 17.80 | 79.18 | 18.46 | [ |
| 两端: ITO/4PADCB/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/SnO2/IZO/PEDOT:PSS/FA0.6MA0.3Cs0.1Sn0.5Pb0.5I3/C60/SnO2/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 2.11 | 15.37 | 83.3 | 27.01 | |||
| BCB- C4PA | -5.25 | ITO/BCB-C4PA/Cs0.07FA0.9MA0.03Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/ C60/BCP/Ag | 1.55 | 1.13 | 24.4 | 80 | 22.2 | [ |
| CbzBF | -5.50 | ITO/CbzBF/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.09 | 24.00 | 83.04 | 21.72 | [ |
| CbzBT | -5.54 | ITO/CbzBT/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.16 | 24.54 | 84.41 | 24.04 | ||
| BCB10Br-C4PA | -5.63 | ITO/BCB10Br-C4PA/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/ ALD-SnO2/Cu | 1.77 | 1.286 | 17.54 | 82.61 | 18.63 | [ |
| 四端: ITO/BCB10Br-C4PA/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/ ALD-SnO2/transparent electrode/ glass/ITO/PEDOT:PSS/(FASnI3)0.6(MAPbI3)0.4/C60/BCP/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 1.264 | — | — | 26.24 | |||
| DCB-BPA | -5.56 | ITO/DCB-BPA/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.77 | 1.33 | 17.75 | 82.70 | 19.53 | [ |
| -5.56 | 四端: ITO/DCB-BPA/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2/C60/SnO2/IZO/transparent electrode/glass/ITO/ PEDOT:PSS/(FASnI3)0.6(MAPbI3)0.4/C60/BCP/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | — | — | — | 26.90 | ||
| MeO- 4PADCB | -5.34 | ITO/NiOx/MeO-4PADCB/Cs0.05FA0.85MA0.1PbI3/ CF3-PEAI+MAI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.19 | 25.4 | 84.6 | 25.6 | [ |
| ITO/NiOx/MeO-4PADCB/Cs0.05FA0.8MA0.15Pb(I0.76Br0.24)3/CF3-PEAI+MAI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.68 | 1.25 | 21.5 | 84.5 | 22.7 | |||
| ITO/NiOx/MeO-4PADCB/Cs0.15FA0.85Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/CF3-PEAI+MAI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.80 | 1.34 | 17.9 | 83.6 | 20.1 | |||
| TPT-H6 | -5.14 | ITO/TPT-H6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 0.714 | 21.54 | 65.19 | 11.97 | [ |
| TPT-S6 | -5.18 | ITO/TPT-S6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 0.998 | 21.50 | 75.31 | 16.16 | ||
| TPT-C6 | -5.20 | ITO/TPT-C6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.077 | 23.32 | 75.46 | 18.87 | ||
| TPT-P6 | -5.20 | ITO/TPT-P6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.125 | 23.49 | 81.08 | 21.43 | ||
| MeO- PhPACz | -5.61 | ITO/MeO-PhPACz/Cs0.05FA0.8MA0.15Pb(I0.75Br0.25)3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.68 | 1.215 | 20.59 | 84.28 | 21.10 | [ |
| PPA | -5.28 | ITO/PPA/Cs0.05FA0.85MA0.1PbI3/OABr/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.14 | 24.83 | 82.0 | 23.24 | [ |
| PPAOMe | -5.02 | ITO/PPA/Cs0.05FA0.85MA0.1PbI3/OABr/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.10 | 24.70 | 79.2 | 21.52 |
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1036 | -4.7 | ITO/V1036+C4/Cs0.05(MA0.17FA0.83)0.95Pb(I0.83- Br0.17)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.63 | 1.09 | 21.4 | 76.5 | 17.8 | [ |
| MeO- 2PACz | -5.1 | ITO/MeO-2PACz/Cs0.05(MA0.17FA0.83)0.95Pb(I0.83- Br0.17)3/C60/BCP/Cu(Ag) | 1.63 | 1.144 | 22.2 | 80.5 | 20.2 | [ |
| 2PACz | -5.6 | ITO/2PACz/Cs0.05(MA0.17FA0.83)0.95Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3/ C60/BCP/Cu(Ag) | 1.60 | 1.188 | 21.9 | 80.2 | 20.8 | |
| 两端: silicon(Si)heterojunction bottom cell/ITO/2PACz/Cs0.22FA0.78Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3+5%MAPbCl3/LiF or PI+C60/SnO2/IZO/LiF/Ag | 顶电池: 1.68 底电池: Si | 1.98 | 20.24 | 81.81 | 32.5 | [ | ||
| DC-PA | -5.38 | ITO/DC-PA+IAHA/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.16 | 24.66 | 82.45 | 23.59 | [ |
| Ph-2PACz | -5.52 | ITO/Ph-2PACz/Cs0.15FA0.65MA0.2Pb(I0.8Br0.2)3/LiF/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.67 | 1.26 | 20.5 | 82.6 | 21.3 | [ |
| 两端: Ag/ITO/<p>a-Si:H/<i>a-Si:H/c-Si(n)/ <i>a-Si:H/<n>a-Si:H/ITO/Ph-2PACz/Cs0.15FA0.65- MA0.2Pb(I0.8Br0.2)3/LiF/C60/SnO2/Ag/ITO/ARC | 顶电池: 1.67 底电池: Si | 1.91 | 19.1 | 79.1 | 28.9 | |||
| Br-2PACz | -5.28 | ITO/Br-2PACz/Cs0.25FA0.75Sn0.5Pb0.5I3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.2~1.3 | 0.81 | 32.1 | 75 | 19.51 | [ |
| Br-2EPT | -5.47 | TCO/Br-2EPT/FA0.92MA0.08Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.56 | 1.09 | 25.11 | 82 | 22.44 | [ |
| Br-2EPO | -5.37 | FTO/Br-2EPO/Cs0.05(FA0.92MA0.08)Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/ C60/BCP/Cu | 1.04 | 24.25 | 80.74 | 21.02 | [ | |
| Br-2EPSe | -5.33 | FTO/Br-2EPSe/Cs0.05(FA0.92MA0.08)Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.12 | 24.49 | 82.86 | 22.73 | ||
| Me- 4PACz | -5.6 | ITO/Me-4PACz/Cs0.05(FA0.77MA0.23)0.95Pb(I0.77- Br0.23)3/(LiF)/C60/SnO2/Ag | 1.68 | 1.22 | 20.7 | 82 | 20.8 | [ |
| 两端: Ag/AZO/a-Si(p)/a-Si(i)/c-Si(n)/a-Si(i)/nc-SiOx(n)/ ITO/Me-4PACz/Cs0.05(FA0.77MA0.23)0.95Pb(I0.77- Br0.23)3/(LiF)/C60/SnO2/IZO/Ag/LiF | 顶电池: 1.68 底电池: Si | 1.90 | 19.26 | 79.52 | 29.15 | |||
| FTO/NiOx/Me-4PACz/Cs0.05MA0.05FA0.90PbI3/ DMDP/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 1.17 | 26.2 | 85.8 | 26.4 | [ | ||
| Poly- 4PACz | -5.28 | ITO/Poly-4PACz/MA0.7FA0.3PbI3 (1,000 nm)/C60/BCP/Cu | — | 1.17 | 24.8 | 83.9 | 24.4 | [ |
| Ph-4PACz | -5.52 | FTO/Al2O3-NPs/Ph-4PACz/Cs0.05(FA0.98MA0.02)0.95Pb(I0.98Br0.02)3/PDI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.55 | 1.207 | 25.18 | 84.23 | 25.6 | [ |
| Cbz2S | -5.45 | ITO/Cbz2S/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 0.997 | 24.15 | 80.20 | 19.23 | [ |
| Cbz2SMe | -5.37 | ITO/Cbz2SMe/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.172 | 25.16 | 82.82 | 24.42 | ||
| 3PATAT- C3 | -5.44 | TCO/3PATAT-C3/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.57 | 1.13 | 24.5 | 83 | 23.0 | [ |
| 2PATAT- C3 | -5.43 | TCO/2PATAT-C3/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.14 | 23.3 | 83 | 22.2 | ||
| 1PATAT- C3 | -5.45 | TCO/1PATAT-C3/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.06 | 24.0 | 82 | 21.1 | ||
| 3PATAT- C4 | -5.41 | TCO/3PATAT-C4/Cs0.05FA0.80MA0.15PbI2.75Br0.25/ EDAI2/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.14 | 23.3 | 83 | 22.1 | ||
| 4dp3PACz | -5.77 | ITO/4dp3PACz/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2/GuBr/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.77 | 1.214 | 17.8 | 79.44 | 17.17 | [ |
| -5.77 | 两端: ITO/4dp3PACz/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2)/C60/ ALDSnO2/IZO/PEDOT:PSS/Cs0.025FA0.475MA0.5- Sn0.5Pb0.5I2.925Br0.075/C60/BCP/Ag | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 1.77 | 17.53 | 85.3 | 26.47 | ||
| 2BrCzPA | -6.15 | ITO/2BrCzPA/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95- Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.62 | 1.10 | 11.43 | 33.77 | 4.24 | [ |
| 2BrPTZPA | -5.77 | ITO/2BrPTZPA/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95- Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.18 | 22.29 | 80.02 | 22.06 | ||
| 2BrPXZPA | -5.59 | ITO/2BrPXZPA/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95Pb(I0.85- Br0.15)3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.19 | 22.51 | 81.69 | 22.93 | ||
| DMAcPA | -5.98 | ITO/(DMAcPA)Perovskite/PEABr/PCBM/BCP/ Ag | 1.56 | 1.187 | 25.69 | 84.73 | 25.86 | [ |
| MeO- BTBT | -5.39 | ITO/MeO-BTBT/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.16 | 24.87 | 85.28 | 24.53 | [ |
| 4PACz | -5.43 | ITO/4PACz/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.07 | 23.20 | 58.43 | 14.5 | [ |
| CbzPh | -5.36 | ITO/CbzPh/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.12 | 23.43 | 73.06 | 19.2 | ||
| CbzNaph | -5.24 | ITO/CbzNaph/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.17 | 24.69 | 83.39 | 24.1 | ||
| 4PADCB | -5.53 | ITO/4PADCB/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/ SnO2/Cu | 1.77 | 1.31 | 17.80 | 79.18 | 18.46 | [ |
| 两端: ITO/4PADCB/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/SnO2/IZO/PEDOT:PSS/FA0.6MA0.3Cs0.1Sn0.5Pb0.5I3/C60/SnO2/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 2.11 | 15.37 | 83.3 | 27.01 | |||
| BCB- C4PA | -5.25 | ITO/BCB-C4PA/Cs0.07FA0.9MA0.03Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/ C60/BCP/Ag | 1.55 | 1.13 | 24.4 | 80 | 22.2 | [ |
| CbzBF | -5.50 | ITO/CbzBF/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56a | 1.09 | 24.00 | 83.04 | 21.72 | [ |
| CbzBT | -5.54 | ITO/CbzBT/Cs0.05MA0.15FA0.80PbI3/PI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.16 | 24.54 | 84.41 | 24.04 | ||
| BCB10Br-C4PA | -5.63 | ITO/BCB10Br-C4PA/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/ ALD-SnO2/Cu | 1.77 | 1.286 | 17.54 | 82.61 | 18.63 | [ |
| 四端: ITO/BCB10Br-C4PA/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/ ALD-SnO2/transparent electrode/ glass/ITO/PEDOT:PSS/(FASnI3)0.6(MAPbI3)0.4/C60/BCP/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 1.264 | — | — | 26.24 | |||
| DCB-BPA | -5.56 | ITO/DCB-BPA/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.77 | 1.33 | 17.75 | 82.70 | 19.53 | [ |
| -5.56 | 四端: ITO/DCB-BPA/FA0.8Cs0.2PbI1.8Br1.2/C60/SnO2/IZO/transparent electrode/glass/ITO/ PEDOT:PSS/(FASnI3)0.6(MAPbI3)0.4/C60/BCP/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | — | — | — | 26.90 | ||
| MeO- 4PADCB | -5.34 | ITO/NiOx/MeO-4PADCB/Cs0.05FA0.85MA0.1PbI3/ CF3-PEAI+MAI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.19 | 25.4 | 84.6 | 25.6 | [ |
| ITO/NiOx/MeO-4PADCB/Cs0.05FA0.8MA0.15Pb(I0.76Br0.24)3/CF3-PEAI+MAI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.68 | 1.25 | 21.5 | 84.5 | 22.7 | |||
| ITO/NiOx/MeO-4PADCB/Cs0.15FA0.85Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/CF3-PEAI+MAI/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.80 | 1.34 | 17.9 | 83.6 | 20.1 | |||
| TPT-H6 | -5.14 | ITO/TPT-H6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 0.714 | 21.54 | 65.19 | 11.97 | [ |
| TPT-S6 | -5.18 | ITO/TPT-S6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 0.998 | 21.50 | 75.31 | 16.16 | ||
| TPT-C6 | -5.20 | ITO/TPT-C6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.077 | 23.32 | 75.46 | 18.87 | ||
| TPT-P6 | -5.20 | ITO/TPT-P6/Cs0.05MA0.12FA0.83Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.125 | 23.49 | 81.08 | 21.43 | ||
| MeO- PhPACz | -5.61 | ITO/MeO-PhPACz/Cs0.05FA0.8MA0.15Pb(I0.75Br0.25)3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.68 | 1.215 | 20.59 | 84.28 | 21.10 | [ |
| PPA | -5.28 | ITO/PPA/Cs0.05FA0.85MA0.1PbI3/OABr/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.14 | 24.83 | 82.0 | 23.24 | [ |
| PPAOMe | -5.02 | ITO/PPA/Cs0.05FA0.85MA0.1PbI3/OABr/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.10 | 24.70 | 79.2 | 21.52 |
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿 带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPA | -5.33 | ITO/TPA/MAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 1.06 | 19.4 | 77 | 15.9 | [ |
| MC-43 | -5.11 | ITO/MC-43/MAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.07 | 20.3 | 80 | 17.3 | ||
| EVAD03 | -5.05 | ITO/EVAD03/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.6 | 1.156 | 22.9 | 80 | 21.2 | [ |
| EVAD04 | -5.06 | ITO/EVAD03/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.164 | 22.6 | 80 | 21.0 | ||
| RC-24 | -5.13 | ITO/RC-24/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Cu | 1.6 | 1.123 | 22.3 | 79 | 19.8 | [ |
| RC-25 | -5.22 | ITO/RC-25/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Cu | 1.116 | 22.1 | 79 | 19.6 | ||
| RC-34 | -5.32 | ITO/RC-34/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Cu | 1.109 | 22.5 | 79 | 19.7 | ||
| MC-45 | -5.12 | ITO/MC-45/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.58 | 1.09 | 20.56 | 74.35 | 16.69 | [ |
| MC-54 | -5.16 | ITO/MC-54/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.10 | 22.32 | 79.15 | 19.52 | ||
| MC-55 | -5.26 | ITO/MC-55/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.09 | 21.90 | 79.32 | 18.99 | ||
| Spiro- Acid | -5.02 | ITO/Spiro-Acid/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95Pb(I0.85- Br0.15)3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.63 | 0.99 | 22.20 | 82.6 | 18.15 | [ |
| 2F | -5.42 | ITO/2F/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/TEACl/C60/SnO2/Cu | 1.77 | 1.31 | 17.93 | 82.31 | 19.33 | [ |
| ITO/2F/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.95Br0.05)3/TEACl/C60/SnO2/ Cu | 1.57 | 1.15 | 23.59 | 82.42 | 22.36 | |||
| ITO/2F/FA0.6MA0.3Cs0.1Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/EDAI2/C60/SnO2/Cu | 1.25 | 0.872 | 32.55 | 81.89 | 23.24 | |||
| 两端: ITO/(PTAA)2F/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/SnO2/ IZO/(PEDOT:PSS)or(PEDOT:PSS/2F)/FA0.6MA0.3Cs0.1Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/C60/ALD-SnO2/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 2.130 | 15.52 | 82.36 | 27.22 | |||
| TPA-PT- C6 | -5.2 | ITO/TPA-PT-C6+CA-Br/MAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 1.039 | 21.80 | 77.35 | 17.49 | [ |
| EA-49 | -5.07 | ITO/EA-49/MAPbI3/PCBM/Ca/Ag | 1.5 | 1.024 | 17.25 | 68.15 | 12.03 | [ |
| P3HT- COOH | -5.42 | ITO/P3HT-COOH/MAPbI3/PCBM-PEI/Ag | 1.58 | 1.010 | 22.83 | 82.6 | 20.74 | [ |
| TT1 | -5.4 | ITO/TT1/MAPbI3/C60/Ag | 1.5 | 1.045±0.01 | 17.85±1.0 | 68.7± 0.6 | 14.85 | [ |
| AC-1 | -5.39 | ITO/AC-1/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.55 | 1.084 | 18.83 | 80.49 | 16.43 | [ |
| AC-3 | -5.39 | ITO/AC-3/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.108 | 24.27 | 82.56 | 22.20 | ||
| AC-5 | -5.39 | ITO/AC-5/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.130 | 24.42 | 84.05 | 23.19 | ||
| 9CPA | -5.19 | FTO/9CPA/Cs0.1FA0.6MA0.3Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.25 | 0.89 | 32.5 | 76 | 22.1 | [ |
| 9CAA | -5.35 | FTO/9CAA/Cs0.1FA0.6MA0.3Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/C60/BCP/ Ag | 0.89 | 32.8 | 79 | 23.1 |
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿 带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPA | -5.33 | ITO/TPA/MAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 1.06 | 19.4 | 77 | 15.9 | [ |
| MC-43 | -5.11 | ITO/MC-43/MAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.07 | 20.3 | 80 | 17.3 | ||
| EVAD03 | -5.05 | ITO/EVAD03/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.6 | 1.156 | 22.9 | 80 | 21.2 | [ |
| EVAD04 | -5.06 | ITO/EVAD03/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.164 | 22.6 | 80 | 21.0 | ||
| RC-24 | -5.13 | ITO/RC-24/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Cu | 1.6 | 1.123 | 22.3 | 79 | 19.8 | [ |
| RC-25 | -5.22 | ITO/RC-25/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Cu | 1.116 | 22.1 | 79 | 19.6 | ||
| RC-34 | -5.32 | ITO/RC-34/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Cu | 1.109 | 22.5 | 79 | 19.7 | ||
| MC-45 | -5.12 | ITO/MC-45/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.58 | 1.09 | 20.56 | 74.35 | 16.69 | [ |
| MC-54 | -5.16 | ITO/MC-54/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.10 | 22.32 | 79.15 | 19.52 | ||
| MC-55 | -5.26 | ITO/MC-55/Cs0.05FA0.79MA0.16Pb(I0.84Br0.16)3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.09 | 21.90 | 79.32 | 18.99 | ||
| Spiro- Acid | -5.02 | ITO/Spiro-Acid/Cs0.05(FA0.85MA0.15)0.95Pb(I0.85- Br0.15)3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.63 | 0.99 | 22.20 | 82.6 | 18.15 | [ |
| 2F | -5.42 | ITO/2F/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/TEACl/C60/SnO2/Cu | 1.77 | 1.31 | 17.93 | 82.31 | 19.33 | [ |
| ITO/2F/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.95Br0.05)3/TEACl/C60/SnO2/ Cu | 1.57 | 1.15 | 23.59 | 82.42 | 22.36 | |||
| ITO/2F/FA0.6MA0.3Cs0.1Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/EDAI2/C60/SnO2/Cu | 1.25 | 0.872 | 32.55 | 81.89 | 23.24 | |||
| 两端: ITO/(PTAA)2F/FA0.8Cs0.2Pb(I0.6Br0.4)3/C60/SnO2/ IZO/(PEDOT:PSS)or(PEDOT:PSS/2F)/FA0.6MA0.3Cs0.1Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/C60/ALD-SnO2/Cu | 顶电池: 1.77 底电池: 1.25 | 2.130 | 15.52 | 82.36 | 27.22 | |||
| TPA-PT- C6 | -5.2 | ITO/TPA-PT-C6+CA-Br/MAPbI3/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.5 | 1.039 | 21.80 | 77.35 | 17.49 | [ |
| EA-49 | -5.07 | ITO/EA-49/MAPbI3/PCBM/Ca/Ag | 1.5 | 1.024 | 17.25 | 68.15 | 12.03 | [ |
| P3HT- COOH | -5.42 | ITO/P3HT-COOH/MAPbI3/PCBM-PEI/Ag | 1.58 | 1.010 | 22.83 | 82.6 | 20.74 | [ |
| TT1 | -5.4 | ITO/TT1/MAPbI3/C60/Ag | 1.5 | 1.045±0.01 | 17.85±1.0 | 68.7± 0.6 | 14.85 | [ |
| AC-1 | -5.39 | ITO/AC-1/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.55 | 1.084 | 18.83 | 80.49 | 16.43 | [ |
| AC-3 | -5.39 | ITO/AC-3/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.108 | 24.27 | 82.56 | 22.20 | ||
| AC-5 | -5.39 | ITO/AC-5/perovskite/PEAI/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.130 | 24.42 | 84.05 | 23.19 | ||
| 9CPA | -5.19 | FTO/9CPA/Cs0.1FA0.6MA0.3Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.25 | 0.89 | 32.5 | 76 | 22.1 | [ |
| 9CAA | -5.35 | FTO/9CAA/Cs0.1FA0.6MA0.3Pb0.5Sn0.5I3/C60/BCP/ Ag | 0.89 | 32.8 | 79 | 23.1 |
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿 带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPA-BT-CA | -5.29 | ITO/MPA-BT-CA/(FA0.17MA0.94PbI3.11)0.95- (PbCl2)0.05/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.13 | 22.25 | 84.8 | 21.24 | [ | |
| MPA-BT-BA | -5.19 | ITO/MPA-BT-BA/(FA0.17MA0.94PbI3.11)0.95- (PbCl2)0.05/C60/ZrAcac/Ag | 1.53 | 1.12 | 22.76 | 81.0 | 20.58 | [ | |
| MPA-BT-RA | -5.24 | ITO/MPA-BT-RA/(FA0.17MA0.94PbI3.11)0.95- (PbCl2)0.05/C60/ZrAcac/Ag | 1.10 | 22.03 | 81.1 | 19.65 | |||
| FMPA-BT-CA | -5.45 | ITO/FMPA-BT-RA/perovskite/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.53 | 1.151 | 23.33 | 83.3 | 22.37 | [ | |
| 2FMPA- BT-CA | -5.37 | ITO/2FMPA-BT-RA/perovskite/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.143 | 22.81 | 83.1 | 21.68 | |||
| BT-T | -5.28 | ITO/NiOx/Cs0.05(FA0.98MA0.02)0.95Pb(I0.98Br0.02)3- (BT-T)/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.59 | 1.17 | 24.60 | 81.6 | 23.48 | [ | |
| PQxD | -5.28 | ITO/PQxD/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.542 | 19.28 | 68.1 | 7.1 | [ | |
| TQxD | -5.30 | ITO/TQxD/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.574 | 21.05 | 68.8 | 8.3 | ||
| Cz-CA | -5.72 | ITO/Cz-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/ PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56 | — | — | — | 20.17 | [ | |
| Cz-Ph-CA | -5.53 | ITO/Cz-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 20.66 | |||
| TPA-CA | -5.87 | ITO/TPA-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 17.58 | |||
| TPA-Ph- CA | -5.61 | ITO/TPA-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 20.26 | |||
| MPA-CA | -5.45 | ITO/MPA-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 20.36 | |||
| MPA-Ph-CA | -5.39 | ITO/MPA-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.139 | 23.55 | 84.02 | 22.53 | |||
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿 带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPA-BT-CA | -5.29 | ITO/MPA-BT-CA/(FA0.17MA0.94PbI3.11)0.95- (PbCl2)0.05/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.13 | 22.25 | 84.8 | 21.24 | [ | |
| MPA-BT-BA | -5.19 | ITO/MPA-BT-BA/(FA0.17MA0.94PbI3.11)0.95- (PbCl2)0.05/C60/ZrAcac/Ag | 1.53 | 1.12 | 22.76 | 81.0 | 20.58 | [ | |
| MPA-BT-RA | -5.24 | ITO/MPA-BT-RA/(FA0.17MA0.94PbI3.11)0.95- (PbCl2)0.05/C60/ZrAcac/Ag | 1.10 | 22.03 | 81.1 | 19.65 | |||
| FMPA-BT-CA | -5.45 | ITO/FMPA-BT-RA/perovskite/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.53 | 1.151 | 23.33 | 83.3 | 22.37 | [ | |
| 2FMPA- BT-CA | -5.37 | ITO/2FMPA-BT-RA/perovskite/C60/BCP/Cu | 1.143 | 22.81 | 83.1 | 21.68 | |||
| BT-T | -5.28 | ITO/NiOx/Cs0.05(FA0.98MA0.02)0.95Pb(I0.98Br0.02)3- (BT-T)/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 1.59 | 1.17 | 24.60 | 81.6 | 23.48 | [ | |
| PQxD | -5.28 | ITO/PQxD/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.542 | 19.28 | 68.1 | 7.1 | [ | |
| TQxD | -5.30 | ITO/TQxD/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.574 | 21.05 | 68.8 | 8.3 | ||
| Cz-CA | -5.72 | ITO/Cz-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/ PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.56 | — | — | — | 20.17 | [ | |
| Cz-Ph-CA | -5.53 | ITO/Cz-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 20.66 | |||
| TPA-CA | -5.87 | ITO/TPA-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 17.58 | |||
| TPA-Ph- CA | -5.61 | ITO/TPA-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 20.26 | |||
| MPA-CA | -5.45 | ITO/MPA-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | — | — | — | 20.36 | |||
| MPA-Ph-CA | -5.39 | ITO/MPA-Ph-CA/Cs0.05(MA0.08FA0.92)0.95Pb(I0.92- Br0.08)3/PEAI/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.139 | 23.55 | 84.02 | 22.53 | |||
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿 带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTPA-BA | -5.48 | ITO/MTPA-BA/Cs0.05(FA0.95MA0.05)0.95Pb(I0.95- Br0.05)3/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.57 | 1.14 | 23.24 | 85.2 | 22.62 | [ |
| MPA-CPA | -5.4 | ITO/MPA-CAP/ Cs0.05(FA0.95MA0.05)0.95Pb(I0.95Br0.05)3/F-PEAI/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.56 | 1.21 | 24.78 | 84.7 | 25.4 | [ |
| PQx | -5.28 | ITO/PQx/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.455 | 19.97 | 66.6 | 6.1 | [ |
| TQx | -5.30 | ITO/TQx/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.546 | 21.30 | 69.0 | 8.0 | |
| TPAC | -5.35 | ITO/TPAC/MAPbI3-xClx/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.6 | 1.12 | 22.07 | 78.89 | 19.42 | [ |
| DMeTPA | -5.36 | ITO/DMeTPA/Cs0.05(FA0.88MA0.12)0.95PbI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.00 | 24.31 | 80.5 | 19.47 | [ |
| DMeTPA-O | -5.41 | ITO/DMeTPA-O/Cs0.05(FA0.88MA0.12)0.95PbI3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.01 | 24.93 | 81.7 | 20.57 | ||
| DMeOTPA-O | -5.32 | ITO/DMeOTPA-O/Cs0.05(FA0.88MA0.12)0.95PbI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 0.97 | 23.82 | 80.8 | 18.67 |
| 分子名 | HOMO (eV) | 器件结构 | 钙钛矿 带隙/eV | Voc/V | Jsc/ (mA•cm−2) | FF/% | PCE/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTPA-BA | -5.48 | ITO/MTPA-BA/Cs0.05(FA0.95MA0.05)0.95Pb(I0.95- Br0.05)3/PCBM/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.57 | 1.14 | 23.24 | 85.2 | 22.62 | [ |
| MPA-CPA | -5.4 | ITO/MPA-CAP/ Cs0.05(FA0.95MA0.05)0.95Pb(I0.95Br0.05)3/F-PEAI/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.56 | 1.21 | 24.78 | 84.7 | 25.4 | [ |
| PQx | -5.28 | ITO/PQx/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.455 | 19.97 | 66.6 | 6.1 | [ |
| TQx | -5.30 | ITO/TQx/FASnI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.4 | 0.546 | 21.30 | 69.0 | 8.0 | |
| TPAC | -5.35 | ITO/TPAC/MAPbI3-xClx/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.6 | 1.12 | 22.07 | 78.89 | 19.42 | [ |
| DMeTPA | -5.36 | ITO/DMeTPA/Cs0.05(FA0.88MA0.12)0.95PbI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 1.53 | 1.00 | 24.31 | 80.5 | 19.47 | [ |
| DMeTPA-O | -5.41 | ITO/DMeTPA-O/Cs0.05(FA0.88MA0.12)0.95PbI3/C60/ BCP/Ag | 1.01 | 24.93 | 81.7 | 20.57 | ||
| DMeOTPA-O | -5.32 | ITO/DMeOTPA-O/Cs0.05(FA0.88MA0.12)0.95PbI3/C60/BCP/Ag | 0.97 | 23.82 | 80.8 | 18.67 |
| [1] |
Kim, H.-S.; Lee, C.-R.; Im, J.-H.; Lee, K.-B.; Moehl, T.; Marchioro, A.; Moon, S.-J.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Yum, J.-H.; Moser, J. E.; Grätzel, M.; Park, N.-G. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 591.
doi: 10.1038/srep00591 |
| [2] |
Best Research-Cell Efficiency Chart. NREL https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html 2023).
|
| [3] |
Kim, J. Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Jung, H. S.; Shin, H.; Park, N.-G. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7867.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00107 |
| [4] |
Shao, J.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-W. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 41, 1447 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202009033 |
|
(邵将洋, 钟羽武, 有机化学, 2021, 41, 1447.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202009033 |
|
| [5] |
Urieta-Mora, J.; García-Benito, I.; Molina-Ontoria, A.; Martín, N. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8541.
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00262b pmid: 30283961 |
| [6] |
Gangala, S.; Misra, R. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18750.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA08503J |
| [7] |
Liu, Q.; Ren, B.; Sun, Y.; Xie, L.; Huang, W. Acta Chim. Sinica 2021, 79, 1181 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A21060253 |
|
(刘庆琳, 任保轶, 孙亚光, 解令海, 黄维, 化学学报, 2021, 79, 1181.)
doi: 10.6023/A21060253 |
|
| [8] |
Liu, X.-P.; Kong, F.-T.; Chen, W.-C.; Yu, T.; Guo, F.-L.; Chen, J.; Dai, S.-Y. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2016, 32, 1347 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201603143 |
|
(刘雪朋, 孔凡太, 陈汪超, 于婷, 郭福领, 陈健, 戴松元, 物理化学学报, 2016, 32, 1347.)
|
|
| [9] |
Marinova, N.; Tress, W.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Dar, M. I.; Bojinov, V.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Grätzel, M. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4200.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b00447 pmid: 25769194 |
| [10] |
Meng, L.; You, J.; Guo, T.-F.; Yang, Y. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 155.
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00404 |
| [11] |
Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lin, F.; Chen, T.; Pan, D.; Guo, X. Acta Chim. Sinica 2019, 77, 964 (in Chinese).
doi: 10.6023/A19040143 |
|
(杨英, 朱从潭, 林飞宇, 陈甜, 潘德群, 郭学益, 化学学报, 2019, 77, 964.)
doi: 10.6023/A19040143 |
|
| [12] |
Isikgor, F. H.; Zhumagali, S.; Merino, L. V. T.; De Bastiani, M.; McCulloch, I.; De Wolf, S. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 89.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-022-00503-3 |
| [13] |
Ali, F.; Roldán-Carmona, C.; Sohail, M.; Nazeeruddin, M. K. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002989.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.48 |
| [14] |
Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y. Materials Futures 2023, 2, 012105.
doi: 10.1088/2752-5724/acbb5a |
| [15] |
Galvis, C. E. P.; Ruiz, D. A. G.; Martinez-Ferrero, E.; Palomares, E. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 1534.
doi: 10.1039/D3SC04668K |
| [16] |
Lan, Z.-R.; Shao, J.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-W. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2023, 8, 1440.
doi: 10.1039/D3ME00144J |
| [17] |
Cheng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Y. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 3958.
doi: 10.1039/D3QM00209H |
| [18] |
Wu, G.; Kong, F.; Weng, J.; Dai, S.; Xi, X.; Zhang, C. Prog. Chem. 2011, 23, 1929 (in Chinese).
|
|
(武国华, 孔凡太, 翁坚, 戴松元, 奚小网, 张昌能, 化学进展, 2011, 23, 1929.)
|
|
| [19] |
Kong, F.; Dai, S.; Wang, K. Huaxue Tongbao 2005, 68, 338 (in Chinese).
|
|
(孔凡太, 戴松元, 王孔嘉, 化学通报, 2005, 68, 338.)
|
|
| [20] |
Dai, S.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Technology and Process, Science Press, Beijing, 2016 (in Chinese).
|
|
(戴松元, 张昌能, 黄阳, 染料敏化太阳电池技术与工艺, 科学出版社, 北京, 2016.)
|
|
| [21] |
Dai, S.; Liu, W.; Yan, J. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell, Science Press, Beijing, 2014 (in Chinese).
|
|
(戴松元, 刘伟庆, 闫金定, 染料敏化太阳电池, 科学出版社, 北京, 2014.)
|
|
| [22] |
Gissler, W.; Memming, R. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1977, 124, 1710.
doi: 10.1149/1.2133141 |
| [23] |
Gerischer, H.; Michel-Beyerle, M.; Rebentrost, F.; Tributsch, H. Electrochim. Acta 1968, 13, 1509.
doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(68)80076-3 |
| [24] |
Gerischer, H.; Tributsch, H. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie 1968, 72, 437.
doi: 10.1002/bbpc.v72.3 |
| [25] |
Anderson, S.; Constable, E. C.; Dare-Edwards, M. P.; Goodenough, J. B.; Hamnett, A.; Seddon, K. R.; Wright, R. D. Nature 1979, 280, 571.
doi: 10.1038/280571a0 |
| [26] |
Tributsch, H. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 1511.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.05.030 |
| [27] |
McEvoy, A.; Grätzel, M. Sol. Energy Mat. Sol. C. 1994, 32, 221.
doi: 10.1016/0927-0248(94)90260-7 |
| [28] |
Tsubomura, H.; Matsumura, M.; Nomura, Y.; Amamiya, T. Nature 1976, 261, 402.
doi: 10.1038/261402a0 |
| [29] |
O'regan, B.; Grätzel, M. Nature 1991, 353, 737.
doi: 10.1038/353737a0 |
| [30] |
Bach, U.; Lupo, D.; Comte, P.; Moser, J.-E.; Weissörtel, F.; Salbeck, J.; Spreitzer, H.; Grätzel, M. Nature 1998, 395, 583.
doi: 10.1038/26936 |
| [31] |
Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y.; Miyasaka, T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050.
doi: 10.1021/ja809598r |
| [32] |
Im, J.-H.; Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.-W.; Park, S.-W.; Park, N.-G. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4088.
doi: 10.1039/c1nr10867k |
| [33] |
Lee, M. M.; Teuscher, J.; Miyasaka, T.; Murakami, T. N.; Snaith, H. J. Science 2012, 338, 643.
doi: 10.1126/science.1228604 |
| [34] |
Jeng, J. Y.; Chiang, Y. F.; Lee, M. H.; Peng, S. R.; Guo, T. F.; Chen, P.; Wen, T. C. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3727.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v25.27 |
| [35] |
Liu, M.; Johnston, M. B.; Snaith, H. J. Nature 2013, 501, 395.
doi: 10.1038/nature12509 |
| [36] |
Li, X.; Chen, C. C.; Cai, M.; Hua, X.; Xie, F.; Liu, X.; Hua, J.; Long, Y. T.; Tian, H.; Han, L. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800715.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.20 |
| [37] |
Zhumagali, S.; Isikgor, F. H.; Maity, P.; Yin, J.; Ugur, E.; De Bastiani, M.; Subbiah, A. S.; Mirabelli, A. J.; Azmi, R.; Harrison, G. T.; Troughton, J.; Aydin, E.; Liu, J.; Allen, T.; Rehman, A. u.; Baran, D.; Mohammed, O. F.; De Wolf, S. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101662.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v11.40 |
| [38] |
Wang, Y.; Liao, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Zhuang, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, B.; Yao, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, M.; He, Z.; Marks, T. J.; Facchetti, A.; Guo, X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16632.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c06373 |
| [39] |
Afraj, S. N.; Kuan, C. H.; Lin, J. S.; Ni, J. S.; Velusamy, A.; Chen, M. C.; Diau, E. W. G. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213939.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.17 |
| [40] |
Kim, S. Y.; Cho, S. J.; Byeon, S. E.; He, X.; Yoon, H. J. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002606.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v10.44 |
| [41] |
Galoppini, E. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 1283.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.03.016 |
| [42] |
Bauer, T.; Schmaltz, T.; Lenz, T.; Halik, M.; Meyer, B.; Clark, T. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6073.
doi: 10.1021/am4008374 |
| [43] |
Zhang, S.; Ye, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, M.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.; Liu, Z.; Ning, Z.; Neher, D.; Han, L.; Lin, Y.; Tian, H.; Chen, W.; Stolterfoht, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, W.-H.; Wu, Y. Science 2023, 380, 404.
doi: 10.1126/science.adg3755 pmid: 37104579 |
| [44] |
Zhu, J.; Luo, Y.; He, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yi, Z.; Thiesbrummel, J.; Wang, C.; Lang, F.; Lai, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, W.; Cui, G.; Ren, S.; Hao, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, F.; Lin, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Stolterfoht, M.; Fu, F.; Zhao, D. Nature Energy 2023, 8, 714.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-023-01274-z |
| [45] |
Park, S. M.; Wei, M.; Lempesis, N.; Yu, W.; Hossain, T.; Agosta, L.; Carnevali, V.; Atapattu, H. R.; Serles, P.; Eickemeyer, F. T.; Shin, H.; Vafaie, M.; Choi, D.; Darabi, K.; Jung, E. D.; Yang, Y.; Kim, D. B.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Chen, B.; Amassian, A.; Filleter, T.; Kanatzidis, M. G.; Graham, K. R.; Xiao, L.; Rothlisberger, U.; Grätzel, M.; Sargent, E. H. Nature 2023, 624, 289.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06745-7 |
| [46] |
Kim, M.; Jeong, J.; Lu, H.; Lee, T. K.; Eickemeyer, F. T.; Liu, Y.; Choi, I. W.; Choi, S. J.; Jo, Y.; Kim, H.-B.; Mo, S.-I.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, H.; An, N. G.; Cho, S.; Tress, W. R.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Hagfeldt, A.; Kim, J. Y.; Grätzel, M.; Kim, D. S. Science 2022, 375, 302.
doi: 10.1126/science.abh1885 |
| [47] |
Phung, N.; Verheijen, M.; Todinova, A.; Datta, K.; Verhage, M.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Köbler, H.; Li, X.; Abate, A.; Albrecht, S.; Creatore, M. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 14, 2166.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c15860 |
| [48] |
Mao, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, P.; Li, F.; Gong, J.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, J.; Han, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Meng, F.; Cui, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2206193.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.40 |
| [49] |
Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, B.; Gao, D.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Gong, J.; Luther, J. M.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z. Science 2023, 382, 284.
doi: 10.1126/science.ade9637 pmid: 37856581 |
| [50] |
Yu, S.; Xiong, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ma, F.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, X.; Zhang, X.; You, J. Science 2023, 382, 1399.
doi: 10.1126/science.adj8858 |
| [51] |
Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, A.; Bati, A. S.; Zhu, H.; Grater, L.; Hadke, S. S.; Huang, C.; Sangwan, V. K.; Cai, T.; Shin, D.; Chen, L. X.; Hersam, M. C.; Mirkin, C. A.; Chen, B.; Kanatzidis, M. G.; Sargent, E. H. Science 2023, 382, 810.
doi: 10.1126/science.adk1633 |
| [52] |
Farag, A.; Feeney, T.; Hossain, I. M.; Schackmar, F.; Fassl, P.; Küster, K.; Bäuerle, R.; Ruiz-Preciado, M. A.; Hentschel, M.; Ritzer, D. B.; Diercks, A.; Li, Y.; Nejand, B. A.; Laufer, F.; Singh, R.; Strarke, U.; Paetzold, U. W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203982.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v13.8 |
| [53] |
Qin, S.; Lu, C.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Lai, W.; Shi, P.; Wang, R.; Zhu, C.; Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Meng, L.; Li, Y. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108829.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v34.11 |
| [54] |
Al-Ashouri, A.; Köhnen, E.; Li, B.; Magomedov, A.; Hempel, H.; Caprioglio, P.; Márquez, J. A.; Morales Vilches, A. B.; Kasparavicius, E.; Smith, J. A.; Phung, N.; Menzel, D.; Grischek, M.; Kegelmann, L.; Skroblin, D.; Gollwitzer, C.; Malinauskas, T.; Jost, M.; MatiČ, G.; Rech, B.; Schlatmann, R.; Topic, M.; Korte, L.; Abate, A.; Stannowski, B.; Neher, D.; Stolterfoht, M.; Unold, T.; Getautis, V.; Albrecht, S. Science 2020, 370, 1300.
doi: 10.1126/science.abd4016 pmid: 33303611 |
| [55] |
Tan, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhang, X.; Che, B.; Chen, G.; Gao, H.; He, D.; Ma, G.; Wang, J.; Xiu, J.; Yi, H.; Chen, T.; He, Z. Nature 2023, 620, 545.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06207-0 |
| [56] |
Radhakrishna, K.; Manjunath, S. B.; Devadiga, D.; Chetri, R.; Nagaraja, A. T. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 3635.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.2c03025 |
| [57] |
Magomedov, A.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Kasparavičius, E.; Strazdaite, S.; Niaura, G.; Jošt, M.; Malinauskas, T.; Albrecht, S.; Getautis, V. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801892.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.32 |
| [58] |
Al-Ashouri, A.; Magomedov, A.; Roß, M.; Jošt, M.; Talaikis, M.; Chistiakova, G.; Bertram, T.; Márquez, J. A.; Köhnen, E.; Kasparavičius, E.; Levcenco, S.; Gil-Escrig, L.; Hages, C. J.; Schlatmann, R.; Rech, B.; Malinauskas, T.; Unold, T.; Kaufmann, C. A.; Korte, L.; Niaura, G.; Getautis, V.; Albrecht, S. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3356.
doi: 10.1039/c9ee02268f |
| [59] |
Mariotti, S.; Köhnen, E.; Scheler, F.; Sveinbjörnsson, K.; Zimmermann, L.; Piot, M.; Yang, F.; Li, B.; Warby, J.; Musiienko, A.; Menzel, D.; Lang, F.; Kessler, S.; Levine, I.; Mantione, D.; Al-Ashouri, A.; Hartel, M. S.; Xu, K.; Cruz, A.; Kurpiers, J.; Wagner, P.; Kobler, H.; Li, J.; Magomedov, A.; Mecerreyes, D.; Unger, E.; Abate, A.; Stolterfoht, M.; Stannowski, B.; Schlatmann, R.; Korte, L.; Albrecht, S. Science 2023, 381, 63.
doi: 10.1126/science.adf5872 pmid: 37410849 |
| [60] |
Zheng, J.; Ying, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wei, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Ye, J. Nature Energy 2023, 8, 1250.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-023-01382-w |
| [61] |
Deng, X.; Qi, F.; Li, F.; Wu, S.; Lin, F. R.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lee, C. S.; Jen, A. K. Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203088.
|
| [62] |
Manthou, V. S.; Pefkianakis, E. K.; Falaras, P.; Vougioukalakis, G. C. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 588.
doi: 10.1002/cssc.v8.4 |
| [63] |
Liu, X.; Ding, B.; Han, M.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, P.; Xue, X.; Ghadari, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Brooks, K.; Tao, L.; Kinge, S.; Dai, S.; Sheng, J.; Dyson, P. J.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Ding, Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304350.
|
| [64] |
Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Duan, W.; Yang, J.; Mahmud, M. A.; Lian, Q.; Tang, S.; Liao, C.; Bing, J.; Yi, J.; Leung, T. L.; Cui, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, F.; Huang, Y.; Lambertz, A.; Jankovec, M.; Topič, M.; Bremner, S.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Cheng, C.; Ding, K.; Ho-Baillie, A. Joule 2023, 7, 2583.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2023.09.007 |
| [65] |
Pitaro, M.; Alonso, J. S.; Di Mario, L.; Romero, D. G.; Tran, K.; Zaharia, T.; Johansson, M. B.; Johansson, E. M.; Loi, M. A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 11755.
doi: 10.1039/D3TA01276J |
| [66] |
Ullah, A.; Park, K. H.; Nguyen, H. D.; Siddique, Y.; Shah, S.; Tran, H.; Park, S.; Lee, S. I.; Lee, K. K.; Han, C. H.; Kim, K.; Ahn, S.; Jeong, I.; Park, Y. S.; Hong, S. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103175.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v12.2 |
| [67] |
Ullah, A.; Park, K. H.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.; Faheem, A. B.; Nguyen, H. D.; Siddique, Y.; Lee, K. K.; Jo, Y.; Han, C. H.; Ahn, S.; Jeong, I.; Cho, S.; Kim, B.; Park, Y. S.; Hong, S. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208793.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v32.49 |
| [68] |
Zheng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, T.; Xiao, C.; Gao, D.; Patel, J. B.; Kuciauskas, D.; Magomedov, A.; Scheidt, R. A.; Wan, X.; Harvey, S. P.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Morales, D.; Pruett, H.; Wieliczka, B. M.; Kirmani, A. R.; Padture, N. P.; Graham, K. R.; Yan, Y.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Mcgehee, M. D.; Zhu, Z.; Luther, J. M. Nature Energy 2023, 8, 462.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-023-01227-6 |
| [69] |
Ren, Z.; Cui, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Dou, Y.; Wang, F.; Lin, H.; Yan, H.; Chen, S. Joule 2023, 7, 2894.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2023.10.014 |
| [70] |
Sun, A.; Tian, C.; Zhuang, R.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Tang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, B.; Du, J.; Li, Z.; Cai, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, C.-C. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 2303941.
|
| [71] |
Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, F.; Lin, F. R.; Jen, A. K.-Y. CCS Chem. 2024, DOI:10.31635/ccschem.024.202303710
|
| [72] |
Truong, M. A.; Funasaki, T.; Ueberricke, L.; Nojo, W.; Murdey, R.; Yamada, T.; Hu, S.; Akatsuka, A.; Sekiguchi, N.; Hira, S.; Xie, L.; Nakamura, T.; Shioya, N.; Kan, D.; Tsuji, Y.; Iikubo, S.; Yoshida, H.; Shimakawa, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Wakamiya, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7528.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c00805 |
| [73] |
Bin, H.; Datta, K.; Wang, J.; van der Pol, T. P.; Li, J.; Wienk, M. M.; Janssen, R. A. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16497.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c01900 |
| [74] |
Bi, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Beresneviciute, R.; Tavgeniene, D.; Kapil, G.; Ding, C.; Baranwal, A. K.; Sahamir, S. R.; Sanehira, Y.; Segawa, H.; Grigalevicius, S.; Shen, Q.; Hayase, S. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3852.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c01275 |
| [75] |
Li, Z.; Tan, Q.; Chen, G.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiu, J.; Chen, W.; He, Z. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 1676.
doi: 10.1039/D2NR05677A |
| [76] |
Liu, M.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; An, Y.; Yao, Z.; Fan, B.; Qi, F.; Liu, K.; Yip, H. L.; Lin, F. R.; Jen, A. K. Y. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 2303742.
|
| [77] |
Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Li, M.; Qi, F.; Lin, F. R.; Jen, A. K. Y. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202213560.
|
| [78] |
Wang, W.; Wei, K.; Yang, L.; Deng, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 2609.
doi: 10.1039/D3MH00219E |
| [79] |
He, R.; Wang, W.; Yi, Z.; Lang, F.; Chen, C.; Luo, J.; Zhu, J.; Thiesbrummel, J.; Shah, S.; Wei, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Lai, H.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zou, B.; Yin, X.; Ren, S.; Hao, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Stolterfoht, M.; Fu, F.; Tang, W.; Zhao, D. Nature 2023, 618, 80.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05992-y |
| [80] |
Jiang, W.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, F.; Jen, A. K. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 2778.
doi: 10.1039/D3SC05485C |
| [81] |
Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Yu, J.; Zhao, D.; Tang, W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2300694.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v13.23 |
| [82] |
Yi, Z.; Wang, W.; He, R.; Zhu, J.; Jiao, W.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Wei, K.; Zhang, J.; Tsang, S.-W.; Chen, C.; Tang, W.; Zhao, D. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 202.
doi: 10.1039/D3EE02839A |
| [83] |
Li, E.; Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, M.; Cao, X. M.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W. H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103847.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.35 |
| [84] |
Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yan, W.; Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Yu, W.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Gao, P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 63, e202315281.
|
| [85] |
Guo, R.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, L.; You, S.; Li, W.; Gong, Z.; Huang, R.; Cui, Y.; Rong, Y.; Zeng, H.; Li, X. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211955.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.10 |
| [86] |
Ozaki, M.; Ishikura, Y.; Truong, M. A.; Liu, J.; Okada, I.; Tanabe, T.; Sekimoto, S.; Ohtsuki, T.; Murata, Y.; Murdey, R.; Wakamiya, A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16947.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA02142F |
| [87] |
Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Ma, L.; Zhan, X. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14675.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00432 |
| [88] |
Yalcin, E.; Can, M.; Rodriguez-Seco, C.; Aktas, E.; Pudi, R.; Cambarau, W.; Demic, S.; Palomares, E. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 230.
doi: 10.1039/c8ee01831f |
| [89] |
Aktas, E.; Phung, N.; Köbler, H.; González, D. A.; Méndez, M.; Kafedjiska, I.; Turren-Cruz, S.-H.; Wenisch, R.; Lauermann, I.; Abate, A.; Palomares, E. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3976.
doi: 10.1039/D0EE03807E |
| [90] |
Aktas, E.; Pudi, R.; Phung, N.; Wenisch, R.; Gregori, L.; Meggiolaro, D.; Flatken, M. A.; De Angelis, F.; Lauermann, I.; Abate, A.; Palomares, E. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 17461.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c01981 |
| [91] |
Li, W.; Cariello, M.; Méndez, M.; Cooke, G.; Palomares, E. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 1239.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.2c02880 |
| [92] |
Yalcin, E.; Aktas, E.; Mendéz, M.; Arkan, E.; Sánchez, J. G.; Martínez-Ferrero, E.; Silvestri, F.; Barrena, E.; Can, M.; Demic, S.; Palomares, E. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 57153.
|
| [93] |
Li, E.; Bi, E.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Han, L.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W. H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909509.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v30.7 |
| [94] |
Arkan, E.; Yalcin, E.; Unal, M.; Arkan, M. Z. Y.; Can, M.; Tozlu, C.; Demic, S. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 254, 123435.
doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123435 |
| [95] |
Arkan, E.; Unal, M.; Yalcin, E.; Arkan, M. Z. Y.; Yurtdas, S.; Can, M.; Tozlu, C.; Demic, S. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2021, 123, 105514.
doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105514 |
| [96] |
Arkan, E.; Arkan, M. Z. Y.; Unal, M.; Yalcin, E.; Aydin, H.; Çelebi, C.; Can, M.; Tozlu, C.; Demic, S. Opt. Mater. 2020, 105, 109910.
doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109910 |
| [97] |
Chang, C. Y.; Huang, H. H.; Tsai, H.; Lin, S. L.; Liu, P. H.; Chen, W.; Hsu, F. C.; Nie, W.; Chen, Y. F.; Wang, L. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002718.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v8.5 |
| [98] |
Aktas, E.; Jiménez-López, J.; Azizi, K.; Torres, T.; Palomares, E. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 1415.
doi: 10.1039/d0nh00443j pmid: 32856637 |
| [99] |
Hung, C. M.; Mai, C. L.; Wu, C. C.; Chen, B. H.; Lu, C. H.; Chu, C. C.; Wang, M. C.; Yang, S. D.; Chen, H. C.; Yeh, C. Y.; Chou, P.-T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202309831.
|
| [100] |
Zhang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Tang, Y.; Su, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Xue, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, G.; Pascual, J.; Abate, A.; Li, M. Adv. Mater. 2024, 2312264.
|
| [101] |
Liao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K.; Shi, Y.; Feng, K.; Li, B.; Huang, J.; Gao, P.; Guo, X. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 68, 87.
doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.11.001 |
| [102] |
Liao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hao, M.; Li, B.; Yang, K.; Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Chi, W.; Guo, X.; Huang, W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 43547.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c10758 |
| [103] |
Li, L.; Wei, M.; Carnevali, V.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, M.; Liu, R.; Lempesis, N.; Eickemeyer, F. T.; Luo, L.; Agosta, L.; Dankl, M.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Roethlisberger, U.; Grätzel, M.; Rong, Y.; Li, X. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2303869.
|
| [104] |
Zhang, S.; Wu, R.; Mu, C.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.-H. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1976.
|
| [105] |
Guo, H.; Liu, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X.; Cao, X.-M.; Ning, Z.; Zhu, W.-H.; Tian, H.; Wu, Y. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad057.
|
| [106] |
Kong, W.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Miao, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Hu, M.; Li, D.; Amini, A.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.; Cheng, C. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1625.
|
| [107] |
Huang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.; Dong, H.; Wu, Z.; Duan, L. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132986.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132986 |
| [108] |
Jiang, Q.; Tirawat, R.; Kerner, R. A.; Gaulding, E. A.; Xian, Y.; Wang, X.; Newkirk, J. M.; Yan, Y.; Berry, J. J.; Zhu, K. Nature 2023, 623, 313.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06610-7 |
| [109] |
Cui, H.; Huang, L.; Zhou, S.; Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Guan, H.; Wang, S.; Shao, W.; Pu, D.; Dong, K.; Zhou, J.; Jia, P.; Wang, W.; Tao, C.; Ke, W.; Fang, G. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 5992.
doi: 10.1039/D3EE02818F |
| [110] |
Zeng, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, W.-H.; Tian, H.; Xie, Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5154.
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b12675 |
| [1] | 苑志祥, 张浩, 胡思伽, 张波涛, 张建军, 崔光磊. 离子聚合原位固态化构建高安全锂电池固态聚合物电解质的研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1064-1080. |
| [2] | 高丰琴, 刘洋, 张引莉, 蒋育澄. 羧基功能化Fe3O4固定化酶反应器的构筑及性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(4): 338-344. |
| [3] | 查汉, 房进, 闫翎鹏, 杨永珍, 马昌期. 有机太阳能电池热失效机制及三元共混提升其热稳定性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 131-145. |
| [4] | 刘彦甫, 李世麟, 荆亚楠, 肖林格, 周惠琼. 有机太阳能电池性能衰减机理研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(7): 993-1009. |
| [5] | 林文源, 朱清哲, 马云龙, 王鹏, 万硕, 郑庆东. 理性调控聚合物给体-非富勒烯受体的混溶性制备高效率有机太阳能电池※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 724-733. |
| [6] | 许宁, 乔庆龙, 刘晓刚, 徐兆超. 基于抑制扭转的分子内电荷转移(TICT)提升有机小分子荧光染料亮度及光稳定性※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(4): 553-562. |
| [7] | 戴敏, 雷钢铁, 张钊, 李智, 曹湖军, 陈萍. 五氧化二钒促进MgH2/Mg室温吸氢※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 303-309. |
| [8] | 田宋炜, 周丽雪, 张秉乾, 张建军, 杜晓璠, 张浩, 胡思伽, 苑志祥, 韩鹏献, 李素丽, 赵伟, 周新红, 崔光磊. 聚环氧乙烷聚合物电解质基高电压固态锂金属电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(10): 1410-1423. |
| [9] | 龚政, 张意, 吕华, 崔树勋. 脯氨酸聚酯的单链力学性质[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(1): 7-10. |
| [10] | 孙稷, 易玖琦, 程龙玖. 定向Monte Carlo格点搜索算法用于氧化铝团簇(Al2O3)n (n=1~50)的结构搜索[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(9): 1154-1163. |
| [11] | 吕泽伟, 韩敏芳, 孙再洪, 孙凯华. 固体氧化物燃料电池运行初期电化学性能演变机制[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 763-770. |
| [12] | 苗俊辉, 丁自成, 刘俊, 王利祥. 小分子给体/高分子受体型有机太阳能电池研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(5): 545-556. |
| [13] | 刘长安, 洪士博, 李蓓. 石墨烯在甘油/尿素剥离液中的稳定行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(4): 530-538. |
| [14] | 赵添堃, 王鹏, 姬明宇, 李善家, 杨明俊, 蒲秀瑛. Salan钛双齿配合物的Sonogashira合成后修饰反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(11): 1385-1393. |
| [15] | 刘庆琳, 任保轶, 孙亚光, 解令海, 黄维. 螺芳基钙钛矿太阳能电池空穴传输材料研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(10): 1181-1196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||