化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (8): 1052-1063.DOI: 10.6023/A23040148 上一篇 下一篇
所属专题: 庆祝《化学学报》创刊90周年合辑
综述
投稿日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-09-14
作者简介: |
杨地, 1998年出生于河南镇平, 2017年毕业于桂林理工大学, 获学士学位. 目前在卜显和教授指导下攻读硕士学位. 研究兴趣为光催化水分解产氢. |
 |
史潇凡, 1997年出生于安徽合肥, 2019年毕业于南京航空航天大学, 获学士学位. 2022年毕业于南开大学, 获材料工程硕士学位, 导师为卜显和教授. 现于武汉大学攻读无机化学博士学位, 导师为邓鹤翔教授. 研究方向为MOF基光催化剂的合成与性能研究. |
 |
张冀杰, 2012年和2018年在天津大学获得学士和博士学位. 2018年至今在南开大学材料科学与工程学院卜显和院士课题组从事博士后研究. 主要研究领域涉及功能金属有机框架材料的设计构筑和太阳能催化转化反应过程中的机理研究. |
 |
卜显和, 教授、博导、国家杰青、长江学者、天津市首批杰出人才、全国政协委员、英国皇家化学会会士、南开大学材料科学与工程学院院长、中国科学院院士. 在配位聚合物的功能导向构筑、结构调控及性能研究等方面取得了系统成果. |
基金资助:
Di Yanga, Xiaofan Shib, Jijie Zhanga( ), Xian-He Bua,c
), Xian-He Bua,c
Received:2023-04-20
Published:2023-09-14
Contact:
*E-mail: zhangjijie@nankai.edu.cn
About author:Supported by:文章分享

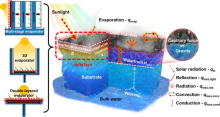
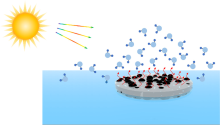
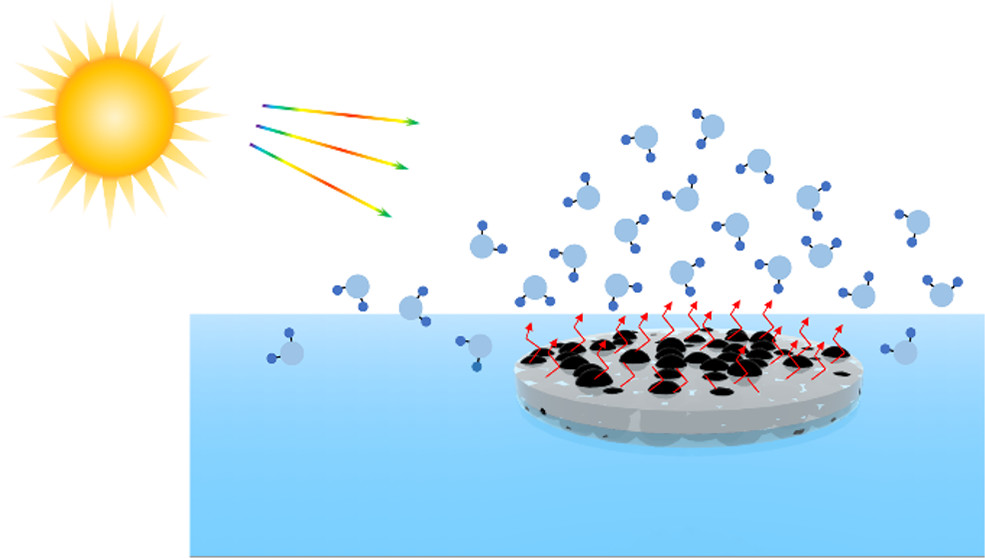
太阳能水蒸发系统成本低、能效高, 对缓解能源危机、减少水污染、促进海水淡化具有重要意义. 然而, 太阳能驱动水蒸发的自然机制往往受到低蒸发率和吸收光谱范围小的影响. 其中, 局部加热并限制热损失的界面水蒸发策略被广泛认可并作为高性能、可持续的太阳能蒸汽产生的有效途径. 随着太阳能水蒸发技术的不断发展, 制备绿色、高效的光热材料已成为研究热点. 根据光热材料的种类将其划分为: 金属材料、半导体材料、碳基材料以及聚合物材料, 详细阐述了不同材料的光热转换机制并总结近年来光热材料在海水淡化领域的研究现状及进展; 讨论了潜在的光热候选材料, 对其未来发展做出了展望. 旨在为海水淡化领域中高效光热材料的合理设计和开发提供可行方案, 对今后光热材料的发展具有总结和指导意义.
杨地, 史潇凡, 张冀杰, 卜显和. 光热材料在海水淡化领域的近期研究进展与展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 1052-1063.
Di Yang, Xiaofan Shi, Jijie Zhang, Xian-He Bu. Recent Research Progress and Prospect of Photothermal Materials in Seawater Desalination★[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(8): 1052-1063.


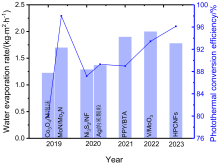

| 样品 | 光强/(kW•m-2) | 水蒸发速率/(kg•m-2•h-1) | 光热转换效率/% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au纳米颗粒(3.4 nm) | 1 | — | 11 | [ |
| Au纳米颗粒(37.7 nm) | 1 | — | 30 | [ |
| Au/MCE | 10 | — | 85 | [ |
| Ag纳米颗粒薄膜 | 1 | 1.37 | 89.3 | [ |
| AuF | 1 | — | 85 | [ |
| Ti2O3 | 1 | 1.32 | — | [ |
| Li2TiO3 | 2 | 0.87 | — | [ |
| MoN/Mo2N | 1 | 1.7 | 98 | [ |
| V/MoO3 | 1 | 2.0 | 93.44 | [ |
| Ni3S2/NF | 1 | 1.29 | 87.2 | [ |
| Co3O4/Ni | 1 | 1.226 | 80 | [ |
| C, N-TiO2纳米片@Ti板 | 1 | 1.57 | — | [ |
| CNPs/PDMS/PVA | 0.85 | 1.26 | 80 | [ |
| F-Wood | 1 | — | 72 | [ |
| 2D C/Cu | 1 | — | 65 | [ |
| N/3D rGO | 1 | — | 80 | [ |
| 3DGN/Wood | 1 | — | 91.8 | [ |
| SPPU@NCS | 1 | 2.18 | — | [ |
| HPCNFs | 1 | 1.78 | 96.13 | [ |
| PPy-Wood | 1 | 1.014 | 72.5 | [ |
| 聚吡咯-木棉纤维气凝胶 | 1 | — | 82.4 | [ |
| 聚乙烯醇/聚吡咯/壳聚糖 | 1 | 3.6 | — | [ |
| BPF | 5 | 0.57 | 48.3 | [ |
| 聚酰亚胺/MXene | 5 | — | 50.6 | [ |
| PFF | 1 | 1.48 | 87.4 | [ |
| PPY/BTA | 1 | 1.90 | 89 | [ |
| 样品 | 光强/(kW•m-2) | 水蒸发速率/(kg•m-2•h-1) | 光热转换效率/% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au纳米颗粒(3.4 nm) | 1 | — | 11 | [ |
| Au纳米颗粒(37.7 nm) | 1 | — | 30 | [ |
| Au/MCE | 10 | — | 85 | [ |
| Ag纳米颗粒薄膜 | 1 | 1.37 | 89.3 | [ |
| AuF | 1 | — | 85 | [ |
| Ti2O3 | 1 | 1.32 | — | [ |
| Li2TiO3 | 2 | 0.87 | — | [ |
| MoN/Mo2N | 1 | 1.7 | 98 | [ |
| V/MoO3 | 1 | 2.0 | 93.44 | [ |
| Ni3S2/NF | 1 | 1.29 | 87.2 | [ |
| Co3O4/Ni | 1 | 1.226 | 80 | [ |
| C, N-TiO2纳米片@Ti板 | 1 | 1.57 | — | [ |
| CNPs/PDMS/PVA | 0.85 | 1.26 | 80 | [ |
| F-Wood | 1 | — | 72 | [ |
| 2D C/Cu | 1 | — | 65 | [ |
| N/3D rGO | 1 | — | 80 | [ |
| 3DGN/Wood | 1 | — | 91.8 | [ |
| SPPU@NCS | 1 | 2.18 | — | [ |
| HPCNFs | 1 | 1.78 | 96.13 | [ |
| PPy-Wood | 1 | 1.014 | 72.5 | [ |
| 聚吡咯-木棉纤维气凝胶 | 1 | — | 82.4 | [ |
| 聚乙烯醇/聚吡咯/壳聚糖 | 1 | 3.6 | — | [ |
| BPF | 5 | 0.57 | 48.3 | [ |
| 聚酰亚胺/MXene | 5 | — | 50.6 | [ |
| PFF | 1 | 1.48 | 87.4 | [ |
| PPY/BTA | 1 | 1.90 | 89 | [ |




| [1] |
Traver E.; Karaballi R. A.; Monfared Y. E.; Daurie H.; Gagnon G. A.; Dasog M. J. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2020, 3, 2787.
doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c00107 |
| [2] |
Jiang C.; Feng X.; Wang B. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 466. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20030088 |
|
( 蒋成浩, 冯霄, 王博, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 466.)
|
|
| [3] |
Drioli E.; Ali A.; Macedonio F. J. Desalination 2015, 356, 56.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.10.028 |
| [4] |
Childress A. E.; Elimelech M. J. Membrane Sci. 1996, 119, 253.
doi: 10.1016/0376-7388(96)00127-5 |
| [5] |
Ortiz J. M.; Sotoca J. A.; Expósito E.; Gallud F.; García-García V.; Montiel V.; Aldaz A. J. Membrane Sci. 2005, 252, 65.
doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2004.11.021 |
| [6] |
Qu K. Y.; Han Q. X. Construction & Design for Engineering 2020, 02, 140. (in Chinese)
|
|
( 曲科宇, 韩庆祥, 工程建设与设计, 2020, 02, 140.)
|
|
| [7] |
Chaplin B. P. Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts 2014, 16, 1182.
doi: 10.1039/C3EM00679D |
| [8] |
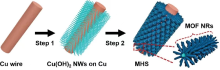
Xu J.; Xu F.; Qian M.; Li Z.; Sun P.; Hong Z.; Huang F. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 425.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.08.067 |
| [9] |
Liu X.; Tian Y.; Chen F.; Caratenuto A.; DeGiorgis J. A.; ELSonbaty M.; Wan Y.; Ahlgren R.; Zheng Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100911.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.27 |
| [10] |
Neumann O.; Feronti C.; Neumann A. D.; Dong A.; Schell K.; Lu B.; Kim E.; Quinn M.; Thompson S.; Grady N. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 11677.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310131110 |
| [11] |
Liu S.; Li S.; Lin M. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 1680.
doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.3c00054 |
| [12] |
(a) Ghasemi H.; Ni G.; Marconnet A. M.; Loomis J.; Yerci S.; Miljkovic N.; Chen G. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4449.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms5449 |
|
(b) Kashyap V.; Ghasemi H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 7035.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA01004A |
|
| [13] |
Miao E.-D.; Ye M.-Q.; Guo C.-L.; Liang L.; Liu Q.; Rao Z.-H. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 149, 1255.
doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.12.123 |
| [14] |
(a) Yao J.; Yang G. J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3869.
doi: 10.1039/C7TA10832J |
|
(b) Zhu G., Wang L.; Zhang Y.; Yu W.; Xie H. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 2019, 125, 151.
doi: 10.1007/s00339-019-2446-7 |
|
| [15] |
(a) Liu H.; Chen C.; Chen G.; Kuang Y.; Zhao X., Song J.; Jia C.; Xu X.; Hitz E.; Xie H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701616.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.8 |
|
(b) Zhu L.; Gao M.; Peh C. K. N.; Wang X.; Ho G. W. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702149.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.16 |
|
| [16] |
Mu P.; Zhang Z.; Bai W.; He J.; Sun H.; Zhu Z.; Liang W.; Li A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802158.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v9.1 |
| [17] |
Wang Y.; Wu X.; Yang. X.; Owens G.; Xu H. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105269.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105269 |
| [18] |
Zhao W.; Gong H.; Song Y.; Li B.; Xu N.; Min X.; Liu G.; Zhu B.; Zhou L.; Zhang, X -X.; Zhu J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100025.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v31.23 |
| [19] |
(a) Song C.; Qi D.; Han Y.; Xu Y.; Xu H.; You S.; Wang W.; Wang C.; Wei Y.; Ma J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9025.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b07903 |
|
(b) Ma J.; An L.; Liu D.; Yao J.; Qi D.; Xu H.; Song C.; Cui F.; Chen X.; Ma J.; Wang W. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9797.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c01874 |
|
|
(c) Qi D.; Liu Y.; Liu Y.; Liu Z.; Luo Y.; Xu H.; Zhou X.; Zhang J.; Yang H.; Wang W.; Chen X. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004401.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v32.50 |
|
| [20] |
Yang H.; Sun Y.; Peng M.; Cai M.; Zhao B.; Li D.; Liang Z.; Jiang L. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 2511.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c09124 |
| [21] |
Xie M.; Zhang P.; Cao Y.; Yan Y.; Wang Z.; Jin C. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 12.
doi: 10.1038/s41545-023-00231-3 |
| [22] |
Zhou X.; Li J.; Liu C.; Wang F.; Chen H.; Zhao C.; Sun H.; Zhu Z. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 9213.
doi: 10.1002/er.v44.11 |
| [23] |
Shi L.; Shi Y.; Li R.; Chang J.; Zaouri N.; Ahmed E.; Jin Y.; Zhang C.; Zhuo S.; Wang P. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8192.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04695 |
| [24] |
(a) Zhu L.; Gao M.; Peh C. K. N.; Ho G. W. Mater. Horiz. 2018, 5, 323.
doi: 10.1039/C7MH01064H |
|
(b) Xiao L.; Chen X.; Yang X.; Sun J.; Geng J. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4273.
doi: 10.1021/acsapm.0c00711 |
|
| [25] |
(a) Jain P. K.; Huang X.; El-Sayed I. H.; El-Sayed M. A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1578.
doi: 10.1021/ar7002804 |
|
(b) Liu G.; Xu J.; Wang K. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 269.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.09.005 |
|
| [26] |
Gao M.; Connor P. K. N.; Ho G. W. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3151.
doi: 10.1039/C6EE00971A |
| [27] |
Yi L.; Ci S.; Luo S.; Shao P.; Hou Y.; Wen Z. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 600.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.09.042 |
| [28] |
Wang J.; Li Y., Deng L.; Wei N.; Weng Y.; Dong S.; Qi D.; Qiu J.; Chen X.; Wu T. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603730.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.3 |
| [29] |
Li W.; Feng W.; Wu S.; Wang W.; Yu D. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120989.
doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120989 |
| [30] |
Vélez-Cordero J. R.; Hernandez-Cordero J. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 96, 12.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.04.009 |
| [31] |
(a) Song X.; Song H.; Xu N.; Yang H.; Zhou L.; Yu L.; Zhu J.; Xu J.; Chen K. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 22976.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA08138G |
|
(b) Yang T.; Lin H.; Lin K.-T.; Jia B. Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00182.
|
|
| [32] |
Kong Y.; Dan H.; Kong W.; Gao Y.; Shang Y.; Ji K.; Yue Q.; Gao B. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 24734.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA07576K |
| [33] |
Gao M.; Peh C. K.; Phan H. T.; Zhu L.; Ho G. W. Adv Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800711.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.25 |
| [34] |
(a) Fang J.; Liu J.; Gu J.; Liu Q.; Zhang W.; Su H.; Zhang D. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 6217.
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b01702 |
|
(b) Zhang W.; Zhu W.; Shi S.; Hu N.; Suo Y.; Wang J. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16220.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA04296A |
|
| [35] |
(a) Wang X.; Liu Q.; Wu S.; Xu B.; Xu H. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807716.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.19 |
|
(b) Wang Y.; Wang C.; Song X.; Huang M.; Megarajan S. K.; Shaukat S. F.; Jiang H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9874.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA01469H |
|
| [36] |
(a) Liu Y.; Liu Z.; Huang Q.; Liang X.; Zhou X.; Fu H.; Wu Q.; Zhang J.; Xie W. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 2581.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA10227A |
|
(b) Liu Y.; Yu S.; Feng R.; Bernard A.; Liu Y.; Zhang Y.; Duan H.; Shang W.; Tao P.; Song C. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2768.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v27.17 |
|
| [37] |
(a) Ren H.; Tang M.; Guan B.; Wang K.; Yang J.; Wang F.; Wang M.; Shan J.; Chen Z.; Wei D. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702590.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201702590 |
|
(b) Sajadi S. M.; Farokhnia N.; Irajizad P.; Hasnain M.; Ghasemi H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4700.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA01205A |
|
| [38] |
(a) Shi L.; Shi Y.; Zhuo S.; Zhang C.; Aldrees Y.; Aleid S.; Wang P. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 222.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.03.039 |
|
(b) Yi L.; Qi D.; Shao P.; Lei C.; Hou Y.; Cai P.; Wang G.; Chen X.; Wen Z. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9958.
doi: 10.1039/C8NR10117E |
|
| [39] |
Li Z.; Wang C.; Su J.; Ling S.; Wang W.; An M. Sol. RRL 2019, 3, 1800206.
doi: 10.1002/solr.v3.3 |
| [40] |
Wang W.; Wen H.; Shi J.; Su J.; Li Z.; Wang C.; Yan X. Sol. RRL 2019, 3, 1900180.
doi: 10.1002/solr.v3.10 |
| [41] |
Jeon J.; Park S.; Lee B. Sol. Energy 2016, 132, 247.
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2016.03.022 |
| [42] |
Chen M.; He Y.; Zhu J.; Kim D. Energy Convers. Manage. 2016, 112, 21.
doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.009 |
| [43] |
Zhou J.; Gu Y.; Deng Z.; Miao L.; Su H.; Wang P.; Shi J. Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2019, 19, e00090.
|
| [44] |
Choi W.; Park J. Y.; Kim Y. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 95, 120.
doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2020.12.012 |
| [45] |
Fu Y.; Mei T.; Wang G.; Guo A.; Dai G.; Wang S.; Wang J.; Li J.; Wang X. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 961.
doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.12.054 |
| [46] |
Zheng Z.; Li H.; Zhang X.; Jiang H.; Geng X.; Li S.; Tu H.; Cheng X.; Yang P.; Wan Y. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104298.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104298 |
| [47] |
Wang Z.; Liu Y.; Tao P.; Shen Q.; Yi N.; Zhang F.; Liu Q.; Song C.; Zhang D.; Shang W. Small 2014, 10, 3234.
doi: 10.1002/smll.v10.16 |
| [48] |
Guo A.; Fu Y.; Wang G.; Wang X. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4815.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA26979F |
| [49] |
Wang X.; He Y.; Liu X.; Cheng G.; Zhu J. Q. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 414.
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.080 |
| [50] |
(a) Beyene H. D.; Werkneh A. A.; Bezabh H. K.; Ambaye T. G. Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2017, 13, 18.
|
|
(b) Iyahraja S.; Rajadurai J. S. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 057103.
doi: 10.1063/1.4919808 |
|
| [51] |
Cao H.; Cui T.; Wang W.; Li S.; Tang X.; Wang H.; Zhu G. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 045005.
doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab815c |
| [52] |
Gao M.; Peh C. K.; Phan H. T.; Zhu L.; Ho G. W., Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800711.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v8.25 |
| [53] |
Gao Y.; Wu J.; Wang J.; Fan Y.; Zhang S.; Dai W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11036.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b23314 |
| [54] |
Su L.; Hu Y.; Ma Z.; Miao L.; Zhou J.; Ning Y.; Chang Z.; Wu B.; Cao M.; Xia R. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 210, 110484.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110484 |
| [55] |
Sheikh M.; Pazirofteh M.; Dehghani M.; Asghari M.; Rezakazemi M.; Valderrama C.; Cortina J.-L. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123475.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123475 |
| [56] |
Ye M.; Wang X.; Zhou P.; Chen R.; Gan Q.; Zhang T. Water Supply 2020, 20, 478.
doi: 10.2166/ws.2019.179 |
| [57] |
(a) Nandi D. K.; Sen U. K.; Choudhury D.; Mitra S.; Sarkar S. K. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6606.
doi: 10.1021/am500285d |
|
(b) Zhu Y.; Chen G.; Xu X.; Yang G.; Liu M.; Shao Z. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3540.
doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00120 |
|
| [58] |
Zhu L.; Sun L.; Zhang H.; Yu D.; Aslan H.; Zhao J.; Li Z.; Yu M.; Besenbacher F.; Sun Y. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 842.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.12.058 |
| [59] |
Bai H.; Hu J.; Lam S. H.; Guo Y.; Zhu X.-M.; Yang Z.; Wang J. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1584.
|
| [60] |
Jiang H.; Ai L.; Chen M.; Jiang J. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10833.
|
| [61] |
Wang P.; Gu Y.; Miao L.; Zhou J.; Su H.; Wei A.; Mu X.; Tian Y.; Shi J.; Cai H. Sustainable Mater. Technol. 2019, 20, e00106.
|
| [62] |
Xue C.; Huang R.; Xue R.; Chang Q.; Li N.; Zhang J.; Hu S.; Yang J. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164843.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164843 |
| [63] |
Song X.; Wang P.; Huang Y.; Zhu X.; Chio U.-F.; Wang F.; Wang G.; Wang W.; Liu B. Nano Res. 2023, DOI: 10.1007/s12274-023-5546-9.
doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-5546-9 |
| [64] |
Wang S.; Almenabawy S. M.; Kherani N. P.; Leung S. N.; O’Brien P. G. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 3378.
doi: 10.1021/acsaem.9b02399 |
| [65] |
(a) Hu X.; Xu W.; Zhou L.; Tan Y.; Wang Y.; Zhu S.; Zhu J. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604031.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.5 |
|
(b) Jiang Q.; Tian L.; Liu K. K.; Tadepalli S.; Raliya R.; Biswas P.; Naik R. R.; Singamaneni S. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9400.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201601819 |
|
| [66] |
(a) Kou H.; Liu Z.; Zhu B.; Macharia D. K.; Ahmed S.; Wu B.; Zhu M.; Liu X.; Chen Z. Desalination 2019, 462, 29.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2019.04.005 |
|
(b) Wang Y.; Zhang L.; Wang P. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1223.
doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01274 |
|
| [67] |
(a) Liu C.; Cai C.; Ma F.; Zhao X.; Ahmad H. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 103.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.055 |
|
(b) Zhang Q.; Xiao X.; Wang G.; Ming X.; Liu X.; Wang H.; Yang H.; Xu W.; Wang X. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17212.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA05193C |
|
| [68] |
Xue G.; Liu K.; Chen Q.; Yang P.; Li J.; Ding T.; Duan J.; Qi B.; Zhou J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15052.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b01992 |
| [69] |
Xu N.; Hu X.; Xu W.; Li X.; Zhou L.; Zhu S.; Zhu J. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606762.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.28 |
| [70] |
Shi L.; Wang Y.; Zhang L.; Wang P. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16212.
doi: 10.1039/C6TA09810J |
| [71] |
(a) Behabtu N.; Young C. C.; Tsentalovich D. E.; Kleinerman O.; Wang X.; Ma A. W.; Bengio E. A.; Waarbeek R. F.; de Jong J. J.; Hoogerwerf R. E. Science 2013, 339, 182.
doi: 10.1126/science.1228061 |
|
(b) Hone J.; Llaguno M.; Nemes N.; Johnson A.; Fischer J.; Walters D., Casavant M.; Schmidt J.; Smalley R. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 77, 666.
doi: 10.1063/1.127079 |
|
| [72] |
Ghafurian M. M.; Niazmand H.; Dastjerd F. T.; Mahian O. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 79.
doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2019.05.043 |
| [73] |
Guo C.-L.; Miao E.-D.; Zhao J.-X.; Liang L.; Liu Q. Sol. Energy 2019, 188, 1283.
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.07.023 |
| [74] |
Chen C.; Li Y.; Song J.; Yang Z.; Kuang Y.; Hitz E.; Jia C.; Gong A.; Jiang F.; Zhu J. Y.; Yang B.; Xie J.; Hu L. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701756.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201701756 |
| [75] |
Song J.; Li J.; Bai X.; Kang L.; Ma L.; Zhao N.; Wu S.; Xue Y.; Li J.; Ji X. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 87, 83.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2021.01.057 |
| [76] |
Deng Z.; Miao L.; Liu P.-F.; Zhou J.; Wang P.; Gu Y.; Wang X.; Cai H.; Sun L., Tanemura S. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 368.
doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.11.002 |
| [77] |
Ito Y.; Tanabe Y.; Han J.; Fujita T.; Tanigaki K.; Chen M. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4302.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v27.29 |
| [78] |
Kim K.; Yu S.; An C.; Kim S.-W.; Jang J.-H. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 15602.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b19584 |
| [79] |
Song C.; Irshad M. S.; Jin Y.; Hu J.; Liu W. Desalination 2022, 544, 116125.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2022.116125 |
| [80] |
Luo Q.; Yang Y.; Wang K.; Yu J.; Wang R.; Ji D.; Qin X. Sci. China Mater. 2023, DOI: 10.1007/s40843-023-2431-3.
doi: 10.1007/s40843-023-2431-3 |
| [81] |
Li L.; Liu Y.; Hao P.; Wang Z.; Fu L.; Ma Z.; Zhou J. Biomaterials 2015, 41, 132.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.075 |
| [82] |
Xiao L.; Sun J.; Liu L.; Hu R.; Lu H.; Cheng C.; Huang Y.; Wang S.; Geng J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5382.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b14473 |
| [83] |
(a) Huang X.; Yu Y.-H.; de Llergo O. L.; Marquez S. M.; Cheng Z. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9495.
doi: 10.1039/C6RA26286D |
|
(b) Yang K.; Xu H.; Cheng L.; Sun C.; Wang J.; Liu Z. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5586.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201202625 |
|
| [84] |
Wang Z.; Yan Y.; Shen X.; Jin C.; Sun Q.; Li H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20706.
doi: 10.1039/C9TA04914B |
| [85] |
Mu P.; Bai W.; Fan Y.; Zhang Z.; Sun H.; Zhu Z.; Liang W.; Li A. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 9673.
doi: 10.1039/C8TA12243A |
| [86] |
Zhou X.; Zhao F.; Guo Y.; Rosenberger B.; Yu G. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw5484.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw5484 |
| [87] |
He J.; Foysal T. R.; Yang H.; Islam M.; Li L.; Li W.; Cui W. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 126962.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126962 |
| [88] |
Zheng Z.; Liu H.; Wu D.; Wang X. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 440, 135862.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135862 |
| [89] |
Xu Y.; Tang C.; Ma J.; Liu D.; Qi D.; You S.; Cui F.; Wei Y.; Wang W. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5150.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b06072 |
| [90] |
Zhang J.; Luo X.; Zhang X.; Xu Y.; Xu H.; Zuo J.; Liu D.; Cui F.; Wang W. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1442.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.10.004 |
| [91] |
Wu Y.; Shen L.; Zhang C.; Gao H.; Chen J.; Jin L.; Lin P.; Zhang H.; Xia Y. Desalination 2021, 505, 114766.
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2020.114766 |
| [92] |
Lu X.; Yuan P.; Zhang W.; Wu Q.; Wang X.; Zhao M.; Sun P.; Huang W.; Fan Q. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3118.
doi: 10.1039/C8PY00215K |
| [93] |
Shao B.; Wang Y.; Wu X.; Lu Y.; Yang X.; Chen G. Y.; Owens G.; Xu H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 11665.
doi: 10.1039/D0TA03799K |
| [94] |
Chen P.; Ma Y.; Zheng Z.; Wu C.; Wang Y.; Liang G. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1192.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09226-6 |
| [95] |
Li H. C.; Li H. N.; Zou L. Y.; Li Q.; Chen P. F.; Quan X. N.; Deng K.; Sheng C. Q.; Ji J.; Fan. Q.; Xu Z. K.; Wan J. H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 2933.
doi: 10.1039/D2TA07628D |
| [96] |
Ma S.; Qarony W.; Hossain M. I.; Yip C. T.; Tsang Y. H. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 196, 36.
doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.02.035 |
| [97] |
(a) Elimelech M.; Phillip W. A. Science 2011, 333, 712.
doi: 10.1126/science.1200488 |
|
(b) Gao M.; Zhu L.; Peh C. K.; Ho G. W. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 841.
doi: 10.1039/C8EE01146J |
|
| [98] |
(a) Shi Y.; Yang J.; Gao F.; Zhang Q. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1879.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c11346 |
|
(b) Kong L.; Liu M.; Huang H.; Xu Y.; Bu X. H. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2100172.
doi: 10.1002/aenm.v12.4 |
|
|
(c) Li L. L.; Liu S.; Zhang Q.; Hu N. T.; Wei L. M.; Yang Z.; Wei H. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 1960. (in Chinese)
|
|
|
( 李路路, 刘帅, 章琴, 胡南滔, 魏良明, 杨志, 魏浩, 物理化学学报, 2017, 33, 1960.)
|
|
|
(d) Zhou B.; Chen L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 487. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15020090 |
|
|
( 周宝龙, 陈龙, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 487.)
|
|
| [99] |
Cui W.-R.; Zhang C.-R.; Liang R.-P.; Liu J.; Qiu J.-D. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 31561.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c04419 |
| [100] |
Xia Z. J.; Yang H. C.; Chen Z.; Waldman R. Z.; Zhao Y.; Zhang C.; Patel S. N.; Darling S. B. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900254.
doi: 10.1002/admi.v6.11 |
| [101] |
Jia S.; Hao L.; Liu Y.; Lin E.; Liu W.; Yang Y.; Tian Y.; Peng Y.; Cheng P.; Chen Y.; Zhang Z. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 458.
|
| [102] |
Fang Z.; Bueken B.; De Vos D. E.; Fischer R. A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7234.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v54.25 |
| [103] |
Chen Z.; Su Y.; Tang X.; Zhang X.; Duan C.; Huang F.; Li Y. Sol. RRL 2021, 5, 2100762.
doi: 10.1002/solr.v5.12 |
| [104] |
(a) Wang H.; Zhao J.; Li Y.; Cao Y.; Zhu Z.; Wang M.; Zhang R.; Pan F.; Jiang Z. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 216.
doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00968-5 |
|
(b) Wang M.; Wang Y.; Zhao J.; Zou J.; Liang X.; Zhu Z.; Zhu J.; Wang H.; Wang Y.; Pan F.; Jang Z. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202219084.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v62.13 |
|
|
(c) Zhou W.; Wei M.; Zhang X.; Xu F.; Wang Y. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 16847.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b01883 |
|
| [105] |
(a) Sumida K.; Rogow D. L.; Mason J. A.; McDonald T. M.; Bloch E. D.; Herm Z. R.; Bae T.-H.; Long J. R. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 724.
doi: 10.1021/cr2003272 |
|
(b) Wang C.; Kim J.; Tang J.; Kim M.; Lim H.; Malgras V.; You J.; Xu Q.; Li J.; Yamauchi Y. Chem 2020, 6, 19.
doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.09.005 |
|
|
(c) Zhong M.; Kong L.; Zhao K.; Zhang Y. H.; Li N.; Bu X. H. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001980.
doi: 10.1002/advs.v8.4 |
|
| [106] |
Chen G.; Jiang Z.; Li A.; Chen X.; Ma Z.; Song H. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 16805.
doi: 10.1039/D1TA03695E |
| [107] |
Ma Q.; Yin P.; Zhao M.; Luo Z.; Huang Y.; He Q.; Yu Y.; Liu Z.; Hu Z.; Chen B. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808249.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v31.17 |
| [108] |
Wang J.; Wang W.; Li J.; Mu X.; Yan X; Wang Z.; Su J.; Lei T.; Wang C. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 45944.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c11176 |
| [109] |
Zhou S.; Kong X.; Strømme M.; Xu C. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1058.
|
| [110] |
Yao Z. Q.; Wang K.; Liu R.; Yuan Y. J.; Pang J. J.; Li Q. W.; Shao T. Y.; Li Z. G.; Feng R.; Zou B.; Li W.; Xu J.; Bu X. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202073.
|
| [1] | 苏东芮, 任小康, 于沄淏, 赵鲁阳, 王天宇, 闫学海. 酪氨酸衍生物调控酶催化路径可控合成功能黑色素★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(11): 1486-1492. |
| [2] | 徐赫, 韩鹏博, 秦安军, 唐本忠. 光热材料的发展现状及应用前景★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(10): 1420-1437. |
| [3] | 蒋成浩, 冯霄, 王博. 共价有机框架膜的制备及其在海水淡化和水处理领域的研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(6): 466-477. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||