化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 81 ›› Issue (9): 1148-1156.DOI: 10.6023/A23040155 上一篇 下一篇
研究论文
吴宇晗, 张栋栋, 尹宏宇, 陈正男, 赵文, 匙玉华*( )
)
投稿日期:2023-04-21
发布日期:2023-06-25
Yuhan Wu, Dongdong Zhang, Hongyu Yin, Zhengnan Chen, Wen Zhao, Yuhua Chi( )
)
Received:2023-04-21
Published:2023-06-25
Contact:
*E-mail: 文章分享

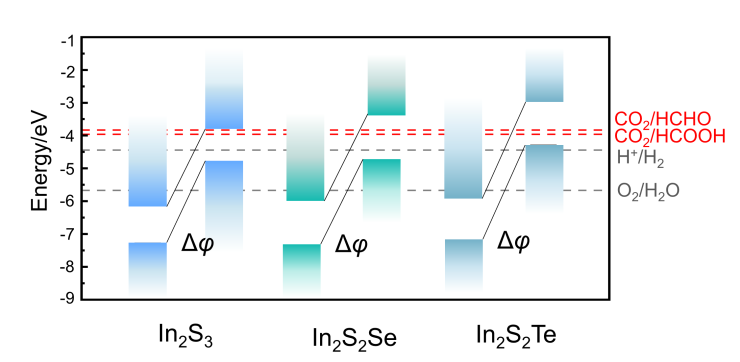
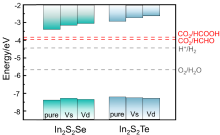
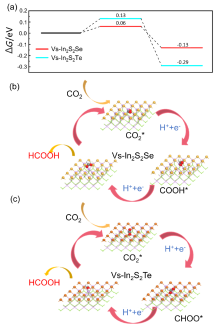
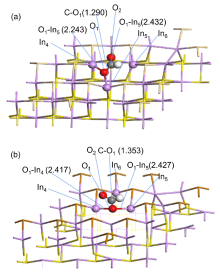
CO2光催化还原转化为可利用的化工产品能够有效地缓解温室效应和资源短缺两大问题, 有助于实现“碳达峰”和“碳中和”的伟大目标. 然而由于量子效率和产物选择性等问题的影响, 目前仍然无法将其大规模应用于工业生产. 其中光催化剂具有关键作用. 金属硫化物因具有良好的光吸收能力和带边电位, 被认为是一类具有巨大应用前景的光催化剂. 本工作以Janus In2S2X为基础, 在表面引入了不同浓度的空位缺陷, 分析了其稳定构型、电子结构以及吸收光谱. 计算CO2还原路径发现, 空位浓度可以有效调控还原产物的选择性, 具有单空位和双空位表面的催化剂分别将CO2还原为HCOOH和HCHO, 进一步揭示了空位浓度对催化性能的影响机理. 这项工作为实验设计和制备高效的光催化剂提供了一定的理论指导.
吴宇晗, 张栋栋, 尹宏宇, 陈正男, 赵文, 匙玉华. “双碳”目标下Janus In2S2X光催化还原CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(9): 1148-1156.
Yuhan Wu, Dongdong Zhang, Hongyu Yin, Zhengnan Chen, Wen Zhao, Yuhua Chi. Density Functional Theory Study of Janus In2S2X Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 under “Double Carbon” Target[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2023, 81(9): 1148-1156.


















| [1] |
Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.-X.; Yang, R.; Dai, T.-Y.; Zhang, N.; Xi, P.-X.; Yan, C.-H. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 1455. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A20070332 |
|
(张宇, 王世兴, 杨蕊, 戴腾远, 张楠, 席聘贤, 严纯华, 化学学报, 2020, 78, 1455.)
doi: 10.6023/A20070332 |
|
| [2] |
Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. B.; Wang, T. H. Renewable Resources and Circular Economy 2020, 13, 5. (in Chinese)
|
|
(赵毅, 王永斌, 王添颢, 再生资源与循环经济, 2020, 13, 5.)
|
|
| [3] |
Zhou, B.-Q.; Zhai, P.-M. Acta Meteorologica Sinica 2021, 79, 8. (in Chinese)
|
|
(周佰铨, 翟盘茂, 气象学报, 2021, 79, 8.)
|
|
| [4] |
Li, L.-R.; Liang, J.; Peng, J. Fine Chemical Industry 2023, 40, 553+696. (in Chinese)
|
|
(李亮荣, 梁娇, 彭建, 精细化工, 2023, 40, 553+696.)
|
|
| [5] |
An, P.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.-X.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, Y.-M.; Jiang, G.-Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2022, 80, 1629. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A22080362 |
|
(安攀, 张庆慧, 杨状, 武佳星, 张佳颖, 王雅君, 李宇明, 姜桂元, 化学学报, 2022, 80, 1629.)
doi: 10.6023/A22080362 |
|
| [6] |
Xue, Q.-F.; Sun, C.; Hu, Z.-C.; Huang, F.; Ye, L.-X.; Cao, Y. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 179. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A14090674 |
|
(薛启帆, 孙辰, 胡志诚, 黄飞, 叶轩立, 曹镛, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 179.)
doi: 10.6023/A14090674 |
|
| [7] |
Zhao, J.-X.; Wei, T.-H.; Ke, S.; Li, Y. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 43, 1102. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202212032 |
|
(赵金晓, 魏彤辉, 柯森, 李毅, 有机化学, 2023, 43, 1102.)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc202212032 |
|
| [8] |
Guo, X.-Y.; Song, Y.-Y.; Qin, C.; Wu, G.-J.; Bu, Y.-H.; Guo, S. L. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) 2020, 44, 70. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郭辛阳, 宋雨媛, 秦川, 吴广军, 步玉环, 郭胜来, 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44, 70.)
|
|
| [9] |
Zeng, X.-S.; Shan, C.-J.; Sun, M.-D.; Ding, D.-N.; Rong, S.-P. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4771.
doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2021.12.085 |
| [10] |
Ren, S.-R.; Li, D.-X.; Zhang, L.; Hang, H.-D. Acta Petrolei Sinica 2014, 35, 591. (in Chinese)
|
|
(任韶然, 李德祥, 张亮, 黄海东, 石油学报, 2014, 35, 591.)
doi: 10.7623/syxb201403024 |
|
| [11] |
Guo, X.-Y.; Wu, G.-J.; Bu, Y.-H.; Guo, S.-L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.-W. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) 2022, 46, 72. (in Chinese)
|
|
(郭辛阳, 吴广军, 步玉环, 郭胜来, 张锐, 王成文, 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46, 72.)
|
|
| [12] |
Liang, L.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Tan, Y.; Jiao, X.; Ju, H.; Qi, Z.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y. Joule 2018, 2, 1004.
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.02.019 |
| [13] |
Habisreutinger, S. N.; Schmidt‐Mende, L.; Stolarczyk, J. K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7372.
doi: 10.1002/anie.201207199 pmid: 23765842 |
| [14] |
Ozer, M. S.; Eroglu, Z.; Yalin, A. S.; Kılıç, M.; Rothlisberger, U.; Metin, O. Appl. Catal. B: Environmental 2022, 304, 120957.
doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120957 |
| [15] |
Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Luo, W.; Sun, T.; Xu, P. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25381.
doi: 10.1002/anie.v60.48 |
| [16] |
Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y. Matter 2020, 2, 842.
doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2020.02.006 |
| [17] |
Wu, J.-X.; Liu, Z.-F.; Peng, H.-L. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 944. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15070513 |
|
(吴金雄, 刘忠范, 彭海琳, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 944.)
doi: 10.6023/A15070513 |
|
| [18] |
Shi, J.-P.; Ma, D.-L.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, Z.-F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2015, 73, 877. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A15030157 |
|
(史建平, 马冬林, 张艳锋, 刘忠范, 化学学报, 2015, 73, 877.)
doi: 10.6023/A15030157 |
|
| [19] |
Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.-M.; Liao, L.; Yang, M.-M.; Xie, Q.; Peng, H. -, L.; Liu, Z.-R.; Liu, Z.-F. Acta Chim. Sinica 2014, 72, 289. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.6023/A13080906 |
|
(周琳, 张黎明, 廖磊, 杨明媚, 谢芹, 彭海琳, 刘志荣, 刘忠范, 化学学报, 2014, 72, 289.)
doi: 10.6023/A13080906 |
|
| [20] |
Huang, W.; Gan, L.; Yang, H.; Zhou, N.; Wang, R.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhai, T. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702448.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v27.36 |
| [21] |
Lu, A.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, J.; Chu, C.; Han, Y.; Chiu, M.; Cheng, C.; Yang, C.; Wei, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sokaras, D.; Nordlund, D.; Yang, P.; Muller, D.; Chou, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 744.
doi: 10.1038/NNANO.2017.100 |
| [22] |
Vu, T. V.; Hieu, N. N. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2021, 34, 115601.
doi: 10.1088/1361-648X/ac4401 |
| [23] |
Hieu, N. N.; Phuc, H. V.; Kartamyshev, A. I.; Vu, T. V. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 105, 075402.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.105.075402 |
| [24] |
Fu, C. F.; Sun, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, W.; Yang, J. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6312.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02561 |
| [25] |
Yu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ong, Z.; Xu, T.; Xin, R.; Pan, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5290.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6290 |
| [26] |
Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Phys. Rev. B, Condens. Matter 1996, 54, 11169.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169 |
| [27] |
Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758 |
| [28] |
Perdew, J. P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 pmid: 10062328 |
| [29] |
White, J. A.; Bird, D. M. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 4954.
pmid: 9976821 |
| [30] |
Ernzerhof, M.; Scuseria, G. E. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 5029.
doi: 10.1063/1.478401 |
| [31] |
Monkhorst, H. J.; Pack, J. D. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.13.5188 |
| [32] |
Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104.
doi: 10.1063/1.3382344 |
| [33] |
Mathew, K.; Kolluru, V. S. C.; Mula, S.; Steinmann, S. N.; Hennig, R. G. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 234101.
doi: 10.1063/1.5132354 |
| [34] |
Mathew, K.; Sundararaman, R.; Letchworth-Weaver, K.; Arias, T. A.; Hennig, R. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 084106.
doi: 10.1063/1.4865107 |
| [35] |
Zhou, W.; Zou, X.; Najmaei, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Kong, J.; Lou, J.; Ajayan, P.; Yakobson, B.; Idrobo, J. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2615.
doi: 10.1021/nl4007479 pmid: 23659662 |
| [36] |
Gajdoš, M.; Hummer, K.; Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J.; Bechstedt, F. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 045112.
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.73.045112 |
| [37] |
Fu, C.-F.; Wu, X.; Yang, J. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802106.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.48 |
| [38] |
Wirth, J.; Neumann, R.; Antonietti, M.; Saalfrank, P. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15917.
doi: 10.1039/C4CP02021A |
| [39] |
Nørskov, J. K.; Rossmeisl, J.; Logadottir, A.; Lindqvist, L.; Kitchin, J. R.; Bligaard, T.; Jónsson, H. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886.
doi: 10.1021/jp047349j |
| [40] |
Xu, J.; Wan, Q.; Anpo, M.; Lin, S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 6624.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b11385 |
| [41] |
Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Shao, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Ju, H.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 690.
doi: 10.1038/s41560-019-0431-1 |
| [42] |
Rossmeisl, J.; Chan, K.; Skulason, E.; Björketun, M.; Tripkovic, V. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 36.
doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.08.016 |
| [1] | 李雅宁, 王晓艳, 唐勇. 自由基聚合的立体选择性调控★[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 213-225. |
| [2] | 王成强, 冯超. 亲核性氟源在碳碳不饱和键选择性氟化官能化反应中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 160-170. |
| [3] | 陈健强, 朱钢国, 吴劼. 镍催化氮杂环丙烷的开环偶联反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(2): 190-212. |
| [4] | 黄涎廷, 韩洪亮, 肖婧, 王帆, 柳忠全. I2O5/KSCN介导的炔烃碘硫氰化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2024, 82(1): 5-8. |
| [5] | 杨蓉婕, 周璘, 苏彬. 基于共价有机框架修饰电极的维生素A和C的选择性检测★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(8): 920-927. |
| [6] | 何明慧, 叶子秋, 林桂庆, 尹晟, 黄心翊, 周旭, 尹颖, 桂波, 汪成. 卟啉基共价有机框架的光催化研究进展★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 784-792. |
| [7] | 张艳东, 朱守非. 环丙烷骨架膦配体的研究展望★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 777-783. |
| [8] | 刘嘉文, 林玮璜, 王惟嘉, 郭学益, 杨英. Cu1.94S-SnS纳米异质结的合成及其光催化降解研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(7): 725-734. |
| [9] | 李飞, 丁汇丽, 李超忠. 基于氟仿衍生的三氟甲基硼络合物参与的烯烃氢三氟甲基化反应[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 577-581. |
| [10] | 刘坜, 郑刚, 范国强, 杜洪光, 谭嘉靖. 4-酰基/氨基羰基/烷氧羰基取代汉斯酯参与的有机反应研究进展[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 657-668. |
| [11] | 坎比努尔•努尔买买提, 王超, 罗时玮, 阿布都热西提•阿布力克木. 电化学条件下α,α,α-三卤(氯, 溴)甲基酮类化合物的选择性脱卤反应研究[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(6): 582-587. |
| [12] | 徐袁利, 潘辉, 杨义, 左智伟. 连续流条件下蒽-铈协同催化的苄位碳氢键选择性氧化反应★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 435-440. |
| [13] | 齐学平, 王飞, 张健. 后合成法构筑钛基金属有机框架及其应用[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 548-558. |
| [14] | 刘露杰, 张建, 王亮, 肖丰收. 生物质基多元醇的多相催化选择性氢解★[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(5): 533-547. |
| [15] | 徐斌, 韦秀芝, 孙江敏, 刘建国, 马隆龙. 原位合成氮掺杂石墨烯负载钯纳米颗粒用于催化香兰素高选择性加氢反应[J]. 化学学报, 2023, 81(3): 239-245. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||