化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 82 ›› Issue (9): 987-1000.DOI: 10.6023/A24040134 上一篇 下一篇
综述
陈宇波a,†, 郑德旭b,†, 王楠a, 刘吉双b, 于凤阳a,*( ), 吴飒建b, 刘生忠a,c,*(
), 吴飒建b, 刘生忠a,c,*( ), 李智鹏b
), 李智鹏b
投稿日期:2024-04-29
发布日期:2024-07-09
作者简介: |
陈宇波, 山西大学2022级硕士研究生, 研究方向为钙钛矿太阳能电池. |
 |
于凤阳, 博士, 2015年于陕西师范大学获材料化学学士学位, 2021年于日本九州工业大学获得工学博士学位, 目前主要从事钙钛矿太阳能光电器件性能研究. |
 |
刘生忠, 教授, 陕西师范大学-中国科学院大连化学物理研究所特聘教授, 洁净能源国家实验室太阳能部副部长、陕西师范大学新能源高等技术研究院院长, 陕西省能源新材料与器件重点实验室主任、陕西师范大学陕西省能源新技术工程实验室主任, 陕西师范大学应用表面与胶体化学教育部重点实验室表界面化学与能源材料方向带头人. 研究领域集中在太阳能电池、钙钛矿单晶材料、纳米材料、薄膜材料、光电功能材料、激光表面处理和光伏技术的开发、放大和生产. |
基金资助:
Yubo Chena,†, Dexu Zhengb,†, Nan Wanga, Jishuang Liub, Fengyang Yua,*( ), Sajian Wub, Shengzhong Liua,c,*(
), Sajian Wub, Shengzhong Liua,c,*( ), Zhipeng Lib
), Zhipeng Lib
Received:2024-04-29
Published:2024-07-09
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:Supported by:文章分享

近年来, 钙钛矿太阳能电池因其优越的光电转换性能而备受关注. 然而, 在扩大规模过程中往往会出现严重的效率损失, 这限制了其进一步商业化. 开发一种低成本、可扩展、可控制的生产方法至关重要. 在各种制备方法中, 溶液两步法具有制备简单、重复性好和操作性高等优点, 有利于实现可控制备大面积高质量钙钛矿薄膜, 在商业应用中潜力巨大. 基于钙钛矿的制备被分成两步这一特性, 两步法的调控方向更多, 目前已有众多研究工作被报道. 本篇综述详细介绍旋涂溶液两步法在添加剂工程、界面修饰、溶剂工程和其他工程的最新进展, 并分析旋涂溶液两步法面临的挑战和未来的研究前景, 旨在对大面积、高性能的钙钛矿太阳能电池研究提供有益参考.
陈宇波, 郑德旭, 王楠, 刘吉双, 于凤阳, 吴飒建, 刘生忠, 李智鹏. 旋涂两步法甲脒铅基钙钛矿太阳能电池近期研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 987-1000.
Yubo Chen, Dexu Zheng, Nan Wang, Jishuang Liu, Fengyang Yu, Sajian Wu, Shengzhong Liu, Zhipeng Li. Recent Progress of Two-step Spin-coated Formamidinium Lead-based Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2024, 82(9): 987-1000.
| Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | ITO/SnO2//FAxMA1-xPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 23.56 | 2023.1.7 | [ |
| EMIMBF4 | ITO/SnO2/FAxMA1-xPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 24.28 | 2023.11.22 | [ |
| GBA | FTO/c-TiO2/FA0.98MA0.02PbI3/o-F-PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.08 | 25.32 | 2023.9.28 | [ |
| CsX | ITO/SnO2/CsX Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.09 | 20.29 | 2023.5.13 | [ |
| EuBr2 | ITO/ SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.089 | 23.04 | 2024.1.1 | [ |
| PFAT | glass ITO/SnO2/perovskite/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0557 | 24.52 | 2023.1.18 | [ |
| MAAc | ITO/SnO2/MAAc-assisted perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 23.36 | 2022.10.27 | [ |
| 2F-PAE | FTO/SnO2/perovskite with 2F-PAE/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.69 | 2023.10.12 | [ |
| HMPA | FTO/TiO2/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 20.84 | 2023.5.11 | [ |
| UiO-66 | ITO/SnO2/UiO-66-assistedperovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.05 | 2023.1.18 | [ |
| EHA | ITO/SnO2/FA0.92MA0.08PbI3/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/MoO3/Ag | 0.04 | 24.10 | 2022.11.10 | [ |
| MZ | PET/ITO/SnO2/Peroskite/SpiroOMeTAD/Au | 0.062 | 23.94 | 2023.8.14 | [ |
| HCOOK | (ITO)/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0902 | 23.8 | 2023.6.9 | [ |
| AtaCl | ITO/2PACz/Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag(p-i-n) | 0.05 | 25.7 | 2023.8.8 | [ |
| EIMS | ITO/SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 22.1 | 2023.3.9 | [ |
| AmG | FTO/c-TiO2/perovskite/Spiro-MeOTAD/Au | 0.125 | 23.46 | 2023.9.5 | [ |
| TMSOI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.125 | 24.65 | 2023.12.13 | [ |
| BU | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 23.5 | 2023.8.14 | [ |
| 4-AcM | FTO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 24.04 | 2024.1.19 | [ |
| BA2PbI4 | glass/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.04 | 24.3 | 2023.12.15 | [ |
| FAAc | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 24.41 | 2024.3.7 | [ |
| Cd(Ac)2 | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.8885 | 24.46 | 2023.6.29 | [ |
| MoSe2 | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 22.8 | 2023.5.13 | [ |
| OETC | PET/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.062 | 23.4 | 2023.1.17 | [ |
| MS | PEN/ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.10128 | 23.6 | 2022.9.28 | [ |
| PA PAD | FTO/SnO2/perovskite (PA and PAD)/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.18 | 2023.2.23 | [ |
| RbCl MDACl2 | Glass/ITO/SnO2/FA0.75MA0.25PbI3/OAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.76 | 2023.11.25 | [ |
| IU | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 23.18 | 2023.12.6 | [ |
| Hydantoin | glass/FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 25.16 | 2024.4.3 | [ |
| Starch-I2 | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.14 | 22.60 | 2024.3.25 | [ |
| BPCSA-S | ITO/NiOx/Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | Unknown | 22.07 | 2024.3.4 | [ |
| BAI | FTO/compact TiO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 20.8 | 2024.3.19 | [ |
| FAPbI3 | ITO/SnO2/Active Layer/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.1 | 23.16 | 2023.1.17 | [ |
| NaHCO3 | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.1 | 24.0 | 2023.5.9 | [ |
| Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | ITO/SnO2//FAxMA1-xPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 23.56 | 2023.1.7 | [ |
| EMIMBF4 | ITO/SnO2/FAxMA1-xPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 24.28 | 2023.11.22 | [ |
| GBA | FTO/c-TiO2/FA0.98MA0.02PbI3/o-F-PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.08 | 25.32 | 2023.9.28 | [ |
| CsX | ITO/SnO2/CsX Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.09 | 20.29 | 2023.5.13 | [ |
| EuBr2 | ITO/ SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.089 | 23.04 | 2024.1.1 | [ |
| PFAT | glass ITO/SnO2/perovskite/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0557 | 24.52 | 2023.1.18 | [ |
| MAAc | ITO/SnO2/MAAc-assisted perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 23.36 | 2022.10.27 | [ |
| 2F-PAE | FTO/SnO2/perovskite with 2F-PAE/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.69 | 2023.10.12 | [ |
| HMPA | FTO/TiO2/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 20.84 | 2023.5.11 | [ |
| UiO-66 | ITO/SnO2/UiO-66-assistedperovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.05 | 2023.1.18 | [ |
| EHA | ITO/SnO2/FA0.92MA0.08PbI3/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/MoO3/Ag | 0.04 | 24.10 | 2022.11.10 | [ |
| MZ | PET/ITO/SnO2/Peroskite/SpiroOMeTAD/Au | 0.062 | 23.94 | 2023.8.14 | [ |
| HCOOK | (ITO)/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0902 | 23.8 | 2023.6.9 | [ |
| AtaCl | ITO/2PACz/Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag(p-i-n) | 0.05 | 25.7 | 2023.8.8 | [ |
| EIMS | ITO/SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 22.1 | 2023.3.9 | [ |
| AmG | FTO/c-TiO2/perovskite/Spiro-MeOTAD/Au | 0.125 | 23.46 | 2023.9.5 | [ |
| TMSOI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.125 | 24.65 | 2023.12.13 | [ |
| BU | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 23.5 | 2023.8.14 | [ |
| 4-AcM | FTO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 24.04 | 2024.1.19 | [ |
| BA2PbI4 | glass/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.04 | 24.3 | 2023.12.15 | [ |
| FAAc | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 24.41 | 2024.3.7 | [ |
| Cd(Ac)2 | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.8885 | 24.46 | 2023.6.29 | [ |
| MoSe2 | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 22.8 | 2023.5.13 | [ |
| OETC | PET/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.062 | 23.4 | 2023.1.17 | [ |
| MS | PEN/ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.10128 | 23.6 | 2022.9.28 | [ |
| PA PAD | FTO/SnO2/perovskite (PA and PAD)/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.18 | 2023.2.23 | [ |
| RbCl MDACl2 | Glass/ITO/SnO2/FA0.75MA0.25PbI3/OAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 23.76 | 2023.11.25 | [ |
| IU | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 23.18 | 2023.12.6 | [ |
| Hydantoin | glass/FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 25.16 | 2024.4.3 | [ |
| Starch-I2 | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.14 | 22.60 | 2024.3.25 | [ |
| BPCSA-S | ITO/NiOx/Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | Unknown | 22.07 | 2024.3.4 | [ |
| BAI | FTO/compact TiO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 20.8 | 2024.3.19 | [ |
| FAPbI3 | ITO/SnO2/Active Layer/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.1 | 23.16 | 2023.1.17 | [ |
| NaHCO3 | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.1 | 24.0 | 2023.5.9 | [ |


| Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Cl-BZH | ITO/RbF-SnO2/CsFAMAPVK/NMABr/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 24.08 | 2023.11.13 | [ |
| PAA | FTO/SnO2/Perovskite/OAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.0514 | 24.19 | 2023.2.28 | [ |
| HFB | FTO/SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0831 | 26.07 | 2023.11.16 | [ |
| SEH+AM1 | glass/FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 20.10 | 2023.1.4 | [ |
| FS-3100 | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.16 | 21.72 | 2023.6.7 | [ |
| FBAD | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro/Au | 0.04 | 24.08 | 2023.3.21 | [ |
| TEMPO | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.04 | 25.03 | 2024.3.26 | [ |
| CF3BZAI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 22.4 | 2022.11.29 | [ |
| CHX | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 22.84 | 2024.3.29 | [ |
| GlyHCl | glass/FTO/SnO2/FAMA-GlyHCl perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 19.40 | 2024.1.23 | [ |
| PTAC | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 24.51 | 2024.2.24 | [ |
| PAD | (ITO)/SnO2/FA0.95Cs0.05PbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag(or Au) | 0.1 | 24.0 | 2023.7.26 | [ |
| NH4X | ITO/SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 24.11 | 2023.4.23 | [ |
| IL | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 24.09 | 2023.5.25 | [ |
| TES | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 22.67 | 2023.12.2 | [ |
| AMIMTFSI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.16 | 24.16 | 2024.1.23 | [ |
| tBAI | FTO/TiO2/Cs0.05tBA0.05(FA0.8MA0.2)0.9PbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 17.08 | 2023.4.10 | [ |
| Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Cl-BZH | ITO/RbF-SnO2/CsFAMAPVK/NMABr/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 24.08 | 2023.11.13 | [ |
| PAA | FTO/SnO2/Perovskite/OAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.0514 | 24.19 | 2023.2.28 | [ |
| HFB | FTO/SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0831 | 26.07 | 2023.11.16 | [ |
| SEH+AM1 | glass/FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 20.10 | 2023.1.4 | [ |
| FS-3100 | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.16 | 21.72 | 2023.6.7 | [ |
| FBAD | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro/Au | 0.04 | 24.08 | 2023.3.21 | [ |
| TEMPO | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.04 | 25.03 | 2024.3.26 | [ |
| CF3BZAI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 22.4 | 2022.11.29 | [ |
| CHX | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 22.84 | 2024.3.29 | [ |
| GlyHCl | glass/FTO/SnO2/FAMA-GlyHCl perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 19.40 | 2024.1.23 | [ |
| PTAC | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.09 | 24.51 | 2024.2.24 | [ |
| PAD | (ITO)/SnO2/FA0.95Cs0.05PbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag(or Au) | 0.1 | 24.0 | 2023.7.26 | [ |
| NH4X | ITO/SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 24.11 | 2023.4.23 | [ |
| IL | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 24.09 | 2023.5.25 | [ |
| TES | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 22.67 | 2023.12.2 | [ |
| AMIMTFSI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.16 | 24.16 | 2024.1.23 | [ |
| tBAI | FTO/TiO2/Cs0.05tBA0.05(FA0.8MA0.2)0.9PbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 17.08 | 2023.4.10 | [ |

| Type | Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETL | FOA | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/SpiroOMeTAD/MoO3/Ag | 0.037 | 25.05 | 2023.7.17 | [ |
| FAI+CsBr | Glass/ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0928 | 24.26 | 2023.3.23 | [ | |
| PAA | FTO/PAA@SnO2/(FAPbI3)0.97(MAPbBr3)0.03/ Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 17.2 | 2024.1.9 | [ | |
| (NH4)10W12O41•xH2O | FTO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 21.83 | 2024.1.18 | [ | |
| HTL | CMABr | FTO/compactTiO2/triple-cation perovskite/ Spiro-OMeTAD with and without CMABr/Au | 0.125 | 23.56 | 2022.10.22 | [ |
| Type | Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETL | FOA | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/SpiroOMeTAD/MoO3/Ag | 0.037 | 25.05 | 2023.7.17 | [ |
| FAI+CsBr | Glass/ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.0928 | 24.26 | 2023.3.23 | [ | |
| PAA | FTO/PAA@SnO2/(FAPbI3)0.97(MAPbBr3)0.03/ Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 17.2 | 2024.1.9 | [ | |
| (NH4)10W12O41•xH2O | FTO/SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 21.83 | 2024.1.18 | [ | |
| HTL | CMABr | FTO/compactTiO2/triple-cation perovskite/ Spiro-OMeTAD with and without CMABr/Au | 0.125 | 23.56 | 2022.10.22 | [ |
| Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3COOK | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 23.63 | 2023.5.24 | [ |
| CsF | ITO/SnO2/CsF/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 23.13 | 2022.11.29 | [ |
| 2-Br-PEAI | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/2-Br-PEAI/spiro-OMeTAD/MoO3/Ag | 0.1 | 24.22 | 2022.1.18 | [ |
| OAI+GACl | Glass/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/passivation layer/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.1196 | 25.43 | 2023.6.26 | [ |
| ZIF-8@FAI | ITO/SnO2/ZIF-8@FAI/PVSK/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 24.08 | 2023.4.22 | [ |
| HTAB | Glass/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/HTAB/P3HT/Carbon | 0.125 | 16.08 | 2023.1.23 | [ |
| FSA | ITO/SnO2/FSA/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.085 | 24.1 | 2022.7.11 | [ |
| KFSI | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/PEAI/spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 23.21 | 2022.12.9 | [ |
| PFACl | glass/FTO/SnO2/3Dperovskite/1D perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.148 | 24.9 | 2023.11.7 | [ |
| SnO2 | FTO/Bilayer SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.05 | 23.86 | 2022.10.22 | [ |
| F-TiOx | PET/ITO/ETL/MHP/HTL/Ag | 0.049 | 22.7 | 2023.1.3 | [ |
| TiO2 | FTO/TiO2/SnO2/perovskite/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.5 | 24.8 | 2024.3.21 | [ |
| SnO2 | PET/ITO/CBD-SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 25.09 | 2024.3.22 | [ |
| TFPhFACl | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/TFPhFACl/spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 24.00 | 2022.11.28 | [ |
| CsBr NCs | ITO/SnO2/ FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 23.22 | 2023.10.24 | [ |
| PFN-Br+PEAI | ITO/PTAA/FAMAPbI3-based perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Cu | Unknown | 23.4 | 2023.12.18 | [ |
| CHCl | ITO/PTAA/cholinehalide/perovskite/CHCl/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 0.05 | 22.61 | 2023.5.8 | [ |
| PyI | ITO/PTAA/perovskite/C60/BCP/Cu | 0.8313 | 24.48 | 2023.1.29 | [ |
| AtaCl | ITO/PTAA/FA0.85Cs0.15PbI3/PCBM/Ag | 0.09 | 24.27 | 2023.10.3 | [ |
| THF/MBM | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/(modification layer)/Spiro-OMeTAD | Unknown | 24.17 | 2023.12.30 | [ |
| Cl4Tm | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Ligand 2D/PTAA/Au | 0.05 | 24.6 | 2023.6.7 | [ |
| PPAI | ITO/PTAA/perovskite/with or without PA iodides/C60/BCP/Ag | 0.044 | 24.2 | 2022.12.19 | [ |
| PMAI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/PMAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.072 | 24.10 | 2023.4.20 | [ |
| MA-WOx | ITO/PTAA/PVSK/C60/bathocuproine (BCP)/Ag | 0.0805 | 23.33 | 2023.4.15 | [ |
| TMSI | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/TMSI/spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 24.03 | 2023.8.26 | [ |
| Rb2CO3 | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.08313 | 22.7 | 2023.3.20 | [ |
| F70PD | ITO/SnO2/fullerene/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.12 | 24.09 | 2023.8.3 | [ |
| (o-AMP)Br | FTO/NiOx:Sr/perovskite/PC61BM/BCP/Ag | 0.0625 | 22.0 | 2023.12.6 | [ |
| R-LIPF | FTO/TiO2/(FAPbI3)0.95(MAPbBr3)0.05/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au or MoO3/Ag | 0.0725 | 22.45 | 2022.12.20 | [ |
| PEOXA | FTO/SnO2/(FAPbI3)0.95(MAPbBr3)0.05/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.049 | 25.51 | 2024.3.26 | [ |
| BPCSA | Substrate/NiOx/In-situ 2D Perovskite/3D Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | Unknown | 23.45 | 2023.5.27 | [ |
| 淀粉-多碘化物 | ITO/ETL/Iodide buffer layer/perovskite/spiro-OMATAD/Au | 0.8313 | 23.9 | 2023.9.21 | [ |
| Materials | Structure | Area/cm2 | PCE/% | Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3COOK | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 23.63 | 2023.5.24 | [ |
| CsF | ITO/SnO2/CsF/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | Unknown | 23.13 | 2022.11.29 | [ |
| 2-Br-PEAI | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/2-Br-PEAI/spiro-OMeTAD/MoO3/Ag | 0.1 | 24.22 | 2022.1.18 | [ |
| OAI+GACl | Glass/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/passivation layer/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.1196 | 25.43 | 2023.6.26 | [ |
| ZIF-8@FAI | ITO/SnO2/ZIF-8@FAI/PVSK/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 24.08 | 2023.4.22 | [ |
| HTAB | Glass/ITO/SnO2/perovskite/HTAB/P3HT/Carbon | 0.125 | 16.08 | 2023.1.23 | [ |
| FSA | ITO/SnO2/FSA/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.085 | 24.1 | 2022.7.11 | [ |
| KFSI | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/PEAI/spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.04 | 23.21 | 2022.12.9 | [ |
| PFACl | glass/FTO/SnO2/3Dperovskite/1D perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.148 | 24.9 | 2023.11.7 | [ |
| SnO2 | FTO/Bilayer SnO2/FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.05 | 23.86 | 2022.10.22 | [ |
| F-TiOx | PET/ITO/ETL/MHP/HTL/Ag | 0.049 | 22.7 | 2023.1.3 | [ |
| TiO2 | FTO/TiO2/SnO2/perovskite/PEAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.5 | 24.8 | 2024.3.21 | [ |
| SnO2 | PET/ITO/CBD-SnO2/Perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 25.09 | 2024.3.22 | [ |
| TFPhFACl | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/TFPhFACl/spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 24.00 | 2022.11.28 | [ |
| CsBr NCs | ITO/SnO2/ FAPbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | Unknown | 23.22 | 2023.10.24 | [ |
| PFN-Br+PEAI | ITO/PTAA/FAMAPbI3-based perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Cu | Unknown | 23.4 | 2023.12.18 | [ |
| CHCl | ITO/PTAA/cholinehalide/perovskite/CHCl/PCBM/BCP/Ag | 0.05 | 22.61 | 2023.5.8 | [ |
| PyI | ITO/PTAA/perovskite/C60/BCP/Cu | 0.8313 | 24.48 | 2023.1.29 | [ |
| AtaCl | ITO/PTAA/FA0.85Cs0.15PbI3/PCBM/Ag | 0.09 | 24.27 | 2023.10.3 | [ |
| THF/MBM | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/(modification layer)/Spiro-OMeTAD | Unknown | 24.17 | 2023.12.30 | [ |
| Cl4Tm | ITO/SnO2/Perovskite/Ligand 2D/PTAA/Au | 0.05 | 24.6 | 2023.6.7 | [ |
| PPAI | ITO/PTAA/perovskite/with or without PA iodides/C60/BCP/Ag | 0.044 | 24.2 | 2022.12.19 | [ |
| PMAI | FTO/SnO2/perovskite/PMAI/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.072 | 24.10 | 2023.4.20 | [ |
| MA-WOx | ITO/PTAA/PVSK/C60/bathocuproine (BCP)/Ag | 0.0805 | 23.33 | 2023.4.15 | [ |
| TMSI | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/TMSI/spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.1 | 24.03 | 2023.8.26 | [ |
| Rb2CO3 | ITO/SnO2/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au | 0.08313 | 22.7 | 2023.3.20 | [ |
| F70PD | ITO/SnO2/fullerene/perovskite/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.12 | 24.09 | 2023.8.3 | [ |
| (o-AMP)Br | FTO/NiOx:Sr/perovskite/PC61BM/BCP/Ag | 0.0625 | 22.0 | 2023.12.6 | [ |
| R-LIPF | FTO/TiO2/(FAPbI3)0.95(MAPbBr3)0.05/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au or MoO3/Ag | 0.0725 | 22.45 | 2022.12.20 | [ |
| PEOXA | FTO/SnO2/(FAPbI3)0.95(MAPbBr3)0.05/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag | 0.049 | 25.51 | 2024.3.26 | [ |
| BPCSA | Substrate/NiOx/In-situ 2D Perovskite/3D Perovskite/PCBM/BCP/Ag | Unknown | 23.45 | 2023.5.27 | [ |
| 淀粉-多碘化物 | ITO/ETL/Iodide buffer layer/perovskite/spiro-OMATAD/Au | 0.8313 | 23.9 | 2023.9.21 | [ |

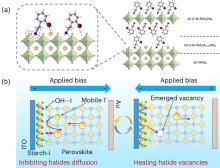

| [1] |
De Wolf-S.; Holovsky J.; Moon S.-J.; Löper P.; Niesen B.; Ledinsky M.; Haug F.-J.; Yum J.-H.; Ballif C. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1035.
|
| [2] |
Lv S.-L.; Pang S.-P.; Zhou Y.-Y.; Padture N.-P.; Hu H.; Wang L.; Zhou X.-H.; Zhu H.-M.; Zhang L.-X.; Huang C.-S.; Cui G.-L. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19206.
|
| [3] |
Miyata A.; Mitioglu A.; Plochocka P.; Portugall O.; Wang J.T.-W.; Stranks S.-D.; Snaith H.-J.; Nicholas R.-J. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 582.
|
| [4] |
Cai Y.; Cui J.; Chen M.; Zhang M.-M.; Han Y.; Qian F.; Zhao H.; Yang S.-M.; Yang Z.; Bian H.-T.; Wang T.; Guo K.-P.; Cai M.-L.; Dai S.-Y.; Liu Z.; Liu S.-Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2005776.
|
| [5] |
Liu Y.-L.; Xiang W.-C.; Xu T.-F.; Zhang H.; Xu H.-J.; Zhang Y.-C.; Qi W.-Z.; Liu L.-D.; Yang T.-T.; Wang Z.-Z.; Liu S.-Z. Small 2023, 19, 2304190.
|
| [6] |
Yang L.; Feng J.-S.; Liu Z.-K.; Duan Y.-W.; Zhan S.; Yang S.-M.; He K.; Li Y.; Zhou Y.-W.; Yuan N.-Y.; Ding J.-N.; Liu S.-Z. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201681.
|
| [7] |
Ma S.-M.; Xue X.-Y.; Wang K.; Wen Q.; Han Y.-H.; Wang J.-Q.; Yao H.; Lu H.; Cui L.-H.; Ma J.-F.; Zhang L.; Liu L.; Zhang H.-X.; Farhadi B.; Wang K.; Liu S.-Z. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303193.
|
| [8] |
Li Y.; Duan Y.-W.; Liu Z.-K.; Yang L.; Li H.-X.; Fan Q.-P.; Zhou H.; Sun Y.-Q.; Wu M.-Z.; Ren X.-D.; Yuan N.-Y.; Ding J.-N.; Yang S.-M.; Liu S.-Z. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 202310711.
|
| [9] |
Wei Q.; Cheng Y.; Gao Y.; Wang N.; Hou X.; Zan L.; Duan Y.; Fu F.; Yang D.; Liu S. Sol. RRL 2024, 8, 2300816.
|
| [10] |
Kojima A.; Teshima K.; Shirai Y.; Miyasaka T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050.
|
| [11] |
NREL. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html
|
| [12] |
Saki Z.; Byranvand M.-M.; Taghavinia N.; Kedia M.; Saliba M. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5690.
|
| [13] |
Huang F.; Li M.-J.; Siffalovic P.; Cao G.-Z.; Tian J.-J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 518.
|
| [14] |
Jung M.; Ji S.-G.; Kim G.; Seok S.-I. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2011.
|
| [15] |
Jeon N.-J.; Noh J.-H.; Kim Y.-C.; Yang W.-S.; Ryu S.; Seok S.-I. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 897.
|
| [16] |
Qin M.-C.; Xue H.-B.; Zhang H.-K.; Hu H.-L.; Liu K.; Li Y.-H.; Qin Z.-T.; Ma J.-J.; Zhu H.-P.; Yan K.-Y.; Fang G.-J.; Li G.; Jeng U.-S.; Brocks G.; Tao S.-X.; Lu X.-H. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004630.
|
| [17] |
Swartwout R.; Hoerantner M.-T.; Bulović V. Energy Environ. Mater. 2019, 2, 119.
|
| [18] |
Sun Q.; Duan S.-C.; Liu G.; Meng X.-X.; Hu D.; Deng J.-G.; Shen B.; Kang B.-N.; Silva S.R.-P. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2301259.
|
| [19] |
Chen H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605654.
|
| [20] |
Kim S.-Y.; Jo H.-J.; Sung S.-J.; Kim D.-H. APL Mater. 2016, 4, 100901.
|
| [21] |
Han Y.-P.; Xie H.-B.; Lim E.-L.; Bi D.-Q. Sol. RRL 2022, 6, 2101007.
|
| [22] |
Wu Z.-F.; Bi E.-B.; Li C.-W.; Chen L.; Song Z.-N.; Yan Y.-F. Sol. RRL 2022, 7, 2200571.
|
| [23] |
Burschka J.; Pellet N.; Moon S.-J.; Humphry-Baker R.; Gao P.; Nazeeruddin M.-K.; Grätzel M. Nature 2013, 499, 316.
|
| [24] |
Zhang T.-Y.; Yang M.-J.; Zhao Y.-X.; Zhu K. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3959.
|
| [25] |
Yang W.-S.; Noh J.-H.; Jeon N.-J.; Kim Y.-C.; Ryu S.; Seo J.; Seok S.-I. Science 2015, 348, 1234.
|
| [26] |
Wu J.-H.; Xu X.; Zhao Y.-H.; Shi J.-J.; Xu Y.-Z.; Luo Y.-H.; Li D.; Wu H.-J.; Meng Q.-B. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26937.
|
| [27] |
Zhao Y.-C.; Tan H.-R.; Yuan H.-F.; Yang Z.-Y.; Fan J.-Z.; Kim J.; Voznyy O.; Gong X.-W.; Quan L.-N.; Tan C.-S.; Hofkens J.; Yu D.-P.; Zhao Q.; Sargent E.-H. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1607.
|
| [28] |
Hui W.; Chao L.-F.; Lu H.; Xia F.; Wei Q.; Su Z.-H.; Niu T.-T.; Tao L.; Du B.; Li D.; Wang Y.; Dong H.; Zuo S.; Li B.-X.; Shi W.; Ran X.-Q.; Li P.; Zhang H.; Wu Z.-B.; Ran C.-X.; Song L.; Xing G.-C.; Gao X.-Y.; Zhang J.; Xia Y.-D.; Chen Y.-H.; Huang W. Science 2021, 371, 1359.
doi: 10.1126/science.abf7652 pmid: 33766883 |
| [29] |
Zhao Y.; Ma F.; Qu Z.-H.; Yu S.-Q.; Shen T.; Deng H.-X.; Chu X.-B.; Peng X.-X.; Yuan Y.-B.; Zhang X.-W.; You J.-B. Science 2022, 377, 531.
|
| [30] |
Jiang Q.; Chu Z.-M.; Wang P.-Y.; Yang X.-L.; Liu H.; Wang Y.; Yin Z.-G.; Wu J.-L.; Zhang X.-W.; You J.-B. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703852.
|
| [31] |
Chauhan M.; Zhong Y.; Schötz K.; Tripathi B.; Köhler A.; Huettner S.; Panzer F. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 5086.
|
| [32] |
Wu Y.-Z.; Islam A.; Yang X.-D.; Qin C.-J.; Liu J.; Zhang K.; Peng W.-Q.; Han L.-Y. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2934.
|
| [33] |
Zhao Y.; Zhang X.; Han X.-F.; Hou C.-Y.; Wang H.-Z.; Qi J.-B.; Li Y.-G.; Zhang Q.-H. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 127912.
|
| [34] |
Gao Y.; Raza H.; Zhang Z.-P.; Chen W.; Liu Z.-H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2215171.
|
| [35] |
Zhou S.-H.; Zhang W.-F.; Jiang Y.-T.; Lin P.-A.; Zhou X.-Q.; Huang Y.-L. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2022, 43, 78 (in Chinese).
|
|
(周生厚, 章文峰, 江雨童, 林埔安, 周祥青, 黄跃龙, 太阳能学报, 2022, 43, 78.)
doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2021-0237 |
|
| [36] |
Bai D.-L.; Zheng D.-X.; Yang S.-A.; Yu F.-Y.; Zhu X.-J.; Peng L.; Wang L.-K.; Liu J.-S.; Yang D.; Liu S.-Z. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 28097.
|
| [37] |
Bai D.-L.; Zheng D.-X.; Yang S.-A.; Peng L.; Wang P.-J.; Liu J.-S.; Zhu X.-J.; Yang D.; Liu S.-Z.F. Sol. RRL 2024, 8, 2301036.
|
| [38] |
Zhang H.; Xu Z.-P.; Zhu C.-T.; Guo X.-Y.; Yang Y. J. Inorg. Mater. 2024, 39, 457 (in Chinese).
|
|
(张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英, 无机材料学报, 2024, 39, 457.)
|
|
| [39] |
He J.-C.; Sheng W.-P.; Yang J.; Zhong Y.; Su Y.; Tan L.-C.; Chen Y.-W. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 629.
|
| [40] |
Du Y.-T.; Wang Y.; Wu J.-H.; Chen Q.; Deng C.-Y.; Ji R.; Sun L.-X.; Tan L.-N.; Chen X.; Xie Y.-M.; Huang Y.-F.; Vaynzof Y.; Gao P.; Sun W.-H.; Lan Z. InfoMat. 2023, 5, e12431
|
| [41] |
Zeng G.-Y.; Liu G.-Y.; Li X. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7664.
|
| [42] |
Liang X.; Zhou K.; Duan D.-W.; Wang F.; Ge C.-Y.; Zhou X.-F.; Yuan M.-J.; Shi Y.-M.; Lin H.-R.; Zhu Q.-Y.; Li G.; Hu H.-L. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141524.
|
| [43] |
Li X.-D.; Zou Y.; Yu S.-B.; Zhao X.; Yu W.-J.; Yang S.; Guo H.-Q.; Xiao L.-X.; Chen Z.-J.; Qu B. Sol. RRL 2023, 7, 2300091.
|
| [44] |
Zhang Y.; Park N. G. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2308577.
|
| [45] |
Zhang Y.-L.; Yang T.-H.; Lee S.-U.; Liu S.-Z.; Zhao K.; Park N.-G. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 9, 159.
|
| [46] |
Guo Z.-H.; Chen W.-X.; Wang H.-X.; Cai W.-S.; Qaid S.M.H.; Zang Z.-G. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 14086.
|
| [47] |
Liang X.; Duan D.-W.; Al-Handawi M.-B.; Wang F.; Zhou X.-F.; Ge C.-Y.; Lin H.-R.; Zhu Q.-Y.; Li L.; Naumov P.; Hu H.-L. Sol. RRL 2022, 7, 2200856.
|
| [48] |
Sun Y.-G.; Hu R.-Y.; Wang F.; Wang T.-M.; Liang X.; Zhou X.-F.; Yang G.; Li Y.-J.; Zhang F.; Zhu Q.-Y.; Li X.-A.; Hu H.-L. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 5175.
|
| [49] |
Liu C.-C.; Su H.-J.; Pu Y.; Guo M.; Zhai P.; Liu Z.-K.; Zhang Z. Nano Energy 2023, 118, 108990.
|
| [50] |
Wu X.-X.; Xu G.-Y.; Yang F.; Chen W.-J.; Yang H.-Y.; Shen Y.-X.; Wu Y.-Y.; Chen H.-Y.; Xi J.-C.; Tang X.-H.; Cheng Q.-R.; Chen Y.-J.; Ou X.-M.; Li Y.-W.; Li Y.-F. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3750.
|
| [51] |
Wang Y.-P.; Xiao Y.-M.; Wang L.-D.; Su Z.-S.; Xu Y.-P.; Fan L.-B.; Yao G.-P.; Qian X.; Lin J.-Y. J. Power Sources 2024, 602, 234383.
|
| [52] |
Ahn S.; Chiu W.-H.; Cheng H.-M.; Suryanarayanan V.; Chen G.; Huang Y.-C.; Wu M.-C.; Lee K.-M. Org. Electron. 2023, 120, 106847.
|
| [53] |
Hou M.-N.; Guo X.; Han M.-D.-X.; Zhao J.-T.; Wang Z.-Y.; Ding Y.; Hou G.-F.; Zhang Z.-S.; Han X.-P. Chin. Phys. B 2024, 33, 047802.
|
| [54] |
Sun D.-R.; Gao Y.; Raza H.; Liu S.-W.; Ren F.-M.; Hu X.-D.; Wang H.-X.; Meng X.; Wang J.-N.; Chen R.; Sun H.-D.; He J.; Zhou J.; Pan Y.-Y.; Sun Z.-X.; Chen W.; Liu Z.-H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303225.
|
| [55] |
Ren N.-Y.; Wang P. - Y.; Jiang J.-K.; Li R.-J.; Han W.; Liu J.-J.; Zhu Z.; Chen B.-B.; Xu Q.-J.; Li T.-T.; Shi B.; Huang Q.; Zhang D.-K.; Apergi S.; Brocks G.; Zhu C.-J.; Tao S.-X.; Zhao Y.; Zhang X.-D. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211806.
|
| [56] |
Yang H.-M.; Hao Y.; Ren J.-K.; Wu Y.-K.; Sun Q.-J.; Zhang C.-X.; Cui Y.-X.; Hao Y.-Y. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 8470.
|
| [57] |
Wu T.; Ji W.-X.; Zhang L.-G.; Chen Q.-Y.; Fu J.-F.; Zhang J.-J.; Zhang Z.-L.; Zhou Y.; Dong B.; Song B. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 3599.
|
| [58] |
Shao C.; He J.-D.; Niu G.-S.; Dong Y.; Yang K.-Y.; Cao X.-F.; Wang J.-Z.; Yang H.-X. Small 2023, 2309009.
|
| [59] |
Zhang D.; Wang X.-F.; Fan Z.-P.; Zhao Y.-X.; Xia X.-F.; Li F. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 12833.
|
| [60] |
Wang Y.-F.; Yuan S.-H.; Feng R.-S.; Diao Z.-C.; Huang J.; Liao J.-C.; Sidhik S.; Shuai X.-T.; Wang M.-C.; Zou T.; Liang Z.-W.; Zhang T.; Mohite A.-D.; Li S.-B. APL Mater. 2024, 12, 031128.
|
| [61] |
Yu R.-N.; Wu G.-Z.; Shi R.; Ma Z.-W.; Dang Q.; Qing Y.-Z.; Zhang C.-Y.; Xu K.-X.; Tan Z.-A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 13, 2203127.
|
| [62] |
Shao W.-L.; Wang H.-B.; Ye F.-H.; Wang C.; Wang C.; Cui H.-S.; Dong K.-L.; Ge Y.-S.; Wang T.; Ke W.-J.; Fang G.-J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 252.
|
| [63] |
He J.-C.; Sheng W.-P.; Yang J.; Zhong Y.; Cai Q.-Q.; Liu Y.-K.; Guo Z.; Tan L.-C.; Chen Y.-W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 63, e202315233
|
| [64] |
Yan L.-Y.; Huang H.; Cui P.; Du S.-X.; Lan Z.-N.; Yang Y.-Y.; Qu S.-J.; Wang X.-X.; Zhang Q.; Liu B.-Y.; Yue X.-P.; Zhao X.; Li Y.-F.; Li H.-F.; Ji J.; Li M.-C. Nat. Energy. 2023, 8, 1158.
|
| [65] |
Wu Y.-Y.; Xu G.-Y.; Xi J.-C.; Shen Y.-X.; Wu X.-X.; Tang X.-H.; Ding J.-Y.; Yang H.-Y.; Cheng Q.-R.; Chen Z.-Y.; Li Y.-W.; Li Y.-F. Joule 2023, 7, 398.
|
| [66] |
Li M.-H.; Zhou J.-J.; Tan L.-G.; Li H.; Liu Y.; Jiang C.-F.; Ye Y.-R.; Ding L.-M.; Tress W.; Yi C.-Y. The Innovation. 2022, 3, 100310.
|
| [67] |
Liu C.-C.; Su H.-J.; Pu Y.; Guo M.; Zhai P.; Liu L.; Fu H.-Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2212577.
|
| [68] |
Yan G.-Y.; Ma Z.; Yu L.; Ge H.; Huang Y.-L. Chem. Eng. Des. Commun. 2024, 50, 7 (in Chinese).
|
|
(晏广元, 马柱, 余朗, 葛浩, 黄跃龙, 化工设计通讯, 2024, 50, 7.)
|
|
| [69] |
Xu Y.-B.; Wang S.-R.; Liu H.-L.; Li X.-G. Adv. Mater. 2024, e2313080.
|
| [70] |
Tu Y.-B.; Li G.-D.; Ye J.-C.; Deng C.-Y.; Liu R.-C.; Yang G.-Y.; Shao T.-X.; Li Y.; Zang Y.; Wang Y.; Zhou Q.; Wu J.-H.; Yan W.-S. Small 2023, e2309033.
|
| [71] |
Jiao B.-X.; Ye Y.-R.; Tan L.-G.; Liu Y.; Ren N.-Y.; Li M.-H.; Zhou J.-J.; Li H.; Chen Y.; Li X.-Y.; Yi C.-Y. Adv. Mater. 2024, 2313673.
|
| [72] |
Wang S.-H.; Luo H.-Q.; Gu Z.-K.; Zhao R.-D.; Guo L.-T.; Wang N.; Lou Y.-J.; Xu Q.; Peng S.; Zhang Y.-Q.; Song Y.-L. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214834.
|
| [73] |
Tuo B.-Y.; Wang Z.-Y.; Ren Z.-Q.; Zhang H.-W.; Lu X.-Q.; Zhang Y.-Q.; Zang S.-Q.; Song Y.-L. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 2945.
|
| [74] |
Lee H.-B.; Kumar N.; Cho S.; Hong S.; Lee H.-H.; Kim H.-J.; Lee J.-S.; Kang J.-W. Adv. Energy Sustainability Res. 2022, 4, 2200128.
|
| [75] |
Dastan D.; Mohammed K.A.-M.; Alnayli Sh.-R.; Majeed S.-M..; Ahmed S.-D.; Al-Mousoi K.-A.; Pandey R.; Hossain L.-M.; Bhattarai S.; Al-Asbahi A.-B.; Rahman F.-M. Langmuir 2024, 40, 7560.
|
| [76] |
Qin L.-N.; Zhu M.-F.; Xia Y.-R.; Ma X.-K.; Hong D.-C.; Tian Y.-X.; Tie Z.-X.; Jin Z. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 5131.
|
| [77] |
Wang H.-H.; Zhang Z.; Wang X.-B.; Duan L.-R.; Luo J.-S. Nano Energy 2024, 109423.
|
| [78] |
Yang W.-G.; Xiong X.-L.; Li Z.-P.; Liu X.; Wei X.-S.; Sun Z.-B.; Huang L.; Wang L.-J. Opt. Mater. 2023, 139, 113781.
|
| [79] |
Xu Y.-T.; Wang X.-J.; Jin Z.-M.; Li B.; An W.; Zhang Q.-H.; Rui Y.-C. Sol. RRL 2023, 7, 2300302.
|
| [80] |
Shi P.-J.; Ding Y.; Ding B.; Xing Q.-Y.; Kodalle T.; Sutter-Fella C.-M.; Yavuz I.; Yao C.-L.; Fan W.; Xu J.-Z.; Tian Y.; Gu D.-Y.; Zhao K.; Tan S.; Zhang X.; Yao L.-B.; Dyson P.-J.; Slack J.-L.; Yang D.; Xue J.-J.; Nazeeruddin M.-K.; Yang Y.; Wang R. Nature 2023, 620, 323.
|
| [81] |
Huang Z.-F.; Ma Z.; Deng C.; Yu T.-J.; Li G.-M.; Du Z.-W.; You W.; Yang J.-B.; Chen Y.; Li Y.-L.; Hou S.-Y.; Yang Q.; Zhang Q.; Du H.; Li Y.-X.; Shu H.; Liu Q.-Y.; Peng C.-T.; Huang Y.-L.; Yu J.; Lin Y.-H.; Sun K.; Long W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 14, 2302769.
|
| [82] |
Huang Z.; Bai Y.; Huang X.; Li J.; Wu Y.; Chen Y.; Li K.; Niu X.; Li N.; Liu G.; Zhang Y.; Zai H.; Chen Q.; Lei T.; Wang L.; Zhou H. Nature 2023, 623, 531.
|
| [83] |
Finkenauer B.-P.; Zhang Y.; Ma K.; Turnley J.-W.; Schulz J.; Gómez M.; Coffey A.-H.; Sun D.; Sun J.; Agrawal R.; Huang L.; Dou L. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 930.
|
| [84] |
Lin S.-Y.; Wu S.-Y.; Guo D.-e.; Huang H.; Zhou X.-F.; Zhang D.; Zhou K.-C.; Zhang W.-H.; Hu Y.; Gao Y.-L.; Zhou C.-H. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2201663.
|
| [85] |
Li S.-W.; Xia J.-M.; Wen Z.-R.; Gu H.; Guo J.; Liang C.; Pan H.; Wang X.-Z.; Chen S. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300056.
|
| [86] |
Wang F.; Zhou K.; Liang X.; Zhou X.-F.; Duan D.-W.; Ge C.-Y.; Zhang X.-T.; Shi Y.-M.; Lin H.-R.; Zhu Q.-Y.; Li L.; Hu H.-L.; Zhang H.-Y. Small Methods 2023, 8, 2300210.
|
| [87] |
Huang Y.-M.; Zhou W.-C.; Zhong H.-Y.; Chen W.; Yu G.-P.; Zhang W.-J.; Wang S.-L.; Sui Y.-J.; Yang X.; Zhuang Y.; Tang J.; Cao L.-F.; Müller-Buschbaum P.; Aierken A.; Han P.-G.; Tang Z.-G. Mater. Today Adv. 2024, 21, 100449.
|
| [88] |
Tian C.-M.; Wu T.-H.; Zhao Y.; Zhou X.-L.; Li B.; Han X.-F.; Li K.-R.; Hou C.-Y.; Li Y.-G.; Wang H.-Z.; Zhang Q.-H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303666.
|
| [89] |
Hoang Huy V. P.; Bark C. W. Polymers 2024, 16, 199.
|
| [90] |
Cheng N.; Li W.-W.; Zheng D.-S.; Yang W.-X. ChemPhotoChem 2024, e202300275.
|
| [91] |
Ji X.-F.; Bi L.-Y.; Fu Q.; Li B.-L.; Wang J.-W.; Jeong S.-Y.; Feng K.; Ma S.-X.; Liao Q.-G.; Lin F.-R.; Woo H.-Y.; Lu L.-F.; Jen K.-Y.-A.; Guo X.-G. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303665.
|
| [92] |
Gao Y.; Ren F.; Sun D.; Li S.; Zheng G.; Wang J.; Raza H.; Chen R.; Wang H.; Liu S.; Yu P.; Meng X.; He J.; Zhou J.; Hu X.; Zhang Z.; Qiu L.; Chen W.; Liu Z. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2295.
|
| [93] |
Wang S.-B.; Cao F.-X.; Chen P.; He R.-W.; Tong A.-L.; Lan Z.; Gao P.; Sun W.-H.; Wu J.-H. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139721.
|
| [94] |
Li W.-Q.; Ding S.; Wu C.-Y.; Qian L.; Xiang C.-Y. Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2023, 7, 2300124.
|
| [95] |
Wang J.; Wang Z.-Y.; Chen S.-M.; Jiang N.; Yuan L.; Zhang J.; Duan Y. Sol. RRL 2023, 7, 2200960.
|
| [96] |
Sheng W.-P.; He J.-C.; Yang J.; Cai Q.-Q.; Xiao S.-Q.; Zhong Y.; Tan L.-C.; Chen Y.-W. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301852.
|
| [97] |
Qin Z.-X.; Chen Y.-T.; Wang X.-T.; Wei N.; Liu X.-M.; Chen H.-R.; Miao Y.-F.; Zhao Y.-X. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203143.
|
| [98] |
Gong C.; Zhang C.; Zhuang Q.-X.; Li H.-Y.; Yang H.; Chen J.-Z.; Zang Z.-G. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 15, 17.
|
| [99] |
Zhang X.-C.; Zhou Y.; Chen M.-Y.; Wang D.-X.; Chao L.-F.; Lv Y.-F.; Zhang H.; Xia Y.-D.; Li M.-J.; Hu Z.-L.; Chen Y.-H. Small 2023, 19, 2303254.
|
| [100] |
Zhang L.-H.; Fu C.; Wang S.; Wang M.-H.; Wang R.-T.; Xiang S.-L.; Wang Z.-Y.; Liu J.; Ma H.-R.; Wang Y.-D.; Yan Y.; Chen M.; Shi L.; Dong Q.-S.; Bian J.-M.; Shi Y.-T. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213961.
|
| [101] |
Zhai Z.-H.; Zhao Y.; Ma F.; You J.-B. Acta Phys. Sin. 2024, 73, 098802 (in Chinese).
|
|
(瞿子涵, 赵洋, 马飞, 游经碧, 物理学报, 2024, 73, 098802.)
|
|
| [102] |
Ren N.-Y.; Tan L.-G.; Li M.-H.; Zhou J.-J.; Ye Y.-R.; Jiao B.-X.; Ding L.-M.; Yi C.-Y. iEnergy 2024, 3, 39.
|
| [103] |
Wang J.; Wang K.-X.; Zhang C.-H.; Liu S.; Guan X.; Liang C.-J.; Chen C.-C.; Xie F.-X. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302169.
|
| [104] |
Zhu C.; Wang X.; Li H.-X.; Wang C.-Y.; Gao Z.-Y.; Zhang P.-X.; Niu X.-X.; Li N.-X.; Xu Z.-P.; Su Z.-H.; Chen Y.-H.; Zai H.-C.; Xie H.-P.; Zhao Y.-Z.; Yang N.; Liu G.-L.; Wang X.-Y.; Zhou H.-P.; Hong J.-W.; Gao X.-Y.; Bai Y.; Chen Q. Interdiscip. Mater. 2023, 2, 348.
|
| [105] |
Song P.-Q.; Hou E.-L.; Liang Y.-M.; Luo J.-F.; Xie L.-Q.; Qiu J.-H.; Tian C.-B.; Wei Z.-H. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303841.
|
| [106] |
Qian J.-J.; He J.-J.; Zhang Q.-H.; Zhu C.-Y.; Chen S.-L.; Wei Z.-P.; Leng X.-S.; Zhou Z.-R.; Shen B.-B.; Peng Y.; Niu Q.; Yang S.; Hou Y. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 90, 496.
|
| [107] |
Li M.-H.; Zhou J.-J.; Tan L.-G.; Liu Y.; Wang S.-Y.; Jiang C.-F.; Li H.; Zhao X.; Gao X.-Y.; Tress W.; Ding L.-M.; Yi C.-Y. Energy Environ. Mater. 2022, 6, e12360
|
| [108] |
Zhang Y.; Song Q.; Liu G.; Chen Y.; Guo Z.; Li N.; Niu X.; Qiu Z.; Zhou W.; Huang Z.; Zhu C.; Zai H.; Ma S.; Bai Y.; Chen Q.; Huang W.; Zhao Q.; Zhou H. Nat. Photonics 2023, 17, 1066.
|
| [109] |
Aung K.K.-S.; Vijayan A.; Karimipour M.; Seetawan T.; Boschloo G. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 443, 141935.
|
| [110] |
Ye F.; Tian T.; Su J. ; Jiang R.-X.; Li J.; Jin C.-K.; Tong J.-H.; Bai S.; Huang F.-Z.; Müller‐Buschbaum P.; Cheng Y.-B.; Bu T.-L. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 14, 2302775.
|
| [111] |
Yue X.-P.; Zhao X.; Fan B.-B.; Yang Y.-Y.; Yan L.-Y.; Qu S.-J.; Huang H.; Zhang Q.; Yan H.-L.; Cui P.; Ji J.; Ma J.-F.; Li M.-C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2209921.
|
| [112] |
Li Y.; Gao F.; Luo C.; Wang X.-J.; Zhan C.-L.; Chen C.-P.; Zhao Q. Small 2024, 20, e2305956
|
| [113] |
Sun Q.; Meng X.; Deng J.; Shen B.; Hu D.; Kang B.; Silva S.R.-P. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 959, 170478.
|
| [114] |
Qiu F.-Z.; Liu Q.-J.; Liu Y.-F.; Wu J.-P. Small 2023, 19, 2304834.
|
| [115] |
Ma Y.; Song Q.-Z.; Yang X.-Y.; Zai H.-C.; Yuan G.-Z.; Zhou W.-T.; Chen Y.-H.; Pei F.-T.; Kang J.-Q.; Wang H.; Song T.-L.; Wang X.-Y.; Zhou H.-P.; Li Y.-J.; Bai Y.; Chen Q. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108250.
|
| [116] |
Sun Y.-P.; Zhang J.-K.; Yu B.; Shi S.-W.; Yu H.-Z. Nano Energy 2024, 121, 109245.
|
| [117] |
Ren G.-H.; Zhang Z.-G.; Deng Y.-Y.; Li Z.-W.; Liu C.-Y.; Wang M.-K.; Guo W.-B. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 565.
|
| [118] |
Ma Y.-Y.; Zeng C.-S.; Zeng P.; Hu Y.-C.; Li F.-M.; Zheng Z.-H.; Qin M.-C.; Lu X.-H.; Liu M.-Z. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2205072.
|
| [119] |
Xiao L.-B.; Xu X.-L.; Lu Z.; Zhao J.; Liu R.-Y.; Ye Y.-Q.; Tang R.-J.; Liao W.-Q.; Xiong R.-G.; Zou G.-F. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108114.
|
| [120] |
Cai W.-X.; Wang Y.-D.; Li W.-Z.; Yin Y.-F.; Liu J.; Cai W.-Q.; Wang S.-H.; Guo J.-Y.; Chang S.; Li S.-K.; Wang X.-Y.; Shi Y.-T. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 2304521.
|
| [121] |
Zhang D.; Wang X.-F.; Tian T.-F.; Xia X.-F.; Duan J.-Y.; Fan Z.-P.; Li F. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 143789.
|
| [122] |
Chen P.; Xiao Y.; Li L.; Zhao L.-C.; Yu M.-T.; Li S.-D.; Hu J.-T.; Liu B.; Yang Y.-G.; Luo D.-Y.; Hou C.-H.; Guo X.-G.; Shyue J.-J.; Lu Z.-H.; Gong Q.-H.; Snait H.-J.; Zhu R. Adv. Mater. 2022, 35, 2206345.
|
| [123] |
Ma K.; Sun J.-N.; Atapattu H.-R.; Larson B.-W.; Yang H.-J.; Sun D.-W.; Chen K.; Wang K.; Lee Y.; Tang Y.-H.; Bhoopalam A.; Huang L.-B.; Graham K.-R.; Mei J.-G.; Dou L.-T. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg0032
|
| [124] |
Shen L.-N.; Song P.-Q.; Zheng L.-F.; Wang L.-P.; Zhang X.-G.; Liu K.-K.; Liang Y.-M.; Tian W.-J.; Luo Y.-J.; Qiu J.-H.; Tian C.-B.; Xie L.-Q.; Wei Z.-H. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301624.
|
| [125] |
Fan R.-D.; Song Q.-Z.; Huang Z.-J.; Ma Y.; Xiao M.-Q.; Huang X.-D.; Zai H.-C.; Kang J.-Q.; Xie H.-P.; Gao Y.-L.; Wang L.-N.; Zhang Y.; Wang L.; Wang F.; Zhang X.; Zhou W.-T.; Li N.-X.; Wang X.-Y.; Bai Y.; Liu G.-L.; Chen Q.; Wang L.-F.; Zhou H.-P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303176
|
| [126] |
Cheng N.; Yu Z.; Li W.-W.; Lei B.; Zi W.; Xiao Z.-Y.; Zhao Z.-Q.; Zong P.-A. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 250, 112107.
|
| [127] |
Nie J.-H.; Zhang Y.-M.; Li L.-J.; Zhang Y. Adv. Devices Instrum. 2023, 4, 0025.
|
| [128] |
Zeng Q.; Ma Q.-M.; Li L.-H.; Zheng B.-L.; Pan Y.-N.; Zhao X.-Y.; Xiao H.-R.; Yan C.; Liu F.-Y. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 5269.
|
| [129] |
Li T.-H.; Xiong Q.; Hu C.-Z.; Wang C.; Zhang N.; Lien S.-Y.; Gao P. Molecules 2023, 28, 4103.
|
| [130] |
Cheng N.; Liu Z.; Li W.-W.; Yu Z.; Lei B.; Zi W.; Xiao Z.-Y.; Sun S.-J.; Zhao Z.-Q.; Zong P.-A. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140146.
|
| [1] | 张林, 张慧, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. CsPbIBr2钙钛矿太阳能电池湿度稳定机制研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(9): 971-978. |
| [2] | 彭亚晶, 赵雨新, 杨金辉, 仉昕昕, 程佳玲. CsPbBrxI3-x全无机钙钛矿量子点的组分及浓度对电子结构及荧光性质影响研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 879-886. |
| [3] | 王馨雨, 许雄文. SnCl2敏化的TiO2表面对PbI2粒子的诱导吸附[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(8): 865-870. |
| [4] | 江雪, 涂开槐, 段泰男, 肖泽云. 添加剂在有机太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(5): 551-564. |
| [5] | 鲍梦凡, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 邓慧娟, 冒爱琴, 檀杰. 低共熔溶剂辅助制备空心球状钙钛矿型高熵氧化物及高倍率储锂性能[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 303-313. |
| [6] | 刘雪朋, 李博桐, 韩明远, 张先付, 陈建林, 戴松元. 自组装单分子空穴传输层在反式钙钛矿太阳电池的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(3): 348-366. |
| [7] | 李萍, 杨琪玉, 曾婧, 张然, 陈秋燕, 闫飞. 氟掺杂对可逆固体氧化物电池性能的影响及相关动力学研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 36-45. |
| [8] | 贾洋刚, 陈诗洁, 邵霞, 程婕, 林娜, 方道来, 冒爱琴, 李灿华. 高性能无钴化钙钛矿型高熵氧化物负极材料的制备及储锂性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 486-495. |
| [9] | 查汉, 房进, 闫翎鹏, 杨永珍, 马昌期. 有机太阳能电池热失效机制及三元共混提升其热稳定性研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(2): 131-145. |
| [10] | 张璇, 熊军, 张旺. 通过聚(3,4-乙烯二氧噻吩)-聚苯乙烯磺酸改性实现高性能蓝色钙钛矿发光二极管[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(12): 1695-1700. |
| [11] | 李东旭, 徐翔, 宋佳鸽, 梁松挺, 付予昂, 路新慧, 邹应萍. 轮烷结构优化聚合物太阳能电池光伏性能★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1500-1507. |
| [12] | 闫彬, 薛丁江, 胡劲松. 硒化亚锗薄膜太阳能电池研究进展※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 797-804. |
| [13] | 林文源, 朱清哲, 马云龙, 王鹏, 万硕, 郑庆东. 理性调控聚合物给体-非富勒烯受体的混溶性制备高效率有机太阳能电池※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(6): 724-733. |
| [14] | 张芬, 李霄琪, 韩世国, 邬发发, 刘希涛, 孙志华, 罗军华. 大尺寸二维卤化物钙钛矿铁电晶体的生长及偏振光电探测性能研究※[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 237-243. |
| [15] | 周静, 田雪迎, 王斌凯, 张沙沙, 刘宗豪, 陈炜. 低温原子层沉积封装技术在OLED上的应用及对有机、钙钛矿太阳能电池封装的启示[J]. 化学学报, 2022, 80(3): 395-422. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||